Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 viewsFour Point Probe
Four Point Probe
Uploaded by
Munira SultanaA four point probe can be used to measure the resistivity of semiconductor samples by passing a current through two outer probes and measuring the voltage through inner probes. This allows calculation of doping concentration from resistivity formulas. Sheet resistivity of a solar cell's top emitter layer can also be measured using a four point probe by passing current through outer probes and measuring the induced voltage in inner probes, with the p-n junction behaving as an insulator. Bulk resistivity is similarly measured but reports a value in cm-3 using layer thickness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter - 4 PDFDocument64 pagesChapter - 4 PDFLily SelwinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Electrical and Optical MeasurementsDocument66 pagesUnit 4 Electrical and Optical MeasurementsUppili BalajiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC:-Resistivity by Four Probe MethodDocument13 pagesTOPIC:-Resistivity by Four Probe Methoduzma100% (2)
- Physics Lab File: Nikanshu CE - 22Document36 pagesPhysics Lab File: Nikanshu CE - 223110Sammar ManglaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2.4 Four ProbeDocument4 pagesExperiment 2.4 Four ProbeAnurag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment b3Document7 pagesExperiment b3Cek AjaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv Measurements & Engineered Semiconductor MaterialsDocument77 pagesUnit - Iv Measurements & Engineered Semiconductor MaterialsAnshul DadwalNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics and Nanotechnology SRM Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument76 pagesDepartment of Physics and Nanotechnology SRM Institute of Science and Technologyvivekk132005No ratings yet
- Question No 1: Experiment: To Measure Electrical Conductivity by Using Two Probe or Four Probe MethodDocument17 pagesQuestion No 1: Experiment: To Measure Electrical Conductivity by Using Two Probe or Four Probe Methodzrish100% (1)
- Four Point ProbeDocument3 pagesFour Point ProbeRock FrancisNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics ProjectYuvan KumarNo ratings yet
- Pengujian Konduktivitas Listrik - 1Document4 pagesPengujian Konduktivitas Listrik - 1AviceniaMarinaIrianiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument21 pagesPhysics ProjectNx GamingYTNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument101 pagesFour Probe MethodPanthoiba AkoijamNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument14 pagesFour Probe MethodjooooooNo ratings yet
- Resistivity by Four Probe Method (Theory) - Solid State Physics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDocument3 pagesResistivity by Four Probe Method (Theory) - Solid State Physics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual Labupanith100% (1)
- Four ProbeDocument3 pagesFour ProbeAmit MandalNo ratings yet
- VDX 01Document2 pagesVDX 01Kulendra BorahNo ratings yet
- Phy 119Document3 pagesPhy 119D4D DREDD ytNo ratings yet
- ECE 421 Lab Experiment No. 1: Resistivity of SemiconductorsDocument7 pagesECE 421 Lab Experiment No. 1: Resistivity of Semiconductorsandy3939No ratings yet
- Topic: Resistivity by Four Probe MethodDocument22 pagesTopic: Resistivity by Four Probe MethoduzmaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Energy Gap by The Four Probe Method: Experiment-265 SDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Energy Gap by The Four Probe Method: Experiment-265 SAsheesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Internal ResistanceDocument5 pagesInternal Resistancenikil dalyNo ratings yet
- Physics IPDocument33 pagesPhysics IPJ. Suba SriNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Resistivity 4point Probe AnDocument4 pagesMeasuring The Resistivity 4point Probe Anmiroslaw_dolata1124No ratings yet
- FAB Resistivity White PaperDocument8 pagesFAB Resistivity White PapervishiwizardNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics ProjectYuvan KumarNo ratings yet
- Life Without ElectroscopesDocument3 pagesLife Without ElectroscopesKanishka SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- 04-Band Gap - Four Probe MethodDocument7 pages04-Band Gap - Four Probe MethodAryan VermaNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Topic: To Study The Factor On Which The SelfDocument7 pagesCertificate: Topic: To Study The Factor On Which The SelfNaman BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5, Day 9: Ohm's Law: Objective QuestionDocument6 pagesUnit 5, Day 9: Ohm's Law: Objective QuestionTyler SmithNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Langmuir Probes - Hiden Analytical Tech Info Sheet531Document8 pagesIntroduction To Langmuir Probes - Hiden Analytical Tech Info Sheet531alexaNo ratings yet
- 1sem Manual 1Document48 pages1sem Manual 1Harry HarryNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Practical ListDocument3 pagesClass 12 Physics Practical ListPragya100% (2)
- E1-Q Experiment 1 QuestionDocument9 pagesE1-Q Experiment 1 QuestionFabiano FerreiraNo ratings yet
- IV New Paper MayDocument10 pagesIV New Paper MayGopal BNo ratings yet
- EE143 - Four-Point Probe ManualDocument3 pagesEE143 - Four-Point Probe ManualJoseline1No ratings yet
- Sem, Tem, DLSDocument84 pagesSem, Tem, DLSMadhuri HarshaNo ratings yet
- 1 Resistivity by Four Probe MethodDocument4 pages1 Resistivity by Four Probe MethodSaurabh ChapleNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0142941884900126 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 0142941884900126 Mainibrahime mohammedNo ratings yet
- Electronic Workshop 3Document4 pagesElectronic Workshop 3Rathore Yuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Four Point Probe: Dr. Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar Uicet Panjab University, ChandigarhDocument15 pagesFour Point Probe: Dr. Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar Uicet Panjab University, ChandigarhAditya KoulNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodDocument22 pagesLecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodNamwangala Rashid NatinduNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 ADocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 AShubham BaghelNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument1 pageFour Probe MethodVita Efellina100% (3)
- 21BCE5419 Exp1Document12 pages21BCE5419 Exp1Anshika RaiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Langmuir Probe Current-Voltage 1Document4 pagesUnderstanding Langmuir Probe Current-Voltage 1Denis_LNo ratings yet
- Insulation ResistanceDocument22 pagesInsulation Resistancewikyarif100% (6)
- ENPHYS15G Laboratory 12 BATTERIES AND BULBSDocument14 pagesENPHYS15G Laboratory 12 BATTERIES AND BULBSB3 Calaguing Ricardo Jr. G.No ratings yet
- JAINILDocument19 pagesJAINILgodedem530No ratings yet
- DEE-61P INSTALLATION,MAINTENANCE& REPAIR OF ELECTRICAL MACHINE LABDocument34 pagesDEE-61P INSTALLATION,MAINTENANCE& REPAIR OF ELECTRICAL MACHINE LABmanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- FourProbe Resistivity AN2Document8 pagesFourProbe Resistivity AN2Winnie MathewsNo ratings yet
- Insultation Resistance: What Is Insulation Resistance?Document2 pagesInsultation Resistance: What Is Insulation Resistance?Paul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conductivity Analyzer TufelDocument19 pagesElectrical Conductivity Analyzer Tufelurvish_soniNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics Lab NotebookDocument25 pagesSolid State Physics Lab NotebookmshhdaltfwqNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII Physics Notes SemiconductorDocument20 pagesCBSE XII Physics Notes Semiconductorkaushik2470% (1)
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
Four Point Probe
Four Point Probe
Uploaded by
Munira Sultana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views2 pagesA four point probe can be used to measure the resistivity of semiconductor samples by passing a current through two outer probes and measuring the voltage through inner probes. This allows calculation of doping concentration from resistivity formulas. Sheet resistivity of a solar cell's top emitter layer can also be measured using a four point probe by passing current through outer probes and measuring the induced voltage in inner probes, with the p-n junction behaving as an insulator. Bulk resistivity is similarly measured but reports a value in cm-3 using layer thickness.
Original Description:
Four Point Probe Resistivity Measurements
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA four point probe can be used to measure the resistivity of semiconductor samples by passing a current through two outer probes and measuring the voltage through inner probes. This allows calculation of doping concentration from resistivity formulas. Sheet resistivity of a solar cell's top emitter layer can also be measured using a four point probe by passing current through outer probes and measuring the induced voltage in inner probes, with the p-n junction behaving as an insulator. Bulk resistivity is similarly measured but reports a value in cm-3 using layer thickness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views2 pagesFour Point Probe
Four Point Probe
Uploaded by
Munira SultanaA four point probe can be used to measure the resistivity of semiconductor samples by passing a current through two outer probes and measuring the voltage through inner probes. This allows calculation of doping concentration from resistivity formulas. Sheet resistivity of a solar cell's top emitter layer can also be measured using a four point probe by passing current through outer probes and measuring the induced voltage in inner probes, with the p-n junction behaving as an insulator. Bulk resistivity is similarly measured but reports a value in cm-3 using layer thickness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Four Point Probe Resistivity Measurements
SEM and EBIC Materials
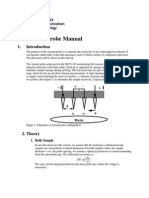
A four point probe is a simple apparatus for measuring the resistivity of semiconductor samples.
By passing a current through two outer probes and measuring the voltage through the inner
probes allows the measurement of the substrate resistivity. The doping concentration can be
calculated from the resistivity using the formulas discussed in the Appendices and the PV
Lighthouse Resistivity Calculator
The Measurement of Sheet Resistivity
The sheet resistivity of the top emitter layer is very easy to measure experimentally using a "four
point probe". A current is passed through the outer probes and induces a voltage in the inner
voltage probes. The junction between the n and p -type materials behaves as an insulating layer
and the cell must be kept in the dark.
Use of a four point probe to measure the sheet resistivity of a solar cell.
Using the voltage and current readings from the probe:[1]
Where:
The typical emitter sheet resistivity of silicon solar cells lies in the range 30-100 / .
In typical usage the current is set to 4.53 mA so that the resistivity is simply the voltage reading
in mV.
The Measurement of Bulk Resistivity
The measurement of bulk resistivity is similar to that of sheet resistivity except that a resistivity
in cm-3 is reported using the wafer thickness, t:
Where t is the layer/wafer thickness in cm.
The simple formula above works for when the wafer thickness less than half the probe spacing (t
< s/2) [2]. For thicker samples the formula becomes:
Where s is the probe spacing.
You might also like
- Chapter - 4 PDFDocument64 pagesChapter - 4 PDFLily SelwinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Electrical and Optical MeasurementsDocument66 pagesUnit 4 Electrical and Optical MeasurementsUppili BalajiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC:-Resistivity by Four Probe MethodDocument13 pagesTOPIC:-Resistivity by Four Probe Methoduzma100% (2)
- Physics Lab File: Nikanshu CE - 22Document36 pagesPhysics Lab File: Nikanshu CE - 223110Sammar ManglaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2.4 Four ProbeDocument4 pagesExperiment 2.4 Four ProbeAnurag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment b3Document7 pagesExperiment b3Cek AjaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv Measurements & Engineered Semiconductor MaterialsDocument77 pagesUnit - Iv Measurements & Engineered Semiconductor MaterialsAnshul DadwalNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics and Nanotechnology SRM Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument76 pagesDepartment of Physics and Nanotechnology SRM Institute of Science and Technologyvivekk132005No ratings yet
- Question No 1: Experiment: To Measure Electrical Conductivity by Using Two Probe or Four Probe MethodDocument17 pagesQuestion No 1: Experiment: To Measure Electrical Conductivity by Using Two Probe or Four Probe Methodzrish100% (1)
- Four Point ProbeDocument3 pagesFour Point ProbeRock FrancisNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics ProjectYuvan KumarNo ratings yet
- Pengujian Konduktivitas Listrik - 1Document4 pagesPengujian Konduktivitas Listrik - 1AviceniaMarinaIrianiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument21 pagesPhysics ProjectNx GamingYTNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument101 pagesFour Probe MethodPanthoiba AkoijamNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument14 pagesFour Probe MethodjooooooNo ratings yet
- Resistivity by Four Probe Method (Theory) - Solid State Physics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDocument3 pagesResistivity by Four Probe Method (Theory) - Solid State Physics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual Labupanith100% (1)
- Four ProbeDocument3 pagesFour ProbeAmit MandalNo ratings yet
- VDX 01Document2 pagesVDX 01Kulendra BorahNo ratings yet
- Phy 119Document3 pagesPhy 119D4D DREDD ytNo ratings yet
- ECE 421 Lab Experiment No. 1: Resistivity of SemiconductorsDocument7 pagesECE 421 Lab Experiment No. 1: Resistivity of Semiconductorsandy3939No ratings yet
- Topic: Resistivity by Four Probe MethodDocument22 pagesTopic: Resistivity by Four Probe MethoduzmaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Energy Gap by The Four Probe Method: Experiment-265 SDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Energy Gap by The Four Probe Method: Experiment-265 SAsheesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Internal ResistanceDocument5 pagesInternal Resistancenikil dalyNo ratings yet
- Physics IPDocument33 pagesPhysics IPJ. Suba SriNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Resistivity 4point Probe AnDocument4 pagesMeasuring The Resistivity 4point Probe Anmiroslaw_dolata1124No ratings yet
- FAB Resistivity White PaperDocument8 pagesFAB Resistivity White PapervishiwizardNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics ProjectYuvan KumarNo ratings yet
- Life Without ElectroscopesDocument3 pagesLife Without ElectroscopesKanishka SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- 04-Band Gap - Four Probe MethodDocument7 pages04-Band Gap - Four Probe MethodAryan VermaNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Topic: To Study The Factor On Which The SelfDocument7 pagesCertificate: Topic: To Study The Factor On Which The SelfNaman BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5, Day 9: Ohm's Law: Objective QuestionDocument6 pagesUnit 5, Day 9: Ohm's Law: Objective QuestionTyler SmithNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Langmuir Probes - Hiden Analytical Tech Info Sheet531Document8 pagesIntroduction To Langmuir Probes - Hiden Analytical Tech Info Sheet531alexaNo ratings yet
- 1sem Manual 1Document48 pages1sem Manual 1Harry HarryNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Practical ListDocument3 pagesClass 12 Physics Practical ListPragya100% (2)
- E1-Q Experiment 1 QuestionDocument9 pagesE1-Q Experiment 1 QuestionFabiano FerreiraNo ratings yet
- IV New Paper MayDocument10 pagesIV New Paper MayGopal BNo ratings yet
- EE143 - Four-Point Probe ManualDocument3 pagesEE143 - Four-Point Probe ManualJoseline1No ratings yet
- Sem, Tem, DLSDocument84 pagesSem, Tem, DLSMadhuri HarshaNo ratings yet
- 1 Resistivity by Four Probe MethodDocument4 pages1 Resistivity by Four Probe MethodSaurabh ChapleNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0142941884900126 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 0142941884900126 Mainibrahime mohammedNo ratings yet
- Electronic Workshop 3Document4 pagesElectronic Workshop 3Rathore Yuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Four Point Probe: Dr. Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar Uicet Panjab University, ChandigarhDocument15 pagesFour Point Probe: Dr. Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar Uicet Panjab University, ChandigarhAditya KoulNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodDocument22 pagesLecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodNamwangala Rashid NatinduNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 ADocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 AShubham BaghelNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument1 pageFour Probe MethodVita Efellina100% (3)
- 21BCE5419 Exp1Document12 pages21BCE5419 Exp1Anshika RaiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Langmuir Probe Current-Voltage 1Document4 pagesUnderstanding Langmuir Probe Current-Voltage 1Denis_LNo ratings yet
- Insulation ResistanceDocument22 pagesInsulation Resistancewikyarif100% (6)
- ENPHYS15G Laboratory 12 BATTERIES AND BULBSDocument14 pagesENPHYS15G Laboratory 12 BATTERIES AND BULBSB3 Calaguing Ricardo Jr. G.No ratings yet
- JAINILDocument19 pagesJAINILgodedem530No ratings yet
- DEE-61P INSTALLATION,MAINTENANCE& REPAIR OF ELECTRICAL MACHINE LABDocument34 pagesDEE-61P INSTALLATION,MAINTENANCE& REPAIR OF ELECTRICAL MACHINE LABmanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- FourProbe Resistivity AN2Document8 pagesFourProbe Resistivity AN2Winnie MathewsNo ratings yet
- Insultation Resistance: What Is Insulation Resistance?Document2 pagesInsultation Resistance: What Is Insulation Resistance?Paul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conductivity Analyzer TufelDocument19 pagesElectrical Conductivity Analyzer Tufelurvish_soniNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics Lab NotebookDocument25 pagesSolid State Physics Lab NotebookmshhdaltfwqNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII Physics Notes SemiconductorDocument20 pagesCBSE XII Physics Notes Semiconductorkaushik2470% (1)
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet