Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gene and Gene Expression
Gene and Gene Expression
Uploaded by
RaviNagiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gene and Gene Expression
Gene and Gene Expression
Uploaded by
RaviNagiCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a Gene?
A gene is the basic unit of inheritance.
Gregor Mendel, 1865. Experiments in Plant Hybridization.
Verhandlungen des naturforschenden Vereines in Brnn, 4:3-47
Probability
# of times outcome is expected/ # of opportunities
Given as a fraction, percentage, or proportion of 1
Product Rule: The probability that two independent events both occurring
is the product of each event occurring separately.
Using a fair die, the chance of rolling a 1 is 1/6, 16.7%, or .167
Using a pair of fair dice, the chance of rolling two 1s is
1/6 X 1/6 = 1/36 or 0.027
Sum Rule: The probability that either of two mutually exclusive events will
occur is the sum of the probability of each event.
Using a fair die, the chance of rolling either a 2 or a 3
1/6 + 1/6 = 1/3 or 0.333
and
or
1/36
Using a pair of fair dice, the chance of rolling two 1s is
1/6 X 1/6 = 1/36 or 0.027
Product Rule: The probability that two independent events both occurring
is the product of each event occurring separately.
1/36
1/36
Sum Rule: The probability that either of two mutually exclusive events will
occur is the sum of the probability of each event.
Using a pair of fair dice, the chance of rolling a 2 and a 3 or
A 3 and a 2 are 1/36 + 1/36= 2/36 or 1/18
You are playing backgammon and your
opponent has you on the ropes.
However you can knock him off the
board with a role of a ten.
What is the probability of rolling a ten
with two die?
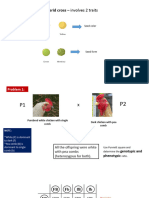
The seven phenotypic pairs studied by Mendel
Gamete
specialized haploid cells that function during reproduction
Egg
Sperm
Plants: Egg is located in Ovule
Sperms cells are located in Pollen
Cross-pollination and selfing are two types of crosses
Figure 2-12 part 2
Figure 2-12 part 3
Yellow trait is dominant
Green is recessive
Figure 2-12 part 4
Figure 2-12 part 5
Figure 2-12 part 6
Figure 2-12 part 7
Figure 2-12 part 8
Figure 2-12 part 9
Figure 2-12 part 10
Figure 2-12 part 11
Figure 2-12 part 12
Figure 2-12 part 13
Figure 2-12 part 14
Figure 2-12 part 15
Punnett Squares
Test Cross
Table 2-1
These data are pretty darn close to the expected 3:1, but are they close
enough to support the hypothesis?
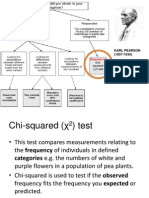
2
(chi-square) Test
Goodness of Fit
2
= (0bserved-Expected)
2
/Expected
Class Observed Expected (O-E)
(O-E)
2
(O-E)
2
/E
round 5474 5493
(75%)
-19 361
361/5493
= 0.065
wrinkled 1850 1831
(25%)
19 361 361/1831
= 0.197
Total 7324 7325
2
= 0.262
Degrees of Freedom = # of independent variables
i.e., # of groups -1
2
Distribution - degrees of freedom
P
r
o
b
a
b
i
l
i
t
y
2
= (0bserved-Expected)
2
/Expected
Class Observed Expected (O-E)
(O-E)
2
(O-E)
2
/E
Yellow 105
Green 95
Total 200
2
=
Degrees of Freedom = # of independent variables
i.e., # of groups -1
Yellow X Green
Test the Hypothesis that it is a Test-Cross
2
(chi-square) Test
Important considerations:
* the P value is the probability of a deviation at
least as large as what was found. A p of 0.05 means that 1 in 20 times,
you may find a deviation this large or larger not never.
* having passed the test means that the results are
consistent, not that the results prove the hypothesis.
* Since the chi-square value is related to 1/# of
expected, the test becomes more accurate
with larger numbers.
1)Recessive trait present in F1
hybrid -heterozygotes. One
maternal copy and One Paternal
copy.
2) Recessive trait in progeny was
same as in grandparent.
3) Traits found in a 3:1 ratio in F
2
generation
Mendels First Law of Inheritance
Begins to differentiate Genotype (internally coded trait) from Phenotype
(outwardly manifested trait).
Figure 3-3 step4
Forked-Line Diagram for
Gamete Frequencies
RrYy
Dihybrid
R
r
Y
y
Y
y
1/2
1/2
1/2
1/2
1/2
1/2
Gamete Frequency
RY X =
Ry X =
ry X =
rY X =
2
(chi-square) Test
2
= (0bserved-Expected)
2
/Expected
Phenotype Observed Expected (O-E) (O-E)
2
(O-E)
2
/E
Round,
Yellow
315 313 2 4 0.013
Round,
Green
108 104 4 16 0.154
Wrinkled,
Yellow
101 104 -3 9 0.087
Wrinkled,
Green
32 35 -3 9 0.257
Total 55566
556
2
=
0.511
Df = 3
Data are consistent with Independent Segregation
Rules of Inheritance
1) The units of inheritance (genes) come in pairs.
Each gamete will get only one of the two units of
inheritance . The progeny then gets one maternal
and one paternal copy.
2) The segregation of one gene pair is most often
independent of the segregation of another gene
pair independent assortment.
You might also like
- Chi Square TutorialDocument4 pagesChi Square TutorialCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Lab: The Chi-Square TestDocument13 pagesLab: The Chi-Square TestJoey Ma100% (1)
- Principles of Genetics Chapter 3 ProblemsDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Genetics Chapter 3 Problemskoolgirl212No ratings yet
- Genetics Problems With AnswersDocument45 pagesGenetics Problems With Answersprofptrajasekharan84% (57)
- Drosophila Lab ReportDocument7 pagesDrosophila Lab ReportTim HepburnNo ratings yet
- Bio3TC17 Chi Square Test NotesDocument9 pagesBio3TC17 Chi Square Test NotesFounder ChaNo ratings yet
- animal breeding lab sampleDocument6 pagesanimal breeding lab samplecalebdl716No ratings yet
- Activity No.7 - Chi Square and Binomial Probability-LEPASANADocument4 pagesActivity No.7 - Chi Square and Binomial Probability-LEPASANAMichael Clyde lepasana100% (2)
- Lec12 Application of Mendel's PrincipleDocument62 pagesLec12 Application of Mendel's PrincipleSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Principles of ProbabilityDocument40 pagesPrinciples of ProbabilityRoleenJohnJavierNo ratings yet
- Chi SquareDocument10 pagesChi Squareaaditya01No ratings yet
- Two Traits Each Gamete Must Have One of Each Letter Two Copies of EACH LetterDocument8 pagesTwo Traits Each Gamete Must Have One of Each Letter Two Copies of EACH LetterLilCocoPuff JuniorNo ratings yet
- Fly Lab JS - Genetics of OrganismsDocument8 pagesFly Lab JS - Genetics of Organismsqsvmq8nzdcNo ratings yet
- Maddogz43 - Stats Layout PracticeDocument4 pagesMaddogz43 - Stats Layout PracticeMahmoud ElsayedNo ratings yet
- The Test Use This Test WhenDocument23 pagesThe Test Use This Test WhenHellen Jeans TutorNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 Exercise 2 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFDocument9 pagesGROUP 2 Exercise 2 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFMary Joy Annika MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Pendugaan Rasio Genotipe Dan Fenotipe, Polihibrid, Chi SquareDocument38 pagesPendugaan Rasio Genotipe Dan Fenotipe, Polihibrid, Chi SquareRose Novita Sari H100% (1)
- Laboratory Assessment 3Document4 pagesLaboratory Assessment 3Juliano, Jhanielle Faye B.No ratings yet
- Chi SquareDocument9 pagesChi SquaregedfireNo ratings yet
- Genetic Exp 1 & 2Document14 pagesGenetic Exp 1 & 2Yap ChinyeowNo ratings yet
- Statistics in GeneticsDocument21 pagesStatistics in GeneticsWONG JIE MIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 5 NotesNandiniNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Q3Document29 pagesStatistics and Probability Q3JayVince DelgadoNo ratings yet
- GC SY Bistatistics III - Chi Square Test Practice SumsDocument2 pagesGC SY Bistatistics III - Chi Square Test Practice SumsVijendraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4-Genetic of Corn The Dhi-Square Analysis (Monohybrid Cross)Document5 pagesExperiment 4-Genetic of Corn The Dhi-Square Analysis (Monohybrid Cross)NUR SABRINA MOHD SHAHNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square Test A Nonparametric Hypothesis TestDocument52 pagesChi-Square Test A Nonparametric Hypothesis Testatul2021No ratings yet
- Lecture Set 5Document32 pagesLecture Set 5Dirt KickNo ratings yet
- Ch02-2 Dihybrid PDFDocument43 pagesCh02-2 Dihybrid PDFLuke LKNo ratings yet
- BARRAQUIAS Probability and Chi SquareDocument3 pagesBARRAQUIAS Probability and Chi SquareFatima Shiera BarraquiasNo ratings yet
- Probabilties and Chi Square TestDocument14 pagesProbabilties and Chi Square TestHarsh Vardhan Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2110 - GeneticsDocument44 pagesBIOL 2110 - GeneticsshaheenNo ratings yet
- Chi Squared TestDocument12 pagesChi Squared Testapi-188431847No ratings yet
- 03a L3 Bio Genetics ActivitiesDocument6 pages03a L3 Bio Genetics ActivitiesPamela CambiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Mendalian GeneticsDocument18 pages2 - Mendalian GeneticssalmaNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument13 pagesMathsfaroukgamer797No ratings yet
- Some Probability Distributions: Marnielle A. Salig LecturerDocument59 pagesSome Probability Distributions: Marnielle A. Salig LecturerPonkan BNo ratings yet
- Basics of Probability and StatisticsDocument161 pagesBasics of Probability and Statisticsmao100% (2)
- Chi-Square Test of Goodness-of-FitDocument6 pagesChi-Square Test of Goodness-of-FitMohammedseid AhmedinNo ratings yet
- Gene$cs IIDocument31 pagesGene$cs IIsyanda139580No ratings yet
- EDA-HYPOTHESIS-TESTING-FOR-TWO-SAMPLE (With Answers)Document6 pagesEDA-HYPOTHESIS-TESTING-FOR-TWO-SAMPLE (With Answers)Maryang DescartesNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Biology 164 Laboratory Genetics and Chi-square (χ 2) Problem SetDocument3 pagesAnswer Key Biology 164 Laboratory Genetics and Chi-square (χ 2) Problem SetReseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 - Knowing The Secret of Inheritance - ppt5Document31 pagesLecture 05 - Knowing The Secret of Inheritance - ppt5Alkhair SangcopanNo ratings yet
- The Study of GeneticsDocument19 pagesThe Study of GeneticsKevin DashNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument25 pagesBinomial DistributionFaiq QaziNo ratings yet
- DIHIBRIDDocument8 pagesDIHIBRIDFata HalaniNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid Cross and Chi SquareDocument22 pagesDihybrid Cross and Chi SquareJL Masangcay DayagNo ratings yet
- Addition Rules MathDocument21 pagesAddition Rules MathkiddistnegashNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument57 pagesProbabilityNeerajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 (Independent Study Unit)Document9 pagesChapter 13 (Independent Study Unit)Lauren StamNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Prob-1Document39 pagesLec 3 - Prob-1Waqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- Chi Squared TestDocument20 pagesChi Squared Testaby251188No ratings yet
- CH 03Document9 pagesCH 03SpringjesJiesiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Genetics PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 8 - Genetics PDFAjelandro AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- 315H Handout ChiSquareDocument3 pages315H Handout ChiSquareShyam PopatNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument32 pagesProbability and Statisticsfeysalshiiq4No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet PDFSaif ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Pedigrees and ProbabilityDocument2 pagesLecture 03 - Pedigrees and ProbabilityRamiroCruzoNo ratings yet
- Impulse Balance Theory and its Extension by an Additional CriterionFrom EverandImpulse Balance Theory and its Extension by an Additional CriterionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Sugarcane Juice MachineDocument1 pageSugarcane Juice MachineRaviNagiNo ratings yet
- Bact0102 0066 PDFDocument20 pagesBact0102 0066 PDFRaviNagiNo ratings yet
- 1234 Burj Dubai Stack Effect Passive Stack Effect Mitigation Measures in The Design of The Worlds Tallest Building PDFDocument7 pages1234 Burj Dubai Stack Effect Passive Stack Effect Mitigation Measures in The Design of The Worlds Tallest Building PDFRaviNagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Transcription, RNA Processing, and TranslationDocument18 pagesChapter 16 - Transcription, RNA Processing, and TranslationRaviNagiNo ratings yet