Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology: Modifiable Risk Factors
Pathophysiology: Modifiable Risk Factors
Uploaded by
Alvin Germo Pasuquin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageThis document discusses risk factors and the pathophysiology of bone fractures. It lists modifiable risk factors like smoking, diet, and activity level, and non-modifiable factors like age, sex, and family history. When trauma exceeds a bone's capacity, it will break. This disrupts blood vessels and cuts off blood flow, causing cell death. An intense inflammatory response occurs as the body tries to repair the damage through callus formation, new bone growth, and eventual bone replacement.
Original Description:
pathphysiology of bone fracture
Original Title
Patho Fracture (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses risk factors and the pathophysiology of bone fractures. It lists modifiable risk factors like smoking, diet, and activity level, and non-modifiable factors like age, sex, and family history. When trauma exceeds a bone's capacity, it will break. This disrupts blood vessels and cuts off blood flow, causing cell death. An intense inflammatory response occurs as the body tries to repair the damage through callus formation, new bone growth, and eventual bone replacement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pagePathophysiology: Modifiable Risk Factors
Pathophysiology: Modifiable Risk Factors
Uploaded by
Alvin Germo PasuquinThis document discusses risk factors and the pathophysiology of bone fractures. It lists modifiable risk factors like smoking, diet, and activity level, and non-modifiable factors like age, sex, and family history. When trauma exceeds a bone's capacity, it will break. This disrupts blood vessels and cuts off blood flow, causing cell death. An intense inflammatory response occurs as the body tries to repair the damage through callus formation, new bone growth, and eventual bone replacement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
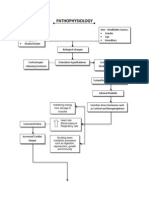
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Modifiable Risk Factors:
Cigarette smoking
Low body weight
Low calcium intake
Alcoholism
Recurrent falls
Inadequate physical activity
Poor health/frailty
Non-modifiable Risk Factors:
Hx of fractures as an adult
Hx of fractures in first degree
relative
Female sex
Advanced age
TRAUMA
Stress placed on the bone excees the capacity
of the bone to absorb it
Bone breakage
Blood vessel disruption
Ecchymosis
Jaundice
RBC Hemolysis
intraosseous blood flow
Bleeding around the site & into
the surrounding soft tissues
Ischemia
Bone cell death
Pain
prostaglandin,
bradykinin, serotonin
Intense inflammatory reaction
Histamine, serotonin, bradykinin,
C3a, C5a, LTC4, LTD4, PGI2, PGE2,
PGD2, PGF2,
Warmth & redness
Vasodilation, vascular
permeability
TXA2, PAF, IL-1, TNF-,
LTB4
Fibrin clot formation &
acts as a new network
upon w/c new cells can
adhere to
True bone replaces callus
& is slowly calcified
Callus/ immature new bone
formation
Osteoprogenitor cells
osteoclastic activity
Stress on the opposing side of the broken
bone accelerates osteoclastic activity
blood flow to injured area
Accumulation of phagocytic cells
Phagocytosis & removal of dead cell debris
Fixation, traction
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureAnne Lorraine Bringas93% (27)
- List of Mineral Function and DeficiencyDocument16 pagesList of Mineral Function and Deficiencyketavmodi100% (8)
- Buerger's Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesBuerger's Disease PathophysiologyBon Guevarra SagunNo ratings yet
- Patho Unit 1 Study GuideDocument2 pagesPatho Unit 1 Study GuideLily ChouNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureVenus Tagaan UcatNo ratings yet
- CROHNSDocument2 pagesCROHNSAlvin Germo Pasuquin100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancerpauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Biochemistry of Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument9 pagesPathophysiology and Biochemistry of Cardiovascular DiseaseAnatomska CentralaNo ratings yet
- PAtho FractureDocument5 pagesPAtho FractureBon JuviNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument14 pagesAtherosclerosisDeepak Raj100% (1)
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics PDFDocument166 pagesPharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics PDFCarolina PosadaNo ratings yet
- Secondary Osteoporosis AssessmentDocument12 pagesSecondary Osteoporosis AssessmentBibiana Prada de Camargo ColenciNo ratings yet
- 12) Circulatory Disturbances-2Document24 pages12) Circulatory Disturbances-2Ravishan De AlwisNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsDocument4 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsHearty ArriolaNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPathophysiologyJosh LazoNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus PathophysiologyAnonymous OU6w8lX9No ratings yet
- PT Ho PhysioDocument3 pagesPT Ho PhysioluanarikoNo ratings yet
- Concept Maps Test 3 410Document12 pagesConcept Maps Test 3 410Ashley BurnsNo ratings yet
- 1 Henry McCraeDocument4 pages1 Henry McCraeAbdullah RajaNo ratings yet
- 8 Fases en IAMDocument14 pages8 Fases en IAMednasu1No ratings yet
- Clase Cardiopatia IsquémicaDocument132 pagesClase Cardiopatia IsquémicaSusy OcampoNo ratings yet
- CVD Infarct-HpniiDocument3 pagesCVD Infarct-HpniilarissedeleonNo ratings yet
- 2019 AtherosclerosisDocument115 pages2019 Atherosclerosisnidhiya sara sabuNo ratings yet
- List of Mineral Functions and Deficiency Symptoms Followed by The Vitamin & Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsDocument17 pagesList of Mineral Functions and Deficiency Symptoms Followed by The Vitamin & Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsJin Kun Yong100% (1)
- List of Most Common Usmle DiseasesDocument3 pagesList of Most Common Usmle DiseaseswcgokulNo ratings yet
- CVS 1 PDFDocument24 pagesCVS 1 PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog60% (5)
- Pathophysiology: Diet Sedentary Lifestyle Familial History of Hypertension Age - Common in 40 and AboveDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Diet Sedentary Lifestyle Familial History of Hypertension Age - Common in 40 and AboveJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVADocument11 pagesPathophysiology CVAallyana kim figueroa lavarias100% (1)
- Chronic Myeloid LeukemiaDocument14 pagesChronic Myeloid Leukemiaaswathymohan1024No ratings yet
- Path o Client BasedDocument3 pagesPath o Client BasedJane TuazonNo ratings yet
- 16-Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument136 pages16-Coronary Heart DiseaseCitra Wulandari SofyanNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis GTDocument15 pagesOsteoporosis GTZelalem AbrhamNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument1 pageNursingReymund Timog TalarocNo ratings yet
- Ortho PAthoDocument4 pagesOrtho PAthoCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- BloodDocument4 pagesBloodTawana MtotelaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument2 pagesSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeRan MaNo ratings yet
- Unit Nine - MSSDocument51 pagesUnit Nine - MSSsaadkadir450No ratings yet
- Correlacion Osteoporosis y Enfermedad CardiovascularDocument3 pagesCorrelacion Osteoporosis y Enfermedad CardiovascularCorin Boice TelloNo ratings yet
- Pathology IcsmDocument84 pagesPathology IcsmAlice TangNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument10 pagesCarbohydratemkolihiohaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aging: It General, The Life Expectancy of An Individual Depends Upon The Following FactorsDocument6 pagesCellular Aging: It General, The Life Expectancy of An Individual Depends Upon The Following FactorssnehagptNo ratings yet
- Arterial Occlusive DiseaseDocument3 pagesArterial Occlusive DiseaseJanel TamNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone Disease & Bone Markers - SlidesDocument46 pagesMetabolic Bone Disease & Bone Markers - Slidesmonday125100% (1)
- Patho. Reviewer On Cellular InjuryDocument21 pagesPatho. Reviewer On Cellular InjurySeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Menopause: UterusDocument10 pagesMenopause: UterusswethashakiNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Treatment of Renal Osteodystrophy: Eduardo Slatopolsky Esther Gonzalez Kevin MartinDocument9 pagesPathogenesis and Treatment of Renal Osteodystrophy: Eduardo Slatopolsky Esther Gonzalez Kevin Martinmohammed makkiNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidis M: Increased Proliferation of CathecholaminesDocument3 pagesHyperthyroidis M: Increased Proliferation of CathecholaminesSergie Paul FernandezNo ratings yet
- ArterosclerozaDocument35 pagesArterosclerozaSevda MemetNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument19 pagesAtherosclerosissanjivdasNo ratings yet
- AMA PhatophysiologyDocument3 pagesAMA PhatophysiologynamonneNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationDocument39 pagesPediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationRaghavendra DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Fab m4Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Fab m4KristaMaeC.Lazo100% (2)
- Group 4 ProjectDocument40 pagesGroup 4 Projectlaiba.akhtarNo ratings yet
- 3 PathophysiologyDocument4 pages3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- MI PathoDocument5 pagesMI PathoAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAtherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Science and Technology of Growing Young: How to Look Younger, Live Longer, and Feel Your Best with New Breakthroughs in Anti-Aging ScienceFrom EverandThe Science and Technology of Growing Young: How to Look Younger, Live Longer, and Feel Your Best with New Breakthroughs in Anti-Aging ScienceNo ratings yet
- May ReflectionDocument4 pagesMay ReflectionAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case - 2019: Alvin Germo PasuquinDocument49 pagesClinical Case - 2019: Alvin Germo PasuquinAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Reflection May-AugDocument4 pagesReflection May-AugAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Seizure - Transient Occurrence of Signs or Symptoms Due To Abnormal Excessive or SynchronousDocument2 pagesSeizure - Transient Occurrence of Signs or Symptoms Due To Abnormal Excessive or SynchronousAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Fever and Rash: Alvin Germo PasuquinDocument70 pagesFever and Rash: Alvin Germo PasuquinAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Advice and Information: ManagementDocument4 pagesAdvice and Information: ManagementAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Journal Appraisal FinslDocument26 pagesJournal Appraisal FinslAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Case Management: Leira Dith R. Castro, MD Presentor 1 Year Im ResidentDocument64 pagesCase Management: Leira Dith R. Castro, MD Presentor 1 Year Im ResidentAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Advice and Information: ManagementDocument4 pagesAdvice and Information: ManagementAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- PEDIA - TachypneaDocument12 pagesPEDIA - TachypneaAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- PID TUboovarian ComplexDocument8 pagesPID TUboovarian ComplexAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Carbuncle, Incision, Drainage, DebridementDocument11 pagesCarbuncle, Incision, Drainage, DebridementAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument9 pagesAcute PancreatitisAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Colonic Diverticulosis: Risk Factors Other Risk FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Colonic Diverticulosis: Risk Factors Other Risk FactorsAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Secondary CHFDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Secondary CHFAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Proceso Marc F. Udarbe: Representative CaseDocument6 pagesProceso Marc F. Udarbe: Representative CaseAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet