Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structure Eukaryotic Cells Function Mitochondrion
Structure Eukaryotic Cells Function Mitochondrion
Uploaded by
Natalia KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structure Eukaryotic Cells Function Mitochondrion
Structure Eukaryotic Cells Function Mitochondrion
Uploaded by
Natalia KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
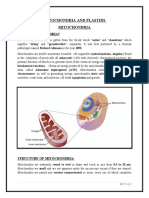
STRUCTURE
Mitochondrion
Ribosomes
Eukaryotic Cells
FUNCTION
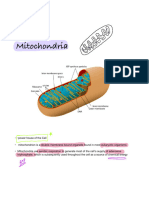
Eukaryotic cells take in glucose through proteins that cross the
plasma membrane and then transport it through the cytoskeleton to
the mitochondria (mitochondria is plural; the singular is
mitochondrion) in the cytoplasm. The mitochondrion is often called
the cell's powerhouse.
In the cytoplasm just outside the mitochondria, glucose is broken
down into smaller molecules through a process called glycolysis
(literally "sugar breaking"), which releases chemical energy. This
energy is temporarily captured by specialized molecules and
transported through the mitochondrial membranes into the
mitochondria. There it is used to make an important molecule called
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process known as cellular
respiration.
Mitochondria can convert a single molecule of glucose into ~38
molecules of ATP! Mitochondria do not mess around with energy
storage; they mean business. You can think of each ATP molecule as
a unit of stored energy ready to be used by the cell whenever
needed.
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Mitochondria PDFDocument10 pagesMitochondria PDFpragya utNo ratings yet
- Proteasome and MitochondriaDocument2 pagesProteasome and MitochondriaVeronica GamosoNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria OriginalDocument12 pagesMitochondria OriginalasmiroshnamsNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyArthur AguilarNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument14 pagesMitochondriaPhoebe KimNo ratings yet
- Gen PhysioDocument2 pagesGen PhysioJude AlabanNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument71 pagesMitochondria and ChloroplastRifai Alfarabi100% (1)
- Mitochondria: Dr. Raheela Jabeen Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry & Biotechnology, WUMDocument30 pagesMitochondria: Dr. Raheela Jabeen Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry & Biotechnology, WUMMah Noor100% (1)
- MITOCHONDRIADocument3 pagesMITOCHONDRIAAbid RazaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: μίτο or mitos thread + χονδρίον or chondrion granuleDocument15 pagesMitochondria: μίτο or mitos thread + χονδρίον or chondrion granuleNitun PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Mitokondria - Glikolisis - LisosomDocument74 pagesMitokondria - Glikolisis - LisosomYulius AriantoNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: PratibhapariharDocument38 pagesMitochondria: PratibhapariharPatel BansariNo ratings yet
- Group G: Lysosome and MitochondriaDocument2 pagesGroup G: Lysosome and MitochondriaFaith Perl NiloNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIADocument20 pagesMITOCHONDRIAannisa fauzia rahmahNo ratings yet
- Mitokondria - Kelompok 2Document21 pagesMitokondria - Kelompok 2Miftahul jannahNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIONDocument6 pagesMITOCHONDRIONCheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Revieweraaleah moscaNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument3 pagesMitochondriaGood AstraNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 2Document4 pagesLesson1 2Cheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Are Sites of EnergyDocument2 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplasts Are Sites of Energyبسمہ فاطمہNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaForm, Function, Anddisease 1705678469777Document11 pagesMitochondriaForm, Function, Anddisease 1705678469777kalitutawa465No ratings yet
- Short Study Poject: Mitochondria - Its' Structure, History and FunctionDocument5 pagesShort Study Poject: Mitochondria - Its' Structure, History and FunctionSarvNo ratings yet
- Control Center of CellDocument2 pagesControl Center of CellAbhishek LeveNo ratings yet
- Presentation by Chirag Sadanand Kudale Subject: Science & Technology (Mitochondria)Document25 pagesPresentation by Chirag Sadanand Kudale Subject: Science & Technology (Mitochondria)JiteshPbhujbalNo ratings yet
- How Mitochondria Produce EnergyDocument1 pageHow Mitochondria Produce EnergyDanial DanialNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria - The Powerhouses of The CellDocument1 pageMitochondria - The Powerhouses of The CellVinícius SouzaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Bot-201Document13 pagesGroup 4 Bot-201Aye ShaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastsDocument2 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplastsatanu mitraNo ratings yet
- Cell Energy Storage and UseDocument13 pagesCell Energy Storage and UseHazel Joy Patria DantesNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Biology - MitochondriaDocument9 pagesBiology - MitochondriaAJ IzaguirreNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument6 pagesMitochondriadeepasanmughamNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRONDocument3 pagesMITOCHONDRONPhoebe Magdurulan100% (1)
- Flow 0f Energy and Life Processes in Ecosystems 2Document17 pagesFlow 0f Energy and Life Processes in Ecosystems 2Erica NatividadNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDDocument73 pagesBIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDJowe VarnalNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria - The Powerhouses of The Cell ExplainedDocument4 pagesMitochondria - The Powerhouses of The Cell Explainedheadboyprince8080No ratings yet
- 4 CellDocument17 pages4 CellNoor ul aminNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument22 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesKrishiaDeVeraNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument10 pagesMitochondriaHanumat SinghNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Science By: Dlshad H. Sati Biology Dept. Lab:3Document5 pagesFaculty of Science By: Dlshad H. Sati Biology Dept. Lab:3Helal HamadNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument20 pagesMitochondriaام احمدNo ratings yet
- Notes For Summative Test 1Document67 pagesNotes For Summative Test 1Phoemela Marie AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument20 pagesMitochondriaSeshadri Seshu100% (1)
- BIO Reviewer - All Abt CellsDocument5 pagesBIO Reviewer - All Abt CellsLeilah Angelique KunkelNo ratings yet
- Biology 212 - ReadingsDocument32 pagesBiology 212 - ReadingsKamille TucaNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument15 pagesBio Projectapi-283573157No ratings yet
- Class XI A Bio Project 31-35Document12 pagesClass XI A Bio Project 31-35Ryan WalkerNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: MitochondriaDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration: MitochondriaMaryRoseTrajada100% (1)
- Mitochondria Are Unusual OrganellesDocument5 pagesMitochondria Are Unusual OrganellesPrecious DerainNo ratings yet
- k2. MItochondria - Muzar Z-Des 2016Document29 pagesk2. MItochondria - Muzar Z-Des 2016Khemal MubaraqNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures: The BasicsDocument4 pagesCell Structures: The BasicsParama CinthyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Structures of Cells and OrganellesDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Structures of Cells and Organelleskeethagurl24No ratings yet
- Notability NotesDocument5 pagesNotability Notesznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Cells and Their FunctionDocument4 pagesCells and Their FunctionMatika John PierreNo ratings yet
- Bio PPT ReviewerDocument13 pagesBio PPT ReviewerEljenColanggoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Index To This PageDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration: Index To This PageVictor VegaNo ratings yet
- Figure 14-5the Relationship Between Mitochondria and MicrotubulesDocument6 pagesFigure 14-5the Relationship Between Mitochondria and MicrotubulesDewi simangunsongNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet