Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evolutionary Biology Zoology
Evolutionary Biology Zoology
Uploaded by
sheebaali21Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evolutionary Biology Zoology
Evolutionary Biology Zoology
Uploaded by
sheebaali21Copyright:
Available Formats
I COURSE II
EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY
THEORY (48 Periods)
Unit 1: Introduction to Evolutionary Theories (4)
Lamarckism, Darwinism, Neo-Darwinism
Unit 2: History of Life (4)
Unit 3: Evidences of Evolution (6)
Fossils as direct evidences, Types of fossils, Reasons for incompleteness of fossil record,
(phylogeny of horse as an example), Molecular evidences (Globin genes).
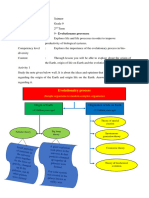
Unit 4: Processes of Evolutionary Change (13)
Causes of organic variations; Role of variations in evolution (with one example); Hardy-
Weinberg equilibrium and Genetic drift; Natural selection: Concept and example (Industrial
melanism)
Unit 5: Products of Evolutionary Change (8)
Biological species concept (Advantages and limitations); Isolating mechanisms, Modes of
speciation (Allopatric, Sympatric)
Unit 6: Mass Extinction (5)
(K-T Extinction)
Unit 7: Origin and Evolution of Man (8)
PRACTICAL
1. Study of fossils from plaster cast models and pictures.
2. Study of homology, analogy and homoplasy from suitable specimens.
3. Study of natural selection under different conditions using simulation exercise.
4. Demonstration of role of natural selection and genetic drift in changing allele
frequencies.
ESSENTIAL READINGS
Ridley, M. (2004). Evolution. III Edition. Blackwell Publishing.
Hall, B. K. and Hallgrimsson, B. (2008). Evolution. IV Edition. Jones and Bartlett
Publishers.
Campbell, N. A. and Reece, J. B. (2011). Biology. IX Edition, Pearson, Benjamin,
Cummings
SUGGESTED READINGS
Moody, P. A. (1962). Introduction to Evolution. New York Harper.
Savage, J. M. (1963). Evolution. Holy, Rinehart and Winston.
You might also like
- 22 ZoologyDocument33 pages22 ZoologyMalsawmkima Maski-aNo ratings yet
- UG Syllabus ZoologyDocument28 pagesUG Syllabus ZoologyHarsh Pandey 9 - BNo ratings yet
- Conditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and ReflectionsDocument15 pagesConditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and Reflectionsapi-3713202No ratings yet
- Organic Evolution TheoriesDocument8 pagesOrganic Evolution TheoriesCynthia Adeline SNo ratings yet
- Evolution: Evidence and Mechanisms: Definitions: The Hypothesis ThatDocument28 pagesEvolution: Evidence and Mechanisms: Definitions: The Hypothesis ThatLeighNo ratings yet
- Evolution: Evidence and Mechanisms: Definitions: The Hypothesis ThatDocument28 pagesEvolution: Evidence and Mechanisms: Definitions: The Hypothesis ThatLeighNo ratings yet
- PaleontologyDocument2 pagesPaleontologyMrNo ratings yet
- Theodosius Dobzhansky - Evolutionary BiologyDocument458 pagesTheodosius Dobzhansky - Evolutionary BiologyHolaq Ola OlaNo ratings yet
- Evidence of EvolutionDocument50 pagesEvidence of EvolutionjosellsulfelixNo ratings yet
- The Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormFrom EverandThe Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Unit 9Document4 pagesGrade 9 Unit 9zainahmoh.21No ratings yet
- 8712 PDFDocument290 pages8712 PDFSantiago TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Zoology 2Document16 pagesZoology 2Amod KumarNo ratings yet
- Day - 1 Zoology 12.04.2024Document3 pagesDay - 1 Zoology 12.04.2024nayakdisha2008No ratings yet
- Invertebrate PaleontologyDocument10 pagesInvertebrate Paleontologypshtiwan majidNo ratings yet
- BiolDocument44 pagesBiolMark Adrian FalcutilaNo ratings yet
- BSC Zoology SyllabusDocument5 pagesBSC Zoology SyllabusUmar BagbanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Evolution: The American Biology Teacher, March 1973, 35 (3) : 125-129Document2 pagesIntro To Evolution: The American Biology Teacher, March 1973, 35 (3) : 125-129Ghie LhaneNo ratings yet
- Jitorres - Herron (2016) Origins of Multicellular Complexity Volvox and The Volvocine AlgaeDocument11 pagesJitorres - Herron (2016) Origins of Multicellular Complexity Volvox and The Volvocine Algaevaleria ocampoNo ratings yet
- 1997 - Morphé and EvolutionDocument30 pages1997 - Morphé and EvolutionGiuseppe DamianiNo ratings yet
- Controversies On The Origin of Life PDFDocument10 pagesControversies On The Origin of Life PDFMarvin OlidNo ratings yet
- 21 BotanyDocument18 pages21 BotanyMalsawmkima Maski-a0% (1)
- Developmental BiologyDocument28 pagesDevelopmental Biologyعمر بن عليNo ratings yet
- University of Allahabad Choice Based Credit System Syllabus (Zoology)Document27 pagesUniversity of Allahabad Choice Based Credit System Syllabus (Zoology)Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Ii SemDocument2 pagesIi SemAnnaNo ratings yet
- Maurizio Meloni, John Cromby, Des Fitzgerald, Stephanie Lloyd (Eds.) - The Palgrave Handbook of Biology and Society-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2018)Document926 pagesMaurizio Meloni, John Cromby, Des Fitzgerald, Stephanie Lloyd (Eds.) - The Palgrave Handbook of Biology and Society-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2018)MariosNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument55 pagesEvolutionAaron Paul TañedoNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Phylogeny Animal ClassificationDocument10 pagesTaxonomy and Phylogeny Animal ClassificationTapan Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Conflicting Models For The Origin of Life 1St Edition Stoyan K Smoukov Full ChapterDocument67 pagesConflicting Models For The Origin of Life 1St Edition Stoyan K Smoukov Full Chapternatalie.schoonmaker930100% (7)
- Vi Sem Zoology Syllabus 2023 24Document4 pagesVi Sem Zoology Syllabus 2023 24DARSHAN KUMAR TNo ratings yet
- Variation and Variability: Central Concepts in Biology: B H B K. HDocument7 pagesVariation and Variability: Central Concepts in Biology: B H B K. HKatleen MartínezNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Prospects For A Return of PDFDocument32 pagesAssessing The Prospects For A Return of PDFManuel Quezada CNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Associative Learning A 20170514 3502 1559lpd With Cover Page v2Document11 pagesThe Evolution of Associative Learning A 20170514 3502 1559lpd With Cover Page v2gg5834256No ratings yet
- General Biology Lecture Note (2Document290 pagesGeneral Biology Lecture Note (2oronew0No ratings yet
- The Evolution of Agency and Other Essays: Kim SterelnyDocument24 pagesThe Evolution of Agency and Other Essays: Kim SterelnyMichael RogersNo ratings yet
- C Bot-201Document3 pagesC Bot-201Abdullah Mukhtar MirzaNo ratings yet
- Perspective: Evo-Devo and An Expanding Evolutionary Synthesis: A Genetic Theory of Morphological EvolutionDocument12 pagesPerspective: Evo-Devo and An Expanding Evolutionary Synthesis: A Genetic Theory of Morphological Evolutionmaurolasso8120No ratings yet
- Amundson The Changing Role of Embryo in Evolutionary ThoughtDocument295 pagesAmundson The Changing Role of Embryo in Evolutionary ThoughtvereniceNo ratings yet
- A Vuelta de Las Potencias en Biología Evolucionista: Hacia Una Ontología de Lo PosibleDocument18 pagesA Vuelta de Las Potencias en Biología Evolucionista: Hacia Una Ontología de Lo PosiblejoshBenNo ratings yet
- Biology: Biology Deals With The Study of Life. Top: and Bottom: andDocument7 pagesBiology: Biology Deals With The Study of Life. Top: and Bottom: andheiNo ratings yet
- Biology As A Science of LifeDocument18 pagesBiology As A Science of LifeAndy TapiaNo ratings yet
- Teoria EvolDocument15 pagesTeoria EvollauraethosNo ratings yet
- History of Evolutionary ThoughtDocument26 pagesHistory of Evolutionary Thoughtss1987maNo ratings yet
- Biology: EtymologyDocument1 pageBiology: EtymologySyimah UmarNo ratings yet
- Evolution3 DJ Futuyma Contents OnlyDocument9 pagesEvolution3 DJ Futuyma Contents OnlyAnonymous 1QvBZ2xYd100% (1)
- Code ZOOL Course DetailsDocument67 pagesCode ZOOL Course DetailsMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Importnt Questions For Practice Class Xii Biology: (1 Mark)Document1 pageImportnt Questions For Practice Class Xii Biology: (1 Mark)IshvaryaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Biology: Ingo BrigandtDocument33 pagesPhilosophy of Biology: Ingo BrigandtHenrique AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Unit 1 OutlineDocument1 pageBio 11 Unit 1 OutlineshahdkaroutNo ratings yet
- Written Report - BIODocument17 pagesWritten Report - BIOLady Lou Ignacio LepasanaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Chromosomal Change in Plant Evolution PDFDocument241 pagesThe Role of Chromosomal Change in Plant Evolution PDFFabio SantosNo ratings yet
- Bio 14 Spring 2021 SyllabusDocument10 pagesBio 14 Spring 2021 SyllabusSayeda JobaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Plant DiversityDocument262 pagesModule 1 Plant DiversityMastermind0% (1)
- Elsc - WeeDocument13 pagesElsc - WeeKai ClavelNo ratings yet
- Morphology (Biology) : Morphology of A Male ShrimpDocument3 pagesMorphology (Biology) : Morphology of A Male ShrimpMyfbook PageNo ratings yet
- Evo-Devo: Evolutionary Developmental Mechanisms: Int. J. Dev. Biol. 47: 491-495 (2003)Document5 pagesEvo-Devo: Evolutionary Developmental Mechanisms: Int. J. Dev. Biol. 47: 491-495 (2003)Marcelo Geraldo TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Zoology 100 NotesDocument12 pagesZoology 100 Notesangel_witchie619No ratings yet
- Syllabus For Lecturer 10+2 ZoologyDocument2 pagesSyllabus For Lecturer 10+2 ZoologyAsad AsadNo ratings yet