Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMP Cheat Sheet
PMP Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
roofiliaqat24Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6Document2 pagesCheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6rimrany87% (15)
- Q & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionFrom EverandQ & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- PMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)Document6 pagesPMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)phongbkac4690% (10)
- PMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- PMP Study SheetDocument3 pagesPMP Study SheetRobincrusoe88% (26)
- PMP Formulas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Cheat SheetAn Nguyen100% (12)
- Matthew Lesko Let Uncle Sam Pay Your Bills PDFDocument33 pagesMatthew Lesko Let Uncle Sam Pay Your Bills PDFCarol100% (4)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Cheat SheetoovijaygNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument5 pagesPMP Formulasbhaveshkumar78100% (8)
- CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsFrom EverandCAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PMP Exam Prep SummaryDocument5 pagesPMP Exam Prep SummaryAshenafi100% (8)
- PMP Memory SheetsDocument6 pagesPMP Memory Sheets1hass197% (30)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PMP Cheat Sheet 6 PagesDocument6 pagesPMP Cheat Sheet 6 PagesSergio Alves92% (12)
- 60 Days - PMP Study PlanDocument3 pages60 Days - PMP Study PlanShahram Karimi100% (7)
- PMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rewrite The Two Goals Below To Make Them SMART. Then Explain What Makes Them Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-BoundDocument2 pagesRewrite The Two Goals Below To Make Them SMART. Then Explain What Makes Them Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-BoundMatthew NowackNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Study Notes PDFDocument83 pagesPMBOK Study Notes PDFshetupuc93% (27)
- Crack PMP in 45 DaysDocument10 pagesCrack PMP in 45 Daysgolfmaniac48% (21)
- ITTO Trick Sheet 49 Process - Jan 18 V 1.0 PMBOK 6th EditionDocument26 pagesITTO Trick Sheet 49 Process - Jan 18 V 1.0 PMBOK 6th EditionAbdulla Jawad Alshemary84% (25)
- Key Acupoints PDFDocument6 pagesKey Acupoints PDFthouartu50% (2)
- Unit4 AuditingDocument37 pagesUnit4 Auditingdangthanhhd79100% (8)
- CAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamFrom EverandCAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamNo ratings yet
- PMP Full ExamDocument51 pagesPMP Full Examrvsreddy197285% (26)
- Edward PMP Study NotesDocument76 pagesEdward PMP Study NotesWaqas Ahmed94% (16)
- PMP Study SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Study SheetAli Abdelmoniem Ahmed75% (4)
- PMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookDocument10 pagesPMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookIbrahimSamir100% (9)
- PMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)Document53 pagesPMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)girishkris92% (25)
- A Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideFrom EverandA Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideNo ratings yet
- IFC2x3 TC1 Entity Hierarchy PDFDocument17 pagesIFC2x3 TC1 Entity Hierarchy PDFthouartuNo ratings yet
- Application For Use of Church FacilitiesDocument1 pageApplication For Use of Church Facilitieseasygoing1No ratings yet
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamFrom EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- PMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdateFrom EverandPMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsFrom Everand50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsNo ratings yet
- PMP Study MaterialsDocument90 pagesPMP Study Materialsamira_salama100% (5)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesPMP Cheat Sheetsachin.nate525782% (11)
- PMP Notes FinalDocument24 pagesPMP Notes Finalumerillias89% (9)
- PMP FormulasDocument3 pagesPMP Formulaspolters100% (8)
- PMP Practice Makes Perfect: Over 1000 PMP Practice Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP Practice Makes Perfect: Over 1000 PMP Practice Questions and AnswersRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationFrom EverandThe Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationNo ratings yet
- PMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasFrom EverandPMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasNo ratings yet
- How to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptFrom EverandHow to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- PMP/CAPM EXAM PREP: A Basic Guide to Activity-On-Node and Critical Path MethodFrom EverandPMP/CAPM EXAM PREP: A Basic Guide to Activity-On-Node and Critical Path MethodNo ratings yet
- PgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PM Interview: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learning and Studying Project Manager Job Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPM Interview: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learning and Studying Project Manager Job Interview Questions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- PMI Certification: Learn The Secrets To Pass All The PMI Exams And Getting Certified Quickly And Easily. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsFrom EverandPMI Certification: Learn The Secrets To Pass All The PMI Exams And Getting Certified Quickly And Easily. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- PMP: Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: Updated for the 2015 ExamFrom EverandPMP: Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: Updated for the 2015 ExamNo ratings yet
- World Religious Views of Health and HealingDocument34 pagesWorld Religious Views of Health and HealingthouartuNo ratings yet
- Acu Chakra ConnectionflowDocument2 pagesAcu Chakra ConnectionflowthouartuNo ratings yet
- Goldsmith MOJO ScorecardDocument3 pagesGoldsmith MOJO ScorecardthouartuNo ratings yet
- Aspect of Prana Prana Apana Udana Samana VyanaDocument3 pagesAspect of Prana Prana Apana Udana Samana VyanathouartuNo ratings yet
- Using A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamDocument28 pagesUsing A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamthouartuNo ratings yet
- MongodbDocument66 pagesMongodbthouartuNo ratings yet
- The Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlDocument27 pagesThe Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlthouartuNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondDocument14 pagesBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondthouartuNo ratings yet
- MX Injection TestingDocument24 pagesMX Injection TestingthouartuNo ratings yet
- Elem Am 98 RepeatabilityDocument13 pagesElem Am 98 RepeatabilitythouartuNo ratings yet
- Helm ClashdetectionDocument7 pagesHelm ClashdetectionMayouran WijayakumarNo ratings yet
- 6 Packet Spring13Document6 pages6 Packet Spring13thouartuNo ratings yet
- The Science of Hindu SpiritualityDocument12 pagesThe Science of Hindu SpiritualitythouartuNo ratings yet
- SanskritDocument8 pagesSanskritthouartu0% (2)
- Aryabhateeya: Trivandrum 695 018, India (0471-2490149)Document27 pagesAryabhateeya: Trivandrum 695 018, India (0471-2490149)thouartuNo ratings yet
- SPI-Software Process ImprovementDocument24 pagesSPI-Software Process ImprovementthouartuNo ratings yet
- CBR Marketing Akshat AVasthiDocument28 pagesCBR Marketing Akshat AVasthiAkshat AvasthiNo ratings yet
- 2024.01.21 Dolphin CompanyDocument2 pages2024.01.21 Dolphin CompanyAlfred CharlesNo ratings yet
- Why Renting Is Better Than BuyingDocument4 pagesWhy Renting Is Better Than BuyingMonali MathurNo ratings yet
- AGREEMENT AntipoloDocument3 pagesAGREEMENT AntipoloLen Lacson MarianoNo ratings yet
- 12 Points) : A B: Over Co de Ex Out Down Re Ultra UnderDocument2 pages12 Points) : A B: Over Co de Ex Out Down Re Ultra UnderRobert CalcanNo ratings yet
- (Pmbok® Guide) Sixth EditionDocument41 pages(Pmbok® Guide) Sixth EditionNaba majeadNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument28 pagesBCG MatrixsatishNo ratings yet
- P 13-9A - SolutionDocument1 pageP 13-9A - SolutionMichelle GraciaNo ratings yet
- A Critical Look at The Movie Office SpaceDocument2 pagesA Critical Look at The Movie Office Spacealiimran080103No ratings yet
- Product Exchange Process - Service Damage: Old Product Old ProductDocument2 pagesProduct Exchange Process - Service Damage: Old Product Old ProductsameerjaleesNo ratings yet
- Apqc How Organizations Are Using Apqc Process PDFDocument13 pagesApqc How Organizations Are Using Apqc Process PDFsergioivanrsNo ratings yet
- PPE Review For A PPE Review For A: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)Document6 pagesPPE Review For A PPE Review For A: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)JANISCHAJEAN RECTONo ratings yet
- 1 Running Head: Grant Proposal Strategic PlanDocument6 pages1 Running Head: Grant Proposal Strategic PlanJoseph WainainaNo ratings yet
- Willem Hoek: This Notes Relates To SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) 5.0Document11 pagesWillem Hoek: This Notes Relates To SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) 5.0m abbasiNo ratings yet
- Makati SEP 2018Document38 pagesMakati SEP 2018Yanni AlmadronesNo ratings yet
- Maintenace Kits - Pavers-ScreedsDocument12 pagesMaintenace Kits - Pavers-ScreedsBruno TrindadeNo ratings yet
- QOS Improvement in MANET Routing by Route Optimization Through Convergence of Mobile AgentDocument6 pagesQOS Improvement in MANET Routing by Route Optimization Through Convergence of Mobile AgentNader JalalNo ratings yet
- Fuel Surcharge - UPS - VietnamDocument3 pagesFuel Surcharge - UPS - VietnamJDS JICENo ratings yet
- Fourth Section: Case of Beşleagă and Others V. RomaniaDocument9 pagesFourth Section: Case of Beşleagă and Others V. Romaniaasm_samNo ratings yet
- OML Determination Complaint 4Document9 pagesOML Determination Complaint 4Robert FucciNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies For Farmers and RanchersDocument6 pagesMarketing Strategies For Farmers and RanchersJASMINE NUR A FNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Guide To Managing Your Partner AccountDocument18 pagesStep-By-Step Guide To Managing Your Partner AccountUsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- Siddharth Jain DMBADocument55 pagesSiddharth Jain DMBApriyanshulunia02No ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument21 pagesManagerial AccountingRam KnowlesNo ratings yet
- MeetFounders Nov 2020 HandoutDocument17 pagesMeetFounders Nov 2020 HandoutAndrew BottNo ratings yet
- Surya Pricelist Compressed 1Document92 pagesSurya Pricelist Compressed 1Raj Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
PMP Cheat Sheet
PMP Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
roofiliaqat24Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMP Cheat Sheet
PMP Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
roofiliaqat24Copyright:
Available Formats
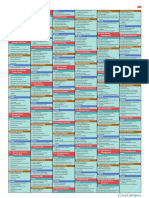
PMP Cheat Sheet and Study Notes
Based on PMBOK V4
The reader is responsible to verify and confirm all information presented herein.
Human Resource Management
Organizational Structures: Functional, Matrix (weak, balanced,
Initiation
strong) , Projectized, Composite
Planning
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs: Physiological, Safety, Social, Self
Execution
-esteem, Self-actualization.
Monitor and Control
McGregor: Theory X, Theory Y.
Closing
Ouchi: Theory Z. Motivated by commitment, opportunity advancement.
Herzbergs Theory of Motivation: Hygiene factors, Motivating Agents.
Knowledge Areas
Leadership Styles: Directing, Facilitating, Coaching, Supporting,
Integration
Autocratic, Consultative, Consensus.
Scope Management
Project Manager Powers: Formal (legitimate,) Reward, Penalty
Time Management
(coercive), Expert, Referent.
Cost Management
Conflict Management: Withdraw (avoid), Smooth (accommodate),
Quality Management
Compromise, Force, Collaborate, Confront (problem solving.)
Quality Management
HR Management
Communications Management Ishikawa = Fishbone Diagram: cause and effect.
Pareto Diagram: Identify problems and frequency. 80/20 Rule.
Procurement Management
Flow
Charts; Control Charts.
Risk Management
Just in Time: Reduces inventory; requires additional quality control.
Professional Responsibility
Quality Theories: Kaizen (continuous improvement,) Six Sigma, TQM
(total quality management.)
Earned Value Management
Kaizen: Small improvements to reduce costs and improve consistency.
BAC = Budget At Completion
Deming Cycle: Plan, Do Check, Act.
EV = Actual % * BAC
Cost Management
PV = Planned % * BAC
Cost Estimating - Accuracy
AC = Sum of all incurred costs Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM): -50% to +100%
Budgetary: -10% to +25%
CV = EV - AC
Definitive: -5% to + 10%
SV = EV - PV
Risk Management
CPI = EV / AC
Risk Strategies (threats): Avoid, Transfer, Mitigate, Accept.
< 1 = Over Budget
Risk Strategies (opportunities): Exploit, Share, Enhance, Accept.
> 1 = Under Budget
Qualitative Risk Analysis: Chance and impact of risk occurrence
SPI = EV / PV
Results in prioritized list of risks; risk ranking.
< 1 = Behind Schedule
Quantitative Risk Analysis: Numerical analysis of probability
> 1 = Ahead of Schedule and impact.
Tools: Interviews, Sensitivity Analysis, Decision Tree Analysis,
EAC = BAC / CPI
Simulation, Monte Carlo Analysis.
EAC = AC + ETC
Closing
EAC = AC + (BAC + EV) / CPI
Contract Close: Before project close
ETC = EAC - AC
Project or Phase Close: Lessons Learned
VAC = BAC - EAC
PMI Code of Ethics: Respect, Fair, Honest.
BCWS = PV
Processes
BCWP = EV
Key Formulas
ACWP = AC
Standard Deviation = (P - O) / 6
Tips:
PERT = (O + 4M + P) / 6
Negative is bad
Positive is good
If Variance: EV - Something
If Index: EV / Something
If Cost related use AC
If Time related use PV
Most formulas start with EV
Total Float = LSES or LF EF
Rules Based on Numbers
80 Hour Rule = Max size of
work packages
Comm Channels = N (N-1) / 2
Where:
P = Pessimistic
O = Optimistic
M = Most likely; Realistic
N = # Project Members
Benefit Cost Ratio =
Cost / Benefits
BCR < 1 Unfavorable
BCR > 1 Higher is Better
Net Present Value =
80/20 Rule = Paretos Law
20% of causes responsible for FV / (1 + r)^n
80% of problems
Future Value =
PV (1 + i)^n
0/50/100 = Work package
completion. No credit until
50% complete. No additional
credit until 100% complete.
Internal Rate of Return
Higher is better
Six Sigma: 99.99% defect free
Time Management
42 Project Management Processes
Project Integration Management
1. Develop Project Charter
2. Develop Project Management Plan
3. Direct / Manage Project Execution
4. Monitor / Control Project Work
5. Perform Integrated Change Control
6. Close Project or Phase
Project Scope Management
7. Collect Requirements
8. Define Scope
9. Create WBS
10. Verify Scope
11. Control Scope
Project Time Management
12. Define Activities
13. Sequence Activities
14. Estimate Activity Resources
15. Estimate Activity Durations
16. Develop Schedule
17. Control Schedule
Project Cost Management
18. Estimate Costs
19. Determine Budget
20. Control Costs
Project Quality Management
21. Plan Quality
22. Perform Quality Assurance
23. Perform Quality Control
Project Human Resource
Management
24. Develop Human Resource Plan
25. Acquire Project Team
26. Develop Project Team
27. Manage Project Team
Project Communications
Management
28. Identify Stakeholders
29. Plan Communications
30. Distribute Information
31. Manage Stakeholder Expectations
Precedence Diagramming Method
PDM: Activity-on-Node (AON)
32. Report Performance
Arrow Diagram Method
ADM: Activity-on-Arrow (AOA)
33. Plan Risk Management
Conditional Diagram Method
Graphical Evaluation and Review
Technique (GERT): Allows loop
35. Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
Project Risk Management
34. Identify Risks
36. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
Crashing: Add more resources
37. Plan Risk Responses
Fast Tracking: Tasks in parallel
38. Monitor and Control Risks
Forward Pass: Early start, early
finish
Backward Pass: Late start, late
finish
Float; Slack: activity margin off
critical path
Free Float: activity margin not
impacting early start of next dependant activity
Project Float
Project Procurement Management
39. Plan Procurements
40. Conduct Procurements
41. Administer Procurements
42. Close Procurements
Copyright 2009 PMServicesNW
All rights reserved
www.PMServicesNW.com
You might also like
- Cheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6Document2 pagesCheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6rimrany87% (15)
- Q & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionFrom EverandQ & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- PMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)Document6 pagesPMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)phongbkac4690% (10)
- PMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- PMP Study SheetDocument3 pagesPMP Study SheetRobincrusoe88% (26)
- PMP Formulas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Cheat SheetAn Nguyen100% (12)
- Matthew Lesko Let Uncle Sam Pay Your Bills PDFDocument33 pagesMatthew Lesko Let Uncle Sam Pay Your Bills PDFCarol100% (4)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Cheat SheetoovijaygNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument5 pagesPMP Formulasbhaveshkumar78100% (8)
- CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsFrom EverandCAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PMP Exam Prep SummaryDocument5 pagesPMP Exam Prep SummaryAshenafi100% (8)
- PMP Memory SheetsDocument6 pagesPMP Memory Sheets1hass197% (30)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PMP Cheat Sheet 6 PagesDocument6 pagesPMP Cheat Sheet 6 PagesSergio Alves92% (12)
- 60 Days - PMP Study PlanDocument3 pages60 Days - PMP Study PlanShahram Karimi100% (7)
- PMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rewrite The Two Goals Below To Make Them SMART. Then Explain What Makes Them Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-BoundDocument2 pagesRewrite The Two Goals Below To Make Them SMART. Then Explain What Makes Them Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-BoundMatthew NowackNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Study Notes PDFDocument83 pagesPMBOK Study Notes PDFshetupuc93% (27)
- Crack PMP in 45 DaysDocument10 pagesCrack PMP in 45 Daysgolfmaniac48% (21)
- ITTO Trick Sheet 49 Process - Jan 18 V 1.0 PMBOK 6th EditionDocument26 pagesITTO Trick Sheet 49 Process - Jan 18 V 1.0 PMBOK 6th EditionAbdulla Jawad Alshemary84% (25)
- Key Acupoints PDFDocument6 pagesKey Acupoints PDFthouartu50% (2)
- Unit4 AuditingDocument37 pagesUnit4 Auditingdangthanhhd79100% (8)
- CAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamFrom EverandCAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamNo ratings yet
- PMP Full ExamDocument51 pagesPMP Full Examrvsreddy197285% (26)
- Edward PMP Study NotesDocument76 pagesEdward PMP Study NotesWaqas Ahmed94% (16)
- PMP Study SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Study SheetAli Abdelmoniem Ahmed75% (4)
- PMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookDocument10 pagesPMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookIbrahimSamir100% (9)
- PMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)Document53 pagesPMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)girishkris92% (25)
- A Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideFrom EverandA Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideNo ratings yet
- IFC2x3 TC1 Entity Hierarchy PDFDocument17 pagesIFC2x3 TC1 Entity Hierarchy PDFthouartuNo ratings yet
- Application For Use of Church FacilitiesDocument1 pageApplication For Use of Church Facilitieseasygoing1No ratings yet
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamFrom EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- PMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdateFrom EverandPMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsFrom Everand50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsNo ratings yet
- PMP Study MaterialsDocument90 pagesPMP Study Materialsamira_salama100% (5)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesPMP Cheat Sheetsachin.nate525782% (11)
- PMP Notes FinalDocument24 pagesPMP Notes Finalumerillias89% (9)
- PMP FormulasDocument3 pagesPMP Formulaspolters100% (8)
- PMP Practice Makes Perfect: Over 1000 PMP Practice Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP Practice Makes Perfect: Over 1000 PMP Practice Questions and AnswersRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationFrom EverandThe Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationNo ratings yet
- PMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasFrom EverandPMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasNo ratings yet
- How to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptFrom EverandHow to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- PMP/CAPM EXAM PREP: A Basic Guide to Activity-On-Node and Critical Path MethodFrom EverandPMP/CAPM EXAM PREP: A Basic Guide to Activity-On-Node and Critical Path MethodNo ratings yet
- PgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PM Interview: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learning and Studying Project Manager Job Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPM Interview: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learning and Studying Project Manager Job Interview Questions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- PMI Certification: Learn The Secrets To Pass All The PMI Exams And Getting Certified Quickly And Easily. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsFrom EverandPMI Certification: Learn The Secrets To Pass All The PMI Exams And Getting Certified Quickly And Easily. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- PMP: Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: Updated for the 2015 ExamFrom EverandPMP: Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: Updated for the 2015 ExamNo ratings yet
- World Religious Views of Health and HealingDocument34 pagesWorld Religious Views of Health and HealingthouartuNo ratings yet
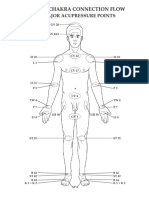
- Acu Chakra ConnectionflowDocument2 pagesAcu Chakra ConnectionflowthouartuNo ratings yet
- Goldsmith MOJO ScorecardDocument3 pagesGoldsmith MOJO ScorecardthouartuNo ratings yet
- Aspect of Prana Prana Apana Udana Samana VyanaDocument3 pagesAspect of Prana Prana Apana Udana Samana VyanathouartuNo ratings yet
- Using A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamDocument28 pagesUsing A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamthouartuNo ratings yet
- MongodbDocument66 pagesMongodbthouartuNo ratings yet
- The Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlDocument27 pagesThe Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlthouartuNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondDocument14 pagesBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondthouartuNo ratings yet
- MX Injection TestingDocument24 pagesMX Injection TestingthouartuNo ratings yet
- Elem Am 98 RepeatabilityDocument13 pagesElem Am 98 RepeatabilitythouartuNo ratings yet
- Helm ClashdetectionDocument7 pagesHelm ClashdetectionMayouran WijayakumarNo ratings yet
- 6 Packet Spring13Document6 pages6 Packet Spring13thouartuNo ratings yet
- The Science of Hindu SpiritualityDocument12 pagesThe Science of Hindu SpiritualitythouartuNo ratings yet
- SanskritDocument8 pagesSanskritthouartu0% (2)
- Aryabhateeya: Trivandrum 695 018, India (0471-2490149)Document27 pagesAryabhateeya: Trivandrum 695 018, India (0471-2490149)thouartuNo ratings yet
- SPI-Software Process ImprovementDocument24 pagesSPI-Software Process ImprovementthouartuNo ratings yet
- CBR Marketing Akshat AVasthiDocument28 pagesCBR Marketing Akshat AVasthiAkshat AvasthiNo ratings yet
- 2024.01.21 Dolphin CompanyDocument2 pages2024.01.21 Dolphin CompanyAlfred CharlesNo ratings yet
- Why Renting Is Better Than BuyingDocument4 pagesWhy Renting Is Better Than BuyingMonali MathurNo ratings yet
- AGREEMENT AntipoloDocument3 pagesAGREEMENT AntipoloLen Lacson MarianoNo ratings yet
- 12 Points) : A B: Over Co de Ex Out Down Re Ultra UnderDocument2 pages12 Points) : A B: Over Co de Ex Out Down Re Ultra UnderRobert CalcanNo ratings yet
- (Pmbok® Guide) Sixth EditionDocument41 pages(Pmbok® Guide) Sixth EditionNaba majeadNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument28 pagesBCG MatrixsatishNo ratings yet
- P 13-9A - SolutionDocument1 pageP 13-9A - SolutionMichelle GraciaNo ratings yet
- A Critical Look at The Movie Office SpaceDocument2 pagesA Critical Look at The Movie Office Spacealiimran080103No ratings yet
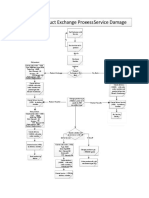
- Product Exchange Process - Service Damage: Old Product Old ProductDocument2 pagesProduct Exchange Process - Service Damage: Old Product Old ProductsameerjaleesNo ratings yet
- Apqc How Organizations Are Using Apqc Process PDFDocument13 pagesApqc How Organizations Are Using Apqc Process PDFsergioivanrsNo ratings yet
- PPE Review For A PPE Review For A: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)Document6 pagesPPE Review For A PPE Review For A: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)JANISCHAJEAN RECTONo ratings yet
- 1 Running Head: Grant Proposal Strategic PlanDocument6 pages1 Running Head: Grant Proposal Strategic PlanJoseph WainainaNo ratings yet
- Willem Hoek: This Notes Relates To SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) 5.0Document11 pagesWillem Hoek: This Notes Relates To SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) 5.0m abbasiNo ratings yet
- Makati SEP 2018Document38 pagesMakati SEP 2018Yanni AlmadronesNo ratings yet
- Maintenace Kits - Pavers-ScreedsDocument12 pagesMaintenace Kits - Pavers-ScreedsBruno TrindadeNo ratings yet
- QOS Improvement in MANET Routing by Route Optimization Through Convergence of Mobile AgentDocument6 pagesQOS Improvement in MANET Routing by Route Optimization Through Convergence of Mobile AgentNader JalalNo ratings yet
- Fuel Surcharge - UPS - VietnamDocument3 pagesFuel Surcharge - UPS - VietnamJDS JICENo ratings yet
- Fourth Section: Case of Beşleagă and Others V. RomaniaDocument9 pagesFourth Section: Case of Beşleagă and Others V. Romaniaasm_samNo ratings yet
- OML Determination Complaint 4Document9 pagesOML Determination Complaint 4Robert FucciNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies For Farmers and RanchersDocument6 pagesMarketing Strategies For Farmers and RanchersJASMINE NUR A FNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Guide To Managing Your Partner AccountDocument18 pagesStep-By-Step Guide To Managing Your Partner AccountUsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- Siddharth Jain DMBADocument55 pagesSiddharth Jain DMBApriyanshulunia02No ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument21 pagesManagerial AccountingRam KnowlesNo ratings yet
- MeetFounders Nov 2020 HandoutDocument17 pagesMeetFounders Nov 2020 HandoutAndrew BottNo ratings yet
- Surya Pricelist Compressed 1Document92 pagesSurya Pricelist Compressed 1Raj Kumar VermaNo ratings yet