Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 2 - SUMMARY: Instrumentation in Engineering & Science Based On
Lecture 2 - SUMMARY: Instrumentation in Engineering & Science Based On
Uploaded by
Erj DaniyaroffCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sulfuric Acid Production in Kazakhstan, StepnogorskDocument4 pagesSulfuric Acid Production in Kazakhstan, StepnogorskErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsSiddarameshwara HNNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Electrical EngineeringDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering Electrical EngineeringPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- EE 303 Introduction 2013Document49 pagesEE 303 Introduction 2013vepnisxaNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesPower Electronicsgrbavithra100% (1)
- Lec-1 Scope of Power ConvertersDocument26 pagesLec-1 Scope of Power Convertersjameelahmad100% (1)
- Introduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Industrial ElectronicsDocument108 pagesIndustrial ElectronicsChristian Dave TamparongNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument32 pagesPower ElectronicsmnamkyNo ratings yet
- Circuits Chapter 1Document102 pagesCircuits Chapter 1Jessica AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument28 pagesPower Electronicspavan96100% (5)
- On Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesOn Power ElectronicsMuhammed Ahmed93% (41)
- Basicconcepts Chapter1Document40 pagesBasicconcepts Chapter1Surafel WorkayehuNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic:: Dr. F. Danang Wijaya, ST, MT Lab. TTLDocument18 pagesPower Electronic:: Dr. F. Danang Wijaya, ST, MT Lab. TTLVeby Enandes StalonyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1bilal alkhNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesPower ElectronicsRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 1: Basic ConceptsDocument47 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 1: Basic Conceptsrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Hanani Abdul Wahab BDA3073Document33 pagesHanani Abdul Wahab BDA3073Shahidin ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 131114022851 Phpapp02 PDFDocument77 pagesChapter1 131114022851 Phpapp02 PDFImran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithDocument40 pagesELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithJameson CongoNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 PSA - IntroDocument32 pagesLect 1 PSA - IntroJunaid ToorNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Circuit Variables PDFDocument25 pagesCH1 - Circuit Variables PDFahmed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Systems: by Waqas AnwarDocument8 pagesElectrical & Electronic Systems: by Waqas AnwarWaqasNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Relation With Multiple Disciplines: Oni CsDocument5 pagesRelation With Multiple Disciplines: Oni CsHossein DavijaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Designing New1Document189 pagesElectrical Designing New1anoop9950No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductionTahmid AlamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraDocument17 pagesElectrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering For Oil and Gas FacilitiesDocument19 pagesElectrical and Instrumentation Engineering For Oil and Gas FacilitiesSyafRizalNo ratings yet
- EE2004 1 Nature of Electrical Energy System UpdateDocument65 pagesEE2004 1 Nature of Electrical Energy System Updateanimation.yeungsinwaiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics IntroductionDocument21 pagesPower Electronics IntroductionJr ReforbaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)Document61 pagesPower Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)chetan100% (1)
- Modeling of Electrical and Electromechanical Systems ME 635Document40 pagesModeling of Electrical and Electromechanical Systems ME 635Fred100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 1 (Basic Concepts)Document55 pagesLecture 1 - Chapter 1 (Basic Concepts)Saleh AlhalgpiNo ratings yet
- ECE1311 Ch1 - FarahIsaDocument24 pagesECE1311 Ch1 - FarahIsaMuhd NaimNo ratings yet
- PowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Document15 pagesPowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Ndunya WestleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electrical BasicsDocument47 pagesChapter 1 - Electrical BasicsGopinath SubramaniNo ratings yet
- ECE 281 - 1 Basic Circuit TheoryDocument101 pagesECE 281 - 1 Basic Circuit TheoryCagri CindiogluNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Talha Asghar 1Document14 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Talha Asghar 1Sohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticsDocument26 pagesElectromagneticskhaleel_anwar2000No ratings yet
- Instrumentation & Measurement SystemsDocument13 pagesInstrumentation & Measurement SystemsAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction Power Systems 08 ADocument161 pagesIntroduction Power Systems 08 Abaosyle9201No ratings yet
- LC1 EE3706 C1 Basic ConceptsDocument16 pagesLC1 EE3706 C1 Basic ConceptsnamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document12 pagesLecture 1Mouath AlsebaieNo ratings yet
- EEE1 Lecture01 PDFDocument4 pagesEEE1 Lecture01 PDFJosh KingNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Dr. Abdul MajidDocument17 pagesPower Electronics: Dr. Abdul MajidAdnankhan BangashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics SystemDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics Systemrakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- Grid Connected Photovoltaic ArrayDocument19 pagesGrid Connected Photovoltaic ArrayahdabmkNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Transient Processes On Overvoltage in Electric Transmission Lines Using ATP-EMTPDocument14 pagesSimulation of Transient Processes On Overvoltage in Electric Transmission Lines Using ATP-EMTPJosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsSathiya NathanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsSathiya NathanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsRajaiah JagariNo ratings yet
- L1 - Power Electronics - Introduction To Power Electronics 20-21 (Temp.)Document38 pagesL1 - Power Electronics - Introduction To Power Electronics 20-21 (Temp.)Fernando Nuño GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Examination PDFDocument7 pagesElectrical Engineering Examination PDFJustine James AdonaNo ratings yet
- Electrical-Engineering-Examination Syllabus PDFDocument7 pagesElectrical-Engineering-Examination Syllabus PDFJoseph JoeNo ratings yet
- Circuit Basics: Dr. Jayashri RavishankarDocument36 pagesCircuit Basics: Dr. Jayashri RavishankarEmzymeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Energy BalanceDocument25 pages1.1 Energy BalancenandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- Elcrc 1Document53 pagesElcrc 1SalmaanCadeXaajiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Systems Chapter 2 - Resistive CircuitsDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Systems Chapter 2 - Resistive CircuitsErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- CRET Class 01 - 10 - 2013Document15 pagesCRET Class 01 - 10 - 2013Erj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering and Thermodynamics PDFDocument2 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering and Thermodynamics PDFErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Application Form To ResitDocument1 pageApplication Form To ResitErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 6Document4 pagesLecture Notes 6Erj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 3Document3 pagesLecture Notes 3Erj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
Lecture 2 - SUMMARY: Instrumentation in Engineering & Science Based On
Lecture 2 - SUMMARY: Instrumentation in Engineering & Science Based On
Uploaded by
Erj DaniyaroffOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 2 - SUMMARY: Instrumentation in Engineering & Science Based On
Lecture 2 - SUMMARY: Instrumentation in Engineering & Science Based On
Uploaded by
Erj DaniyaroffCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Electrical Systems
Lecture 2 - SUMMARY
Instrumentation in Engineering & Science based on
Electrical Sensors
Electronics
Computers
Areas in Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)
1)
Communications Systems data transmission
2)
Computer Systems process & storage
3)
Control Systems physical process control
4)
Electromagnetics antennas & electrical machines
5)
Electronics circuits
6)
Photonics use light to perform operations
7)
Power & Energy Systems energy conversion & transportation
8)
Signal Processing treatment of information (analog & digital)
Introduction to Electrical Systems
Lecture 1 - SUMMARY
Element
Electrical Current
Flow of electric charge through element
dc: direct current, ac: alternative current
Units
[ Amperes ] = [ Coulombs / second ]
[A] = [ C / s ]
Voltage
Energy transferred per unit of charge
Units
[ Volts ] = [ Joules / Coulomb ]
[V]=[J/C]
Power
Rate of energy transfer
Units
[ Watts] = [ Volts ] x [ Amperes ]
[ W ] = [ V ] x [A]
If (p>0) energy absorbed
If (p<0) energy supplied
2
Introduction to Electrical Systems
Lecture 1 - SUMMARY
Node
Node
KCL : Kirchhoffs Current Law
Sum of currents entering node = Sum of currents leaving node
KVL : Kirchhoffs Voltage Law
Sum of the voltages = 0 for any closed path (loop)
+
-
+
Loop
Introduction to Electrical Systems
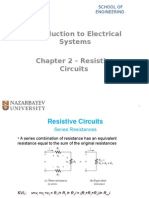
Lecture 1 - SUMMARY
Series Circuit
Parallel Circuit
Identical currents
Identical voltages
Ohms Law
Resistance (R)
[ Ohms ] = [ Volts / Amperes ]
[ ] = [ V / A]
Conductance (G = 1 / R)
[ Siemens ] = [ 1 / Ohms ]
[S]=[1/]
Introduction to Electrical Systems
Lecture 1 - SUMMARY
Independent & Controlled Sources
Voltage
Current
You might also like
- Sulfuric Acid Production in Kazakhstan, StepnogorskDocument4 pagesSulfuric Acid Production in Kazakhstan, StepnogorskErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsSiddarameshwara HNNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Electrical EngineeringDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering Electrical EngineeringPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- EE 303 Introduction 2013Document49 pagesEE 303 Introduction 2013vepnisxaNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesPower Electronicsgrbavithra100% (1)
- Lec-1 Scope of Power ConvertersDocument26 pagesLec-1 Scope of Power Convertersjameelahmad100% (1)
- Introduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Industrial ElectronicsDocument108 pagesIndustrial ElectronicsChristian Dave TamparongNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument32 pagesPower ElectronicsmnamkyNo ratings yet
- Circuits Chapter 1Document102 pagesCircuits Chapter 1Jessica AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument28 pagesPower Electronicspavan96100% (5)
- On Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesOn Power ElectronicsMuhammed Ahmed93% (41)
- Basicconcepts Chapter1Document40 pagesBasicconcepts Chapter1Surafel WorkayehuNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic:: Dr. F. Danang Wijaya, ST, MT Lab. TTLDocument18 pagesPower Electronic:: Dr. F. Danang Wijaya, ST, MT Lab. TTLVeby Enandes StalonyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1bilal alkhNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesPower ElectronicsRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 1: Basic ConceptsDocument47 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 1: Basic Conceptsrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Hanani Abdul Wahab BDA3073Document33 pagesHanani Abdul Wahab BDA3073Shahidin ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 131114022851 Phpapp02 PDFDocument77 pagesChapter1 131114022851 Phpapp02 PDFImran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithDocument40 pagesELG4126: Sustainable Power Systems: Concepts and Applications: You Should Be Familiar WithJameson CongoNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 PSA - IntroDocument32 pagesLect 1 PSA - IntroJunaid ToorNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Circuit Variables PDFDocument25 pagesCH1 - Circuit Variables PDFahmed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Systems: by Waqas AnwarDocument8 pagesElectrical & Electronic Systems: by Waqas AnwarWaqasNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Relation With Multiple Disciplines: Oni CsDocument5 pagesRelation With Multiple Disciplines: Oni CsHossein DavijaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Designing New1Document189 pagesElectrical Designing New1anoop9950No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductionTahmid AlamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraDocument17 pagesElectrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering For Oil and Gas FacilitiesDocument19 pagesElectrical and Instrumentation Engineering For Oil and Gas FacilitiesSyafRizalNo ratings yet
- EE2004 1 Nature of Electrical Energy System UpdateDocument65 pagesEE2004 1 Nature of Electrical Energy System Updateanimation.yeungsinwaiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics IntroductionDocument21 pagesPower Electronics IntroductionJr ReforbaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)Document61 pagesPower Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)chetan100% (1)
- Modeling of Electrical and Electromechanical Systems ME 635Document40 pagesModeling of Electrical and Electromechanical Systems ME 635Fred100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 1 (Basic Concepts)Document55 pagesLecture 1 - Chapter 1 (Basic Concepts)Saleh AlhalgpiNo ratings yet
- ECE1311 Ch1 - FarahIsaDocument24 pagesECE1311 Ch1 - FarahIsaMuhd NaimNo ratings yet
- PowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Document15 pagesPowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Ndunya WestleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electrical BasicsDocument47 pagesChapter 1 - Electrical BasicsGopinath SubramaniNo ratings yet
- ECE 281 - 1 Basic Circuit TheoryDocument101 pagesECE 281 - 1 Basic Circuit TheoryCagri CindiogluNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Talha Asghar 1Document14 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Talha Asghar 1Sohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticsDocument26 pagesElectromagneticskhaleel_anwar2000No ratings yet
- Instrumentation & Measurement SystemsDocument13 pagesInstrumentation & Measurement SystemsAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering: By:-Rudra Kumar MishraRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction Power Systems 08 ADocument161 pagesIntroduction Power Systems 08 Abaosyle9201No ratings yet
- LC1 EE3706 C1 Basic ConceptsDocument16 pagesLC1 EE3706 C1 Basic ConceptsnamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document12 pagesLecture 1Mouath AlsebaieNo ratings yet
- EEE1 Lecture01 PDFDocument4 pagesEEE1 Lecture01 PDFJosh KingNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Dr. Abdul MajidDocument17 pagesPower Electronics: Dr. Abdul MajidAdnankhan BangashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics SystemDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics Systemrakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- Grid Connected Photovoltaic ArrayDocument19 pagesGrid Connected Photovoltaic ArrayahdabmkNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Transient Processes On Overvoltage in Electric Transmission Lines Using ATP-EMTPDocument14 pagesSimulation of Transient Processes On Overvoltage in Electric Transmission Lines Using ATP-EMTPJosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsSathiya NathanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsSathiya NathanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsRajaiah JagariNo ratings yet
- L1 - Power Electronics - Introduction To Power Electronics 20-21 (Temp.)Document38 pagesL1 - Power Electronics - Introduction To Power Electronics 20-21 (Temp.)Fernando Nuño GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Examination PDFDocument7 pagesElectrical Engineering Examination PDFJustine James AdonaNo ratings yet
- Electrical-Engineering-Examination Syllabus PDFDocument7 pagesElectrical-Engineering-Examination Syllabus PDFJoseph JoeNo ratings yet
- Circuit Basics: Dr. Jayashri RavishankarDocument36 pagesCircuit Basics: Dr. Jayashri RavishankarEmzymeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Energy BalanceDocument25 pages1.1 Energy BalancenandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- Elcrc 1Document53 pagesElcrc 1SalmaanCadeXaajiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Systems Chapter 2 - Resistive CircuitsDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Systems Chapter 2 - Resistive CircuitsErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Systems (Introduction To Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 2015 Spring SemesterErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- CRET Class 01 - 10 - 2013Document15 pagesCRET Class 01 - 10 - 2013Erj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering and Thermodynamics PDFDocument2 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering and Thermodynamics PDFErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Application Form To ResitDocument1 pageApplication Form To ResitErj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 6Document4 pagesLecture Notes 6Erj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 3Document3 pagesLecture Notes 3Erj DaniyaroffNo ratings yet