Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 Modification
9 Modification
Uploaded by
api-281840010Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 Modification
9 Modification
Uploaded by
api-281840010Copyright:
Available Formats
Mike Kielpinski, ACT
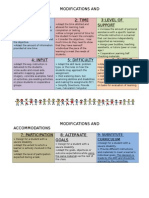
9 Types of Accommodations and Modifications for Disabilities
SIZE
1.
Adapt the number of items
that the learner is expected to
learn or complete.
2.
Allow completion of tasks in
chunks until the student has
met the objective.
3.
Adapt the amount of
information provided at one
time.
DIFFICULTY
1.
Adapt the skill level, problem
type, or the rules on how the
student may approach the
assignment.
2.
Not watering down, but
examining abilities and
disabilities and making the
assignment fit.
3.
Simplify directions, provide
cues, provide calculator.
OUTPUT
1.
Adapt HOW the learner can
respond to the instructions.
2.
Does everything need to be
pencil and paper tasks?
3.
Instead of answering
questions in writing use verbal
techniques, projects, games,
portfolios, hands on tasks for
evaluation of learning.
LEVEL OF SUPPORT
1.
Increase the amount of
personal assistance with a
specific learner.
2.
Provide instruction in a
manner that can become
independently supported as
necessary.
3.
Assign peer buddies, teaching
assistants, or tutors, and selfchecking materials.
ALTERNATE GOALS
1.
Designed for a student with a
severe disability.
2.
Adapt the goals, objectives, or
outcome expectations while
using the same materials as
the rest of the class.
DEGREE OF PARTICIPATION
1.
Designed for a student with a
severe disability.
2.
Adapt the extent to which a
learner is actively involved in
the task.
3.
Adapt the level of participation
expected during a task.
INPUT
1.
Adapt the way instruction is
delivered to the students.
2.
Use audio and visual aids,
semantic mapping, guided
imagery, concrete examples,
hands on activities, prereading activities, or place
students in cooperative
groups.
3.
This is teacher behavior.
Teach in a different way!
TIME
1.
Adapt the time allotted and
allowed for learning, task
completion or testing.
2.
Allow for longer period of time
for the student to learn the
concepts.
3.
Consider the objective how
much time do they need to
show that they have learned?
SUBSTITUTE CURRICULUM
1.
Designed for a student with a
severe disability.
2.
Provide different instruction
and materials to meet a
learners individual goals.
3.
This decision is made by the
ARD and should be planned
by the committee.
You might also like
- TRF Movs For Objective 9Document3 pagesTRF Movs For Objective 9Lovely Mae Mateo93% (27)
- The Multicultural Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesThe Multicultural Lesson Planapi-516586218No ratings yet
- Adaptations and ModificationsDocument2 pagesAdaptations and Modificationsapi-290401140No ratings yet
- ModificationsDocument2 pagesModificationsapi-336690274No ratings yet
- QuantityDocument1 pageQuantityapi-269364795No ratings yet
- ModificationsDocument1 pageModificationsapi-282294119No ratings yet
- Ninetypes GuideDocument1 pageNinetypes Guideapi-282044405No ratings yet
- 9 Types of ModificationsDocument1 page9 Types of Modificationsapi-269259144No ratings yet
- Modifications and AccomDocument1 pageModifications and Accomapi-312285446No ratings yet
- FinalDocument2 pagesFinalapi-298712273No ratings yet
- Modifications and AccommodationsDocument1 pageModifications and Accommodationsapi-323424342No ratings yet
- ModsaccommsDocument1 pageModsaccommsapi-232529874No ratings yet
- ModificationsDocument1 pageModificationsapi-248961865No ratings yet
- ModificationsDocument1 pageModificationsapi-269755385No ratings yet
- Modification AccommidationsDocument1 pageModification Accommidationsapi-290527567100% (1)
- ModaccDocument2 pagesModaccapi-249467590No ratings yet
- ModaccDocument1 pageModaccapi-249159056No ratings yet
- Nine TypesDocument1 pageNine Typesapi-291295091No ratings yet
- Nine Types of Accommodations and ModificationsDocument1 pageNine Types of Accommodations and Modificationsapi-281609796No ratings yet
- Modifications AccommidationsDocument2 pagesModifications Accommidationsapi-291349134No ratings yet
- Modifications PWPDocument1 pageModifications PWPapi-281358466No ratings yet
- Act Modifications and AccommodationsDocument1 pageAct Modifications and Accommodationsapi-281964838No ratings yet
- ModificationsDocument1 pageModificationsapi-239066916No ratings yet
- 9 Types of Accommodations and ModificationsDocument1 page9 Types of Accommodations and Modificationsapi-259393079No ratings yet
- ModificationsDocument1 pageModificationsapi-281834935No ratings yet
- 9 Acc and ModsDocument2 pages9 Acc and Modsapi-290531298No ratings yet
- 9 AcccDocument1 page9 Acccapi-269179875No ratings yet
- Modifications and AccomodationsDocument2 pagesModifications and Accomodationsapi-280717315No ratings yet
- Guide To DiDocument1 pageGuide To Diapi-199440830No ratings yet
- Elem Basic Lesson FormatDocument1 pageElem Basic Lesson FormatIP G0% (1)
- TRF Movs For Objective 9 1Document4 pagesTRF Movs For Objective 9 1HIEN TALIPASANNo ratings yet
- GridDocument2 pagesGridapi-281291412No ratings yet
- 3.0 Teachers Reflection FormDocument9 pages3.0 Teachers Reflection FormIessej Onabat NomolosNo ratings yet
- 9 TypesDocument10 pages9 Typesapi-232170430No ratings yet
- Act ModificationsDocument1 pageAct Modificationsapi-269458883No ratings yet
- Mod AccomDocument1 pageMod Accomapi-298369880No ratings yet
- TRF Teacher Reflection On Obj. 9 - 2ndDocument4 pagesTRF Teacher Reflection On Obj. 9 - 2ndAnna Patricia MaruyaNo ratings yet
- LEARNING-TASK-5-6 (3)Document16 pagesLEARNING-TASK-5-6 (3)Melvin SumalinogNo ratings yet
- EquityDocument1 pageEquityapi-249718817No ratings yet
- Modifications and AccomodationsDocument1 pageModifications and Accomodationsapi-290757724No ratings yet
- Seven TypesDocument1 pageSeven Typesapi-336512670No ratings yet
- Walking Through Grade 9 English: Module 3: Connecting To The WorldDocument44 pagesWalking Through Grade 9 English: Module 3: Connecting To The Worlderlinda tibusNo ratings yet
- TRF Movs For Objective 9Document3 pagesTRF Movs For Objective 9Jake Lester DafangNo ratings yet
- Module 3A:: Designing Instruction in The Different Learning Delivery ModalitiesDocument87 pagesModule 3A:: Designing Instruction in The Different Learning Delivery ModalitiesGilbert Mores EsparragoNo ratings yet
- RPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Document5 pagesRPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Giel RyzenNo ratings yet
- ModificationsDocument2 pagesModificationsapi-280981984No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledVANESSA MAE NAVERANo ratings yet
- The Lesson PlanDocument48 pagesThe Lesson PlanDesiree BenavidezNo ratings yet
- RPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Document10 pagesRPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Propsero Luke Godfrey CaberteNo ratings yet
- TRF Movs For Objective 9Document3 pagesTRF Movs For Objective 9MilettAlegroNo ratings yet
- Topik9 m3Document18 pagesTopik9 m3Vijayan MariaapanNo ratings yet
- QuantityDocument2 pagesQuantityapi-298525392No ratings yet
- Task Analysis - 032241Document4 pagesTask Analysis - 032241Titofelix GalletoNo ratings yet
- RPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Document3 pagesRPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Giel RyzenNo ratings yet
- Movs For Obj 9Document10 pagesMovs For Obj 9Leizel Labindao VicenteNo ratings yet
- Rpms 2021-2022 AnnotationDocument31 pagesRpms 2021-2022 AnnotationJayna LevantinoNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesSample QuestionnairerynNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Multigrade TeachingDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Multigrade TeachingRheia TangonanNo ratings yet
- 21st Century AssessmentDocument52 pages21st Century AssessmentMedaReynado100% (1)