Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Colonies PPT 2014 Final
Colonies PPT 2014 Final
Uploaded by
api-233748343Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Colonies PPT 2014 Final
Colonies PPT 2014 Final
Uploaded by
api-233748343Copyright:
Available Formats
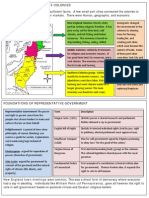
The Thirteen Colonies
Review
Roanoke 1587
Sir Walter Raleigh
Jamestown 1607
Charter: document granting
permission to establish a
colony in the name of England
Headright: 50acres/person
Tobacco saves Jamestown
Bacons Rebellion
Three Colonial Regions
New England Colonies
Connecticut, Massachusetts,
New Hampshire, Rhode
Island
Middle Colonies
New York, New Jersey,
Pennsylvania, Delaware
Southern Colonies
Maryland, Virginia, South
Carolina, North Carolina,
Georgia
Three Colonial Regions
Topography
New England
Harsh climate 4 seasons,
Rocky soil, Forest, Rivers
fast, narrow, shallow
Middle
4 mild seasons, fertile land,
flat/hilly
Southern
Warm year round, Fertile
soil, Flat terrain, Rivers
wide, slow, deep
New England Colonies
Pilgrims in New England
Puritans vs. Pilgrims
Move from Netherlands to
Americas
1620 Plymouth (outside
Virginia government)
Mayflower Compact
First effort at self
government
Squanto
Kidnapped by English in
1615
Taught Pilgrims how to
farm
Peaceful relations with NA
Pilgrim lifestyle
Separatist (Pilgrims)
Women
Widows = own land
Bring cases to court
Family
Educated children/ indentured servants
Farming = low profit for England
Large families!
Puritans in New England
Great Migration 1620s and 1630s
Dissenters (Puritans)
People who disagree with religious or political
opinions in England
Massachusetts Bay Company
Build an ideal Christian community in New England
What advantage did the Puritans have upon arrival that the
Pilgrims did not?
1630 Massachusetts Bay Colony
Heavily supplied
Plymouths help
Traded animals/grain
Little problems with NA
Reduced in #s
1,000 people move to
this area
New England: Family Life
Married in their 20s
Many children to help work on farm
Womens duty:
Obey husband
Have children
Manage household
New England: Education
1636 John Harvard
creates first college for
ministers
Education Law in 1647
Parents must teach
children to read and
understand the bible
First public education
law
New England: Economy
New England -
topography
Climate harsh, soil rocky,
few rivers = few cash
crops
Farmed by families-
gardens
Little slavery
Fishing/ shipbuilding/
whaling/ fur trading
Craftsmen- blacksmiths,
weavers, printers-
apprentices
Dissent in Massachusetts
Religious disagreements among colonist led to
Many banished
Create Connecticut Thomas Hooker
Create Rhode Island Roger Williams/Anne
Hutchinson
Salem Witch Trials
Summary: New England Lifestyle
Religion is important
Created towns
Skilled labor created diverse economy
Conflict led to new colonies
Middle Colonies
Middle Colonies
New York/New Jersey
Dutch (New Netherland)
New Netherland = New York
New Jersey diverse population, created by English
Pennsylvania
Quakers from New Jersey
Penn advertises in Europe
Land and freedom of religion
A city plan checkerboard pattern
Middle Colonies: Economy
Middle - topography
Combination of
Southern/New England
Colonies
Rivers???
Staple crops wheat, barley,
oats
More slaves than NE but
more indentured servants that
S
Summary: Middle Colonies
Indentured Servants
Staple crops
Rural and urban city planning
Southern Colonies
Maryland
English Catholics
Proprietors
Owners controlled govt,
wealthy
Starts with farming corn, wants
to make profit so switches to
Protestants begin to move in
Religious conflict
Toleration Act of 1649
First law supporting religious
tolerance
Carolinas
Started as one, split in 1729
because of size and distance
North
Poor farmers from Virginia
South
One of the first to rely on slave
labor
More African slaves than
whites
Grow rice
Georgia
Colony of Debtors
Savannah
Blocks for housing set up
Farms by poor, few rich
Rules on Slaves
Outlawed slaves, farmers
did not like
Eventually slaves will be
allowed because they get
rid of charter, allow royal
rule instead.
Southern: Economy
Southern - topography
Agriculture
Large and small plantations
Cash crops
Tobacco, rice, indigo
Southern:
Economy
Southern
Plantations/Slavery
Cash crops = large labor
force
Slaves > Indentured
Servants
SC most slaves
Slave Codes
Laws to control slaves
Home schooled - sent to
towns
Religion practiced at
home
Summary: Southern Lifestyle
Based on agriculture/cash crops
Religion important
Spread out therefore self-dependent
Slavery
Government in the Colonies
Starting a Colony - Charter
Three forms-
Proprietary (MD)
Company (VA, MA)
Royal (GA)
Privy Council
Governing the Colonies
Colonies govern themselves, how?
Governor-
enforce English policy
Advisory councils
Colonial Assemblies (General Court in NE)
ex. House of Burgesses in VA
Make laws, taxes, organize local govt, military
Governing the Colonies:
Governors
Royal
King appoints
Company
Colonial Assemblies elect
Proprietary
Proprietor appoints, approved by King
Governing the Colonies:
Advisory Councils
Advisory Councils (in all three)
Appointed by Governor
Elected by public
Governing the Colonies:
Colonial Assemblies
Modeled on English Parliament
bicameral legislature
Colonist Elect the Assembly
Run by town/county meetings
Legislature: makes laws
Each town 2-3 reps
Boston, Salem, Mystic, Newton and more from New Hampshire to
Massachusetts
Reps elect governor ( vs. a Royal Governor)
Example: Jamestown, VA
House of Burgesses
Council of State/House of Burgesses
Government
King/Queen (President)
Privy Council (Cabinet)
Governor (State Governor)
Advisory Council (Governors advisors)
Colonial Assembly (Congress)
Town Meetings
(public voice in government = democracy)
Governing the Colonies
Town meetings
In New England (each
towns affairs)
County meetings
Southern Colonies
Both
Middle Colonies
Governing the Colonies: Courts
Courts
Reflect each colony
Religious? (MA)
Summary: Government
Three types of colonies: Company, Proprietary,
Royal
Structured like England
Governor- enforce English/colonial policies
Advisory Council advise governor
Colonial Assemblies make laws
James II
New York, New Jersey, and
really ALL colonies
Wants more control
Dominion of New England
Edmund Andros
Glorious Revolution- James
II overthrown
Colonies kick out Andros
EFFECT: Conflict begins
between Colonies and
England.
Trading
England made $ by Mercantilism (Wealth
from Trading)
Favorable Balance of Trade: More Exports and
Fewer Imports
Trading
Navigation Acts Regulate trade with colonies
Enumerated Articles: Specific items can only be
traded with England
Sugar, tobacco, cotton
Use English ships
Stop at English ports and pay Duties
Trading
English View
Colonies have a Protected Market
Pros outweigh Cons
Colonist View
English demand determines price
Tobacco (too much and couldnt sell to other countries)
Smuggling up
Triangular Trade
British West Indies important in trade
Slave trade successful ships made in New England
Middle Passage Slave trade from Africa to Americas
You might also like
- Unto a Good Land: A History of the American People, Volume 1: To 1900From EverandUnto a Good Land: A History of the American People, Volume 1: To 1900No ratings yet
- Ekiti State Civil Service Commission Test Questions PDFDocument40 pagesEkiti State Civil Service Commission Test Questions PDFghyy100% (3)
- One Pager by Period Review PacketDocument11 pagesOne Pager by Period Review PacketJul TolNo ratings yet
- American Colonies ChartDocument1 pageAmerican Colonies ChartkaycockNo ratings yet
- Pakistan and Changing Regional Apparatus PDFDocument6 pagesPakistan and Changing Regional Apparatus PDFsalmanyz6100% (5)
- Study Cards Colony GroupsDocument3 pagesStudy Cards Colony Groupsapi-241517653100% (1)
- Heneral Luna Study Guide PDFDocument30 pagesHeneral Luna Study Guide PDFKarl Bruno AbenojarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 UsaDocument99 pagesLecture 2 UsaZeenat IshfaqNo ratings yet
- Apush Final Review GuideDocument24 pagesApush Final Review GuideLauren WeldonNo ratings yet
- The Road To RevolutionDocument50 pagesThe Road To RevolutionBob PoolNo ratings yet
- The Colonial Era - Spring 2014Document41 pagesThe Colonial Era - Spring 2014api-261097177No ratings yet
- Ch.2 Thirteen ColoniesDocument23 pagesCh.2 Thirteen ColoniesKira YoshikageNo ratings yet
- I. First European Explorations of North America: A) SpainDocument20 pagesI. First European Explorations of North America: A) SpainaelythNo ratings yet
- Colonial Regions ReadingsDocument4 pagesColonial Regions Readingsapi-274356655No ratings yet
- The Official APUSH Cram PacketDocument20 pagesThe Official APUSH Cram PacketAnna PawlowiczNo ratings yet
- APUSH Year 1 ReviewDocument30 pagesAPUSH Year 1 ReviewLise RubleNo ratings yet
- 13 Colonies ComparisonDocument30 pages13 Colonies Comparisonapi-244459124No ratings yet
- AP Us History ReviewDocument76 pagesAP Us History ReviewGregarious JCNo ratings yet
- 13 Colonies Flashcards With AnswersDocument3 pages13 Colonies Flashcards With Answersapi-264814345No ratings yet
- 8:22 - Puritans and New EnglandDocument2 pages8:22 - Puritans and New EnglandTyler PerryNo ratings yet
- American Pageant Chapter 3Document5 pagesAmerican Pageant Chapter 3Stephanie WangNo ratings yet
- United States History: Cram PacketDocument20 pagesUnited States History: Cram PacketDaniel ShimNo ratings yet
- AP US History Study Guide 2Document59 pagesAP US History Study Guide 2dssguy99No ratings yet
- One Pager by Period Review PacketDocument11 pagesOne Pager by Period Review Packetone of manyNo ratings yet
- 13 British ColoniesDocument46 pages13 British ColoniesSarah SunNo ratings yet
- New England ColoniesDocument6 pagesNew England ColoniesDennis PincayNo ratings yet
- AP US History Study GuideDocument19 pagesAP US History Study Guidedssguy9983% (6)
- Amsco Period 2 Colonial AmericaDocument15 pagesAmsco Period 2 Colonial AmericaMarijuli RodriguezNo ratings yet
- History Exam Notes 3Document1 pageHistory Exam Notes 3Sally KishiNo ratings yet
- Middle & Southern ColoniesDocument13 pagesMiddle & Southern ColoniesRebecca DukeNo ratings yet
- AP US History ReviewDocument76 pagesAP US History Revieweddie209No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3jp654No ratings yet
- American Colonies: Colony Founded Region Founder Religion Government Original Purpose Economics NoteDocument2 pagesAmerican Colonies: Colony Founded Region Founder Religion Government Original Purpose Economics NotetheconformistNo ratings yet
- 1st Chunk of US History VocabDocument15 pages1st Chunk of US History VocabiameunwoobaeNo ratings yet
- US HISTORY+Colonial RegimeDocument37 pagesUS HISTORY+Colonial RegimeElena Garcia-PaullierNo ratings yet
- Founding of English Colonies in North American Continent LECTURE # 2Document8 pagesFounding of English Colonies in North American Continent LECTURE # 2Noor Muhammad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- British Society Leading To Civil WarDocument11 pagesBritish Society Leading To Civil WarAnnie Antet Nini ShaNo ratings yet
- 13 Colonies FoundedDocument3 pages13 Colonies FoundedBilly BoyNo ratings yet
- Test 1 HISTDocument6 pagesTest 1 HISTbrekkea007No ratings yet
- The Thirteen English Colonies Power PointDocument51 pagesThe Thirteen English Colonies Power PointTimothy FolkinsNo ratings yet
- Wk2 - BritishColony and SlaveryDocument28 pagesWk2 - BritishColony and SlaveryTempleton KimNo ratings yet
- Colonies AssignmentDocument5 pagesColonies AssignmentGigi trazaNo ratings yet
- APUSH Quick ReviewDocument19 pagesAPUSH Quick ReviewakanareillyNo ratings yet
- The Thirteen Colonies and The British Empire 1607-1750Document5 pagesThe Thirteen Colonies and The British Empire 1607-1750TheGreatHelper50% (2)
- Questions To AddressDocument7 pagesQuestions To AddressAlexa SchleinNo ratings yet
- The Institutions of American Economic Growth: Prof. Wojciech Bieńkowski Warsaw University - OSA Spring, 2016Document44 pagesThe Institutions of American Economic Growth: Prof. Wojciech Bieńkowski Warsaw University - OSA Spring, 2016Julia SkakunNo ratings yet
- Ultimate APUSH Terms! :DDocument92 pagesUltimate APUSH Terms! :DPandaManderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Colonial LifeDocument16 pagesChapter 2-Colonial LifeAustin Rosenberg LeeNo ratings yet
- Thirteen Colonies and English Empire Amsco ch2Document16 pagesThirteen Colonies and English Empire Amsco ch2ftacct5No ratings yet
- 1.3 Early British ColoniesDocument7 pages1.3 Early British ColoniesAnisaaulia ZaviaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 US History Review 2Document3 pagesUnit 1 US History Review 2Li LeoNo ratings yet
- American Revolution NotesDocument32 pagesAmerican Revolution NotesCharles Bell100% (1)
- OboiDocument6 pagesOboiVera WuNo ratings yet
- DBQ Essay Example 2Document2 pagesDBQ Essay Example 2gurukasikhNo ratings yet
- History of the United States I CLEP Quick Prep SheetFrom EverandHistory of the United States I CLEP Quick Prep SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Understanding British Culture Through American EyesFrom EverandUnderstanding British Culture Through American EyesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Comparison and Contextualization (Seventh Grade Social Science Lesson, Activities, Discussion Questions and Quizzes)From EverandComparison and Contextualization (Seventh Grade Social Science Lesson, Activities, Discussion Questions and Quizzes)No ratings yet
- 5th Grade US History Textbook: Colonial America - Birth of A Nation: Fifth Grade Books US Colonial PeriodFrom Everand5th Grade US History Textbook: Colonial America - Birth of A Nation: Fifth Grade Books US Colonial PeriodNo ratings yet
- Igor YuriDocument23 pagesIgor Yuri10131No ratings yet
- Digest Heirs of Julao Vs AlejandroDocument2 pagesDigest Heirs of Julao Vs AlejandroDhin CaragNo ratings yet
- Intergroup and Third Party Peacemaking InterventionsDocument23 pagesIntergroup and Third Party Peacemaking InterventionsSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Akta Pelajaran 1961 - Education (Grants) (Amendment) Regulation 1966Document3 pagesAkta Pelajaran 1961 - Education (Grants) (Amendment) Regulation 1966Onie YunusNo ratings yet
- Textbook Controlling The Electoral Marketplace How Established Parties Ward Off Competition 1St Edition Joost Van Spanje Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument54 pagesTextbook Controlling The Electoral Marketplace How Established Parties Ward Off Competition 1St Edition Joost Van Spanje Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFaurelia.obrien991100% (15)
- Christian Response To AIDS, Homophobia and Violence Against WomenDocument62 pagesChristian Response To AIDS, Homophobia and Violence Against WomenbobbyramakantNo ratings yet
- Ras Doumeira IncidentDocument4 pagesRas Doumeira IncidentZoltan NagyNo ratings yet
- Effects of Foot Patrol 4 3 2 1Document4 pagesEffects of Foot Patrol 4 3 2 1Nelson OroscaNo ratings yet
- Agdangan MassacreDocument1 pageAgdangan MassacreKat BatanNo ratings yet
- Economic of MiracleDocument18 pagesEconomic of MiraclenabilahNo ratings yet
- Minority Stress Scale-Balsam Et Al., 2013Document23 pagesMinority Stress Scale-Balsam Et Al., 2013Ioni SerbanNo ratings yet
- Appointment RecieptDocument3 pagesAppointment RecieptManan RavalNo ratings yet
- Administrator Wolfe Letter To LegislatorsDocument1 pageAdministrator Wolfe Letter To LegislatorsAnthony DaBruzziNo ratings yet
- Sadia Essay GCUFDocument5 pagesSadia Essay GCUFSadia HakimNo ratings yet
- Tan Vs Comelec 142 SCRA 727Document1 pageTan Vs Comelec 142 SCRA 727Raffy Roncales100% (1)
- ChronicleDocument72 pagesChronicleJean HainoNo ratings yet
- Contract Marriage Racket Busted in Hyderabad, Two Sudanese HeldDocument2 pagesContract Marriage Racket Busted in Hyderabad, Two Sudanese Heldabad bookNo ratings yet
- MP Booth ListDocument72 pagesMP Booth ListRavi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Sir Syed Political ThoughtDocument2 pagesSir Syed Political ThoughtMuhammed RafiNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Social Science Practice PaperDocument7 pagesClass 9 Social Science Practice PaperShreya GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Emmanuel Terray An Encounter Althusser and MachiavelliDocument21 pagesEmmanuel Terray An Encounter Althusser and MachiavelligrljadusNo ratings yet
- One World Under AllahDocument47 pagesOne World Under AllahAli ShivaieNo ratings yet
- Solidarity Humanity HonourDocument1 pageSolidarity Humanity HonourBoris GoranovNo ratings yet
- Great American Dream Research PaperDocument10 pagesGreat American Dream Research PaperKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- Business2019 9 10641778Document9 pagesBusiness2019 9 10641778Vinoth RNo ratings yet
- Baza Medici Primari Timisoara 01112020 DSPDocument6 pagesBaza Medici Primari Timisoara 01112020 DSPDoman MihaelaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Permit To Carry Report PDFDocument359 pages2014 Permit To Carry Report PDFRachel E. Stassen-BergerNo ratings yet