Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mobile Charger
Mobile Charger
Uploaded by
Tanmay Bhagat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageMobile Charger
Mobile Charger
Uploaded by
Tanmay BhagatCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
CCI IRRC UCIU
T II TD E IADS E A S
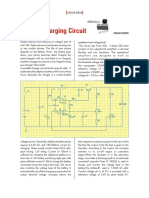
MOBILE CELLPHONE CHARGER
D. MOHAN KUMAR
harging of the cellphone battery is
a big problem while travelling as
power supply source is not generally accessible. If you keep your cellphone
switched on continuously, its battery will
go flat within five to six hours, making
the cellphone useless. A fully charged battery becomes necessary especially when
your distance from the nearest relay station increases. Heres a simple charger that
replenishes the cellphone battery within
two to three hours.
Basically, the charger is a current-lim-
ited voltage source. Generally, cellphone
battery packs require 3.6-6V DC and 180200mA current for charging. These usually
contain three NiCd cells, each having 1.2V
rating. Current of 100mA is sufficient for
charging the cellphone battery at a slow
rate. A 12V battery containing eight pen
ELECTRONICS FOR YOU
MARCH 2004
SAN
I THE
cells gives sufficient
LED Status for Different Charging Conditions
current (1.8A) to
charge the battery con- Load across the output
Output frequency (at pin 3)
LED1
nected across the out765 kHz
On
put terminals. The cir- No battery connected
Charging
battery
4.5
Hz
Blinks
cuit also monitors the
0
Off
voltage level of the bat- Fully charged battery
tery. It automatically
cuts off the charging process when its out- to take output pin 3 high. When the battery
put terminal voltage increases above the is fully charged, the output terminal voltage
increases the voltage at pin 2 of IC1 above
predetermined voltage level.
Timer IC NE555 is used to charge and the trigger point threshold. This switches off
monitor the voltage level in the battery. the flip-flop and the output goes low to
Control voltage pin 5 of IC1 is provided terminate the charging process. Threshold
with a reference voltage of 5.6V by zener pin 6 of IC1 is referenced at 2/3Vcc set by
VR1. Transistor T1 is used to enhance the
charging current. Value of R3 is critical in
providing the required current for charging.
With the given value of 39-ohm the charging current is around 180 mA.
The circuit can be constructed on a
small general-purpose PCB. For calibration
of cut-off voltage level, use a variable DC
power source. Connect the output terminals of the circuit to the variable power
supply set at 7V. Adjust VR1 in the middle
position and slowly adjust VR2 until LED1
goes off, indicating low output. LED1
should turn on when the voltage of the
variable power supply reduces below 5V.
Enclose the circuit in a small plastic case
and use suitable connector for connecting
diode ZD1. Threshold pin 6 is supplied to the cellphone battery.
Note. At EFY lab, the circuit was tested
with a voltage set by VR1 and trigger pin
with a Motorola make cellphone battery
2 is supplied with a voltage set by VR2.
When the discharged cellphone battery rated at 3.6V, 320 mAH. In place of 5.6V
is connected to the circuit, the voltage given zener, a 3.3V zener diode was used. The
to trigger pin 2 of IC1 is below 1/3Vcc and charging current measured was about 200
hence the flip-flop in the IC is switched on mA.The status of LED1 is shown in the table.
You might also like
- Automatyczna Ładowarka Akumulatorów Ołowiowych: Kity AVTDocument8 pagesAutomatyczna Ładowarka Akumulatorów Ołowiowych: Kity AVTadyhansoloNo ratings yet
- FsaDocument6 pagesFsainsan_soft6498No ratings yet
- Mobile Phone Battery Charger: Circuit IdeasDocument1 pageMobile Phone Battery Charger: Circuit IdeasKuntaweeNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedDocument3 pagesCircuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedMashood NasirNo ratings yet
- Add A Composite Video Input To A TVDocument6 pagesAdd A Composite Video Input To A TVEnya Andrea Ribba HernandezNo ratings yet
- Mobile ChargerDocument1 pageMobile ChargerVaz Patrick100% (1)
- Auto Emergency LightDocument1 pageAuto Emergency LightAsad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Qa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitDocument3 pagesQa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitShivam JainNo ratings yet
- Lead-Acid Battery Charger With Voltage AnalyzerDocument2 pagesLead-Acid Battery Charger With Voltage AnalyzerhyperseraphimNo ratings yet
- Charger For Mobile PhonesDocument2 pagesCharger For Mobile PhonessivaganeshanNo ratings yet
- Qa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitDocument3 pagesQa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitShayan FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Constant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasDocument54 pagesConstant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasKliffy Fernandes100% (1)
- Mini UPS System PDFDocument1 pageMini UPS System PDFShrivlsi RamNo ratings yet
- Project Report of Visitor Counter CircuitDocument13 pagesProject Report of Visitor Counter Circuitshital shermaleNo ratings yet
- Project Report of Visitor Counter CircuitDocument13 pagesProject Report of Visitor Counter CircuitMuhammad Rizwan Haider Durrani50% (2)
- Low-Power Voltage DoublerDocument1 pageLow-Power Voltage Doublerxcfmhg hNo ratings yet
- Solar Battery Charging Indicator: T.K. HareendranDocument2 pagesSolar Battery Charging Indicator: T.K. HareendranRakeshNo ratings yet
- Mobile Cellphone Battery ChargerDocument2 pagesMobile Cellphone Battery ChargerWahyu NovendiNo ratings yet
- Automatic Phase ChangerDocument2 pagesAutomatic Phase Changervinay reddy100% (3)
- Voltage DoublerDocument7 pagesVoltage DoublerDheeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Automatic Battery Switchover: Small CircuitscollectionDocument2 pagesAutomatic Battery Switchover: Small CircuitscollectionOmar DionisiNo ratings yet
- DSE5103datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesDSE5103datasheet PDFabduallah muhammadNo ratings yet
- Const CT Battery ChargerDocument2 pagesConst CT Battery Chargervinay_98493722556954No ratings yet
- Tda 4605Document21 pagesTda 4605Salim SaeidyNo ratings yet
- Over Voltage Protection Circuit For Automotive Load DumpDocument6 pagesOver Voltage Protection Circuit For Automotive Load Dumplennon rNo ratings yet
- Infrared Remote Switch ReportDocument3 pagesInfrared Remote Switch ReportsivamskrNo ratings yet
- Automatic Evening LampDocument4 pagesAutomatic Evening LampRamkrishna ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Water Level Cum Motor ProtectorDocument1 pageWater Level Cum Motor Protectorj_alagesan1990No ratings yet
- Load Detecting Power Supply: 1.0 Design SpecificationsDocument17 pagesLoad Detecting Power Supply: 1.0 Design SpecificationsLucre SandovalNo ratings yet
- Circuit 1Document1 pageCircuit 1sakthiNo ratings yet
- 0-30V 1a PDFDocument1 page0-30V 1a PDFVas VvasNo ratings yet
- E3 Charger Manual-New PDFDocument2 pagesE3 Charger Manual-New PDFअभिजीत कुमारNo ratings yet
- Potencia PDFDocument109 pagesPotencia PDFdavidNo ratings yet
- IC Controlled Emergency Light With Charger: Ircuit IdeasDocument1 pageIC Controlled Emergency Light With Charger: Ircuit Ideasindracahayaku100% (2)
- ShangHai Consonance Elec CN3165 - C559035Document12 pagesShangHai Consonance Elec CN3165 - C559035Yosef GordonNo ratings yet
- Smart Phone Light PDFDocument2 pagesSmart Phone Light PDFPavan Kumar ThopaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Workshop Project ReportDocument5 pagesElectronic Workshop Project ReportAbubakr AtiqueNo ratings yet
- Basic Power Electronics Notes 2.1 To 2.3 PDFDocument8 pagesBasic Power Electronics Notes 2.1 To 2.3 PDFEscape From EngineeringNo ratings yet
- E430 Instruction Manual EN V5.0Document2 pagesE430 Instruction Manual EN V5.0Jan waNo ratings yet
- An Imprint of IC IC 555 Timer in The Contemporary World He ContemporaryDocument4 pagesAn Imprint of IC IC 555 Timer in The Contemporary World He ContemporaryChinnapogula dineshNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONOTES.comDocument8 pagesELECTRONOTES.comJairus TanNo ratings yet
- T.D.A 4605-3Document20 pagesT.D.A 4605-3Jose M PeresNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547Document3 pagesLight Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547yeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- Mobile Battery Charging Circuit: Deepak GuptaDocument2 pagesMobile Battery Charging Circuit: Deepak Guptaujjwalgupta4No ratings yet
- Microcontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument5 pagesMicrocontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorFuh ValleryNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- BC548 - Datashet PDFDocument2 pagesBC548 - Datashet PDFBraian KonzgenNo ratings yet
- Tda 2320Document5 pagesTda 2320api-3747180No ratings yet
- SpeedometerDocument2 pagesSpeedometerSrikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- CA3162, CA3162A: Features DescriptionDocument7 pagesCA3162, CA3162A: Features Descriptionapi-3747180100% (2)
- LM4700Document19 pagesLM4700api-3747180No ratings yet
- Over Under VoltDocument1 pageOver Under Voltapi-3747180100% (1)
- LM4766Document19 pagesLM4766api-3747180No ratings yet
- CI 06 Mar05Document1 pageCI 06 Mar05api-3747180No ratings yet
- Ding-Dong Bell PDFDocument1 pageDing-Dong Bell PDFShrivlsi RamNo ratings yet
- BCR 8 CMDocument5 pagesBCR 8 CMapi-3747180No ratings yet
- Ca 3161Document4 pagesCa 3161api-3747180No ratings yet
- Mje 13007Document10 pagesMje 13007arao_filhoNo ratings yet
- FUse ShneiderDocument40 pagesFUse ShneiderThị Huyền CuNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Measurement SystemDocument8 pagesSolar Energy Measurement SystemLuke Nihal DasariNo ratings yet
- RDTDDocument7 pagesRDTDDon Roseller DumayaNo ratings yet
- MRP111233Document3 pagesMRP111233pinku_thakkarNo ratings yet
- 74 HC 42Document6 pages74 HC 42Kiran ParuNo ratings yet
- Samsung DVD TV Chassis C16ADocument82 pagesSamsung DVD TV Chassis C16Acclodoaldo1577No ratings yet
- Product Datasheet: Acti 9 - Fuse-Disconnector STI - 1 Pole - 10 A - For Fuse 8.5 X 31.5 MMDocument2 pagesProduct Datasheet: Acti 9 - Fuse-Disconnector STI - 1 Pole - 10 A - For Fuse 8.5 X 31.5 MMaditya agasiNo ratings yet
- E-03 Single Line Diagram D1Document1 pageE-03 Single Line Diagram D1hwang2No ratings yet
- Mode of Arc Extinction Mode of Arc Extinction: High Resistance Arc Interruption High Resistance Arc InterruptionDocument9 pagesMode of Arc Extinction Mode of Arc Extinction: High Resistance Arc Interruption High Resistance Arc Interruptionwan anisNo ratings yet
- ABB Price Book 517Document1 pageABB Price Book 517EliasNo ratings yet
- Peserta Dan Materi Kls ADocument3 pagesPeserta Dan Materi Kls ARuri nabillahNo ratings yet
- Altronix - PD8Document1 pageAltronix - PD8Tv Chacon ChaconNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Universal Cable Joint Kits: (Excludes Connectors)Document2 pagesLow Voltage Universal Cable Joint Kits: (Excludes Connectors)sridharanNo ratings yet
- Siemens 5SX5216 7 DatasheetDocument1 pageSiemens 5SX5216 7 DatasheetintrudentalertNo ratings yet
- Checking of Electrical PanelDocument7 pagesChecking of Electrical PanelReneboy LambarteNo ratings yet
- 6 - Miscellaneous Items Lighting SystemDocument9 pages6 - Miscellaneous Items Lighting SystemZeckrey JikurunNo ratings yet
- 24M Motor Grader Electrical System: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsDocument4 pages24M Motor Grader Electrical System: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsRicardo HarringtonNo ratings yet
- Ujc-S Underground Junction Chamber: Catalogue 2018Document6 pagesUjc-S Underground Junction Chamber: Catalogue 2018Anonymous tCb9gF0No ratings yet
- Tesla Word DocumentsDocument2 pagesTesla Word Documentsdiannedecastro43No ratings yet
- Experiment No.8: OBJECT: To Determine The High Resistance by Method of Leakage of ChargeDocument4 pagesExperiment No.8: OBJECT: To Determine The High Resistance by Method of Leakage of ChargeBhavanshu SainiNo ratings yet
- 3 DG Auto Load Sharing SchemeDocument9 pages3 DG Auto Load Sharing Schemeuump100% (1)
- FT30 SaffireDocument2 pagesFT30 SaffireAshik M RasheedNo ratings yet
- 1kr Fe ChargingDocument92 pages1kr Fe Chargingfguij33% (3)
- Datasheet 5A 180Khz 36V Buck DC To DC Converter Xl4015 Features General DescriptionDocument10 pagesDatasheet 5A 180Khz 36V Buck DC To DC Converter Xl4015 Features General DescriptionAgung NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Cy-100 e CataDocument6 pagesCy-100 e Cataluis fernando noche monroyNo ratings yet
- VLSI Rabaey Lecture Videos ContentsDocument3 pagesVLSI Rabaey Lecture Videos ContentsSujatha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - IDocument2 pagesElectrical Machines - Idhirajbharat20No ratings yet
- BSM151F EupecDocument7 pagesBSM151F EupecRomuald Eric TefongNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram: DTC P2122, P2123 APP SENSORDocument2 pagesWiring Diagram: DTC P2122, P2123 APP SENSORdan1993100% (1)