Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Openstack Orchestration Heat: How It Works
Openstack Orchestration Heat: How It Works
Uploaded by
Abdul RashidCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Software-Defined Optical TransmissionDocument4 pagesSoftware-Defined Optical TransmissionRavi KishoreNo ratings yet
- Opnet Lab 0Document6 pagesOpnet Lab 0Mohamed Mazhar100% (1)
- Lbaas v2 OpenstackDocument2 pagesLbaas v2 OpenstackShabeer UppotungalNo ratings yet
- Pxe BootDocument19 pagesPxe BootJhunior Cuadros RamosNo ratings yet
- InfoBlox SNMP Enterprise MIBDocument20 pagesInfoBlox SNMP Enterprise MIBKali PsyNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Open StackDocument20 pagesTroubleshooting Open StackVignesh KumarNo ratings yet
- OpenStack Orchestration - Sample ChapterDocument17 pagesOpenStack Orchestration - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- TXLF2011 OpenStackDocument83 pagesTXLF2011 OpenStackNadia MetouiNo ratings yet
- Ants TutorialDocument119 pagesAnts TutorialjuanchirilinNo ratings yet
- 10 - HeatDocument17 pages10 - HeatPedro BrizuelaNo ratings yet
- Perl Scripting: Dr. Ayman WahbaDocument68 pagesPerl Scripting: Dr. Ayman Wahbaspiderman86No ratings yet
- 1 Sr. Devops ArchitectDocument6 pages1 Sr. Devops ArchitectRahul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Openstack Comp 1Document28 pagesOpenstack Comp 1achbilling7No ratings yet
- RallyDocument305 pagesRallyBlakee Griffinn Jr.100% (1)
- Rhcsa 7 LabDocument2 pagesRhcsa 7 LabPingutuNo ratings yet
- Devops Training Curriculum - Course ContentDocument4 pagesDevops Training Curriculum - Course ContentImranNo ratings yet
- Redhat 7 Boot ProcessDocument14 pagesRedhat 7 Boot ProcesskeshavNo ratings yet
- Btech Trainings GuideDocument26 pagesBtech Trainings GuideAlfian Pamungkas SakawigunaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Iperf CommandDocument5 pagesLab 2 Iperf CommandEvelina DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- VSFTPD With AnonymousDocument3 pagesVSFTPD With Anonymousblackhorse20032001No ratings yet
- Cloud OpenstackDocument5 pagesCloud OpenstackBinank PatelNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputinganilkarriiNo ratings yet
- MVHLUG SystemdDocument67 pagesMVHLUG SystemdHenk SnelNo ratings yet
- Regular Expression NotationDocument4 pagesRegular Expression NotationRajinder SinghNo ratings yet
- OpenstackDocument336 pagesOpenstackRupendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding OPNFV Ebook PDFDocument145 pagesUnderstanding OPNFV Ebook PDFRafik Kafel100% (1)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Booting ProcessDocument4 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Booting ProcessD Suneel100% (1)
- Advanced Policy Lab Activities GuideDocument15 pagesAdvanced Policy Lab Activities GuideTestla GavanNo ratings yet
- 2 Day Bootcamp For OpenStack - MirantisDocument66 pages2 Day Bootcamp For OpenStack - MirantisdoraemonkNo ratings yet
- Fuel 8.0 InstallGuideDocument67 pagesFuel 8.0 InstallGuideR.s. Félix100% (1)
- OpenShift BootCamp Series - DevTrack Virtual ModeDocument3 pagesOpenShift BootCamp Series - DevTrack Virtual ModeMushtaq ShaikNo ratings yet
- Ceph Cookbook - Sample ChapterDocument28 pagesCeph Cookbook - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Openvswitch enDocument27 pagesOpenvswitch enLoris StrozziniNo ratings yet
- A Container Stack For OpenStackDocument30 pagesA Container Stack For OpenStackDario RisoNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To Setting Up An OpenStack Development EnvironmentDocument4 pagesComplete Guide To Setting Up An OpenStack Development Environmentssitha6No ratings yet
- Learning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) Sample ChapterDocument18 pagesLearning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Manage Service Guard 2Document44 pagesManage Service Guard 2Tran Nguyen Khong ChinNo ratings yet
- Iptables To Stop DdosDocument3 pagesIptables To Stop DdosSatishKumarSinhaNo ratings yet
- SDN Controller and Implementation PDFDocument63 pagesSDN Controller and Implementation PDFhadje benilhaNo ratings yet
- OpenVSwitch PDFDocument21 pagesOpenVSwitch PDFShahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- h13 611 - v4.5 EnuDocument8 pagesh13 611 - v4.5 EnuBirdNo ratings yet
- Ansible AdsfgfgngnDocument388 pagesAnsible Adsfgfgngnsunil kumarNo ratings yet
- h323 Call FlowDocument4 pagesh323 Call Flowchellamanis9953No ratings yet
- Prepared by - , Deptt of Information Technology Assam University SilcharDocument29 pagesPrepared by - , Deptt of Information Technology Assam University Silchararifch2009scribdNo ratings yet
- Installing OpenStack On Ubuntu 12Document13 pagesInstalling OpenStack On Ubuntu 12Sahad SaliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SELinuxDocument11 pagesIntroduction To SELinuxAlan FoxNo ratings yet
- Terraform CH 1 Intoduction To IacDocument18 pagesTerraform CH 1 Intoduction To IacNitinNo ratings yet
- Mariadb Maxscale HADocument12 pagesMariadb Maxscale HADang Huu AnhNo ratings yet
- DPDK Packet Processing Ia Overview PresentationDocument35 pagesDPDK Packet Processing Ia Overview PresentationHassan WiloNo ratings yet
- Cacti Install CentosDocument16 pagesCacti Install Centosmilos_arNo ratings yet
- Configuring The Firewalld & Virtualhosts ProjectDocument9 pagesConfiguring The Firewalld & Virtualhosts ProjectAhmed chelsieNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Routing Platform: Self-Deployment GuideDocument14 pagesIntelligent Routing Platform: Self-Deployment Guidejheisson nunesNo ratings yet
- IperfDocument3 pagesIperfmymothman69No ratings yet
- Ansible Hands On IntroductionDocument33 pagesAnsible Hands On IntroductionMastanvaliNo ratings yet
- Strings (The Type) : Python Documentation For This VideoDocument2 pagesStrings (The Type) : Python Documentation For This VideoFaisal Saeed SaeedNo ratings yet
- Edu 010 Iintroduction To CybersecurityDocument1 pageEdu 010 Iintroduction To Cybersecurityjoy thejaksNo ratings yet
- Yet Another Technology Blog.: How To Configure PXE Server in RHEL 6 ?Document6 pagesYet Another Technology Blog.: How To Configure PXE Server in RHEL 6 ?jitendra_kasotia9917No ratings yet
- What Is Another Word ForDocument20 pagesWhat Is Another Word ForAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Sundew PlantDocument3 pagesSundew PlantAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- ChlorineDocument1 pageChlorineAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Awakening Effects of BlueDocument3 pagesAwakening Effects of BlueAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Joel AchenbachDocument10 pagesJoel AchenbachAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- DATADocument1 pageDATAAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Claude Shannon Boolean Cpus Punch Cards Magnetic Tape Hard DiskDocument1 pageClaude Shannon Boolean Cpus Punch Cards Magnetic Tape Hard DiskAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Home Earth Continents Countries of The WorldDocument3 pagesHome Earth Continents Countries of The WorldAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Ubqari - The Center For Peace and SpiritualityDocument1 pageUbqari - The Center For Peace and SpiritualityAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- A World Countries ListDocument1 pageA World Countries ListAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Atom Molecule KelvinDocument1 pageAtom Molecule KelvinAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- 3D Printer: Termed Their New Method of Printing: FLEX (Fused Layer Extrusion)Document2 pages3D Printer: Termed Their New Method of Printing: FLEX (Fused Layer Extrusion)Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Estudio 350Document30 pagesToshiba Estudio 350Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Sc990 On Aficio 1035Document2 pagesSc990 On Aficio 1035Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- The BasicsDocument1 pageThe BasicsAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Magnetism Is A Force of Attraction or Repulsion That Acts at A Distance. It Is Due ToDocument1 pageMagnetism: Magnetism Is A Force of Attraction or Repulsion That Acts at A Distance. It Is Due ToAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Service Hints: Model NameDocument2 pagesService Hints: Model NameAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
Openstack Orchestration Heat: How It Works
Openstack Orchestration Heat: How It Works
Uploaded by
Abdul RashidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Openstack Orchestration Heat: How It Works
Openstack Orchestration Heat: How It Works
Uploaded by
Abdul RashidCopyright:
Available Formats
OpenStack Orchestration
The mission of the OpenStack Orchestration program is to create a human- and
machine-accessible service for managing the entire lifecycle of infrastructure and
applications within OpenStack clouds.
Heat
Heat is the main project in the OpenStack Orchestration program. It implements an
orchestration engine to launch multiple composite cloud applications based on
templates in the form of text files that can be treated like code. A native Heat template
format is evolving, but Heat also endeavours to provide compatibility with the AWS
CloudFormation template format, so that many existing CloudFormation templates can
be launched on OpenStack. Heat provides both an OpenStack-native ReST API and a
CloudFormation-compatible Query API.
Why Heat? It makes the clouds rise!
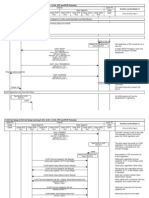
How it works
A Heat template describes the infrastructure for a cloud application in a text file
that is readable and writable by humans, and can be checked into version control,
diffed, &c.
Infrastructure resources that can be described include: servers, floating ips,
volumes, security groups, users, etc.
Heat also provides an autoscaling service that integrates with Ceilometer, so you
can include a scaling group as a resource in a template.
Templates can also specify the relationships between resources (e.g. this volume
is connected to this server). This enables Heat to call out to the OpenStack APIs to
create all of your infrastructure in the correct order to completely launch your
application.
Heat manages the whole lifecycle of the application - when you need to change
your infrastructure, simply modify the template and use it to update your existing
stack. Heat knows how to make the necessary changes. It will delete all of the
resources when you are finished with the application, too.
Heat primarily manages infrastructure, but the templates integrate well with
software configuration management tools such as Puppet and Chef. The Heat team
is working on providing even better integration between infrastructure and software.
You might also like
- Software-Defined Optical TransmissionDocument4 pagesSoftware-Defined Optical TransmissionRavi KishoreNo ratings yet
- Opnet Lab 0Document6 pagesOpnet Lab 0Mohamed Mazhar100% (1)
- Lbaas v2 OpenstackDocument2 pagesLbaas v2 OpenstackShabeer UppotungalNo ratings yet
- Pxe BootDocument19 pagesPxe BootJhunior Cuadros RamosNo ratings yet
- InfoBlox SNMP Enterprise MIBDocument20 pagesInfoBlox SNMP Enterprise MIBKali PsyNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Open StackDocument20 pagesTroubleshooting Open StackVignesh KumarNo ratings yet
- OpenStack Orchestration - Sample ChapterDocument17 pagesOpenStack Orchestration - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- TXLF2011 OpenStackDocument83 pagesTXLF2011 OpenStackNadia MetouiNo ratings yet
- Ants TutorialDocument119 pagesAnts TutorialjuanchirilinNo ratings yet
- 10 - HeatDocument17 pages10 - HeatPedro BrizuelaNo ratings yet
- Perl Scripting: Dr. Ayman WahbaDocument68 pagesPerl Scripting: Dr. Ayman Wahbaspiderman86No ratings yet
- 1 Sr. Devops ArchitectDocument6 pages1 Sr. Devops ArchitectRahul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Openstack Comp 1Document28 pagesOpenstack Comp 1achbilling7No ratings yet
- RallyDocument305 pagesRallyBlakee Griffinn Jr.100% (1)
- Rhcsa 7 LabDocument2 pagesRhcsa 7 LabPingutuNo ratings yet
- Devops Training Curriculum - Course ContentDocument4 pagesDevops Training Curriculum - Course ContentImranNo ratings yet
- Redhat 7 Boot ProcessDocument14 pagesRedhat 7 Boot ProcesskeshavNo ratings yet
- Btech Trainings GuideDocument26 pagesBtech Trainings GuideAlfian Pamungkas SakawigunaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Iperf CommandDocument5 pagesLab 2 Iperf CommandEvelina DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- VSFTPD With AnonymousDocument3 pagesVSFTPD With Anonymousblackhorse20032001No ratings yet
- Cloud OpenstackDocument5 pagesCloud OpenstackBinank PatelNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputinganilkarriiNo ratings yet
- MVHLUG SystemdDocument67 pagesMVHLUG SystemdHenk SnelNo ratings yet
- Regular Expression NotationDocument4 pagesRegular Expression NotationRajinder SinghNo ratings yet
- OpenstackDocument336 pagesOpenstackRupendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding OPNFV Ebook PDFDocument145 pagesUnderstanding OPNFV Ebook PDFRafik Kafel100% (1)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Booting ProcessDocument4 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Booting ProcessD Suneel100% (1)
- Advanced Policy Lab Activities GuideDocument15 pagesAdvanced Policy Lab Activities GuideTestla GavanNo ratings yet
- 2 Day Bootcamp For OpenStack - MirantisDocument66 pages2 Day Bootcamp For OpenStack - MirantisdoraemonkNo ratings yet
- Fuel 8.0 InstallGuideDocument67 pagesFuel 8.0 InstallGuideR.s. Félix100% (1)
- OpenShift BootCamp Series - DevTrack Virtual ModeDocument3 pagesOpenShift BootCamp Series - DevTrack Virtual ModeMushtaq ShaikNo ratings yet
- Ceph Cookbook - Sample ChapterDocument28 pagesCeph Cookbook - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Openvswitch enDocument27 pagesOpenvswitch enLoris StrozziniNo ratings yet
- A Container Stack For OpenStackDocument30 pagesA Container Stack For OpenStackDario RisoNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To Setting Up An OpenStack Development EnvironmentDocument4 pagesComplete Guide To Setting Up An OpenStack Development Environmentssitha6No ratings yet
- Learning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) Sample ChapterDocument18 pagesLearning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Manage Service Guard 2Document44 pagesManage Service Guard 2Tran Nguyen Khong ChinNo ratings yet
- Iptables To Stop DdosDocument3 pagesIptables To Stop DdosSatishKumarSinhaNo ratings yet
- SDN Controller and Implementation PDFDocument63 pagesSDN Controller and Implementation PDFhadje benilhaNo ratings yet
- OpenVSwitch PDFDocument21 pagesOpenVSwitch PDFShahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- h13 611 - v4.5 EnuDocument8 pagesh13 611 - v4.5 EnuBirdNo ratings yet
- Ansible AdsfgfgngnDocument388 pagesAnsible Adsfgfgngnsunil kumarNo ratings yet
- h323 Call FlowDocument4 pagesh323 Call Flowchellamanis9953No ratings yet
- Prepared by - , Deptt of Information Technology Assam University SilcharDocument29 pagesPrepared by - , Deptt of Information Technology Assam University Silchararifch2009scribdNo ratings yet
- Installing OpenStack On Ubuntu 12Document13 pagesInstalling OpenStack On Ubuntu 12Sahad SaliNo ratings yet
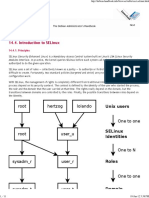
- Introduction To SELinuxDocument11 pagesIntroduction To SELinuxAlan FoxNo ratings yet
- Terraform CH 1 Intoduction To IacDocument18 pagesTerraform CH 1 Intoduction To IacNitinNo ratings yet
- Mariadb Maxscale HADocument12 pagesMariadb Maxscale HADang Huu AnhNo ratings yet
- DPDK Packet Processing Ia Overview PresentationDocument35 pagesDPDK Packet Processing Ia Overview PresentationHassan WiloNo ratings yet
- Cacti Install CentosDocument16 pagesCacti Install Centosmilos_arNo ratings yet
- Configuring The Firewalld & Virtualhosts ProjectDocument9 pagesConfiguring The Firewalld & Virtualhosts ProjectAhmed chelsieNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Routing Platform: Self-Deployment GuideDocument14 pagesIntelligent Routing Platform: Self-Deployment Guidejheisson nunesNo ratings yet
- IperfDocument3 pagesIperfmymothman69No ratings yet
- Ansible Hands On IntroductionDocument33 pagesAnsible Hands On IntroductionMastanvaliNo ratings yet
- Strings (The Type) : Python Documentation For This VideoDocument2 pagesStrings (The Type) : Python Documentation For This VideoFaisal Saeed SaeedNo ratings yet
- Edu 010 Iintroduction To CybersecurityDocument1 pageEdu 010 Iintroduction To Cybersecurityjoy thejaksNo ratings yet
- Yet Another Technology Blog.: How To Configure PXE Server in RHEL 6 ?Document6 pagesYet Another Technology Blog.: How To Configure PXE Server in RHEL 6 ?jitendra_kasotia9917No ratings yet
- What Is Another Word ForDocument20 pagesWhat Is Another Word ForAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Sundew PlantDocument3 pagesSundew PlantAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- ChlorineDocument1 pageChlorineAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Awakening Effects of BlueDocument3 pagesAwakening Effects of BlueAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Joel AchenbachDocument10 pagesJoel AchenbachAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- DATADocument1 pageDATAAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Claude Shannon Boolean Cpus Punch Cards Magnetic Tape Hard DiskDocument1 pageClaude Shannon Boolean Cpus Punch Cards Magnetic Tape Hard DiskAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Home Earth Continents Countries of The WorldDocument3 pagesHome Earth Continents Countries of The WorldAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Ubqari - The Center For Peace and SpiritualityDocument1 pageUbqari - The Center For Peace and SpiritualityAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- A World Countries ListDocument1 pageA World Countries ListAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Atom Molecule KelvinDocument1 pageAtom Molecule KelvinAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- 3D Printer: Termed Their New Method of Printing: FLEX (Fused Layer Extrusion)Document2 pages3D Printer: Termed Their New Method of Printing: FLEX (Fused Layer Extrusion)Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Estudio 350Document30 pagesToshiba Estudio 350Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Sc990 On Aficio 1035Document2 pagesSc990 On Aficio 1035Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- The BasicsDocument1 pageThe BasicsAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Magnetism Is A Force of Attraction or Repulsion That Acts at A Distance. It Is Due ToDocument1 pageMagnetism: Magnetism Is A Force of Attraction or Repulsion That Acts at A Distance. It Is Due ToAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Service Hints: Model NameDocument2 pagesService Hints: Model NameAbdul RashidNo ratings yet