Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I) : (Gate 1987: 2 Marks)
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I) : (Gate 1987: 2 Marks)
Uploaded by
Siva GuruOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I) : (Gate 1987: 2 Marks)
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I) : (Gate 1987: 2 Marks)
Uploaded by
Siva GuruCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
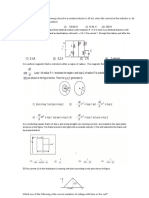
1. A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across 1 mH ideal inductor. The current
through the inductor is a . wave of peak amplitude.
-1 1V 0 0.5 t (m sec) 1
[Gate 1987: 2 Marks]
0.5 1.5 1 t m sec 1V
Ans. The current through the inductor is = . The integration of a square wave is
a triangular wave so the current through the inductor is a triangular wave of 1 volt peak
amplitude. Slope of triangular wave is 2
2. Two 2H inductance coils are connected in series and are also magnetically coupled to each
other the coefficient of coupling being 0.1. The total inductance of the combination can be
(a) 0.4 H
(b) 3.2 H
(c) 4.0 H
(d) 4.4 H
M L1 L2 2H 2H
Ans. (d)
The equivalent inductance = +
= + .
= = .
= . , .
3. The current i4 in the circuit of Figure is equal to
i1 = 5A i2 = 3A i4 = ? i3 = 4A i0 = 7A I
(a) 12 A
(b) -12 A
(c) 4 A
(d) None of these
[Gate 1997: 1 Mark]
Ans. (b)
= +
=
=
You might also like
- Mastering Physics HW11Document18 pagesMastering Physics HW11siow26100% (1)
- Square Waveform 68686Document3 pagesSquare Waveform 68686Siva GuruNo ratings yet
- Topper Sample Paper I Class XII-Physics Solutions: H H P MKDocument8 pagesTopper Sample Paper I Class XII-Physics Solutions: H H P MKGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 3Document8 pagesPhysics Test 3Arulkumar MuthuramalingamNo ratings yet
- Gate 1998 556856Document3 pagesGate 1998 556856Siva GuruNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document10 pagesUnit 3Rajaganapathi RajappanNo ratings yet
- (Gate 2000: 2 Marks) Apply KVLDocument3 pages(Gate 2000: 2 Marks) Apply KVLSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 1 (Planar Optical Waveguides) : PYL-791 (Fiber Optics), Ist Semester 2020-2021Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet - 1 (Planar Optical Waveguides) : PYL-791 (Fiber Optics), Ist Semester 2020-2021deepanshuNo ratings yet
- 50Q - EM WavesDocument4 pages50Q - EM WavesNaman MahawarNo ratings yet
- Inductor and InductanceDocument2 pagesInductor and InductanceSmurf TanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Assignment Ec: 5.time Varying Fields & Electro-Magnetic WavesDocument5 pagesElectromagnetics Assignment Ec: 5.time Varying Fields & Electro-Magnetic WavesudayNo ratings yet
- NPCIL Sample Question PaperDocument22 pagesNPCIL Sample Question Paperreky_georgeNo ratings yet
- Waves&Optics Assignment PDFDocument4 pagesWaves&Optics Assignment PDFTanisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sonometer ManualDocument4 pagesSonometer Manualfreesia.09876No ratings yet
- PHY12 Report 4Document8 pagesPHY12 Report 4Paul JavenNo ratings yet
- Advanced Physics ReviewDocument3 pagesAdvanced Physics ReviewalNo ratings yet
- Group Group Group Diane Phys 121A Lab Professor Towfik Lab 223: Faraday's LawDocument4 pagesGroup Group Group Diane Phys 121A Lab Professor Towfik Lab 223: Faraday's LawHillary AvecillasNo ratings yet
- Quantum ExerciseDocument2 pagesQuantum ExercisebigevilNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering - Class 2Document24 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering - Class 2kenze bijuNo ratings yet
- Electronics Week 8 AddDocument14 pagesElectronics Week 8 AddJansen YarteNo ratings yet
- Electronics Week 8 AddDocument14 pagesElectronics Week 8 AddJansen YarteNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument21 pagesInductorsSamuel Matthew AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- E6 Questions-2Document7 pagesE6 Questions-2Raajvir DeoraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Physics New SyllabusDocument14 pagesUnit 2 Physics New SyllabusKasshaf AhmadNo ratings yet
- Examples of Uniform EM Plane WavesDocument26 pagesExamples of Uniform EM Plane WavesMehmar AsadNo ratings yet
- Sine WavesDocument2 pagesSine WavesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves in Bounded Open Media: Cristian VillegasDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic Waves in Bounded Open Media: Cristian VillegasCristian VillegasNo ratings yet
- 2013 CBSE XIIScience 4 1 SET1 SectioncDocument9 pages2013 CBSE XIIScience 4 1 SET1 SectioncShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Paper 1Document55 pagesJee Main Paper 1venishettisaicharanNo ratings yet
- Topper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70Document14 pagesTopper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70coolspanky_227053No ratings yet
- Question 1057518Document5 pagesQuestion 1057518priyanshu339.aNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Materials Assignment HelpDocument19 pagesMagnetic Materials Assignment HelpEdu Assignment Help100% (1)
- ENGR367 Inductance)Document25 pagesENGR367 Inductance)Ras MasNo ratings yet
- 5 Sets Model Questions of PhysicsDocument27 pages5 Sets Model Questions of Physicsdast DonNo ratings yet
- R b (both ρDocument9 pagesR b (both ρCyrus JiaNo ratings yet
- EE ProblemsDocument33 pagesEE ProblemsSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Taller Física Eléctrica MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument3 pagesTaller Física Eléctrica MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionSergio Cuellar0% (1)
- AIIMS Full Paper 2007Document33 pagesAIIMS Full Paper 2007Sombir Ahlawat100% (1)
- Physics Model Paper XIIDocument4 pagesPhysics Model Paper XIIKamal KishoreNo ratings yet
- 1973 Chapt2ProblemsDocument4 pages1973 Chapt2ProblemsdazzlingstarlightNo ratings yet
- KCET Sample Paper-8 (Kcet 2013 Physics Paper)Document8 pagesKCET Sample Paper-8 (Kcet 2013 Physics Paper)Firdosh Khan0% (1)
- UG Physics PH1101-wave-3Document21 pagesUG Physics PH1101-wave-3negi.ya.12No ratings yet
- Screening Test Repeaters 2025 Sample QuestionsDocument27 pagesScreening Test Repeaters 2025 Sample QuestionsAmina sabu06No ratings yet
- ELE101/102 Dept of E&E, MIT Manipal 1Document9 pagesELE101/102 Dept of E&E, MIT Manipal 1Faraz HaiderNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Electromagnetic Waves Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFDocument9 pagesJEE Main Electromagnetic Waves Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFTarun Krishna ManivannanNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 - Electrodynamics: Physics 201 NameDocument2 pagesExam 3 - Electrodynamics: Physics 201 Namecherinet SNo ratings yet
- Det1013 - Electrical Technology: Inductors & InductanceDocument45 pagesDet1013 - Electrical Technology: Inductors & InductanceSuhaila SharifNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Unit 2BDocument2 pagesProblem Set Unit 2BKool PrashantNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre-Board I 2022-23Document6 pagesPhysics Pre-Board I 2022-23Ayushi KayalNo ratings yet
- 10 InductanceDocument16 pages10 InductanceAde Nur HidayatNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current: Question BankDocument8 pagesUnit 4: Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Free VibrationDocument5 pagesFree VibrationLokesh DandgavalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 8 Melde's Tuning ForkDocument7 pagesLab Report 8 Melde's Tuning ForkazarmechNo ratings yet
- Ece 3323 Experiment 1Document11 pagesEce 3323 Experiment 1TANQUERO_WW20% (1)
- EEN 330 Electromagnetics I: Dr. M. Bou SanayehDocument32 pagesEEN 330 Electromagnetics I: Dr. M. Bou SanayehjulioNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Spring 2017Document2 pagesAssignment2 Spring 2017Omar Bahgat100% (1)
- Electromangnetic Waves - PDFDocument9 pagesElectromangnetic Waves - PDFPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Review Paper On Development of Mobile Wireless TechnologiesDocument3 pagesReview Paper On Development of Mobile Wireless TechnologiesSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Technical Publications Book 1Document2 pagesTechnical Publications Book 1Siva GuruNo ratings yet
- Technical Publications Book 2 PDFDocument1 pageTechnical Publications Book 2 PDFSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Distinction Between Related SubjectsDocument5 pagesDistinction Between Related SubjectsSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Ece Gate Reference BooksDocument3 pagesEce Gate Reference BooksSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- It Is A Complex SaltDocument2 pagesIt Is A Complex SaltSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- India. The Day Commemorates The Return of Mahatma Gandhi From South Africa in Bombay On 9 January 1915Document3 pagesIndia. The Day Commemorates The Return of Mahatma Gandhi From South Africa in Bombay On 9 January 1915Siva GuruNo ratings yet
- TitlesDocument2 pagesTitlesSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission 52353Document5 pagesData Transmission 52353Siva GuruNo ratings yet
- The Emic ApproachDocument3 pagesThe Emic ApproachSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Seismic Waves (Seismicity) : General Principles of Volcano SeismologyDocument6 pagesSeismic Waves (Seismicity) : General Principles of Volcano SeismologySiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Robotic Hand: 1robotic Hand 2types 3notable Robotic Arms 4see Also 5references 6external LinksDocument3 pagesRobotic Hand: 1robotic Hand 2types 3notable Robotic Arms 4see Also 5references 6external LinksSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- PuranasDocument2 pagesPuranasSiva Guru100% (3)
- Manipulator Are Connected by JointsDocument3 pagesManipulator Are Connected by JointsSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Robo 458965874Document3 pagesRobo 458965874Siva GuruNo ratings yet