Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rugosidad
Rugosidad
Uploaded by
Victor Manuel Uribe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageThis document reviews several methods for measuring rock surface roughness, including profiles from ISRM and Barton and Choubey, Laubscher's roughness curves, and the method used in the SSPC system. It describes Laubscher's roughness curves which categorize roughness into two scales that can be seen or felt. It also discusses how Hack et al. developed an empirical relation between tactile and visible roughness based on previous profiles to classify slope stability for their SSPC system.
Original Description:
rugosidad, mecanica de rocas, geomecanica, barton, rock mechanics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document reviews several methods for measuring rock surface roughness, including profiles from ISRM and Barton and Choubey, Laubscher's roughness curves, and the method used in the SSPC system. It describes Laubscher's roughness curves which categorize roughness into two scales that can be seen or felt. It also discusses how Hack et al. developed an empirical relation between tactile and visible roughness based on previous profiles to classify slope stability for their SSPC system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageRugosidad
Rugosidad
Uploaded by
Victor Manuel UribeThis document reviews several methods for measuring rock surface roughness, including profiles from ISRM and Barton and Choubey, Laubscher's roughness curves, and the method used in the SSPC system. It describes Laubscher's roughness curves which categorize roughness into two scales that can be seen or felt. It also discusses how Hack et al. developed an empirical relation between tactile and visible roughness based on previous profiles to classify slope stability for their SSPC system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
REVIEW OF ROUGHNESS MEASUREMENT METHODS
Figure 2-5 Typical ISRM profiles and Suggested
nomenclatures. The length of each profile is in
the range of 1 to 10m. (ISRM, 1978).
Figure 2- 4 Typical roughness profiles for a range
of JRC. (after Barton and Choubey, 1977)
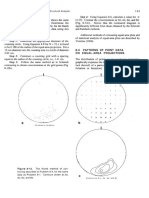
2.2.1.3. Laubschers Roughness Curves
Laubscher (1990) in Geomechanics classification
system for rating of rock mass in mine design has
developed a set of descriptive terms for discontinuity
surface roughness determination with factors rating
the influence on the stability of underground
excavations. The description of the profiles is partly
based on the profiles of ISRM (1978) and (1981). The
roughness is categorized in to two roughnesses that
can be seen at different scales and can not be seen, but
can be felt by using fingers (so called tactile
roughness). See Figure 2-6.
This is developed and applicable for underground
excavations, hence it is not applied in this study.
Figure 2- 6 Laubschers roughness
profiles (after Laubscher, 1990)
2.2.1.4. Method used in SSPC System
Hack et al. (1998) have developed an empirical relation between tactile and visible roughness based
on the (ISRM, 1978, 1981; Laubscher, 1990) profiles and the friction along discontinuity plane
resulting from roughness for his slope stability probability classification (SSPC) system for the slopes.
Hack et al. (1998), categorized the roughness in to two (large scale and small scale) roughness. The
15
You might also like
- Instalacion Minesight 9.2Document12 pagesInstalacion Minesight 9.2Carlos AyamamaniNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Rock Slope Stability Using The Rock Mass Rating (RMR) SystemDocument5 pagesAssessment of Rock Slope Stability Using The Rock Mass Rating (RMR) SystemrannscribdNo ratings yet
- MRMR System (Laubscher 1990) : Intact Rock StrengthDocument2 pagesMRMR System (Laubscher 1990) : Intact Rock StrengthnasrullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 NotesDocument18 pagesLecture3 NotestejeswarNo ratings yet
- Lectura Complementaria MRMR PDFDocument6 pagesLectura Complementaria MRMR PDFIsabel Alejandra CasadoNo ratings yet
- Rock Mass RatingDocument16 pagesRock Mass RatingDubSooTaeh GyuLiaJayKeNo ratings yet
- 2cracteristic of DiscontinuDocument5 pages2cracteristic of DiscontinuAms JumrotinNo ratings yet
- Empirical Rock Slope DesignDocument62 pagesEmpirical Rock Slope DesignBrian ConnerNo ratings yet
- GSI For Geological Trip (1st Edition)Document6 pagesGSI For Geological Trip (1st Edition)Nur Nazhifah Binti Md.lazamNo ratings yet
- 3 - 2007-Determination of Slope Mass Rating PDFDocument9 pages3 - 2007-Determination of Slope Mass Rating PDFJampani HymavathiNo ratings yet
- Application of Rock Mass Classification Systems As A Tool For Rock Mass Strength DeterminationDocument18 pagesApplication of Rock Mass Classification Systems As A Tool For Rock Mass Strength Determinationwilma flintstoneNo ratings yet
- 1992 RMRSlope Stability Relationship To RMSDocument5 pages1992 RMRSlope Stability Relationship To RMSi2cMOTNo ratings yet
- GROUP5.Project ReportDocument6 pagesGROUP5.Project ReportMuhammad Hazim Bin Ahmad FauziNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between RMRB and Gsi Based On in Situ Data: Conference PaperDocument7 pagesRelationship Between RMRB and Gsi Based On in Situ Data: Conference PaperManish Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between RMRB and Gsi Based On in Situ Data: Conference PaperDocument7 pagesRelationship Between RMRB and Gsi Based On in Situ Data: Conference Paperthomas_ugdersNo ratings yet
- Rockmass Classification UpdatedDocument70 pagesRockmass Classification UpdatedSuryaKanthNo ratings yet
- J Enggeo 2016 03 007Document26 pagesJ Enggeo 2016 03 007NestorJoseMamaniMamaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Rock Mass ClassificationDocument57 pagesUnit 2 - Rock Mass ClassificationAyush tiwariNo ratings yet
- SMR RomanaDocument5 pagesSMR RomanaRoni Marquez100% (1)
- Hack Dan Price 1995-1Document6 pagesHack Dan Price 1995-1101 Laksmita Chitrayuna SyahiraNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechn Question ReviewDocument11 pagesRock Mechn Question ReviewJoseph IRANZINo ratings yet
- Bieniawski'S RMR System: Geomechanical RocksDocument3 pagesBieniawski'S RMR System: Geomechanical Rockssubhajit majiNo ratings yet
- Hif12003-Erodibility IndexDocument6 pagesHif12003-Erodibility IndexJuan GuivernauNo ratings yet
- Metodo MRMRDocument12 pagesMetodo MRMRRaul Carrasco PolancoNo ratings yet
- Modification of Slope Mass Rating (SMR) by Continuous FunctionsDocument8 pagesModification of Slope Mass Rating (SMR) by Continuous FunctionsArthur MatosNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between RMRB and Gsi Based On in Situ Data: Conference PaperDocument7 pagesRelationship Between RMRB and Gsi Based On in Situ Data: Conference PaperJuan Pablo Alvarado RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- Dam Mass RatingDocument4 pagesDam Mass Ratingfededa100% (1)
- 7-Haftanietal.2015 RMRE RQDfromWJDDocument8 pages7-Haftanietal.2015 RMRE RQDfromWJDVanco AdziskiNo ratings yet
- Método Del Índice MRMR: ReferenciasDocument12 pagesMétodo Del Índice MRMR: ReferenciasJuan Pablo Tilano MonsalveNo ratings yet
- Sop - Geot - 05 v0.0 Calculating Slope Mass RatingDocument7 pagesSop - Geot - 05 v0.0 Calculating Slope Mass RatingSidikNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Rock Mass Deformation Modulus Using Different ApproachesDocument12 pagesComparative Study of Rock Mass Deformation Modulus Using Different ApproachesGanjarAsandiPutraPratamaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology: R. Tomás, A. Cuenca, M. Cano, J. García-BarbaDocument10 pagesEngineering Geology: R. Tomás, A. Cuenca, M. Cano, J. García-BarbaNestorJoseMamaniMamaniNo ratings yet
- Rock Mass ClassificationDocument8 pagesRock Mass ClassificationM JaffaNo ratings yet
- Is 13365 Part4 DraftDocument15 pagesIs 13365 Part4 DraftPalak Shivhare0% (1)
- SCC Met SyllabusDocument9 pagesSCC Met SyllabusBoago KeofetlhileNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Rock Mass ClassificationDocument32 pagesChapter 7 Rock Mass ClassificationsyafiqNo ratings yet
- 2003 SRC Rock Mass ClassificationDocument13 pages2003 SRC Rock Mass ClassificationYiset Ramirez AvalosNo ratings yet
- Cai and Kaiser 2006 Visualization of The Rock Mass Classification SystemsDocument14 pagesCai and Kaiser 2006 Visualization of The Rock Mass Classification SystemsReza OsgouiNo ratings yet
- Quantification of Rock Mass Influence On Cuttability With RoadheadersDocument12 pagesQuantification of Rock Mass Influence On Cuttability With RoadheadersHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- Rock Mass ClassificationDocument9 pagesRock Mass ClassificationdarbosNo ratings yet
- Geotek-Rock Engineering For UndergroundDocument48 pagesGeotek-Rock Engineering For UndergroundKiky Rizky IsalNo ratings yet
- Empirical Methods To Estimate The Strength of Jointed Rock MassesDocument11 pagesEmpirical Methods To Estimate The Strength of Jointed Rock MassesMohammed KhennoufNo ratings yet
- Rock Mass ClassificationDocument4 pagesRock Mass ClassificationMumtaz Ali BukhariNo ratings yet
- Use of The Mining Rock Mass Rating (MRMR) Classification: Industry ExperienceDocument6 pagesUse of The Mining Rock Mass Rating (MRMR) Classification: Industry ExperienceDaigoro ItohNo ratings yet
- Aplicacion de La Mecanica de Rocas (1) (061-120)Document60 pagesAplicacion de La Mecanica de Rocas (1) (061-120)Jesus PerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Rock MassDocument116 pagesChapter 9 - Rock MassZulaikha Kamal50% (2)
- Modification of Slope Mass Rating (SMR) by Continuous FunctionsDocument9 pagesModification of Slope Mass Rating (SMR) by Continuous FunctionsZola1stNo ratings yet
- Rock Bolt Supporting FactorDocument9 pagesRock Bolt Supporting FactorInes KahoulNo ratings yet
- Determining Situ Deformation Modulus Using A Flexible Volumetric DilatometerDocument26 pagesDetermining Situ Deformation Modulus Using A Flexible Volumetric DilatometerelenaNo ratings yet
- The Geological Strength Index: Applications and LimitationsDocument11 pagesThe Geological Strength Index: Applications and LimitationsJinChongNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2016Document9 pagesZhang 2016Carlos AyamamaniNo ratings yet
- Part 09 - Classification of Rock MassDocument21 pagesPart 09 - Classification of Rock MassAfendi AriffNo ratings yet
- Is 13365 3 1997Document12 pagesIs 13365 3 1997Chandramouleeswar Sundara IyerNo ratings yet
- Application of Slope Mass Rating System in Slope Stability Class Evaluation - Nursetya - Panjaitan - 212865064Document11 pagesApplication of Slope Mass Rating System in Slope Stability Class Evaluation - Nursetya - Panjaitan - 212865064Nursetya Yusika PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Lithospheric DiscontinuitiesFrom EverandLithospheric DiscontinuitiesHuaiyu YuanNo ratings yet
- Fault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureFrom EverandFault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureMarion Y. ThomasNo ratings yet
- Integrated Imaging of the Earth: Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandIntegrated Imaging of the Earth: Theory and ApplicationsMax MoorkampNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingFrom EverandShallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsFrom EverandCoupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsNo ratings yet
- Proyecicon Esterografica PracticaDocument17 pagesProyecicon Esterografica PracticaVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Geolgia - Estructural-Stress Rev 0Document23 pagesGeolgia - Estructural-Stress Rev 0Victor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Strusievicz 2000Document1 pageStrusievicz 2000Victor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Clivaje y FracturaDocument7 pagesClivaje y FracturaVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology and Resources 2022Document3 pagesStructural Geology and Resources 2022Victor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- StructuralGeologyRes Kal22 Jan22 BrochureDocument8 pagesStructuralGeologyRes Kal22 Jan22 BrochureVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- HUTCHINSON EPOCH 1988 Landslide Slope Instability Geohazard Classification Scheme GeologiaDocument3 pagesHUTCHINSON EPOCH 1988 Landslide Slope Instability Geohazard Classification Scheme GeologiaVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Neotectonics and Fluvial Geomorphology oDocument23 pagesNeotectonics and Fluvial Geomorphology oVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Therapy: A Review: Marko S. MarkovDocument23 pagesMagnetic Field Therapy: A Review: Marko S. MarkovVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Joints and FracturesDocument14 pagesJoints and FracturesVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- The Andean Orogenic Period and Its Major Structures in Central and Northern PeruDocument8 pagesThe Andean Orogenic Period and Its Major Structures in Central and Northern PeruVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Shortening and Crustal Thickness in The Central Andes: How Good Is The Correlation?Document4 pagesTectonic Shortening and Crustal Thickness in The Central Andes: How Good Is The Correlation?Victor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- 1983 Jordanetal GSADiscussionDocument5 pages1983 Jordanetal GSADiscussionVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Estrella Arbol de Navidad PapercraftDocument5 pagesEstrella Arbol de Navidad PapercraftVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Landslide & Slope Instability Geohazards: Classification Schemes - Dikau Et AlDocument3 pagesLandslide & Slope Instability Geohazards: Classification Schemes - Dikau Et AlVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology and TectonicsDocument848 pagesStructural Geology and TectonicsVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Proportional Error of The Terzaghi Correction Factors: January 2006Document7 pagesProportional Error of The Terzaghi Correction Factors: January 2006Victor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- T. Russell - Research Report PDFDocument174 pagesT. Russell - Research Report PDFVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Core Logging Manual - 20120420 - SRKDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Core Logging Manual - 20120420 - SRKVictor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet
- Dimitrijevicetal 2012Document8 pagesDimitrijevicetal 2012Victor Manuel UribeNo ratings yet