Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsDerm 4
Derm 4
Uploaded by
JUSASBThis document discusses several diagnostic skin pathology terms including: Schaumann body, shadow cells, Verocay body, spongiform pustule of Kogoj, spongiosis, squamotization, squamous eddies, and storiform. It also discusses skin anatomy and staining techniques. Several figures are included to illustrate examples of these terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Metachromasia Pagetoid Scatter: Figure 1-26Document1 pageMetachromasia Pagetoid Scatter: Figure 1-26JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Document89 pagesKuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Oman SetiyantoNo ratings yet
- 58 60Document28 pages58 60Romina ReidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye Opthalmology LectureDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Eye Opthalmology LectureJaikrit SinghNo ratings yet
- Uvea and Sclera.Document30 pagesUvea and Sclera.Nur Wajihah Bt KhalipsaNo ratings yet
- Pathos (Suffering) Logos: Pathology Is The Study of The Causes and Effects ofDocument70 pagesPathos (Suffering) Logos: Pathology Is The Study of The Causes and Effects ofahmed mokhtar100% (1)
- Histo Paper 2Document117 pagesHisto Paper 2SATVIK RAMNo ratings yet
- Tissues in AnimalsDocument72 pagesTissues in AnimalsyvetteNo ratings yet
- Sweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument72 pagesSweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Daulat Ram DhakedNo ratings yet
- Hyper-/hypopigmentation Interface Koilocytes: Figure 1-7Document1 pageHyper-/hypopigmentation Interface Koilocytes: Figure 1-7JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Histologi MataDocument47 pagesKuliah Histologi MataLuna Litami100% (1)
- 14.kuliah-Histologi MataDocument35 pages14.kuliah-Histologi MataRahmat NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Injury Necrosis ApoptosisDocument43 pagesCellular Injury Necrosis ApoptosisOman SetiyantoNo ratings yet
- Dermathopathology MuluDocument87 pagesDermathopathology MuluhanalexianNo ratings yet
- Review Perubahan-Perubahan Patologi: Kuliah Pendahuluan PPDHDocument34 pagesReview Perubahan-Perubahan Patologi: Kuliah Pendahuluan PPDHDiksifableNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandDocument118 pagesSalivary GlandtdxdvnddmfNo ratings yet
- EYE Histology: Dr. OkoloDocument60 pagesEYE Histology: Dr. OkoloAbiola NerdNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.DDocument78 pagesPathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.Drush73No ratings yet
- ANATOMy 2018 SkinTissuesDocument49 pagesANATOMy 2018 SkinTissuestassiatavares.workNo ratings yet
- Cytology IN Gynecological Disorders: Pertemuan Ilmiah Regional Iapi Jateng Purwokerto, 7 September 2019Document49 pagesCytology IN Gynecological Disorders: Pertemuan Ilmiah Regional Iapi Jateng Purwokerto, 7 September 2019doc holidayNo ratings yet
- 03mata NewDocument120 pages03mata NewYuliaFitrianiNo ratings yet
- 2.malignant Tumours of Epithelial Cell Origin-2Document86 pages2.malignant Tumours of Epithelial Cell Origin-2Dinesh Kr. YadavNo ratings yet
- Block D Histology Complete Important Points.Document9 pagesBlock D Histology Complete Important Points.sarooshmahsoodNo ratings yet
- Epi IndiaDocument54 pagesEpi Indiaapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Ophthalmology-Development of EyeDocument20 pagesOphthalmology-Development of EyeRahul Kumar DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Epithelia & Glands: Dr. Madhan KumarDocument49 pagesEpithelia & Glands: Dr. Madhan KumarTan DesmondNo ratings yet
- Retina: Zarieh Dawn L. Novela Medicine 2Document50 pagesRetina: Zarieh Dawn L. Novela Medicine 2Zari NovelaNo ratings yet
- 04 EpitheliumDocument39 pages04 EpitheliumMartha Orendu Oche AttahNo ratings yet
- Basic Histology-1Document51 pagesBasic Histology-1Zechariah NggitaNo ratings yet
- Cornea Clinic Interactive Part 2Document151 pagesCornea Clinic Interactive Part 2Cojocaru Stelica100% (1)
- DR Hany Abo Alwafa - Pathology GlossaryDocument31 pagesDR Hany Abo Alwafa - Pathology GlossaryHalimatunSyadiah ARNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument82 pagesCellsK.R. LiberosisNo ratings yet
- The Eye: Evy SulistyoningrumDocument52 pagesThe Eye: Evy SulistyoningrumLeti BhieNo ratings yet
- His To PathologyDocument4 pagesHis To PathologysayerNo ratings yet
- HE YE: Evy SulistyoningrumDocument82 pagesHE YE: Evy SulistyoningrumPandu Nugroho KantaNo ratings yet
- Histo Module 2Document27 pagesHisto Module 2princesssana.337No ratings yet
- NecrosisDocument13 pagesNecrosisarun j.rNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi MataDocument70 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi MataRisalatulNo ratings yet
- Master Plan Patho!Document94 pagesMaster Plan Patho!chiarastanziola01No ratings yet
- Anat Revision SampleDocument30 pagesAnat Revision Samplesafalife11No ratings yet
- General Principle & Eye Development EZRADocument28 pagesGeneral Principle & Eye Development EZRAezradamanikNo ratings yet
- CLLS 3231 Urinalysis and Body Fluids: Microscopic Examination Formed Elements: Cellular, Casts, Bacteria and YeastDocument55 pagesCLLS 3231 Urinalysis and Body Fluids: Microscopic Examination Formed Elements: Cellular, Casts, Bacteria and Yeaststrider_sdNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - CytologyDocument3 pagesLec1 - CytologyEloisa Trina GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Pathology Images MarrowDocument21 pagesPathology Images MarrowRAJDEEP DASNo ratings yet
- Marrow High Yield Pathology Slides @docinmaykingDocument21 pagesMarrow High Yield Pathology Slides @docinmaykingprasannaipad324No ratings yet
- 5 Malig Conn Tum PDFDocument19 pages5 Malig Conn Tum PDFDrrafiullahNo ratings yet
- Glandular Cells & Benign Disorders The Uterine CervixDocument41 pagesGlandular Cells & Benign Disorders The Uterine CervixSara VinamdNo ratings yet
- Robbin'S and Cotran'S: Pathologic Basis of DiseaseDocument6 pagesRobbin'S and Cotran'S: Pathologic Basis of Diseasenge257No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture NotesDocument94 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notesbiddyusmc100% (2)
- Special Senses - I: Histology of EyeDocument25 pagesSpecial Senses - I: Histology of EyeRessam NazirNo ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument55 pagesOphthalmologyapi-19916399100% (3)
- Traktus UveaDocument90 pagesTraktus UveaAudrey Ira Yunita100% (1)
- Anatomy-Physiology Eyeball 2023Document75 pagesAnatomy-Physiology Eyeball 2023debdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- NecrosisDocument23 pagesNecrosisSaradha Pellati100% (2)
- DegenerationDocument28 pagesDegenerationdr atul jainNo ratings yet
- CATARACTDocument82 pagesCATARACTRavi KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Plates illustrating the natural and morbid changes of the human eyeFrom EverandPlates illustrating the natural and morbid changes of the human eyeNo ratings yet
- COMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesDocument5 pagesCOMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesJUSASBNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics - FactsheetDocument12 pagesAntipsychotics - FactsheetColonNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics Factsheet pg2Document1 pageAntipsychotics Factsheet pg2JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37JUSASBNo ratings yet
- FA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesDocument2 pagesFA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesJUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33JUSASBNo ratings yet
- References: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015Document1 pageReferences: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35JUSASB50% (2)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 8Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 8JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22JUSASB0% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 19Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 19JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 9Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 9JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 6Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 6JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 4Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 4JUSASBNo ratings yet
Derm 4
Derm 4
Uploaded by
JUSASB0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageThis document discusses several diagnostic skin pathology terms including: Schaumann body, shadow cells, Verocay body, spongiform pustule of Kogoj, spongiosis, squamotization, squamous eddies, and storiform. It also discusses skin anatomy and staining techniques. Several figures are included to illustrate examples of these terms.
Original Description:
Derm 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several diagnostic skin pathology terms including: Schaumann body, shadow cells, Verocay body, spongiform pustule of Kogoj, spongiosis, squamotization, squamous eddies, and storiform. It also discusses skin anatomy and staining techniques. Several figures are included to illustrate examples of these terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageDerm 4
Derm 4
Uploaded by
JUSASBThis document discusses several diagnostic skin pathology terms including: Schaumann body, shadow cells, Verocay body, spongiform pustule of Kogoj, spongiosis, squamotization, squamous eddies, and storiform. It also discusses skin anatomy and staining techniques. Several figures are included to illustrate examples of these terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Chapter
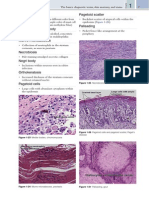
The basics: diagnostic terms, skin anatomy, and stains
Schaumann body
Vacuolar change
Laminated calcified structure seen in sarcoidosis
Formation of clear spaces within the basal layer
Shadow cells
Verocay body
Cells with barely visible outlines of nuclei
Structure composed of two nuclear palisades
enclosing pink cytoplasmic processes, seen in
schwannoma
Spongiform pustule of Kogoj
Neutrophils in the stratum spinosum,
associated with spongiosis at periphery
(typical of psoriasis)
Spongiosis
Intercellular edema in epidermis with
stretching of cellcell junctions
Squamotization (or squamatization)
Loss of cuboidal/columnar basal cells, with
deepest layer now being polyhedral, pink
squamous cells
Squamous eddies
Circular whorls of squamous cells
Storiform
Figure 1-33 Shadow cells, pilomatricoma
Cartwheel or basket-weave pattern
Figure 1-31 Reticular degeneration, variola
Figure 1-32 Russell body, rhinoscleroma
Figure 1-34 Squamous eddies, irritated seborrheic
keratosis
Figure 1-35 Verocay body, schwannoma
You might also like
- Metachromasia Pagetoid Scatter: Figure 1-26Document1 pageMetachromasia Pagetoid Scatter: Figure 1-26JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Document89 pagesKuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Oman SetiyantoNo ratings yet
- 58 60Document28 pages58 60Romina ReidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye Opthalmology LectureDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Eye Opthalmology LectureJaikrit SinghNo ratings yet
- Uvea and Sclera.Document30 pagesUvea and Sclera.Nur Wajihah Bt KhalipsaNo ratings yet
- Pathos (Suffering) Logos: Pathology Is The Study of The Causes and Effects ofDocument70 pagesPathos (Suffering) Logos: Pathology Is The Study of The Causes and Effects ofahmed mokhtar100% (1)
- Histo Paper 2Document117 pagesHisto Paper 2SATVIK RAMNo ratings yet
- Tissues in AnimalsDocument72 pagesTissues in AnimalsyvetteNo ratings yet
- Sweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument72 pagesSweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Daulat Ram DhakedNo ratings yet
- Hyper-/hypopigmentation Interface Koilocytes: Figure 1-7Document1 pageHyper-/hypopigmentation Interface Koilocytes: Figure 1-7JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Histologi MataDocument47 pagesKuliah Histologi MataLuna Litami100% (1)
- 14.kuliah-Histologi MataDocument35 pages14.kuliah-Histologi MataRahmat NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Injury Necrosis ApoptosisDocument43 pagesCellular Injury Necrosis ApoptosisOman SetiyantoNo ratings yet
- Dermathopathology MuluDocument87 pagesDermathopathology MuluhanalexianNo ratings yet
- Review Perubahan-Perubahan Patologi: Kuliah Pendahuluan PPDHDocument34 pagesReview Perubahan-Perubahan Patologi: Kuliah Pendahuluan PPDHDiksifableNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandDocument118 pagesSalivary GlandtdxdvnddmfNo ratings yet
- EYE Histology: Dr. OkoloDocument60 pagesEYE Histology: Dr. OkoloAbiola NerdNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.DDocument78 pagesPathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.Drush73No ratings yet
- ANATOMy 2018 SkinTissuesDocument49 pagesANATOMy 2018 SkinTissuestassiatavares.workNo ratings yet
- Cytology IN Gynecological Disorders: Pertemuan Ilmiah Regional Iapi Jateng Purwokerto, 7 September 2019Document49 pagesCytology IN Gynecological Disorders: Pertemuan Ilmiah Regional Iapi Jateng Purwokerto, 7 September 2019doc holidayNo ratings yet
- 03mata NewDocument120 pages03mata NewYuliaFitrianiNo ratings yet
- 2.malignant Tumours of Epithelial Cell Origin-2Document86 pages2.malignant Tumours of Epithelial Cell Origin-2Dinesh Kr. YadavNo ratings yet
- Block D Histology Complete Important Points.Document9 pagesBlock D Histology Complete Important Points.sarooshmahsoodNo ratings yet
- Epi IndiaDocument54 pagesEpi Indiaapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Ophthalmology-Development of EyeDocument20 pagesOphthalmology-Development of EyeRahul Kumar DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Epithelia & Glands: Dr. Madhan KumarDocument49 pagesEpithelia & Glands: Dr. Madhan KumarTan DesmondNo ratings yet
- Retina: Zarieh Dawn L. Novela Medicine 2Document50 pagesRetina: Zarieh Dawn L. Novela Medicine 2Zari NovelaNo ratings yet
- 04 EpitheliumDocument39 pages04 EpitheliumMartha Orendu Oche AttahNo ratings yet
- Basic Histology-1Document51 pagesBasic Histology-1Zechariah NggitaNo ratings yet
- Cornea Clinic Interactive Part 2Document151 pagesCornea Clinic Interactive Part 2Cojocaru Stelica100% (1)
- DR Hany Abo Alwafa - Pathology GlossaryDocument31 pagesDR Hany Abo Alwafa - Pathology GlossaryHalimatunSyadiah ARNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument82 pagesCellsK.R. LiberosisNo ratings yet
- The Eye: Evy SulistyoningrumDocument52 pagesThe Eye: Evy SulistyoningrumLeti BhieNo ratings yet
- His To PathologyDocument4 pagesHis To PathologysayerNo ratings yet
- HE YE: Evy SulistyoningrumDocument82 pagesHE YE: Evy SulistyoningrumPandu Nugroho KantaNo ratings yet
- Histo Module 2Document27 pagesHisto Module 2princesssana.337No ratings yet
- NecrosisDocument13 pagesNecrosisarun j.rNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi MataDocument70 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi MataRisalatulNo ratings yet
- Master Plan Patho!Document94 pagesMaster Plan Patho!chiarastanziola01No ratings yet
- Anat Revision SampleDocument30 pagesAnat Revision Samplesafalife11No ratings yet
- General Principle & Eye Development EZRADocument28 pagesGeneral Principle & Eye Development EZRAezradamanikNo ratings yet
- CLLS 3231 Urinalysis and Body Fluids: Microscopic Examination Formed Elements: Cellular, Casts, Bacteria and YeastDocument55 pagesCLLS 3231 Urinalysis and Body Fluids: Microscopic Examination Formed Elements: Cellular, Casts, Bacteria and Yeaststrider_sdNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - CytologyDocument3 pagesLec1 - CytologyEloisa Trina GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Pathology Images MarrowDocument21 pagesPathology Images MarrowRAJDEEP DASNo ratings yet
- Marrow High Yield Pathology Slides @docinmaykingDocument21 pagesMarrow High Yield Pathology Slides @docinmaykingprasannaipad324No ratings yet
- 5 Malig Conn Tum PDFDocument19 pages5 Malig Conn Tum PDFDrrafiullahNo ratings yet
- Glandular Cells & Benign Disorders The Uterine CervixDocument41 pagesGlandular Cells & Benign Disorders The Uterine CervixSara VinamdNo ratings yet
- Robbin'S and Cotran'S: Pathologic Basis of DiseaseDocument6 pagesRobbin'S and Cotran'S: Pathologic Basis of Diseasenge257No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture NotesDocument94 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notesbiddyusmc100% (2)
- Special Senses - I: Histology of EyeDocument25 pagesSpecial Senses - I: Histology of EyeRessam NazirNo ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument55 pagesOphthalmologyapi-19916399100% (3)
- Traktus UveaDocument90 pagesTraktus UveaAudrey Ira Yunita100% (1)
- Anatomy-Physiology Eyeball 2023Document75 pagesAnatomy-Physiology Eyeball 2023debdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- NecrosisDocument23 pagesNecrosisSaradha Pellati100% (2)
- DegenerationDocument28 pagesDegenerationdr atul jainNo ratings yet
- CATARACTDocument82 pagesCATARACTRavi KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Plates illustrating the natural and morbid changes of the human eyeFrom EverandPlates illustrating the natural and morbid changes of the human eyeNo ratings yet
- COMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesDocument5 pagesCOMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesJUSASBNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics - FactsheetDocument12 pagesAntipsychotics - FactsheetColonNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics Factsheet pg2Document1 pageAntipsychotics Factsheet pg2JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37JUSASBNo ratings yet
- FA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesDocument2 pagesFA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesJUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33JUSASBNo ratings yet
- References: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015Document1 pageReferences: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35JUSASB50% (2)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 8Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 8JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22JUSASB0% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 19Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 19JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 9Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 9JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 6Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 6JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 4Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 4JUSASBNo ratings yet