Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometrical Construction: AE EB AB
Geometrical Construction: AE EB AB
Uploaded by
Krishna MurthyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometrical Construction: AE EB AB
Geometrical Construction: AE EB AB
Uploaded by
Krishna MurthyCopyright:
Available Formats
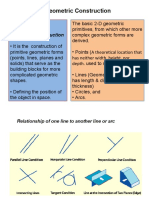
Geometrical Construction
1. Bisecting a line.
2. To draw perpendiculars.
3. To draw parallel lines.
4. To divide a line.
5. To bisect an angle.
6. To trisect an angle.
7. To find centre of an arc.
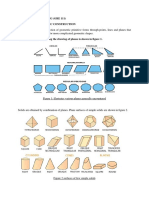
8. To construct equilateral le.
9. To construct squares.
10. To construct regular polygon.
11. Special method for drawing regular polygon.
12. Regular polygon inscribed in circles.
13. To draw regular figures using T-square and set square.
14. To draw tangents.
15. To find length of arcs.
16. Circles and lines in contact.
17. Inscribed circles
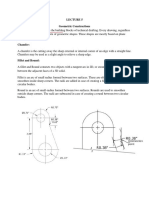
Bisecting a line (line length = 10 cm)
Procedure
1. Let AB be the given line with center A and radius greater than half of AB draw
an arcs on both sides of AB.
2. With centre B and the same radius draw arcs intersecting the previous arcs at C
and D. Draw a line joining C and D, cutting A and B at E. Then,
1
AE=EB= AB
2
3. Further CD bisects AB at right angles.
To bisect a given Arc (R = 5cm)
1. Let AB be the given arc with centre A and radius greater D half of AB draw arcs
on either side of AB.
2. Centre B with same radius draw arcs intersecting previous arcs at C and D.
Draw a line joining C and D cutting AB at E then
1
AE=EB= AB
2
To draw perpendicular lines (10 cm, P = 4 cm from B)
- To draw a perpendicular to a given line from a point within it.
Procedure-Case-I
1. Let the point is near middle of the line. Let AB be the given line and P the
point in it.
2. With P as centre and any convenient radius draw an arc cutting AB at C
and D.
3. With any radius r2 > r1 and centre C and D draw arcs intersecting each
other at O. Draw a line joining P and O, then PO is required perpendicular
You might also like
- Engineering Drowing Chapter 4Document33 pagesEngineering Drowing Chapter 4DT artNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Geometric ConstructionDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Geometric ConstructionYohannis Reta100% (1)
- Important Questions ICSE Class 10th Maths Construction Year 2009Document4 pagesImportant Questions ICSE Class 10th Maths Construction Year 2009Rishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 7 Math Chapter 10 Practical GeometryDocument18 pagesNcert Solutions Class 7 Math Chapter 10 Practical GeometrySatvik Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometric ConstructionDocument73 pagesGeometric Constructionmauvitz.alfoughreNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 Geometric Constructions PolygonsDocument4 pagesWEEK 7 Geometric Constructions PolygonsADAMU MUSA SANINo ratings yet
- Geometrical ConstructionsDocument14 pagesGeometrical ConstructionsmwarirukiaNo ratings yet
- GRE Lecture 3 Geometric ConstructionDocument12 pagesGRE Lecture 3 Geometric ConstructionPrecious SundayNo ratings yet
- Construction of Plane ShapesDocument17 pagesConstruction of Plane Shapesblankfail75% (4)
- Lect - 5 - HO - 3 - Applied - Geometry - Ellipse - 16-17 - HBE - PDF Filename - UTF-8''Lect 5 - HO - 3 Applied Geometry+Ellipse (16-17) - HBE-1Document14 pagesLect - 5 - HO - 3 - Applied - Geometry - Ellipse - 16-17 - HBE - PDF Filename - UTF-8''Lect 5 - HO - 3 Applied Geometry+Ellipse (16-17) - HBE-1Gaylan BarwariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Geometrical ConstractionDocument38 pagesLecture 2 - Geometrical Constractionmmarybenson11No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Construction and LociDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Construction and LociAtif Muhammad100% (1)
- Simple Geometrical Constructions (Part 1)Document19 pagesSimple Geometrical Constructions (Part 1)SundayNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 11 ConstructionDocument11 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 11 Constructionrai venugopalNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 2 2Document14 pagesGeometric Construction 2 2benmatt08060No ratings yet
- Topic 2: Geometrical ConstructionDocument16 pagesTopic 2: Geometrical ConstructionEmir Emir SyaminNo ratings yet
- Level 3 FinalDocument274 pagesLevel 3 FinalRas RNo ratings yet
- Excercise 1Document4 pagesExcercise 1kevs balacanaoNo ratings yet
- Week 4b, Geometric Construction (Polygons)Document4 pagesWeek 4b, Geometric Construction (Polygons)Muhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- ME 111 Engineering Drawing: Geometric Construction-IDocument53 pagesME 111 Engineering Drawing: Geometric Construction-IAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Unit D Geometric Construction PowerpointDocument34 pagesUnit D Geometric Construction PowerpointShiela Fherl S. BudionganNo ratings yet
- CIT GE8152 Engineering Graphics MCQ - UNIT 1Document53 pagesCIT GE8152 Engineering Graphics MCQ - UNIT 1Bala NandaNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 10 Chapter 11 Constructions SolutionsDocument9 pagesRD Sharma Class 10 Chapter 11 Constructions SolutionsAbhiNo ratings yet
- ConstructionsDocument11 pagesConstructionsSripriyan DandayuthapaniNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 1Document18 pagesGeometric Construction 1aryanNo ratings yet
- 004.00 Geometric ConstructionDocument34 pages004.00 Geometric ConstructionTeboho Clement MoahloliNo ratings yet
- Construction of Polygons - Summary NotesDocument6 pagesConstruction of Polygons - Summary Notesdankandie2No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 ContructionsDocument25 pagesChapter 17 ContructionsNasir SohailNo ratings yet
- Geometric ConstructionDocument60 pagesGeometric ConstructionKim Kenneth AsiaNo ratings yet
- Construction of Geometrical FiguresDocument3 pagesConstruction of Geometrical Figuresjoseph42No ratings yet
- Geometrical Constructions Ppt2Document18 pagesGeometrical Constructions Ppt2coolba442No ratings yet
- Lecture 8.1 Geometric ConstructionDocument26 pagesLecture 8.1 Geometric ConstructionIriama RobertNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 2Document84 pagesGeometric Construction 2juncos0729100% (1)
- Lecture 5Document4 pagesLecture 5abdul raoufNo ratings yet
- KIL1004 Lecture 2Document51 pagesKIL1004 Lecture 2Esfa AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Practical GeometryDocument38 pagesChapter 14 Practical GeometryVARUNI 3484No ratings yet
- Construction PDFDocument6 pagesConstruction PDFSahasra SagiNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 Engineering Curves and Theory of ProjectionsDocument34 pagesLecture4 Engineering Curves and Theory of ProjectionsShahebaz WandrickNo ratings yet
- Geometric ConstructionDocument30 pagesGeometric ConstructionHarshikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 - Geometric Construction PDFDocument24 pagesChapter1 - Geometric Construction PDFAli SabbahNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering DrawingDocument4 pagesBasic Engineering DrawingAldrean TinayaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Geometric ConstructionsDocument26 pagesLecture 3 - Geometric Constructionsjmensah67No ratings yet
- Access NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpDocument5 pagesAccess NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpKamjith PadinjareveeduNo ratings yet
- Access NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpDocument5 pagesAccess NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpKamjith PadinjareveeduNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 1Document78 pagesGeometric Construction 1juncos0729No ratings yet
- Solution:: Long Answer Type Questions (4 Marks)Document25 pagesSolution:: Long Answer Type Questions (4 Marks)rai venugopalNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument5 pagesConstructionjaga.45673No ratings yet
- Geometrical DrawingDocument31 pagesGeometrical Drawingnormanjames966No ratings yet
- Ce 100: Civil Engineering Drawing: Lecture - 2Document58 pagesCe 100: Civil Engineering Drawing: Lecture - 2Muhammad Ridwanul IslamNo ratings yet
- Math7 Q3 Week4 Abellana RoldanDocument15 pagesMath7 Q3 Week4 Abellana RoldanJoshua Meir DumandanNo ratings yet
- ConstructionsDocument9 pagesConstructionsthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Ellipse ConstructionDocument5 pagesEllipse ConstructionOyedotun TundeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 ConstructionsDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Constructionsmlb_blmNo ratings yet
- JSS2 Second Term Basic Technology NoteDocument17 pagesJSS2 Second Term Basic Technology NoteJohn EgbongNo ratings yet
- INVOLUTESDocument5 pagesINVOLUTESMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Math 7 GuroformsDocument10 pagesWeek 8 Math 7 GuroformsJORDAN ONGAYONo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesFrom EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Euclid for the Use of Schools and Colleges (Illustrated)From EverandThe Elements of Euclid for the Use of Schools and Colleges (Illustrated)No ratings yet
- Gate 2020Document3 pagesGate 2020Krishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Operation Research Model Paper 5Document3 pagesOperation Research Model Paper 5Krishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Operation Research Model Paper 4Document4 pagesOperation Research Model Paper 4Krishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Operation Research Model Paper 3Document3 pagesOperation Research Model Paper 3Krishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Operation Research Model Paper 1Document3 pagesOperation Research Model Paper 1Krishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Operation Research Model Paper 2Document3 pagesOperation Research Model Paper 2Krishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- II & III B.Tech I Sem Time TablesDocument2 pagesII & III B.Tech I Sem Time TablesKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Academic Audit Checklist 1. Student ActivitiesDocument21 pagesAcademic Audit Checklist 1. Student ActivitiesKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 4Document18 pagesStrength of Materials 4Krishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- ME 314 Design of Machine Elements (3-0-0-6) : TextsDocument9 pagesME 314 Design of Machine Elements (3-0-0-6) : TextsKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- SWAYAM-NPTEL Local Chapter - Mentors ListDocument2 pagesSWAYAM-NPTEL Local Chapter - Mentors ListKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question BankKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- DMM Ii-CdsDocument5 pagesDMM Ii-CdsKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- List of JR Colleges in Bhimavaram RouteDocument3 pagesList of JR Colleges in Bhimavaram RouteKrishna Murthy100% (1)
- Crre Wise SRKRDocument20 pagesCrre Wise SRKRKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- MRR GA Submission DetailsDocument2 pagesMRR GA Submission DetailsKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Process Parameters For Optimal Material Removal Rate Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) TechniqueDocument7 pagesPrediction of Process Parameters For Optimal Material Removal Rate Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) TechniqueKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Session Unit Date Topic: Stress Strain RelationsDocument3 pagesSession Unit Date Topic: Stress Strain RelationsKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Gears Selected QuestionsDocument1 pageGears Selected QuestionsKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Ductile To Brittle TransitionDocument1 pageDuctile To Brittle TransitionKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet