Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elektronika Daya: Oleh: Umi Karuniawati (125514220)
Elektronika Daya: Oleh: Umi Karuniawati (125514220)
Uploaded by
Umi Karuniawati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesThis document contains the solutions to several problems related to electronic power. It provides the answers and calculations for problems involving buck, boost, and buck-boost converter circuits. Key parameters given include voltage, current, duty cycle, inductance, capacitance, and frequency. Formulas from electronic power are used to calculate output voltage, ripple voltage, peak current, and equivalent components values.
Original Description:
tugas minggu 2
Original Title
Problem 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains the solutions to several problems related to electronic power. It provides the answers and calculations for problems involving buck, boost, and buck-boost converter circuits. Key parameters given include voltage, current, duty cycle, inductance, capacitance, and frequency. Formulas from electronic power are used to calculate output voltage, ripple voltage, peak current, and equivalent components values.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesElektronika Daya: Oleh: Umi Karuniawati (125514220)
Elektronika Daya: Oleh: Umi Karuniawati (125514220)
Uploaded by
Umi KaruniawatiThis document contains the solutions to several problems related to electronic power. It provides the answers and calculations for problems involving buck, boost, and buck-boost converter circuits. Key parameters given include voltage, current, duty cycle, inductance, capacitance, and frequency. Formulas from electronic power are used to calculate output voltage, ripple voltage, peak current, and equivalent components values.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
ELEKTRONIKA DAYA
Oleh :
Umi Karuniawati
(125514220)
JURUSAN TEKNIK ELEKTRO
FAKULTAS TEKNIK
UNIVERSITAS NEGERI SURABAYA
2014
5.11. Knowed: Vs = 12V
K = 0,6
Ia = 1,5 A
F = 25 khz
L = 250 H
C = 220 F
Answer:
a. From eq. (5-78), Va = -12 x 0,6/(1 0,6) = -18 V
b. From eq. (5-87), the peak to peak output ripple voltage is c = 1,5 x 0,6/(25000
x 220 x 10-6) = 163,64 mV
c. From eq. (5-84), the peak to peak output ripple voltage is I = 12 x 0,6/(25000
x 220 x 10-6) = 1,152 A
d. From eq. (5-81) Is = 1,5 x 0,6/(1 0,6) = 2,25 A
Since Is is the average of duration kT, the peak to peak current of transistor, Ip =
Is/K + I/2 = 2,25/0.6 + 1,152/2 = 4,326 A
R = 12
e.
From eq. (5-88) Lc(k) =
From eq. (5-89) Cc(k) =
=
(
)
)
Lc(k) = 0,96 mH
Lc(k) = 0,01 mF
5.12. Knowed: Vs = 15 V
k = 0,4
Ia = 1,25 A
f = 25 kHz
L1 = 350H
C1 = 400 F
L2 = 350 H
C2 = 220 F
Answer:
a. From Eq. (5-100), Va = - 0,4 x 15/(1 0,4) = -10 V
b. From Eq. (5-103), Is = 1,25 x 0,4/(1 0,4) = 0,83 A
c. From Eq. (5-106), l1 =15 x 0,4/(25000 x 250 x 10-6) = 0,96 A
d. From Eq. (5-112), Vc1 = 0,83 (1 0,4)/(25000 x 400 x 10-6) = 50 mV
e. From Eq. (5-109), I2 = 0,4 x 15/(25000 x 350 x 10-6) = 0,69 A
f. From Eq. (5-113), Vc2 = 0,69/(8 x 25000 x 220 x 10-6) = 15,58 mV
g. From Eq. (5-120), IL2 = 1,25/(1,0- 2 X 0,4) = 6,25 A
IP = Is + I1/2 + IL2 + l2/2 = 0,83 + 0,96/2 + 6,25 + 0,69/2 = 7,91 A
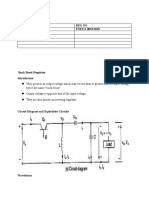
5.13. Knowed: Vs = 15 V
k = 0,4
Ia = 1,25 A
f = 25 kHz
L1 = 250 H
C1 = 400 F
L2 =350 H
C2 = 220 F
Answer:
From Eq. (5-115) Lc1 (k) =
From Eq. (5-116) Lc2 (k) =
Lc1 (0,4) . 1000 = 4,32 mH
Lc2 (0,4) . 1000 = 0,14 mH
From Eq. (5-117) Cc1 (k) =
Cc1 (0,5) . 106 = 0,83 F
From Eq. (5-118) Cc2 (k) =
Cc2 (0,5) . 106 = 0,42 F
5.14. Knowed: Vs = 110 V
Va = 80 V
Ia = 20 A
Answer:
Vc = 0,05 x Va = 0,05 x 80 = 4 V
R = Va/Ia = 80/20 = 4
From Eq. (5-48), k = Va/Vs = 80/110 = 0,7273
From Eq. (5-49) Is = k.Ia = 0,7273 x 20 = 14,55 A
IL = 0,025 x Ia = 0,025 x 20 = 0,5 A
I = 0,1 x la = 0,1 x20 = 2 A
From Eq. (5-51), we get the value of Le
(
From Eq. (5-128), we get the value of Ce
Assuming a linear rise of load current iL during the time from t = 0 to ti = k
T, Eq. (5-129) gives the approximate value of L as
5.15. Knowed: k = 0,4
R = 150
rL = 1
rc = 0,2
Answer:
a. Buck
( )
G(0,5) = 0,5
b. Boost
( )
(
(
G(0,5) = 1,95
c. Buck - Boost
( )
(
(
)
(
G(0,5) = -0,97
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualDocument86 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualKenneth Vogt100% (1)
- Physics II Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics II Finals ReviewerCarter SiyNo ratings yet
- MD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 02Document3 pagesMD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 02Anoop Mathew67% (6)
- Electrical Engineering 2016 2016 2016 2016 2016Document13 pagesElectrical Engineering 2016 2016 2016 2016 2016arunNo ratings yet
- ZZ - Electricity & MagnetismDocument137 pagesZZ - Electricity & Magnetismvenkyrocker777750% (4)
- Exercise Solutions EX11.1: I I V V V V V V V V VDocument12 pagesExercise Solutions EX11.1: I I V V V V V V V V VLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument25 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsHariPonnanaNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost Regulator PresentationDocument6 pagesBuck Boost Regulator PresentationBoutros MongareNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits Analysis and Design 3rd Edition Rashid Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits Analysis and Design 3rd Edition Rashid Solutions Manualanagogegirdler.kycgr100% (21)
- Problem Solutions: R R R R V I R R IDocument69 pagesProblem Solutions: R R R R V I R R IAkhila RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Pspice Simulation of Mosfet Amplifier Configurations: 2.1 ObjectiveDocument8 pagesPspice Simulation of Mosfet Amplifier Configurations: 2.1 ObjectivePreet PatelNo ratings yet
- Taller 1 ElectrotecniaDocument17 pagesTaller 1 ElectrotecniaAlejoGonzalezNo ratings yet
- 2020 July Eeng101Document7 pages2020 July Eeng101senawayne191No ratings yet
- TUGAS ELEKTRONIKA - Kelompok 2Document11 pagesTUGAS ELEKTRONIKA - Kelompok 2Christine SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Iecep Elex Ps 5Document6 pagesIecep Elex Ps 5Julio Gabriel AseronNo ratings yet
- Electronics: Selected Answers ForDocument16 pagesElectronics: Selected Answers ForLim Jin FeiNo ratings yet
- Sadiku Practice Problem Solution PDFDocument177 pagesSadiku Practice Problem Solution PDFIshan Solanki0% (1)
- 67655-NilssonSM Ch10Document57 pages67655-NilssonSM Ch10Ly RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Problems UpdatedDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Problems UpdatedDrGopikrishna PasamNo ratings yet
- Med3_High Voltage (2) 2022-2023_WithAnswersDocument1 pageMed3_High Voltage (2) 2022-2023_WithAnswersZayed ALariqiNo ratings yet
- Chapt14Prob41 60Document11 pagesChapt14Prob41 60oriontheoneNo ratings yet
- ECE320 HW3 SolutionDocument3 pagesECE320 HW3 Solutiondigital2000No ratings yet
- Project 2Document8 pagesProject 2marisaliuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 ReportDocument13 pagesAssignment 01 ReportSalaudeen IlyasNo ratings yet
- M Yusuf Rizaldi-206060300111011Document3 pagesM Yusuf Rizaldi-206060300111011M YUSUF RIZALDYNo ratings yet
- Class Test - 2015: Electrical EngineeringDocument6 pagesClass Test - 2015: Electrical EngineeringMichael DavisNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Capitulo 21 Física Serway and FaughnDocument13 pagesSolucionario Capitulo 21 Física Serway and FaughnRafael ColindresNo ratings yet
- Assessment Clo1 Clo2 Clo3 Clo4 Clo5 Plo1 Plo2 Plo2 Plo1Document12 pagesAssessment Clo1 Clo2 Clo3 Clo4 Clo5 Plo1 Plo2 Plo2 Plo1Ma Liu Hun VuiNo ratings yet
- UsefulSolutions T&DDocument7 pagesUsefulSolutions T&Dkobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- M35 Knig9404 Ism C35 PDFDocument26 pagesM35 Knig9404 Ism C35 PDFnorma_jeannNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Elec - & - Magnetism - WS PDFDocument2 pagesModule 3 - Elec - & - Magnetism - WS PDFdraketheduckNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesElectrical EngineeringLol LololNo ratings yet
- OPTO817Document6 pagesOPTO817ifmatosNo ratings yet
- Problem Solutions: V V P I V R R VDocument24 pagesProblem Solutions: V V P I V R R Vapi-3741518No ratings yet
- Solutions For Microelectronic Circuits 3rd Edition by RashidDocument29 pagesSolutions For Microelectronic Circuits 3rd Edition by RashidDoron DadiaNo ratings yet
- Transform Sheet - Solution PDFDocument16 pagesTransform Sheet - Solution PDFNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- SPWM Inverter Bipolar - 2d3elinbDocument12 pagesSPWM Inverter Bipolar - 2d3elinbMochammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document24 pagesChapter 10kamal__singhNo ratings yet
- Transform Sheet SolutionDocument16 pagesTransform Sheet SolutionSanjaya Srinath0% (1)
- Amplifier StagesDocument5 pagesAmplifier StagesNelsonLucioRodriguezPenagosNo ratings yet
- Elektrik Di RumahDocument10 pagesElektrik Di RumahAzhari FatimahNo ratings yet
- Power Engineering Questions and SolutionDocument7 pagesPower Engineering Questions and SolutionMoz Asik0% (1)
- Assignment On PscadDocument15 pagesAssignment On PscaddinukaeeNo ratings yet
- (379315304) 151221525-Deber-2Document19 pages(379315304) 151221525-Deber-2Daniel Armas100% (3)
- Tutorial Synch GeneratorDocument4 pagesTutorial Synch GeneratorEyad A. FeilatNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Elo S5Document12 pagesMarking Scheme Elo S5ves vegasNo ratings yet
- ELEC-E8427-transmission Lines Home Exercise With SolutionDocument4 pagesELEC-E8427-transmission Lines Home Exercise With SolutionOskari OllilaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS STPM 2007 AnswerDocument16 pagesPHYSICS STPM 2007 AnswersuhailieliasNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Suitable Capacitor Size in Farads & kVAR For PF ImprovementDocument4 pagesCalculate The Suitable Capacitor Size in Farads & kVAR For PF ImprovementmaungsoekhinNo ratings yet
- Gilbert: Basic Formulas and DerivationsDocument5 pagesGilbert: Basic Formulas and Derivationsfree123456789No ratings yet
- Met Problems-1Document14 pagesMet Problems-1Shikhar SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Met Problems-1Document14 pagesMet Problems-1Jotiram Ghadge PatilNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)