Professional Documents
Culture Documents
We Know, + + Where H Step Size 0.1 (0.5) - + Substituting The Values From The Table in The Above Equation, We Get (0.5) 2.71766
We Know, + + Where H Step Size 0.1 (0.5) - + Substituting The Values From The Table in The Above Equation, We Get (0.5) 2.71766
Uploaded by
ArvindVenkatesanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Finding Roots Using Numerical MethodDocument8 pagesFinding Roots Using Numerical MethodAfri WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Bisection: Literasi Ke x1 x2 x3 F (x1) F (x2)Document9 pagesBisection: Literasi Ke x1 x2 x3 F (x1) F (x2)Arafa ZahiraNo ratings yet
- Menoza - Problem Set 1Document1 pageMenoza - Problem Set 1Jhon Ford Biol MeñozaNo ratings yet
- MM C3 SolutionsDocument39 pagesMM C3 Solutionschunyin.22028914No ratings yet
- Met EulerDocument7 pagesMet EulerWalterNo ratings yet
- Met EulerDocument7 pagesMet EulerWalterNo ratings yet
- Newton Sistem AsDocument8 pagesNewton Sistem AsJosé Enrique LopezNo ratings yet
- NumericalDocument6 pagesNumericalsz4sk5xccvNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 - MEC500 - Muhamad Hafiz B Rusli - 2020975393Document4 pagesAssignment1 - MEC500 - Muhamad Hafiz B Rusli - 2020975393MOHAMAD AKMAL MOHAMAD ZAINALNo ratings yet
- LiliDocument8 pagesLiliSelly The SpiceNo ratings yet
- F (X) X 2 - 3x + 1 0: Iterasi Fixed PointDocument5 pagesF (X) X 2 - 3x + 1 0: Iterasi Fixed PointChristian FebyNo ratings yet
- Metodo BiseccionDocument2 pagesMetodo Biseccionlaura cortesNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1 30.01.13Document3 pagesEjercicio 1 30.01.13Daniel Alberto Mendoza SotoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledJoaquin Vega HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Simple Distillation1Document5 pagesSimple Distillation1Pinjala AnoopNo ratings yet
- Conker ZDocument4 pagesConker Ztaffykate torrefielNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 Thermodynamic ShammilDocument17 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 Thermodynamic ShammilNor Hamizah HassanNo ratings yet
- P4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Document5 pagesP4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Tegar gayuh pambudhiNo ratings yet
- P4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Document5 pagesP4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Tegar gayuh pambudhiNo ratings yet
- BisectionDocument17 pagesBisectionRiswan RiswanNo ratings yet
- Metode Tabel: Iterasi 0,0 - 1,0Document9 pagesMetode Tabel: Iterasi 0,0 - 1,0Roma BamegaNo ratings yet
- All The Excel File Was Prepared by Dr. Harimi Djamila Is A Senior Lecturer at The Universiti Malaysia SabahDocument26 pagesAll The Excel File Was Prepared by Dr. Harimi Djamila Is A Senior Lecturer at The Universiti Malaysia SabahAhmadMoaazNo ratings yet
- LimitesDocument2 pagesLimites1cgral.lopezmorataya25No ratings yet
- 28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaDocument7 pages28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaKatherine GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaDocument7 pages28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaKatherine GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Nur Asnita Eka Musrifah Taqwa STB: 152111 Kelas: E (Teknik Informatika)Document3 pagesNama: Nur Asnita Eka Musrifah Taqwa STB: 152111 Kelas: E (Teknik Informatika)Nur Asnita Eka MusrifahNo ratings yet
- Plan Till AsDocument52 pagesPlan Till AskerlynNo ratings yet
- Asset 1 Asset 2 Asset 3Document7 pagesAsset 1 Asset 2 Asset 3PiyushPurohitNo ratings yet
- Numme Secant MethodDocument5 pagesNumme Secant MethodAngelina SoguilonNo ratings yet
- 1 Resoluci0n Datos 2 2 Gracos 5 3 Picos en Gracos 7Document7 pages1 Resoluci0n Datos 2 2 Gracos 5 3 Picos en Gracos 7Mayner Javier Moran PaladinesNo ratings yet
- Therminol 66 Proprieties TableDocument12 pagesTherminol 66 Proprieties TablespittalokaNo ratings yet
- InvesrsaDocument7 pagesInvesrsaYenerit HernandezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document9 pagesAssignment 3Peng GuinNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document4 pagesExp 5ahmadalialhamaida19971015No ratings yet
- Data Lingkungan - RevDocument137 pagesData Lingkungan - RevGallend SNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document4 pagesWorksheet 1Phoenella Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Metodo EulerDocument10 pages2.2 - Metodo Euleralejesus.cb8No ratings yet
- Tugas Metoda NumerikDocument8 pagesTugas Metoda NumerikAjeng Zulfa SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 1 (B 1) NewnewDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT 1 (B 1) NewnewAshebirNo ratings yet
- Examenes 201Document16 pagesExamenes 201leo rfgrNo ratings yet
- Tugas PSO - Refky G7-04Document4 pagesTugas PSO - Refky G7-04RefkyZaheriNo ratings yet
- N x1 F (X) Pbest Gbest Vi Xi+1Document4 pagesN x1 F (X) Pbest Gbest Vi Xi+1RefkyZaheriNo ratings yet
- AyeuDocument12 pagesAyeunguyenleduchoang1213No ratings yet
- Book 1Document2 pagesBook 1Vand SetiNo ratings yet
- Kingrynormalized Data Set AssignmentDocument24 pagesKingrynormalized Data Set Assignment20013122-001No ratings yet
- Laboratorio 5Document9 pagesLaboratorio 5josiel 25No ratings yet
- Libro 2Document3 pagesLibro 2brendalezliiNo ratings yet
- Lantin Increment Num LabDocument15 pagesLantin Increment Num LabAlwin LantinNo ratings yet
- Econometria TallerDocument20 pagesEconometria TallerLorena VelandiaNo ratings yet
- Math160-2l Act 4Document13 pagesMath160-2l Act 4Mina MyoiNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 SolutionDocument2 pagesQuiz1 SolutionJames NeoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics: Assignment-2Document10 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics: Assignment-2Asad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Sebelum UTS - Metode NumerikDocument7 pagesTugas 1 Sebelum UTS - Metode NumerikBagas Ade SetyoNo ratings yet
- Aggregate - Purchases - Full - Info vUGDocument1,615 pagesAggregate - Purchases - Full - Info vUGug8No ratings yet
- Book 2 UjDocument2 pagesBook 2 UjVNabillaNo ratings yet
- 32 - Nguyễn Ngọc Trân - T10Document7 pages32 - Nguyễn Ngọc Trân - T10Ngọc TrânNo ratings yet
- Aldaba Ibnmiguel R Cve208 SS21-22 Ce2b PN1Document27 pagesAldaba Ibnmiguel R Cve208 SS21-22 Ce2b PN1EmmanNo ratings yet
- Correccion Por Torsion 1° Piso Direccion X Kx Kx * H Y Kx * Y Ӯ = Y -Ycr Kx * Ӯ Vfinal (Tn) Σ Kx Kx*Ӯ* Mt /JDocument2 pagesCorreccion Por Torsion 1° Piso Direccion X Kx Kx * H Y Kx * Y Ӯ = Y -Ycr Kx * Ӯ Vfinal (Tn) Σ Kx Kx*Ӯ* Mt /JMarbil MirandaNo ratings yet
- Calculator Unifactorial de Regresie LilearaDocument7 pagesCalculator Unifactorial de Regresie LilearaCiocoiu AriannaNo ratings yet
We Know, + + Where H Step Size 0.1 (0.5) - + Substituting The Values From The Table in The Above Equation, We Get (0.5) 2.71766
We Know, + + Where H Step Size 0.1 (0.5) - + Substituting The Values From The Table in The Above Equation, We Get (0.5) 2.71766
Uploaded by
ArvindVenkatesanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
We Know, + + Where H Step Size 0.1 (0.5) - + Substituting The Values From The Table in The Above Equation, We Get (0.5) 2.71766
We Know, + + Where H Step Size 0.1 (0.5) - + Substituting The Values From The Table in The Above Equation, We Get (0.5) 2.71766
Uploaded by
ArvindVenkatesanCopyright:
Available Formats
VENKATESAN, ARVIND, 1072
Problem 1
x
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2
f (x )
-1.3591
-1.1528
-1.0345
-0.9674
-0.9336
-0.9236
-0.9323
-0.9569
-0.9958
-1.0488
-1.1159
-1.1979
-1.296
-1.412
-1.5478
-1.7062
f (x )
0.2063
0.1183
0.0671
0.0338
0.01
-0.0087
-0.0245
-0.039
-0.0529
-0.0671
-0.082
-0.0981
-0.1159
-0.1359
-0.1584
f (x )
-0.08799
-0.05123
-0.0333
-0.02385
-0.01866
-0.01583
-0.01443
-0.01396
-0.01417
-0.01492
-0.01613
-0.0178
-0.01991
-0.02251
2
f (x )
0.03677
0.01793
0.00945
0.00519
0.00283
0.0014
0.00047
-0.00021
-0.00075
-0.00122
-0.00166
-0.00212
-0.0026
3
f (x )
-0.018837
-0.008476
-0.004267
-0.002359
-0.001423
-0.000937
-0.000676
-0.000538
-0.00047
-0.000446
-0.000453
-0.000483
4
f (x )
0.010361302
0.004209126
0.001907237
0.000936493
0.000486384
0.000260395
0.000138454
6.7816E-05
2.3556E-05
-6.795E-06
-2.9862E-05
5
f (x )
-0.00615218
-0.00230189
-0.00097074
-0.00045011
-0.00022599
-0.00012194
-7.0638E-05
-4.426E-05
-3.0351E-05
-2.3067E-05
6
f (x )
0.00385
0.00133
0.00052
0.00022
0.0001
5.1E-05
2.6E-05
1.4E-05
7.3E-06
7
f (x )
-0.0025191
-0.0008105
-0.0002965
-0.0001201
-5.274E-05
-2.493E-05
-1.247E-05
-6.625E-06
8
9 f (x )
0.00171
0.00051
0.00018
6.7E-05
2.8E-05
1.2E-05
5.8E-06
We know,
=
(0.5) =
2
2
3
3
|0.5
4
4
+ Where h = step size = 0.1
2 |0.5
2
3 |0.5
3
Substituting the values from the table in the above equation, we get
(0.5) = 2.71766
13
14
15
f (x ) 11 f (x )
12 f (x )
f (x )
f (x )
f (x )
-0.0011946 0.00086 -0.00062865 0.00047 -0.00035646 0.00027
-0.0003376 0.00023 -0.00015883 0.00011 -8.3286E-05
-0.0001091
7E-05 -4.5466E-05
3E-05
-3.951E-05 2.4E-05 -1.5391E-05
-1.536E-05 8.8E-06
-6.612E-06
10
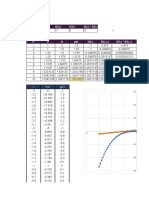
Problem 2
(i)
f(x)
f(x)
5
2.25
-5
-2.75
4
1.75
-4
-2.25
3
1.25
-3
-1.75
2
0.75
-2
-1.24
1
0.26
-1
-0.73
0.5
0.059
-0.5
-0.44
0.25
0.004
-0.25
-0.24
0.01
3.72E-46
-0.01
-0.01
To check if there is any discontinuity in the function f(x), we need to evaluate the limit x->0 from both sides of
the point x=0.
The table above gives the values of f(x) for values of x on either side of x=0. If we notice carefully, as x reaches 0 from
the positive side, the denominator approaches infinity and hence f(x) approaches 0. The graph will be asymptotic with
the x-axis.
On the negative side, as x approaches 0, the denominator approaches 1 and hence f(x) approaches x itself.
Since the limits on both sides of x=0 are not equal, there is a discontinuity in f(x) at x= 0.
(ii)
Since the function is not continuous at x=0, f(x) is not differentiable at x=0.
You might also like
- Finding Roots Using Numerical MethodDocument8 pagesFinding Roots Using Numerical MethodAfri WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Bisection: Literasi Ke x1 x2 x3 F (x1) F (x2)Document9 pagesBisection: Literasi Ke x1 x2 x3 F (x1) F (x2)Arafa ZahiraNo ratings yet
- Menoza - Problem Set 1Document1 pageMenoza - Problem Set 1Jhon Ford Biol MeñozaNo ratings yet
- MM C3 SolutionsDocument39 pagesMM C3 Solutionschunyin.22028914No ratings yet
- Met EulerDocument7 pagesMet EulerWalterNo ratings yet
- Met EulerDocument7 pagesMet EulerWalterNo ratings yet
- Newton Sistem AsDocument8 pagesNewton Sistem AsJosé Enrique LopezNo ratings yet
- NumericalDocument6 pagesNumericalsz4sk5xccvNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 - MEC500 - Muhamad Hafiz B Rusli - 2020975393Document4 pagesAssignment1 - MEC500 - Muhamad Hafiz B Rusli - 2020975393MOHAMAD AKMAL MOHAMAD ZAINALNo ratings yet
- LiliDocument8 pagesLiliSelly The SpiceNo ratings yet
- F (X) X 2 - 3x + 1 0: Iterasi Fixed PointDocument5 pagesF (X) X 2 - 3x + 1 0: Iterasi Fixed PointChristian FebyNo ratings yet
- Metodo BiseccionDocument2 pagesMetodo Biseccionlaura cortesNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1 30.01.13Document3 pagesEjercicio 1 30.01.13Daniel Alberto Mendoza SotoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledJoaquin Vega HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Simple Distillation1Document5 pagesSimple Distillation1Pinjala AnoopNo ratings yet
- Conker ZDocument4 pagesConker Ztaffykate torrefielNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 Thermodynamic ShammilDocument17 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 Thermodynamic ShammilNor Hamizah HassanNo ratings yet
- P4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Document5 pagesP4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Tegar gayuh pambudhiNo ratings yet
- P4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Document5 pagesP4 (X) x4-1,1x3+2,3x2+0,5x+3,3 0 Metode Bairstow: Nama: Rahmad Denny Aulia Nim: 16521241Tegar gayuh pambudhiNo ratings yet
- BisectionDocument17 pagesBisectionRiswan RiswanNo ratings yet
- Metode Tabel: Iterasi 0,0 - 1,0Document9 pagesMetode Tabel: Iterasi 0,0 - 1,0Roma BamegaNo ratings yet
- All The Excel File Was Prepared by Dr. Harimi Djamila Is A Senior Lecturer at The Universiti Malaysia SabahDocument26 pagesAll The Excel File Was Prepared by Dr. Harimi Djamila Is A Senior Lecturer at The Universiti Malaysia SabahAhmadMoaazNo ratings yet
- LimitesDocument2 pagesLimites1cgral.lopezmorataya25No ratings yet
- 28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaDocument7 pages28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaKatherine GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaDocument7 pages28 Mayo KatherineGarcíaKatherine GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Nur Asnita Eka Musrifah Taqwa STB: 152111 Kelas: E (Teknik Informatika)Document3 pagesNama: Nur Asnita Eka Musrifah Taqwa STB: 152111 Kelas: E (Teknik Informatika)Nur Asnita Eka MusrifahNo ratings yet
- Plan Till AsDocument52 pagesPlan Till AskerlynNo ratings yet
- Asset 1 Asset 2 Asset 3Document7 pagesAsset 1 Asset 2 Asset 3PiyushPurohitNo ratings yet
- Numme Secant MethodDocument5 pagesNumme Secant MethodAngelina SoguilonNo ratings yet
- 1 Resoluci0n Datos 2 2 Gracos 5 3 Picos en Gracos 7Document7 pages1 Resoluci0n Datos 2 2 Gracos 5 3 Picos en Gracos 7Mayner Javier Moran PaladinesNo ratings yet
- Therminol 66 Proprieties TableDocument12 pagesTherminol 66 Proprieties TablespittalokaNo ratings yet
- InvesrsaDocument7 pagesInvesrsaYenerit HernandezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document9 pagesAssignment 3Peng GuinNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document4 pagesExp 5ahmadalialhamaida19971015No ratings yet
- Data Lingkungan - RevDocument137 pagesData Lingkungan - RevGallend SNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document4 pagesWorksheet 1Phoenella Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Metodo EulerDocument10 pages2.2 - Metodo Euleralejesus.cb8No ratings yet
- Tugas Metoda NumerikDocument8 pagesTugas Metoda NumerikAjeng Zulfa SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 1 (B 1) NewnewDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT 1 (B 1) NewnewAshebirNo ratings yet
- Examenes 201Document16 pagesExamenes 201leo rfgrNo ratings yet
- Tugas PSO - Refky G7-04Document4 pagesTugas PSO - Refky G7-04RefkyZaheriNo ratings yet
- N x1 F (X) Pbest Gbest Vi Xi+1Document4 pagesN x1 F (X) Pbest Gbest Vi Xi+1RefkyZaheriNo ratings yet
- AyeuDocument12 pagesAyeunguyenleduchoang1213No ratings yet
- Book 1Document2 pagesBook 1Vand SetiNo ratings yet
- Kingrynormalized Data Set AssignmentDocument24 pagesKingrynormalized Data Set Assignment20013122-001No ratings yet
- Laboratorio 5Document9 pagesLaboratorio 5josiel 25No ratings yet
- Libro 2Document3 pagesLibro 2brendalezliiNo ratings yet
- Lantin Increment Num LabDocument15 pagesLantin Increment Num LabAlwin LantinNo ratings yet
- Econometria TallerDocument20 pagesEconometria TallerLorena VelandiaNo ratings yet
- Math160-2l Act 4Document13 pagesMath160-2l Act 4Mina MyoiNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 SolutionDocument2 pagesQuiz1 SolutionJames NeoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics: Assignment-2Document10 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics: Assignment-2Asad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Sebelum UTS - Metode NumerikDocument7 pagesTugas 1 Sebelum UTS - Metode NumerikBagas Ade SetyoNo ratings yet
- Aggregate - Purchases - Full - Info vUGDocument1,615 pagesAggregate - Purchases - Full - Info vUGug8No ratings yet
- Book 2 UjDocument2 pagesBook 2 UjVNabillaNo ratings yet
- 32 - Nguyễn Ngọc Trân - T10Document7 pages32 - Nguyễn Ngọc Trân - T10Ngọc TrânNo ratings yet
- Aldaba Ibnmiguel R Cve208 SS21-22 Ce2b PN1Document27 pagesAldaba Ibnmiguel R Cve208 SS21-22 Ce2b PN1EmmanNo ratings yet
- Correccion Por Torsion 1° Piso Direccion X Kx Kx * H Y Kx * Y Ӯ = Y -Ycr Kx * Ӯ Vfinal (Tn) Σ Kx Kx*Ӯ* Mt /JDocument2 pagesCorreccion Por Torsion 1° Piso Direccion X Kx Kx * H Y Kx * Y Ӯ = Y -Ycr Kx * Ӯ Vfinal (Tn) Σ Kx Kx*Ӯ* Mt /JMarbil MirandaNo ratings yet
- Calculator Unifactorial de Regresie LilearaDocument7 pagesCalculator Unifactorial de Regresie LilearaCiocoiu AriannaNo ratings yet