Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Measuring Eigenstates
4 Measuring Eigenstates
Uploaded by
Lin Xian XingOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Measuring Eigenstates
4 Measuring Eigenstates
Uploaded by
Lin Xian XingCopyright:
Available Formats
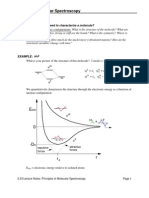
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY: The Determination of Energy Eigenstates
NACruz Q4 09-10
Steps in the measurement of energy eigenstates
1. Define an initial state, , with energy, .
2. Allow the system at to interact w/ an external stimulant of
known properties. This causes a change in state from to
with a corresponding energy change from .
3. Applying conservation laws, means = , i.e.,
the is measured.
Remarks
The measurement of a physical variable involves indeterminacy.
& .
,
.
The energy, , of the initial state, , is well-defined, i.e., is an
eigenstate of the energy operator corresponding to .
Problem: Most systems contain many components, e.g., molecules,
whose energy states change rapidly over time. Some components
have lowest energy, , some have energies greater( ) than this.
Facts: # of components having is a constant.
The higher the temperature, the greater the # of components
having .
The mean translational energy of colliding molecules is given by
.
Collision obeys conservation laws and causes the ff
.
many have .
& many
molecules
have
, , . . , their energies are NOT WELL-DEFINED.
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY: The Determination of Energy Eigenstates
NACruz Q4 09-10
For physically constrained systems, the energy eigenstates are
discrete.
The energy spectrum is made up of discrete eigenvalues, =
, , , , usually represented by an E level diagram (fig 1).
Remarks
Horizontal lines represent eigenvalues.
Energy changes represented by arrows (transitions) occur as a
response to external stimuli.
Fig 1
Examples
System
Eigenvalue equation
Particle in 1D
=
box
2
For = 1, 2, . . ,
Vibration of
1
a diatomic
= +
molecule
2
1
+
2
For = 0,1, . . ,
Eigenstates
=
of H
24
For = 1,2, ,
2
Remarks
Only energy corresponding to
can cause a transition
Constrain the molecule only
vibrational motion is manifested.
=
= . .
=
=
=
QUANTUM CHEMISTRY: The Determination of Energy Eigenstates
NACruz Q4 09-10
For H atom the ff energy levels are generated from the eigenstate
equation in the table.
values
4
-0.0850
3
-1.511
2
-3.400
-13.597
Fig 2
You might also like
- StatisticalPhysics Part1 HandoutDocument27 pagesStatisticalPhysics Part1 HandoutMauro LaraNo ratings yet
- Basic ThermoDocument22 pagesBasic ThermoRoselyn BoNo ratings yet
- 2 Statistical Description of SystemsDocument51 pages2 Statistical Description of SystemsSebastian mdalahelaNo ratings yet
- L1 - Dynamic Models and AnalogiesDocument4 pagesL1 - Dynamic Models and AnalogiesSana DINo ratings yet
- Derivation of 1D Harmonic OscillatorDocument12 pagesDerivation of 1D Harmonic OscillatorKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Work and HeatDocument39 pagesChapter Three: Work and Heatamare mitkuNo ratings yet
- The Canonical Partition FunctionDocument15 pagesThe Canonical Partition FunctionWellington ZorzettiNo ratings yet
- Basic Quantum MechanicsDocument38 pagesBasic Quantum MechanicsAlmas GulfNo ratings yet
- 2 Energy Conversion and General Energy Analysis PDFDocument64 pages2 Energy Conversion and General Energy Analysis PDFCabagnot Piolo JuliusNo ratings yet
- Lab Work 4. Motion of A Charged Particle in An Electric Field 222131Document6 pagesLab Work 4. Motion of A Charged Particle in An Electric Field 222131daniyar.kanuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: Cengel Florio 14FDocument29 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction: Cengel Florio 14Fs73a1thNo ratings yet
- Molecular Dynamics SimulationDocument49 pagesMolecular Dynamics SimulationredaelwanNo ratings yet
- Lagrange Equation 1Document32 pagesLagrange Equation 1Gthulasi78No ratings yet
- Energy ConceptsDocument20 pagesEnergy Conceptscarlos peñaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Thermodynamic - : Chapter 2: Energy, Energy Transfer & General Energy AnalysisDocument14 pagesAdvanced Thermodynamic - : Chapter 2: Energy, Energy Transfer & General Energy AnalysisRezza SimieNo ratings yet
- End SEM SyllabusDocument45 pagesEnd SEM SyllabusShreyans KothariNo ratings yet
- Principles of Molecular SpectrosDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Molecular SpectrosShaheentariq_4No ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Rotational SpectrosDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy Rotational SpectrosMONERAH D ALOSAIMINo ratings yet
- Lagrange Equations: Use Kinetic and Potential Energy To Solve For Motion!Document32 pagesLagrange Equations: Use Kinetic and Potential Energy To Solve For Motion!Ribal KhreisNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Statistical MechanicsDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Statistical MechanicsM8Rirmpi01No ratings yet
- Análisis Transp de EnergíaDocument52 pagesAnálisis Transp de EnergíaCarlos ParedesNo ratings yet
- 1) ScriptDocument55 pages1) Scriptyamanappagouda gudagaladinnyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Energy Balances: 9.2. Types of Energy To Be Included in Energy BalancesDocument7 pagesChapter 9. Energy Balances: 9.2. Types of Energy To Be Included in Energy Balancesاحمد ماجد زبنNo ratings yet
- DS - Lec 1Document7 pagesDS - Lec 1Sherif SaidNo ratings yet
- EMEDocument38 pagesEMErajwinder234No ratings yet
- Exp 6Document13 pagesExp 6GlenNo ratings yet
- Elements 1Document5 pagesElements 1ckg rmyNo ratings yet
- The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesThe First Law of ThermodynamicsJOHN ROLIE MAMELOCONo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document13 pagesThermodynamics 1steyvohmannaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Molecular SpectrosDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Molecular SpectrosoomganapathiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Energy Equations 094651Document22 pagesPart 2 Energy Equations 094651CedricNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual ThermodynamicsDocument0 pagesSolution Manual ThermodynamicsVigna Ruban Ram100% (1)
- Advanced ThermodynamicsDocument209 pagesAdvanced ThermodynamicsDangsony DangNo ratings yet
- The Flying Ice CubeDocument15 pagesThe Flying Ice Cubebitted2No ratings yet
- Energy Lesson 1Document32 pagesEnergy Lesson 1liumarr36No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2Document11 pagesTutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2JoserineNo ratings yet
- Microwave Infrared: SpectrosDocument66 pagesMicrowave Infrared: SpectrosPrathamesh Dash100% (2)
- 4 Lasers 2 PDFDocument10 pages4 Lasers 2 PDFDark WolfNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spin System: 1 GradingDocument4 pagesQuantum Spin System: 1 GradingSouzaSantosNo ratings yet
- The First Law of Thermodynamics:: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesThe First Law of Thermodynamics:: Objectiveshussain dawoodNo ratings yet
- 2intro To Physical SystemDocument4 pages2intro To Physical SystemMehmet Akif DemirlekNo ratings yet
- AstaInfrared SpectrosDocument14 pagesAstaInfrared SpectrosEub EuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lecture Notes For Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 3 Ed by Cengel and BolesDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Lecture Notes For Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 3 Ed by Cengel and Bolessam_kamali85100% (1)
- ch1 PDFDocument26 pagesch1 PDFDono SusilNo ratings yet
- SCY1612Document59 pagesSCY1612rieNo ratings yet
- Art 04Document6 pagesArt 04INVICTA.lew.roNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document45 pagesChapter 3aberamamo15No ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactionsDocument22 pagesNuclear ReactionsSparsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- 1 - Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeDocument6 pages1 - Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeSagi IbiNo ratings yet
- 6 - ImpactDocument20 pages6 - ImpactAbdallah HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2Ishin MatoiNo ratings yet
- 3 Thermo I Chapter 3 Lec2Document51 pages3 Thermo I Chapter 3 Lec2tarikus893No ratings yet
- Intro and Basic ConceptsDocument12 pagesIntro and Basic ConceptsShane BuragaNo ratings yet
- Year 3 FormulaDocument13 pagesYear 3 Formulaapi-250366166No ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactions LecDocument32 pagesNuclear Reactions Lecjon alex100% (1)
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureFrom EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6No ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Chapter 10-Work Energy and PowerDocument15 pagesChapter 10-Work Energy and PowerLin Xian Xing100% (1)
- Lec07 Special RelativityDocument20 pagesLec07 Special RelativityLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Chem 154 LE4 SamplexDocument3 pagesChem 154 LE4 SamplexLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- CHM12 3lu6 PDFDocument97 pagesCHM12 3lu6 PDFLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- 111 Prob Set 3Document1 page111 Prob Set 3Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Composition of MuscleDocument41 pagesComposition of MuscleLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Wpe WorksheetDocument2 pagesWpe WorksheetLin Xian Xing0% (1)
- 060 Half Life WorksheetDocument3 pages060 Half Life WorksheetLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Use Your Time Wisely.: Exam 3 Chemistry 122 April 20, 2009Document7 pagesUse Your Time Wisely.: Exam 3 Chemistry 122 April 20, 2009Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Test 07 Energy 05dkDocument13 pagesTest 07 Energy 05dkLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- PHY11 Lesson 9 Fluids in MotionDocument18 pagesPHY11 Lesson 9 Fluids in MotionLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- CHEM443 Fall 2014 Oldquiz1 SolutionDocument4 pagesCHEM443 Fall 2014 Oldquiz1 SolutionLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibria PDFDocument30 pagesAcid Base Equilibria PDFLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Rect Comp 2dDocument39 pagesRect Comp 2dLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- CHM11-3Lecture Unit #1 PDFDocument57 pagesCHM11-3Lecture Unit #1 PDFLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Fef 11Document15 pagesFef 11Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Knight27 Gauss LectDocument14 pagesKnight27 Gauss LectLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Projectile Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesProjectile Multiple ChoiceLin Xian XingNo ratings yet