Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solvation Ionic Compound Solvent
Solvation Ionic Compound Solvent
Uploaded by
Selina Leow0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageWhen an ionic compound dissolves in a solvent like water, it separates into positively and negatively charged ions. These ions are mobile in the electrolyte. During electrolysis, an electrical potential applied across electrodes in the electrolyte causes positively charged cations to move toward the cathode and negatively charged anions to move toward the anode. Electrons are either absorbed or released by ions at the electrodes, changing their charge and allowing deposition of new substances like copper or production of gases like hydrogen and oxygen.
Original Description:
c3
Original Title
Sol Vation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWhen an ionic compound dissolves in a solvent like water, it separates into positively and negatively charged ions. These ions are mobile in the electrolyte. During electrolysis, an electrical potential applied across electrodes in the electrolyte causes positively charged cations to move toward the cathode and negatively charged anions to move toward the anode. Electrons are either absorbed or released by ions at the electrodes, changing their charge and allowing deposition of new substances like copper or production of gases like hydrogen and oxygen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageSolvation Ionic Compound Solvent
Solvation Ionic Compound Solvent
Uploaded by
Selina LeowWhen an ionic compound dissolves in a solvent like water, it separates into positively and negatively charged ions. These ions are mobile in the electrolyte. During electrolysis, an electrical potential applied across electrodes in the electrolyte causes positively charged cations to move toward the cathode and negatively charged anions to move toward the anode. Electrons are either absorbed or released by ions at the electrodes, changing their charge and allowing deposition of new substances like copper or production of gases like hydrogen and oxygen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
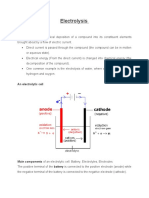
Solvation or reaction of an ionic compound with a solvent (such as water) to produce
mobile ions
An ionic compound is fused by heating
An electrical potential is applied across a pair of electrodes immersed in the electrolyte.
Each electrode attracts ions that are of the opposite charge. Positively charged ions (cations)
move towards the electron-providing (negative) cathode. Negatively charged ions (anions)
move towards the electron-extracting (positive) anode.
In this process electrons are either absorbed or released. Neutral atoms gain or lose
electrons and become charged ions that then pass into the electrolyte. The formation of
uncharged atoms from ions is called discharging. When an ion gains or loses enough
electrons to become uncharged (neutral) atoms, the newly formed atoms separate from the
electrolyte. Positive metal ions like Cu++ deposit onto the cathode in a layer. The terms for
this are electroplating electrowinning and electrorefining. When an ion gains or loses
electrons without becoming neutral, its electronic charge is altered in the process. In
chemistry the loss of electrons is called oxidation while electron gain is called reduction.
You might also like
- Process of ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesProcess of ElectrolysisSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Is The Chemical Deposition of A Compound Into Its Constituent ElementsDocument3 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Is The Chemical Deposition of A Compound Into Its Constituent ElementsEngrDebashisMallickNo ratings yet
- U-3 (Electrochemistry) HandoutDocument6 pagesU-3 (Electrochemistry) HandoutbluejackbroNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSISDocument1 pageELECTROLYSISJordan DanielNo ratings yet
- Chap 11: Electrolysis: ProcessDocument2 pagesChap 11: Electrolysis: ProcessAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument18 pagesElectrochemistryesotericgraphicapparelNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis - NotesDocument3 pagesElectrolysis - NotesAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Chemistry Note - SS 2Document50 pages2nd Term Chemistry Note - SS 2ebhojiayeemmanuel1No ratings yet
- Electrolysis: ElectrologyDocument17 pagesElectrolysis: ElectrologyFrederic WustNo ratings yet
- Electrodes: Electrolysis and Redox ReactionDocument2 pagesElectrodes: Electrolysis and Redox Reactionvinod kumarNo ratings yet
- Electrodes: Electrolysis and Redox ReactionDocument2 pagesElectrodes: Electrolysis and Redox Reactionvinod kumarNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesElectrolysisrayyankamran10No ratings yet
- Overview : Process of ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesOverview : Process of Electrolysisn73686861No ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2015Document13 pagesElectrolysis 2015martinmbondjo062No ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 9.ABakshDocument16 pagesChemistry Chapter 9.ABakshNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL EFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ,,,,,,,, Topic - ELECTROLYTEDocument5 pagesCHEMICAL EFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ,,,,,,,, Topic - ELECTROLYTESanjaya SahooNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document53 pagesUnit 7tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2022-23Document18 pagesElectrolysis 2022-23Yasha RizviNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - ElectrolysisDocument41 pagesChapter I - ElectrolysisRodella ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Notes On ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesNotes On ElectrolysisAnonymous FS4fOiNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis NotesDocument19 pagesElectrolysis NotesXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- BT f5 Bab 6 DLP NniDocument43 pagesBT f5 Bab 6 DLP NniNURUL NADIAH BINTI IDRIS KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellDocument6 pagesElectrolytic CellJohn Israel R. CatedralNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry-12 2 11Document49 pagesElectrochemistry-12 2 11Vic VickyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellDocument2 pagesElectrochemical CellKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Cations: Etc. AnionsDocument2 pagesElectrolysis: Cations: Etc. AnionsVIKRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- ICSE 10 Chemistry ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesICSE 10 Chemistry ElectrolysisShreyas.HNo ratings yet
- CellDocument12 pagesCellrachit agarwalNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: by Aryan Gupta Class 12 A (Non-Medical) Roll No.26604942Document47 pagesElectrochemistry: by Aryan Gupta Class 12 A (Non-Medical) Roll No.26604942Aryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis PDFDocument13 pagesElectrolysis PDFShaikh Irad100% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesElectrolysisPrashiNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument8 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Notes On ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesNotes On Electrolysiskhizermehmood2008No ratings yet
- Ions and Ionic Compounds-NotesDocument3 pagesIons and Ionic Compounds-NotesKiran PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chemisty Note Yr 11ADocument6 pagesChemisty Note Yr 11AUchenna OfomaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectrolysisDocument14 pagesIntroduction To ElectrolysisFaiza RizwanNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 7Document21 pagesNotes - Chapter 7Chemistry Experts Tutors of ScienceNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument7 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- CTSC Matric Masterclasses Electrochemistry 2020-1Document17 pagesCTSC Matric Masterclasses Electrochemistry 2020-1Nika ReleniNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 1Document14 pagesElectrochemistry 1Warda Qasim AwanNo ratings yet
- GCFGCGCFGFDGDocument15 pagesGCFGCGCFGFDGZabrinaRuizNo ratings yet
- Olevel NotesDocument110 pagesOlevel Notestatendachimbandi1No ratings yet
- Electrode PotentialDocument24 pagesElectrode PotentialZoeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Laboratory ReportDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry Laboratory ReportSteven LeeNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec NotesDocument21 pagesChem Lec NotesErianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 1 TEDocument5 pagesElectrolysis 1 TETom TommmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument152 pagesElectrochemistrypapaioasNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: ConductorDocument20 pagesElectrochemistry: ConductorMithun Madhukar MaskeNo ratings yet
- Voltaic CellsDocument10 pagesVoltaic CellsJm EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesChapter 15 - ElectrolysisKayla WNo ratings yet
- II Semester/Unit 1/electrochemistryDocument25 pagesII Semester/Unit 1/electrochemistryapi-26041653100% (1)
- What Are Redox Reactions?Document18 pagesWhat Are Redox Reactions?Mr. Zee KhanNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument10 pagesElectrolysisFaithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electrochemistry 16thDocument95 pagesChapter 1 Electrochemistry 16thTravis McmillanNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 2Document27 pagesChapter17 2Mr. NaveenNo ratings yet
- Why Don't Covalent Bonds Form Ions?Document10 pagesWhy Don't Covalent Bonds Form Ions?api-470106119No ratings yet
- CH No 3Document22 pagesCH No 3Ultimate chemistryNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical CellsAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and ElectrolysisDocument42 pagesElectrochemistry and ElectrolysisAnthonya KnightNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- HS3214 - Final - Case Presentation RubricDocument5 pagesHS3214 - Final - Case Presentation RubricSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Master Problem ListDocument6 pagesMaster Problem ListSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Qiu Rong Say Jin Man Yi Sin Yin Sin Hui Yi Wen Selina Selina Wei TingDocument2 pagesQiu Rong Say Jin Man Yi Sin Yin Sin Hui Yi Wen Selina Selina Wei TingSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Algebra Over A FieldDocument1 pageAlgebra Over A FieldSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Abstract Algebra Galois Theory Constructibility George Peacock Augustus de Morgan Relation Algebra Josiah Willard Gibbs Arthur CayleyDocument1 pageAbstract Algebra Galois Theory Constructibility George Peacock Augustus de Morgan Relation Algebra Josiah Willard Gibbs Arthur CayleySelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Elementary AlgebraDocument1 pageElementary AlgebraSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Different Meanings ofDocument1 pageDifferent Meanings ofSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- The Persian MathematicianDocument1 pageThe Persian MathematicianSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- La Résolution Algébrique Des Équations Devoted To Solutions of Algebraic Equations, in Which HeDocument1 pageLa Résolution Algébrique Des Équations Devoted To Solutions of Algebraic Equations, in Which HeSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- History: Main Articles: andDocument1 pageHistory: Main Articles: andSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Algebra Is The Language Through Which We Describe Patterns. Think of It As ADocument1 pageAlgebra Is The Language Through Which We Describe Patterns. Think of It As ASelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Arabic Language Al-Khwarizmi Late Middle English Medieval LatinDocument1 pageEtymology: Arabic Language Al-Khwarizmi Late Middle English Medieval LatinSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Algebra (From: Arabic Mathematics Number Theory Geometry AnalysisDocument1 pageAlgebra (From: Arabic Mathematics Number Theory Geometry AnalysisSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Process of ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesProcess of ElectrolysisSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes During Electrolysis: Gas Diffusion ElectrodeDocument1 pageEnergy Changes During Electrolysis: Gas Diffusion ElectrodeSelina LeowNo ratings yet