Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C Binary Tree With An Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
C Binary Tree With An Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
Uploaded by
Deepak Kumar RaiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C Binary Tree With An Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
C Binary Tree With An Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
Uploaded by
Deepak Kumar RaiCopyright:
Available Formats
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 1/14
16 69 Like
Home
Free eBook
Contact
About
Start Here
C Binary Tree with an Example C Code
(Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
by Himanshu Arora on February 27, 2013
Tweet 14
Binary tree is the data structure to maintain data into memory of program. There exists many data
structures, but they are chosen for usage on the basis of time consumed in insert/search/delete
operations performed on data structures.
Binary tree is one of the data structures that are efficient in insertion and searching operations. Binary
tree works on O (logN) for insert/search/delete operations.
Binary tree is basically tree in which each node can have two child nodes and each child node can
itself be a small binary tree. To understand it, below is the example figure of binary tree.
Binary tree works on the rule that child nodes which are lesser than root node keep on the left side and
child nodes which are greater than root node keep on the right side. Same rule is followed in child
nodes as well that are itself sub-trees. Like in above figure, nodes (2, 4, 6) are on left side of root node
(9) and nodes (12, 15, 17) are on right side of root node (9).
We will understand binary tree through its operations. We will cover following operations.
Create binary tree
Search into binary tree
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 2/14
Delete binary tree
Displaying binary tree
Creation of binary tree
Binary tree is created by inserting root node and its child nodes. We will use a C programming
language for all the examples. Below is the code snippet for insert function. It will insert nodes.
11 void insert(node ** tree, int val) {
12 node *temp = NULL;
13 if(!(*tree)) {
14 temp = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
15 temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
16 temp->data = val;
17 *tree = temp;
18 return;
19 }
20
21 if(val < (*tree)->data) {
22 insert(&(*tree)->left, val);
23 } else if(val > (*tree)->data) {
24 insert(&(*tree)->right, val);
25 }
26 }
This function would determine the position as per value of node to be added and new node would be
added into binary tree. Function is explained in steps below and code snippet lines are mapped to
explanation steps given below.
[Lines 13-19] Check first if tree is empty, then insert node as root.
[Line 21] Check if node value to be inserted is lesser than root node value, then
a. [Line 22] Call insert() function recursively while there is non-NULL left node
b. [Lines 13-19] When reached to leftmost node as NULL, insert new node.
[Line 23] Check if node value to be inserted is greater than root node value, then
a. [Line 24] Call insert() function recursively while there is non-NULL right node
b. [Lines 13-19] When reached to rightmost node as NULL, insert new node.
Searching into binary tree
Searching is done as per value of node to be searched whether it is root node or it lies in left or right
sub-tree. Below is the code snippet for search function. It will search node into binary tree.
46 node* search(node ** tree, int val) {
47 if(!(*tree)) {
48 return NULL;
49 }
50 if(val == (*tree)->data) {
51 return *tree;
52 } else if(val < (*tree)->data) {
53 search(&((*tree)->left), val);
54 } else if(val > (*tree)->data){
55 search(&((*tree)->right), val);
56 }
57 }
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 3/14
This search function would search for value of node whether node of same value already exists in
binary tree or not. If it is found, then searched node is returned otherwise NULL (i.e. no node) is
returned. Function is explained in steps below and code snippet lines are mapped to explanation steps
given below.
1. [Lines 47-49] Check first if tree is empty, then return NULL.
2. [Lines 50-51] Check if node value to be searched is equal to root node value, then return node
3. [Lines 52-53] Check if node value to be searched is lesser than root node value, then call
search() function recursively with left node
4. [Lines 54-55] Check if node value to be searched is greater than root node value, then call
search() function recursively with right node
5. Repeat step 2, 3, 4 for each recursion call of this search function until node to be searched is
found.
Deletion of binary tree
Binary tree is deleted by removing its child nodes and root node. Below is the code snippet for
deletion of binary tree.
38 void deltree(node * tree) {
39 if (tree) {
40 deltree(tree->left);
41 deltree(tree->right);
42 free(tree);
43 }
44 }
This function would delete all nodes of binary tree in the manner left node, right node and root
node. Function is explained in steps below and code snippet lines are mapped to explanation steps
given below.
[Line 39] Check first if root node is non-NULL, then
a. [Line 40] Call deltree() function recursively while there is non-NULL left node
b. [Line 41] Call deltree() function recursively while there is non-NULL right node
c. [Line 42] Delete the node.
Displaying binary tree
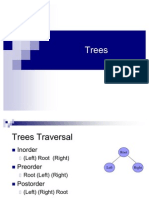
Binary tree can be displayed in three forms pre-order, in-order and post-order.
Pre-order displays root node, left node and then right node.
In-order displays left node, root node and then right node.
Post-order displays left node, right node and then root node.
Below is the code snippet for display of binary tree.
28 void print_preorder(node * tree) {
29 if (tree) {
30 printf("%d\n",tree->data);
31 print_preorder(tree->left);
32 print_preorder(tree->right);
33 }
34 }
35 void print_inorder(node * tree) {
36 if (tree) {
37 print_inorder(tree->left);
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 4/14
38 printf("%d\n",tree->data);
39 print_inorder(tree->right);
40 }
41 }
42 void print_postorder(node * tree) {
43 if (tree) {
44 print_postorder(tree->left);
45 print_postorder(tree->right);
46 printf("%d\n",tree->data);
47 }
48 }
These functions would display binary tree in pre-order, in-order and post-order respectively. Function
is explained in steps below and code snippet lines are mapped to explanation steps given below.
Pre-order display
a. [Line 30] Display value of root node.
b. [Line 31] Call print_preorder() function recursively while there is non-NULL left node
c. [Line 32] Call print_preorder() function recursively while there is non-NULL right node
In-order display
a. [Line 37]Call print_inorder() function recursively while there is non-NULL left node
b. [Line38] Display value of root node.
c. [Line 39] Call print_inorder() function recursively while there is non-NULL right node
Post-order display
a. [Line 44] Call print_postorder() function recursively while there is non-NULL left node
b. [Line 45] Call print_postorder() function recursively while there is non-NULL right node
c. [Line46] Display value of root node.
Working program
It is noted that above code snippets are parts of below C program. This below program would be
working basic program for binary tree.
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
struct bin_tree {
int data;
struct bin_tree * right, * left;
};
typedef struct bin_tree node;
void insert(node ** tree, int val)
{
node *temp = NULL;
if(!(*tree))
{
temp = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = val;
*tree = temp;
return;
}
if(val < (*tree)->data)
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 5/14
{
insert(&(*tree)->left, val);
}
else if(val > (*tree)->data)
{
insert(&(*tree)->right, val);
}
}
void print_preorder(node * tree)
{
if (tree)
{
printf("%d\n",tree->data);
print_preorder(tree->left);
print_preorder(tree->right);
}
}
void print_inorder(node * tree)
{
if (tree)
{
print_inorder(tree->left);
printf("%d\n",tree->data);
print_inorder(tree->right);
}
}
void print_postorder(node * tree)
{
if (tree)
{
print_postorder(tree->left);
print_postorder(tree->right);
printf("%d\n",tree->data);
}
}
void deltree(node * tree)
{
if (tree)
{
deltree(tree->left);
deltree(tree->right);
free(tree);
}
}
node* search(node ** tree, int val)
{
if(!(*tree))
{
return NULL;
}
if(val < (*tree)->data)
{
search(&((*tree)->left), val);
}
else if(val > (*tree)->data)
{
search(&((*tree)->right), val);
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 6/14
}
else if(val == (*tree)->data)
{
return *tree;
}
}
void main()
{
node *root;
node *tmp;
//int i;
root = NULL;
/* Inserting nodes into tree */
insert(&root, 9);
insert(&root, 4);
insert(&root, 15);
insert(&root, 6);
insert(&root, 12);
insert(&root, 17);
insert(&root, 2);
/* Printing nodes of tree */
printf("Pre Order Display\n");
print_preorder(root);
printf("In Order Display\n");
print_inorder(root);
printf("Post Order Display\n");
print_postorder(root);
/* Search node into tree */
tmp = search(&root, 4);
if (tmp)
{
printf("Searched node=%d\n", tmp->data);
}
else
{
printf("Data Not found in tree.\n");
}
/* Deleting all nodes of tree */
deltree(root);
}
Output of Program:
It is noted that binary tree figure used at top of article can be referred to under output of program and
display of binary tree in pre-order, in-order and post-order forms.
$ ./a.out
Pre Order Display
9
4
2
6
15
12
17
In Order Display
2
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 7/14
16 Tweet 14
69 Like
4
6
9
12
15
17
Post Order Display
2
6
4
12
17
15
9
Searched node=4
> Add your comment
Linux provides several powerful administrative tools and utilities
which will help you to manage your systems effectively. If you dont know what these tools are and
how to use them, you could be spending lot of time trying to perform even the basic administrative
tasks. The focus of this course is to help you understand system administration tools, which will help
you to become an effective Linux system administrator.
Get the Linux Sysadmin Course Now!
If you enjoyed this article, you might also like..
1. 50 Linux Sysadmin Tutorials
2. 50 Most Frequently Used Linux Commands
(With Examples)
3. Top 25 Best Linux Performance Monitoring
and Debugging Tools
4. Mommy, I found it! 15 Practical Linux Find
Command Examples
5. Linux 101 Hacks 2nd Edition eBook
Awk Introduction 7 Awk Print
Examples
Advanced Sed Substitution Examples
8 Essential Vim Editor Navigation
Fundamentals
25 Most Frequently Used Linux
IPTables Rules Examples
Turbocharge PuTTY with 12 Powerful
Add-Ons
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 8/14
Tags: Binary Tree Deletion, Binary Tree in C, Binary Tree Remove, Binary Tree Remove Node,
Binary Tree Search C Code, C Binary Tree Insert, C Binary Tree Search, Display Binary Tree,
Optimal Binary Search Tree
{ 21 comments read them below or add one }
1 Bob February 27, 2013 at 9:45 am
Cool. Thanks for the explanation.
With C++ STL Libraries, we dont have to write this but it is good to know basics.
If you have time, it may be a good idea of going thru the C++ STL libraries and give example
code to do this as well as others (e.g. maps, vectors) to show to use them
2 marcio February 27, 2013 at 10:18 am
When you say O (log N): N is the number of nodes or the height of the tree?
3 bhupesh February 27, 2013 at 12:36 pm
nice explanation. But binary tree doesnt have any rule regarding the key value of a node. Its
binary search tree.
4 Gaurang S February 27, 2013 at 1:41 pm
Hello,
Good article!
1. I think the explanation and algorithms mentioned are of a Binary search tree (BST)
2. Also for a Binary search tree worst case insert/delete/search would be O(N), where N is the
number of elements. The worst case for insertion would occur when the elements are in
ascending or descending order in which nodes will keep on appending to right or to left
respectively.
5 Georgi K March 1, 2013 at 2:22 am
It is nice to have a simple C implementation a lot of embedded micros have no C++ at all,
neither STL.
For me search() didnt find the 4 element, so I added this one:
node* search2(node * tree, int val) {
if( ! tree ) return NULL;
if(val data) {
return search2(tree->left, val);
} else if(val > tree->data) {
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 9/14
return search2(tree->right, val);
}
return tree;
}
6 DuskoKoscica March 4, 2013 at 2:43 am
It is nice, but in some case binary tree is not good enough, and yes you can use the hip.
But, what I would like to read about, is the tree that can have many sub trees..
Like multy way tree..
That would be nice article
7 Robert Nix March 27, 2013 at 1:07 pm
A function missing from your program and description is balancing the binary tree
Given your implementation, the worst possible data you could feed the program would be a pre-
sorted list, because all the values would cascade down the right side of the tree, never using the
left nodes at all. This, effectively, would simply be a linked list, with a lot of non-useful
compares of the left node addresses.
Adding a tree balancing routine to be called after insertions would solve this problem.
8 Payal April 7, 2013 at 4:46 am
search isnt working:(
9 Joe May 6, 2013 at 5:36 pm
Can you point me in the direction to applying this to strings instead of integers? Saying building
a tree with H,G,A, etc
10 Robert Nix May 7, 2013 at 6:45 pm
Since its just a comparison, the code should work equally well for numbers or letters. Just
change the variable type used.
11 DuskoKoscica May 8, 2013 at 7:08 am
Now it might sound funny, but if you wanna combine the char and int or float, and some other
things you could use unions, and struct, and so on
12 wisnusakti May 27, 2013 at 6:46 pm
tanks. but function search isnt working, and in function insert temp that never used
13 debbie xu June 19, 2013 at 12:26 pm
tmp = search(&root, 4); could be tmp = search(root,4), of course you need to change the
prototype of search into node* search(node * tree, int val) and implementation inside
accordingly.
Either way, I also ran into problem with search: actually the code found the searched node, its
just that the simple assignment of tmp=xxx doesnt work. I printed out the value returned
from search() before it returns, and the tmp after it has been assigned to the search() result, they
dont match !!! cant figure out why. so I added a third parameter into search() to get the result
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 10/14
as following:
node* search(node * tree, int val, node **found)
{
*found = NULL;
if(!(tree))
{
return NULL;
}
if(val data)
{
search(((tree)->left), val, found);
}
else if(val > (tree)->data)
{
search(((tree)->right), val, found);
}
else if(val == (tree)->data)
{
*found = tree;
return tree;
}
}
and call it in main like this:
tmp1 = search(root, 15, &tmp2);
Now tmp2 points to the right node, but tmp1 points to some garbage.
Anybody can figure out why the original search() result cant be assigned correctly? I used gcc
on Linux 2.6.25.
14 debbie June 19, 2013 at 1:15 pm
figured it out, the recursive call didnt return the value. should be like this:
if(val data)
{
return search(((tree)->left), val, found);
}
else if(val > (tree)->data)
{
return search(((tree)->right), val, found);
}
and forget about adding a third parameter into search, no need for it.
15 Habib Beidoun September 26, 2013 at 2:48 am
Fix the search function by adding return in front of the two recursive search calls, e.g.,
return search(&((*tree)->left), val);
The function search does not really require a pointer to a pointer in the first argument (a pointer
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 11/14
would suffice), as that value is not used by the caller and there is already a return.
16 Andrew November 2, 2013 at 12:06 pm
Hi. Its a good explanation of BST. But I have a question about your deltree function.
C language is the language where function parameters are always passed by value.
In this function you pass root pointer as node *root. How free()-function can delete its value
and free a memory?
17 M.Z.M.Hanafy January 30, 2014 at 12:16 am
Thank you so much. Its really excellent work.
18 arul April 15, 2014 at 7:54 am
awesome examples
19 Raghu April 28, 2014 at 3:16 am
Hi.. I just have clarification Please some one help me
When calling insert function what is the need to pass root it with & rather than just root and
De-refrenecing it **?
We can achieve it by passing just root and with single * De-referencing?.
20 NB.Gowri July 31, 2014 at 8:11 am
but tis is program for binary search tree not binary tree.plz anybody post the code for binary
tree.
21 Nirav August 6, 2014 at 9:40 am
This is Binary Search Tree, not Binary Tree.
Leave a Comment
Name
E-mail
Website
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
Submit
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 12/14
Previous post: Linux Sticky Bit Concept Explained with Examples
Next post: How to Copy Files in Linux and Unix? 10 cp Command Examples
RSS | Email | Twitter | Facebook | Google+
Search
COURSE
Linux Sysadmin CentOS 6 Course - Master the Tools, Configure it Right, and be Lazy
EBOOKS
Linux 101 Hacks 2nd Edition eBook - Practical Examples to Build a Strong
Foundation in Linux
Bash 101 Hacks eBook - Take Control of Your Bash Command Line and Shell Scripting
Sed and Awk 101 Hacks eBook - Enhance Your UNIX / Linux Life with Sed and Awk
Vim 101 Hacks eBook - Practical Examples for Becoming Fast and Productive in Vim
Editor
Nagios Core 3 eBook - Monitor Everything, Be Proactive, and Sleep Well
The Geek Stuff
7,963 people like The Geek Stuff.
Facebook social plugin
Like
POPULAR POSTS
12 Amazing and Essential Linux Books To Enrich Your Brain and Library
50 UNIX / Linux Sysadmin Tutorials
50 Most Frequently Used UNIX / Linux Commands (With Examples)
How To Be Productive and Get Things Done Using GTD
30 Things To Do When you are Bored and have a Computer
Linux Directory Structure (File System Structure) Explained with Examples
Linux Crontab: 15 Awesome Cron Job Examples
Get a Grip on the Grep! 15 Practical Grep Command Examples
Unix LS Command: 15 Practical Examples
15 Examples To Master Linux Command Line History
Top 10 Open Source Bug Tracking System
Vi and Vim Macro Tutorial: How To Record and Play
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 13/14
Mommy, I found it! -- 15 Practical Linux Find Command Examples
15 Awesome Gmail Tips and Tricks
15 Awesome Google Search Tips and Tricks
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
Can You Top This? 15 Practical Linux Top Command Examples
Top 5 Best System Monitoring Tools
Top 5 Best Linux OS Distributions
How To Monitor Remote Linux Host using Nagios 3.0
Awk Introduction Tutorial 7 Awk Print Examples
How to Backup Linux? 15 rsync Command Examples
The Ultimate Wget Download Guide With 15 Awesome Examples
Top 5 Best Linux Text Editors
Packet Analyzer: 15 TCPDUMP Command Examples
The Ultimate Bash Array Tutorial with 15 Examples
3 Steps to Perform SSH Login Without Password Using ssh-keygen & ssh-copy-id
Unix Sed Tutorial: Advanced Sed Substitution Examples
UNIX / Linux: 10 Netstat Command Examples
The Ultimate Guide for Creating Strong Passwords
6 Steps to Secure Your Home Wireless Network
Turbocharge PuTTY with 12 Powerful Add-Ons
CATEGORIES
Linux Tutorials
Vim Editor
Sed Scripting
Awk Scripting
Bash Shell Scripting
Nagios Monitoring
OpenSSH
IPTables Firewall
Apache Web Server
MySQL Database
Perl Programming
Google Tutorials
Ubuntu Tutorials
PostgreSQL DB
Hello World Examples
C Programming
C++ Programming
DELL Server Tutorials
Oracle Database
VMware Tutorials
Ramesh Natarajan
Follow
About The Geek Stuff
10/9/2014 C Binary Tree with an Example C Code (Search, Delete, Insert Nodes)
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/02/c-binary-tree/ 14/14
My name is Ramesh Natarajan. I will be posting instruction guides, how-to,
troubleshooting tips and tricks on Linux, database, hardware, security and web. My focus is to
write articles that will either teach you or help you resolve a problem. Read more about Ramesh
Natarajan and the blog.
Support Us
Support this blog by purchasing one of my ebooks.
Bash 101 Hacks eBook
Sed and Awk 101 Hacks eBook
Vim 101 Hacks eBook
Nagios Core 3 eBook
Contact Us
Email Me : Use this Contact Form to get in touch me with your comments, questions or
suggestions about this site. You can also simply drop me a line to say hello!.
Follow us on Google+
Follow us on Twitter
Become a fan on Facebook
Copyright 20082014 Ramesh Natarajan. All rights reserved | Terms of Service
You might also like
- TreeDocument654 pagesTreesumitNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Assignment 4Document2 pagesData Structures Assignment 4Priyanshu JainNo ratings yet
- Lec-10 Trees - BSTDocument41 pagesLec-10 Trees - BSTTaqi ShahNo ratings yet
- Microproject DsuDocument10 pagesMicroproject Dsumrpython456No ratings yet
- PROGRAM 3.a, B, CDocument17 pagesPROGRAM 3.a, B, CPRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Lab Record Assignment 2024Document57 pagesLab Record Assignment 2024amonakdan123No ratings yet
- How Would You Check If A Binary Tree Is BalancedDocument11 pagesHow Would You Check If A Binary Tree Is BalancedZubair AlamNo ratings yet
- Program-1: Write A Program To Implement Binary Tree Traversals (Preorder, Inorder and Postorder)Document12 pagesProgram-1: Write A Program To Implement Binary Tree Traversals (Preorder, Inorder and Postorder)Carl JacksonNo ratings yet
- Me - Ads Lab 2022Document39 pagesMe - Ads Lab 2022roshni mohan kumarNo ratings yet
- Daa FileDocument45 pagesDaa FileLeena SehrawatNo ratings yet
- Write A C Program To (I.e, Free Up Its Nodes)Document23 pagesWrite A C Program To (I.e, Free Up Its Nodes)Umesh NarayananNo ratings yet
- Binary Tree - Set 1 (Introduction) : 8.implementation of Trees, Tree TraversalsDocument30 pagesBinary Tree - Set 1 (Introduction) : 8.implementation of Trees, Tree TraversalsAnand DuraiswamyNo ratings yet
- Mahedi 4.1 4.2Document7 pagesMahedi 4.1 4.2Mahedi HassanNo ratings yet
- Ex. No: 1 Date: Recursive Function For Tree Traversal and FibonacciDocument79 pagesEx. No: 1 Date: Recursive Function For Tree Traversal and FibonacciKARTHI KEYANNo ratings yet
- Unit8 TreeDocument12 pagesUnit8 TreeBabuNo ratings yet
- 16Document7 pages16Big BuddyNo ratings yet
- IGU 3rd Sem Pratical FileDocument33 pagesIGU 3rd Sem Pratical Filemohit9812228845No ratings yet
- BSEM-F20-113-Assignment No #4-DSADocument11 pagesBSEM-F20-113-Assignment No #4-DSAMuhammad zafar JahangirNo ratings yet
- DSFILEDocument30 pagesDSFILErkbhaskar222No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Summer 2019Document8 pagesMidterm Exam Summer 2019ExcaliburNo ratings yet
- EX10Document4 pagesEX10Surendar 07No ratings yet
- C++ Full Course 2Document80 pagesC++ Full Course 2Tarandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Kenny 230723 Data Structures Interview QuestionsDocument16 pagesKenny 230723 Data Structures Interview QuestionsvanjchaoNo ratings yet
- Data Strucutre Que Paper Solution1Document20 pagesData Strucutre Que Paper Solution1Raider GamingNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 9 Implement Binary Search Tree ADT Using Linked ListDocument18 pagesExperiment No.: 9 Implement Binary Search Tree ADT Using Linked ListHarsh AlashiNo ratings yet
- Linked List Using C Homework Help: The Problems: PS3.0: Node and ListDocument13 pagesLinked List Using C Homework Help: The Problems: PS3.0: Node and ListProgramming Homework HelpNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Struktur Data BAB 7 TREEDocument5 pagesPraktikum Struktur Data BAB 7 TREEbek bek 01No ratings yet
- Questions 2.5Document12 pagesQuestions 2.521E135 MAHIESHWAR.JNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document118 pagesWeek 3Điệp TônNo ratings yet
- Technical 2Document3 pagesTechnical 2NIRANJAN BEHERANo ratings yet
- Daa Lab Manual Iii Cse I SemDocument55 pagesDaa Lab Manual Iii Cse I SemRemiNo ratings yet
- DSA Practical PDFDocument23 pagesDSA Practical PDFDheeraj SonkhlaNo ratings yet
- Btree All Operations Notes With ProgramsDocument16 pagesBtree All Operations Notes With ProgramsakurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- DS ModuleDocument39 pagesDS ModuleÇháråñ ÇhèrryNo ratings yet
- Boundary Traversal of Binary Tree - GeeksforGeeksDocument17 pagesBoundary Traversal of Binary Tree - GeeksforGeeksAlok Kumar HotaNo ratings yet
- 22CSP02 - DS Lab Question BankDocument24 pages22CSP02 - DS Lab Question Banksreekumaran1102No ratings yet
- CP4161 Adsa Lab RecordDocument109 pagesCP4161 Adsa Lab RecordDayana dossNo ratings yet
- Major AssignDocument26 pagesMajor Assign3wpaoNo ratings yet
- Asd Assignment - Nadia CasmerDocument8 pagesAsd Assignment - Nadia CasmerNadia CasmerNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductionSiddhant JakinkarNo ratings yet
- BST Lecture 1 - Class NotesDocument7 pagesBST Lecture 1 - Class Notesvignesh waranNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument103 pagesData Structures and Algorithmspranjit1No ratings yet
- Computer Science & Engineering Computer Science & EngineeringDocument6 pagesComputer Science & Engineering Computer Science & Engineeringlostinspace981No ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document10 pagesLab Report 5abinashreddy792No ratings yet
- DSAL Ass5 WriteupDocument10 pagesDSAL Ass5 WriteupGaurav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Dsa Assignment 2Document30 pagesDsa Assignment 2Devendhiran DasarathanNo ratings yet
- Prog 7Document40 pagesProg 7capiron22No ratings yet
- Program and OutputDocument69 pagesProgram and Outputpriyadharshinimr50No ratings yet
- Tree TraversalsDocument4 pagesTree TraversalsSiddharth AfriaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Binary TreeDocument7 pagesImplementation of Binary TreenehaNo ratings yet
- CSD201Document11 pagesCSD201Nguyen Hai Anh (K17 HL)No ratings yet
- ADSA lab manual finalDocument129 pagesADSA lab manual finalvinithadevibe1998No ratings yet
- Slip 14Document2 pagesSlip 14Suyash ThoratNo ratings yet
- C Prom 2Document23 pagesC Prom 2joshua18012005No ratings yet
- DS & AlgDocument10 pagesDS & Algjadhavkaran203No ratings yet
- Exe8 1 2Document6 pagesExe8 1 2srikakarla1No ratings yet
- Binary Tree TraversalDocument6 pagesBinary Tree TraversalShabaz MondalNo ratings yet
- 1 CBookPart2Document80 pages1 CBookPart2SAIDHANYA SUDHAN T C B 18BES7004No ratings yet
- DsaDocument64 pagesDsaPrajwal PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)