Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathcad - 22 - 7-Water #F7A5A
Mathcad - 22 - 7-Water #F7A5A
Uploaded by
cymyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Thermofluids Formula SheetDocument16 pagesThermofluids Formula Sheetpaul_evos100% (6)
- DQ13Document4 pagesDQ13Jan Adrian Galang FranciscoNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document11 pagesHW 1Kenneth Mendoza SorianoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Capa LimiteDocument16 pagesEjercicios Capa LimitedanteunmsmNo ratings yet
- Problems 0Document15 pagesProblems 0Pasha Tan100% (1)
- Convection SummaryDocument10 pagesConvection SummarycacafaruqNo ratings yet
- 84 Picon NunezDocument6 pages84 Picon Nunez1940LaSalleNo ratings yet
- Fixed Bed Reactor, Modelling&Optimal DesignDocument74 pagesFixed Bed Reactor, Modelling&Optimal DesignRana Uzair100% (1)
- Applications of First Order DEs-1 PDFDocument49 pagesApplications of First Order DEs-1 PDFHithesh U Warrier100% (1)
- P (Atm.) : Solution of Problem No. 3 Compression and Expansion of A Two Gases SystemDocument4 pagesP (Atm.) : Solution of Problem No. 3 Compression and Expansion of A Two Gases SystemPopovici DraganNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of EthanolDocument46 pagesManufacture of EthanolRam DevNo ratings yet
- Midterm 4Document5 pagesMidterm 4Yedra GadeaNo ratings yet
- 2010-Ch 5..456 PDFDocument32 pages2010-Ch 5..456 PDFAthulNo ratings yet
- PS9Soln 2014Document13 pagesPS9Soln 2014Eddz Del Rosario RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document33 pagesChap 2AbhimanNo ratings yet
- 7 1. Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument9 pages7 1. Vapor Liquid Equilibriumwaseemkhan49No ratings yet
- Discharge From VesselsDocument6 pagesDischarge From VesselsMr ChuNo ratings yet
- ρ = ρ = constant: One-Dimensional, One-Phase Reservoir SimulationDocument10 pagesρ = ρ = constant: One-Dimensional, One-Phase Reservoir SimulationAmir MNo ratings yet
- V2 2023 Class Works Correction D ElzoDocument8 pagesV2 2023 Class Works Correction D ElzobennytenezeuNo ratings yet
- m c θ c θ c c: n vi liDocument4 pagesm c θ c θ c c: n vi liVanessa SimNo ratings yet
- Mech 221 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 3: (Fall 06/07)Document28 pagesMech 221 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 3: (Fall 06/07)kamihNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SolnDocument7 pagesFinal Exam SolnrickcjmacNo ratings yet
- VLEDocument20 pagesVLEIjal Jamin50% (2)
- 0 23122019 Always MindDocument4 pages0 23122019 Always MindM VenkatNo ratings yet
- 07-Absorption For HAP and VOCcontrolDocument118 pages07-Absorption For HAP and VOCcontrolTakeshi Tanohuye TanohuyeNo ratings yet
- Flow Around Immersed ObjectsDocument23 pagesFlow Around Immersed Objectsninju1No ratings yet
- P2Document55 pagesP2Abdulla BaderNo ratings yet
- Ques Ans After Lecture 7Document6 pagesQues Ans After Lecture 7UsamaIjazNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech. EFM Assignment 2 (Answers)Document4 pagesFluid Mech. EFM Assignment 2 (Answers)Tik HonNo ratings yet
- Dispersion: M U Lti Ple-Bed Reactor For Am Mon Ia SynthesisDocument11 pagesDispersion: M U Lti Ple-Bed Reactor For Am Mon Ia SynthesisCesar ZacNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Engineering: Fluid FlowDocument32 pagesPipeline Engineering: Fluid Flowzahidwahla1No ratings yet
- 1 The Diffusion Equation: 1.1 One-Dimensional CaseDocument8 pages1 The Diffusion Equation: 1.1 One-Dimensional CaseDiego A. Martínez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Azdoc - Tips White Fluid Mechanics 5e Solutions Fluidmechwhite5ech02part2bDocument10 pagesAzdoc - Tips White Fluid Mechanics 5e Solutions Fluidmechwhite5ech02part2bMohit KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Final - 4th - Assignment - Shallow Foundation Design1222Document47 pagesFinal - 4th - Assignment - Shallow Foundation Design1222Refisa JiruNo ratings yet
- HW 3 SolDocument10 pagesHW 3 SolMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Absorption (Part 1)Document41 pagesChapter 5 - Absorption (Part 1)La Casa Jordan100% (1)
- Composition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeDocument30 pagesComposition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeNgoc Le LeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Convection: Flow and Thermal ConsiderationsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Convection: Flow and Thermal ConsiderationsChris MustacchioNo ratings yet
- Duct Designing: Laminar and Turbulent Flow in TubesDocument18 pagesDuct Designing: Laminar and Turbulent Flow in TubesMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document36 pagesChapter 4siva sachaphibulkijNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Equipment DesignDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer Equipment DesignBhawani Pratap Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ChemistryDocument48 pagesChapter 7 ChemistryRubhan kumarNo ratings yet
- ME3122 Handbook of Heat Transfer Equations 2014Document22 pagesME3122 Handbook of Heat Transfer Equations 2014Nian Wee WuNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium-Constant NOTESDocument5 pagesEquilibrium-Constant NOTESAlex Jethro TigoyNo ratings yet
- ENME 332, Spring 2013 Transfer Processes: Instructors: Reinhard Radermacher & Bao YangDocument18 pagesENME 332, Spring 2013 Transfer Processes: Instructors: Reinhard Radermacher & Bao YangZain BaqarNo ratings yet
- Final Mass Transfer - I All Practical WriteupsDocument36 pagesFinal Mass Transfer - I All Practical WriteupsvkpaithankarNo ratings yet
- Cálculo de PresiónDocument4 pagesCálculo de PresiónBellahadid GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger: - DesigningDocument18 pagesShell & Tube Heat Exchanger: - DesigningKusmakar100% (1)
- Axial Dispersion ModelDocument2 pagesAxial Dispersion ModelDigvijay Singh BhadouriaNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument4 pagesPumpJulian TremontNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Chapter One: What Is The Fluid ???Document10 pagesChapter One Chapter One: What Is The Fluid ???AhmedYasharNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering MCQs SolvedDocument20 pagesChemical Engineering MCQs Solvedashish24294100% (1)
- CHE654 2012 Homework5 SolutionsDocument37 pagesCHE654 2012 Homework5 Solutionsmadithak100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change: Follow-Up ProblemsDocument30 pagesChapter 6 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change: Follow-Up ProblemsLarsen Atega AlexanderssonNo ratings yet
- Absorption 1Document41 pagesAbsorption 1Nabayan SahaNo ratings yet
- Bell Delaware Math Cad ExampleDocument8 pagesBell Delaware Math Cad ExampleMohammed A IsaNo ratings yet
- Installed Flow CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesInstalled Flow CharacteristicscymyNo ratings yet
- Counter Current Heat Exchanger CarnahanDocument4 pagesCounter Current Heat Exchanger CarnahancymyNo ratings yet
- Example 6.16aDocument1 pageExample 6.16acymyNo ratings yet
- Nox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetDocument13 pagesNox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Live Solution Tank ExampleDocument6 pagesLive Solution Tank ExamplecymyNo ratings yet
- Combustion Equilibrium Calculations: A1 A2 A3 A4Document6 pagesCombustion Equilibrium Calculations: A1 A2 A3 A4cymyNo ratings yet
- Mass Flowrates and Weight %: Styrene FlowsheetDocument1 pageMass Flowrates and Weight %: Styrene FlowsheetcymyNo ratings yet
- 0.25 Reaction N + 3H NH: Ammonia Material Balance Using Gauss Jordan Elimination and Newton RaphsonDocument1 page0.25 Reaction N + 3H NH: Ammonia Material Balance Using Gauss Jordan Elimination and Newton RaphsoncymyNo ratings yet
- Linear Data Reconciliation: Narasimhan and Jordache (2000)Document1 pageLinear Data Reconciliation: Narasimhan and Jordache (2000)cymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 10.9bDocument2 pagesProblem 10.9bcymyNo ratings yet
- Air Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)Document6 pagesAir Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)cymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 8.6 L (160.67F)Document3 pagesProblem 8.6 L (160.67F)cymyNo ratings yet
- Air Standard Cycle - Off Design 2: W - AC (KJ/S)Document8 pagesAir Standard Cycle - Off Design 2: W - AC (KJ/S)cymyNo ratings yet
- SI - Real Gas - Design: VariablesDocument9 pagesSI - Real Gas - Design: VariablescymyNo ratings yet
- Example 5.6aDocument1 pageExample 5.6acymyNo ratings yet
- X (0) X (1) X (2) RHS X X X: Newton-Raphson Method All VBA CodeDocument1 pageX (0) X (1) X (2) RHS X X X: Newton-Raphson Method All VBA CodecymyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Unit Operations: Linear Data ReconciliationDocument1 pageMultiple Unit Operations: Linear Data ReconciliationcymyNo ratings yet
- Feed Reactor in Reactor Out Product Vapor Out Recycle Purge RHSDocument1 pageFeed Reactor in Reactor Out Product Vapor Out Recycle Purge RHScymyNo ratings yet
- Air Standard Cycle With HRSG Supplemental Firing: Overall Energy Balance MethodDocument6 pagesAir Standard Cycle With HRSG Supplemental Firing: Overall Energy Balance MethodcymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.5dDocument16 pagesProblem 5.5dcymyNo ratings yet
- Knopf: Ammonia Process FlowsheetDocument1 pageKnopf: Ammonia Process FlowsheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Example 3.10Document1 pageExample 3.10cymyNo ratings yet
- CGAM Problem - Ideal Gas: Variables PhysicalDocument6 pagesCGAM Problem - Ideal Gas: Variables PhysicalcymyNo ratings yet
- Turbine Combustion Kinetics PFR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetDocument14 pagesTurbine Combustion Kinetics PFR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.6a Ammonia Process - Energy Balance For Mixer Into R2Document1 pageProblem 5.6a Ammonia Process - Energy Balance For Mixer Into R2cymyNo ratings yet
- Turbine Combustion Kinetics PSR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetDocument14 pagesTurbine Combustion Kinetics PSR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Cvode: Initial y ComponentsDocument1 pageCvode: Initial y ComponentscymyNo ratings yet
- Trigger 0 (Either 0 To Reset or 1 To Iterate) Iterations 0.00000000 Reaction Iteration Count X 10Document1 pageTrigger 0 (Either 0 To Reset or 1 To Iterate) Iterations 0.00000000 Reaction Iteration Count X 10cymyNo ratings yet
Mathcad - 22 - 7-Water #F7A5A
Mathcad - 22 - 7-Water #F7A5A
Uploaded by
cymyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathcad - 22 - 7-Water #F7A5A
Mathcad - 22 - 7-Water #F7A5A
Uploaded by
cymyCopyright:
Available Formats
Water Gas Shift Reaction: Rates and Composition Profiles
Consider the water gas shift reaction:
CO + H2O = CO2 + H2
( 1)
( 2)
( 3)
( 4)
This reaction occurs in a porous catalyst under the following conditions:
temperature and pressure
composition and partial
pressures of bulk gas
T := 672 K
p := 2.5 10
y1o := 0.10
p1o := y1o p
y2o := 0.60
p2o := y2o p
y3o := 0.08
p3o := y3o p
y4o := 0.22
p4o := y4o p
Under these conditions, the equilibrium pressure of CO is:
p1e := 1.398 10
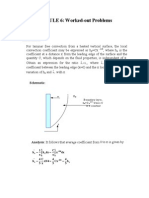
The catalyst consists of cylinders with a height and diameter of:
H := 0.014
D := 0.014
:= 0.4
The catalyst has a porosity
You may regard the catalyst as a slab, with a thickness 2 given by:
volume :=
:=
4
volume
D H
area := D H + 2
= 2.333 10
area
the original catalyst with no hole
The rate of the reaction can be expressed in terms of the partial pressure of the limiting
reactant (CO):
75
r :=
p1e
( p1e p1 )
r = k1 ( p1e p1 )
or
k1 :=
75
mol ( CO )
p1e
m ( catalyst)
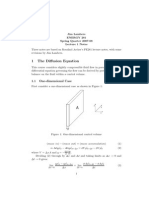
Diffusion into the slab is governed by:
dp1
= 1eff N1
dz
1eff := 8.163 10
A balance over a layer with thickness dz yields:
dz
( p1 = 1eff )
or (see Figure 22.13)
2
dZ
( P = K P)
K :=
k1 1eff
The solution to this equation is:
1
B :=
1+
(
exp (
)
K)
exp K
A := 1 B
A = 2.494 10
B=1
11
Q ( Z) := A exp Z K + B exp Z K
Here, only the second term is important. We plot this profile below
i := 0 .. 20
Zi :=
i
20
( )
Q Zi 0.5
0.5
Zi
We see that the driving force for the reaction is practically zero at Z = 0.4, or at one fifth of
the slab thickness.
The effectiveness factor of the catalyst is the ratio of the actual conversion to that when there
is no mass transfer resistance (and the driving force Q = 1 throughout the catalyst). It is given
by:
E :=
Q ( Z) dZ
E = 0.082
To calculate the flux through the catalyst surface, we need the pressure gradient at Z = 0:
Z := 0
p1' :=
p1o p1e d
Q ( Z)
dZ
N1 :=
1eff
p1'
N1 = 0.061
mol
2
m s
The effectiveness of the catalyst is not very good. You are to investigate what
happens if we use the same cylindrical catalyst, but now with a hole of one half of
the diameter along the axis (see Fig. 22.2).
You might also like
- Thermofluids Formula SheetDocument16 pagesThermofluids Formula Sheetpaul_evos100% (6)
- DQ13Document4 pagesDQ13Jan Adrian Galang FranciscoNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document11 pagesHW 1Kenneth Mendoza SorianoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Capa LimiteDocument16 pagesEjercicios Capa LimitedanteunmsmNo ratings yet
- Problems 0Document15 pagesProblems 0Pasha Tan100% (1)
- Convection SummaryDocument10 pagesConvection SummarycacafaruqNo ratings yet
- 84 Picon NunezDocument6 pages84 Picon Nunez1940LaSalleNo ratings yet
- Fixed Bed Reactor, Modelling&Optimal DesignDocument74 pagesFixed Bed Reactor, Modelling&Optimal DesignRana Uzair100% (1)
- Applications of First Order DEs-1 PDFDocument49 pagesApplications of First Order DEs-1 PDFHithesh U Warrier100% (1)
- P (Atm.) : Solution of Problem No. 3 Compression and Expansion of A Two Gases SystemDocument4 pagesP (Atm.) : Solution of Problem No. 3 Compression and Expansion of A Two Gases SystemPopovici DraganNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of EthanolDocument46 pagesManufacture of EthanolRam DevNo ratings yet
- Midterm 4Document5 pagesMidterm 4Yedra GadeaNo ratings yet
- 2010-Ch 5..456 PDFDocument32 pages2010-Ch 5..456 PDFAthulNo ratings yet
- PS9Soln 2014Document13 pagesPS9Soln 2014Eddz Del Rosario RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document33 pagesChap 2AbhimanNo ratings yet
- 7 1. Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument9 pages7 1. Vapor Liquid Equilibriumwaseemkhan49No ratings yet
- Discharge From VesselsDocument6 pagesDischarge From VesselsMr ChuNo ratings yet
- ρ = ρ = constant: One-Dimensional, One-Phase Reservoir SimulationDocument10 pagesρ = ρ = constant: One-Dimensional, One-Phase Reservoir SimulationAmir MNo ratings yet
- V2 2023 Class Works Correction D ElzoDocument8 pagesV2 2023 Class Works Correction D ElzobennytenezeuNo ratings yet
- m c θ c θ c c: n vi liDocument4 pagesm c θ c θ c c: n vi liVanessa SimNo ratings yet
- Mech 221 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 3: (Fall 06/07)Document28 pagesMech 221 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 3: (Fall 06/07)kamihNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SolnDocument7 pagesFinal Exam SolnrickcjmacNo ratings yet
- VLEDocument20 pagesVLEIjal Jamin50% (2)
- 0 23122019 Always MindDocument4 pages0 23122019 Always MindM VenkatNo ratings yet
- 07-Absorption For HAP and VOCcontrolDocument118 pages07-Absorption For HAP and VOCcontrolTakeshi Tanohuye TanohuyeNo ratings yet
- Flow Around Immersed ObjectsDocument23 pagesFlow Around Immersed Objectsninju1No ratings yet
- P2Document55 pagesP2Abdulla BaderNo ratings yet
- Ques Ans After Lecture 7Document6 pagesQues Ans After Lecture 7UsamaIjazNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech. EFM Assignment 2 (Answers)Document4 pagesFluid Mech. EFM Assignment 2 (Answers)Tik HonNo ratings yet
- Dispersion: M U Lti Ple-Bed Reactor For Am Mon Ia SynthesisDocument11 pagesDispersion: M U Lti Ple-Bed Reactor For Am Mon Ia SynthesisCesar ZacNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Engineering: Fluid FlowDocument32 pagesPipeline Engineering: Fluid Flowzahidwahla1No ratings yet
- 1 The Diffusion Equation: 1.1 One-Dimensional CaseDocument8 pages1 The Diffusion Equation: 1.1 One-Dimensional CaseDiego A. Martínez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Azdoc - Tips White Fluid Mechanics 5e Solutions Fluidmechwhite5ech02part2bDocument10 pagesAzdoc - Tips White Fluid Mechanics 5e Solutions Fluidmechwhite5ech02part2bMohit KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Final - 4th - Assignment - Shallow Foundation Design1222Document47 pagesFinal - 4th - Assignment - Shallow Foundation Design1222Refisa JiruNo ratings yet
- HW 3 SolDocument10 pagesHW 3 SolMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Absorption (Part 1)Document41 pagesChapter 5 - Absorption (Part 1)La Casa Jordan100% (1)
- Composition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeDocument30 pagesComposition of The Atmosphere Gas Solubility Gas Exchange Fluxes Effect of Wind Global CO Fluxes by Gas ExchangeNgoc Le LeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Convection: Flow and Thermal ConsiderationsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Convection: Flow and Thermal ConsiderationsChris MustacchioNo ratings yet
- Duct Designing: Laminar and Turbulent Flow in TubesDocument18 pagesDuct Designing: Laminar and Turbulent Flow in TubesMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document36 pagesChapter 4siva sachaphibulkijNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Equipment DesignDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer Equipment DesignBhawani Pratap Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ChemistryDocument48 pagesChapter 7 ChemistryRubhan kumarNo ratings yet
- ME3122 Handbook of Heat Transfer Equations 2014Document22 pagesME3122 Handbook of Heat Transfer Equations 2014Nian Wee WuNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium-Constant NOTESDocument5 pagesEquilibrium-Constant NOTESAlex Jethro TigoyNo ratings yet
- ENME 332, Spring 2013 Transfer Processes: Instructors: Reinhard Radermacher & Bao YangDocument18 pagesENME 332, Spring 2013 Transfer Processes: Instructors: Reinhard Radermacher & Bao YangZain BaqarNo ratings yet
- Final Mass Transfer - I All Practical WriteupsDocument36 pagesFinal Mass Transfer - I All Practical WriteupsvkpaithankarNo ratings yet
- Cálculo de PresiónDocument4 pagesCálculo de PresiónBellahadid GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger: - DesigningDocument18 pagesShell & Tube Heat Exchanger: - DesigningKusmakar100% (1)
- Axial Dispersion ModelDocument2 pagesAxial Dispersion ModelDigvijay Singh BhadouriaNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument4 pagesPumpJulian TremontNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Chapter One: What Is The Fluid ???Document10 pagesChapter One Chapter One: What Is The Fluid ???AhmedYasharNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering MCQs SolvedDocument20 pagesChemical Engineering MCQs Solvedashish24294100% (1)
- CHE654 2012 Homework5 SolutionsDocument37 pagesCHE654 2012 Homework5 Solutionsmadithak100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change: Follow-Up ProblemsDocument30 pagesChapter 6 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change: Follow-Up ProblemsLarsen Atega AlexanderssonNo ratings yet
- Absorption 1Document41 pagesAbsorption 1Nabayan SahaNo ratings yet
- Bell Delaware Math Cad ExampleDocument8 pagesBell Delaware Math Cad ExampleMohammed A IsaNo ratings yet
- Installed Flow CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesInstalled Flow CharacteristicscymyNo ratings yet
- Counter Current Heat Exchanger CarnahanDocument4 pagesCounter Current Heat Exchanger CarnahancymyNo ratings yet
- Example 6.16aDocument1 pageExample 6.16acymyNo ratings yet
- Nox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetDocument13 pagesNox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Live Solution Tank ExampleDocument6 pagesLive Solution Tank ExamplecymyNo ratings yet
- Combustion Equilibrium Calculations: A1 A2 A3 A4Document6 pagesCombustion Equilibrium Calculations: A1 A2 A3 A4cymyNo ratings yet
- Mass Flowrates and Weight %: Styrene FlowsheetDocument1 pageMass Flowrates and Weight %: Styrene FlowsheetcymyNo ratings yet
- 0.25 Reaction N + 3H NH: Ammonia Material Balance Using Gauss Jordan Elimination and Newton RaphsonDocument1 page0.25 Reaction N + 3H NH: Ammonia Material Balance Using Gauss Jordan Elimination and Newton RaphsoncymyNo ratings yet
- Linear Data Reconciliation: Narasimhan and Jordache (2000)Document1 pageLinear Data Reconciliation: Narasimhan and Jordache (2000)cymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 10.9bDocument2 pagesProblem 10.9bcymyNo ratings yet
- Air Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)Document6 pagesAir Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)cymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 8.6 L (160.67F)Document3 pagesProblem 8.6 L (160.67F)cymyNo ratings yet
- Air Standard Cycle - Off Design 2: W - AC (KJ/S)Document8 pagesAir Standard Cycle - Off Design 2: W - AC (KJ/S)cymyNo ratings yet
- SI - Real Gas - Design: VariablesDocument9 pagesSI - Real Gas - Design: VariablescymyNo ratings yet
- Example 5.6aDocument1 pageExample 5.6acymyNo ratings yet
- X (0) X (1) X (2) RHS X X X: Newton-Raphson Method All VBA CodeDocument1 pageX (0) X (1) X (2) RHS X X X: Newton-Raphson Method All VBA CodecymyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Unit Operations: Linear Data ReconciliationDocument1 pageMultiple Unit Operations: Linear Data ReconciliationcymyNo ratings yet
- Feed Reactor in Reactor Out Product Vapor Out Recycle Purge RHSDocument1 pageFeed Reactor in Reactor Out Product Vapor Out Recycle Purge RHScymyNo ratings yet
- Air Standard Cycle With HRSG Supplemental Firing: Overall Energy Balance MethodDocument6 pagesAir Standard Cycle With HRSG Supplemental Firing: Overall Energy Balance MethodcymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.5dDocument16 pagesProblem 5.5dcymyNo ratings yet
- Knopf: Ammonia Process FlowsheetDocument1 pageKnopf: Ammonia Process FlowsheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Example 3.10Document1 pageExample 3.10cymyNo ratings yet
- CGAM Problem - Ideal Gas: Variables PhysicalDocument6 pagesCGAM Problem - Ideal Gas: Variables PhysicalcymyNo ratings yet
- Turbine Combustion Kinetics PFR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetDocument14 pagesTurbine Combustion Kinetics PFR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.6a Ammonia Process - Energy Balance For Mixer Into R2Document1 pageProblem 5.6a Ammonia Process - Energy Balance For Mixer Into R2cymyNo ratings yet
- Turbine Combustion Kinetics PSR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetDocument14 pagesTurbine Combustion Kinetics PSR-1 : CVODE Starts at Line 100 On EXCEL SheetcymyNo ratings yet
- Cvode: Initial y ComponentsDocument1 pageCvode: Initial y ComponentscymyNo ratings yet
- Trigger 0 (Either 0 To Reset or 1 To Iterate) Iterations 0.00000000 Reaction Iteration Count X 10Document1 pageTrigger 0 (Either 0 To Reset or 1 To Iterate) Iterations 0.00000000 Reaction Iteration Count X 10cymyNo ratings yet