Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P Wave, PR Interval, PR Segment, QRS Complex, ST Segment, QT Interval and T Wave
P Wave, PR Interval, PR Segment, QRS Complex, ST Segment, QT Interval and T Wave
Uploaded by
Roby4Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasFrom EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- ECG SyllabusDocument27 pagesECG SyllabusSue HuangNo ratings yet
- The Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayDocument16 pagesThe Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayFourth YearNo ratings yet
- Conduction and EcgDocument32 pagesConduction and EcgRadijska Postaja KoprivnicaNo ratings yet
- ECG DocumentDocument10 pagesECG Document'SheenMarkReal'No ratings yet
- How To Read A EKG StripDocument2 pagesHow To Read A EKG StripJill Putman BeistlineNo ratings yet
- ECG Lecture 1 by Dr. RoomiDocument18 pagesECG Lecture 1 by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (3)
- ECG (Electrocardiogram) Tracings: Capitol University College of NursingDocument5 pagesECG (Electrocardiogram) Tracings: Capitol University College of NursingRiel TumandaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointDocument37 pagesEcg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointJara Maris Moreno BudionganNo ratings yet
- Basis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationDocument10 pagesBasis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationKristin SmithNo ratings yet
- FeatureDocument2 pagesFeatureLilian KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography ECGDocument60 pagesElectrocardiography ECGSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument3 pagesElectrocardiogramgaratoh099No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: What Is An ECG?Document8 pagesElectrocardiogram: What Is An ECG?Ali dhyaa100% (1)
- Cardiac Monitoring: Basics of ElectrocardiographyDocument15 pagesCardiac Monitoring: Basics of ElectrocardiographyKristina SolisNo ratings yet
- ECG PracticalDocument48 pagesECG PracticalbvkjtzrvnyNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument41 pagesECGmiguel mendezNo ratings yet
- A Typical ECG Tracing of The Cardiac CycleDocument3 pagesA Typical ECG Tracing of The Cardiac CycleMhiyciel UyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document24 pagesClinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)soniya josephNo ratings yet
- ECG1Document67 pagesECG1Farhan RosliNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Jovel Balaba Tangonan InstructorDocument77 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Jovel Balaba Tangonan InstructorNecky AlbaciteNo ratings yet
- Nageen 4Document6 pagesNageen 4saadshahab622No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogra (M) PhyDocument26 pagesElectrocardiogra (M) PhyyansliyaNo ratings yet
- How Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramDocument10 pagesHow Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramJonathan AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNDocument34 pagesBasic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNMavic Martinez BuntalesNo ratings yet
- Normal ECGDocument46 pagesNormal ECGMohamed HamdyNo ratings yet
- Resumen EKGDocument22 pagesResumen EKGWarlan Steven Soto FloresNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 5 PDFDocument50 pagesLab Exercise 5 PDFE1- Villapaz, Aiemarie R. (Aie)No ratings yet
- Recognizing Normal ECGDocument50 pagesRecognizing Normal ECGJosiephine Bucalon100% (3)
- Cheong Kuan Loong Medical Department Hospital Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah, Temerloh 12/5/10Document99 pagesCheong Kuan Loong Medical Department Hospital Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah, Temerloh 12/5/10Haq10No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyDocument27 pagesUnit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyJack TomarNo ratings yet
- Depolarization and RepolarizationDocument3 pagesDepolarization and Repolarizationمحمد سعد طه احمدNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument8 pagesBasic ECG Interpretationamesb100% (1)
- Experiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderDocument7 pagesExperiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderVISHWESH KULKARNINo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument29 pagesElectrocardiogramMahnoor ZafarNo ratings yet
- Cal EcgDocument7 pagesCal EcgNur Amirah FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Aaa Ejempl TraductDocument8 pagesAaa Ejempl TraductJm GamaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDocument155 pagesElectrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDeepika PatelNo ratings yet
- Ecg Didacs-SampianoDocument88 pagesEcg Didacs-SampianoCC Samson, Caesar AnthonyNo ratings yet
- 26A. ECG tutorial _ Basic principles of ECG analysis - UpToDate_101216Document23 pages26A. ECG tutorial _ Basic principles of ECG analysis - UpToDate_101216johundaphNo ratings yet
- 5 - EcgDocument37 pages5 - EcgMonika MeriyaNo ratings yet
- KalaiDocument47 pagesKalaiArya VikneshNo ratings yet
- DYSRHYTMIASDocument16 pagesDYSRHYTMIASVictor StevenNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceDocument25 pagesBasic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceSoySauceNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECGDocument25 pagesBasics of ECGsofiamansoorNo ratings yet
- ECG Lecture 1: DR Ahmed Murtaz Khalid Assistant Professor Physiology CKMCDocument27 pagesECG Lecture 1: DR Ahmed Murtaz Khalid Assistant Professor Physiology CKMCRai AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoDocument53 pagesCardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoAnisha NallasamyNo ratings yet
- Ecg PrsentationDocument33 pagesEcg Prsentationtehillahkabwe100No ratings yet
- Understanding The 12 Lead ECGDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The 12 Lead ECGccbrown7No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document25 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)Laraib KanwalNo ratings yet
- 231FA16011 231FA16019 231FA16033 231FA16047: Done by BATCH-7 (BME-32)Document16 pages231FA16011 231FA16019 231FA16033 231FA16047: Done by BATCH-7 (BME-32)official6705No ratings yet
- DYSRHYTHMIAS AND CONDUCTION DISORDERS №1Document6 pagesDYSRHYTHMIAS AND CONDUCTION DISORDERS №1z8pwywrxf2No ratings yet
- Heart Conduction 081627Document11 pagesHeart Conduction 081627chiemerieagana3No ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument73 pagesECG Interpretationsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument50 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAMamitava2010No ratings yet
- ECG PracticalDocument32 pagesECG Practicalmuhammedarif199No ratings yet
- Introduction To ECGDocument6 pagesIntroduction To ECGAbigail ChristisnNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography (Ii) Morphological Description of The ElectrocardiogramDocument8 pagesElectrocardiography (Ii) Morphological Description of The ElectrocardiogramAisleenHNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Intro: Ferdian M.arief Annisa RD Iin Yani Katarina Ayu FDocument17 pagesIntro: Ferdian M.arief Annisa RD Iin Yani Katarina Ayu FRoby4No ratings yet
- Jurnal Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesJurnal Sistem EndokrinRoby4No ratings yet
- Ffisiologi EkgDocument29 pagesFfisiologi EkgRoby4No ratings yet
- Er Hospital Pupuk Kaltim Siaga RamaniaDocument3 pagesEr Hospital Pupuk Kaltim Siaga RamaniaRoby4No ratings yet
- Nama: Renaldy Hermawan Kelas: X Akuntansi 1 Sekolah: SMK Negeri 15 SMD Describing PeopleDocument3 pagesNama: Renaldy Hermawan Kelas: X Akuntansi 1 Sekolah: SMK Negeri 15 SMD Describing PeopleRoby4No ratings yet
- Perspektif Keperawatan Pediatrik: Oleh: Rita Puspa Sari, A.Md - Kep, S.PD, MPH Akper Pemprov. KaltimDocument28 pagesPerspektif Keperawatan Pediatrik: Oleh: Rita Puspa Sari, A.Md - Kep, S.PD, MPH Akper Pemprov. KaltimRoby4No ratings yet
- MEILLER REVISI Jadwal Promosi Kas July 2013Document7 pagesMEILLER REVISI Jadwal Promosi Kas July 2013Roby4No ratings yet
- U-Kiss Neverland LyricsDocument1 pageU-Kiss Neverland LyricsRoby4No ratings yet
- Guyton Physiology 11th EditionDocument8 pagesGuyton Physiology 11th EditionRoby4No ratings yet
P Wave, PR Interval, PR Segment, QRS Complex, ST Segment, QT Interval and T Wave
P Wave, PR Interval, PR Segment, QRS Complex, ST Segment, QT Interval and T Wave
Uploaded by
Roby4Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P Wave, PR Interval, PR Segment, QRS Complex, ST Segment, QT Interval and T Wave
P Wave, PR Interval, PR Segment, QRS Complex, ST Segment, QT Interval and T Wave
Uploaded by
Roby4Copyright:
Available Formats
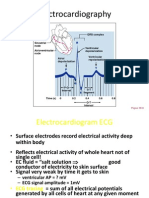
Introduction
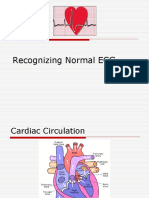
The SA node spontaneously depolarize to initiate an action impulse that is rapidly
propagated through the atria (causing atrial contract), then slowly through the AV node
and rapidly via the bundle branches and Purkinje system to the ventricles, causing
ventricular contraction.
The electrical activity of the heart can be recorded at the surface of the body using an
electrocardiogram. The electrocardiogram (EKG) is simply a voltmeter that uses up to 12
different leads (electrodes) placed on designated areas of the body.
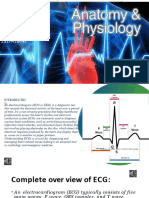
The electrocardiogram is composed of waves and complexes. Waves and complexes in
the normal sinus rhythm are the P wave, PR Interval, PR Segment, QRS Complex, ST
Segment, QT Interval and T wave (shown below).
Click here for an animation of the normal sinus rhythm from the P wave to T
wave. You will need shockwave.
he P wave is caused by atrial depolarization. The P wave is usually smooth and
positive. The P wave duration is normally less than 0.12 sec. More...
he PR interval is the portion of the EKG wave from the beginning of the P
wave ( onset of atrial depolarization) to the beginning of the QRS complex ( onset
of ventricular depolarization). It is normally 0.12 - 0.20 seconds. More...
he PR segment is the portion on the EKG wave from the end of the P wave to
the beginning of the QRS complex. The PR segment corresponds to the time
between the end of atrial depolarization to the onset of ventricular depolarization.
It is an isoelectric segment, during which the impulse travels from the AV node
through the conducting tissue (bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers) towards the
ventricles. More...
he QRS complex represents the time it takes for depolarization of the
ventricles. - due to ventricular depolarization. The normal QRS interval range is
from 0.04 sec - 0.12 sec measured from the first deflection to the end of the QRS
complex. More...
The ST Segment represents the period of ventricular muscle contraction before
repolarization. The ST segment is normally isoelectric (no electrical activity is
recorded). however, the ventricles are contracting. More...
The QT interval begins at the onset of the QRS complex and to the end of the T
wave. It represents the time of ventricular depolarization until ventricular
repolarization. More...
The T wave due to ventricular repolarization The wave is normally rounded and
positive. More...
You might also like
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasFrom EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- ECG SyllabusDocument27 pagesECG SyllabusSue HuangNo ratings yet
- The Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayDocument16 pagesThe Electrocardiogram: Normal Conduction PathwayFourth YearNo ratings yet
- Conduction and EcgDocument32 pagesConduction and EcgRadijska Postaja KoprivnicaNo ratings yet
- ECG DocumentDocument10 pagesECG Document'SheenMarkReal'No ratings yet
- How To Read A EKG StripDocument2 pagesHow To Read A EKG StripJill Putman BeistlineNo ratings yet
- ECG Lecture 1 by Dr. RoomiDocument18 pagesECG Lecture 1 by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (3)
- ECG (Electrocardiogram) Tracings: Capitol University College of NursingDocument5 pagesECG (Electrocardiogram) Tracings: Capitol University College of NursingRiel TumandaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointDocument37 pagesEcg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointJara Maris Moreno BudionganNo ratings yet
- Basis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationDocument10 pagesBasis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationKristin SmithNo ratings yet
- FeatureDocument2 pagesFeatureLilian KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography ECGDocument60 pagesElectrocardiography ECGSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument3 pagesElectrocardiogramgaratoh099No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: What Is An ECG?Document8 pagesElectrocardiogram: What Is An ECG?Ali dhyaa100% (1)
- Cardiac Monitoring: Basics of ElectrocardiographyDocument15 pagesCardiac Monitoring: Basics of ElectrocardiographyKristina SolisNo ratings yet
- ECG PracticalDocument48 pagesECG PracticalbvkjtzrvnyNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument41 pagesECGmiguel mendezNo ratings yet
- A Typical ECG Tracing of The Cardiac CycleDocument3 pagesA Typical ECG Tracing of The Cardiac CycleMhiyciel UyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document24 pagesClinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)soniya josephNo ratings yet
- ECG1Document67 pagesECG1Farhan RosliNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Jovel Balaba Tangonan InstructorDocument77 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Jovel Balaba Tangonan InstructorNecky AlbaciteNo ratings yet
- Nageen 4Document6 pagesNageen 4saadshahab622No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogra (M) PhyDocument26 pagesElectrocardiogra (M) PhyyansliyaNo ratings yet
- How Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramDocument10 pagesHow Procedure Is Performed: ElectrocardiogramJonathan AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNDocument34 pagesBasic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNMavic Martinez BuntalesNo ratings yet
- Normal ECGDocument46 pagesNormal ECGMohamed HamdyNo ratings yet
- Resumen EKGDocument22 pagesResumen EKGWarlan Steven Soto FloresNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 5 PDFDocument50 pagesLab Exercise 5 PDFE1- Villapaz, Aiemarie R. (Aie)No ratings yet
- Recognizing Normal ECGDocument50 pagesRecognizing Normal ECGJosiephine Bucalon100% (3)
- Cheong Kuan Loong Medical Department Hospital Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah, Temerloh 12/5/10Document99 pagesCheong Kuan Loong Medical Department Hospital Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah, Temerloh 12/5/10Haq10No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyDocument27 pagesUnit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyJack TomarNo ratings yet
- Depolarization and RepolarizationDocument3 pagesDepolarization and Repolarizationمحمد سعد طه احمدNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument8 pagesBasic ECG Interpretationamesb100% (1)
- Experiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderDocument7 pagesExperiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderVISHWESH KULKARNINo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument29 pagesElectrocardiogramMahnoor ZafarNo ratings yet
- Cal EcgDocument7 pagesCal EcgNur Amirah FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Aaa Ejempl TraductDocument8 pagesAaa Ejempl TraductJm GamaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDocument155 pagesElectrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDeepika PatelNo ratings yet
- Ecg Didacs-SampianoDocument88 pagesEcg Didacs-SampianoCC Samson, Caesar AnthonyNo ratings yet
- 26A. ECG tutorial _ Basic principles of ECG analysis - UpToDate_101216Document23 pages26A. ECG tutorial _ Basic principles of ECG analysis - UpToDate_101216johundaphNo ratings yet
- 5 - EcgDocument37 pages5 - EcgMonika MeriyaNo ratings yet
- KalaiDocument47 pagesKalaiArya VikneshNo ratings yet
- DYSRHYTMIASDocument16 pagesDYSRHYTMIASVictor StevenNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceDocument25 pagesBasic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceSoySauceNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECGDocument25 pagesBasics of ECGsofiamansoorNo ratings yet
- ECG Lecture 1: DR Ahmed Murtaz Khalid Assistant Professor Physiology CKMCDocument27 pagesECG Lecture 1: DR Ahmed Murtaz Khalid Assistant Professor Physiology CKMCRai AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoDocument53 pagesCardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoAnisha NallasamyNo ratings yet
- Ecg PrsentationDocument33 pagesEcg Prsentationtehillahkabwe100No ratings yet
- Understanding The 12 Lead ECGDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The 12 Lead ECGccbrown7No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document25 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)Laraib KanwalNo ratings yet
- 231FA16011 231FA16019 231FA16033 231FA16047: Done by BATCH-7 (BME-32)Document16 pages231FA16011 231FA16019 231FA16033 231FA16047: Done by BATCH-7 (BME-32)official6705No ratings yet
- DYSRHYTHMIAS AND CONDUCTION DISORDERS №1Document6 pagesDYSRHYTHMIAS AND CONDUCTION DISORDERS №1z8pwywrxf2No ratings yet
- Heart Conduction 081627Document11 pagesHeart Conduction 081627chiemerieagana3No ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument73 pagesECG Interpretationsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument50 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAMamitava2010No ratings yet
- ECG PracticalDocument32 pagesECG Practicalmuhammedarif199No ratings yet
- Introduction To ECGDocument6 pagesIntroduction To ECGAbigail ChristisnNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography (Ii) Morphological Description of The ElectrocardiogramDocument8 pagesElectrocardiography (Ii) Morphological Description of The ElectrocardiogramAisleenHNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Intro: Ferdian M.arief Annisa RD Iin Yani Katarina Ayu FDocument17 pagesIntro: Ferdian M.arief Annisa RD Iin Yani Katarina Ayu FRoby4No ratings yet
- Jurnal Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesJurnal Sistem EndokrinRoby4No ratings yet
- Ffisiologi EkgDocument29 pagesFfisiologi EkgRoby4No ratings yet
- Er Hospital Pupuk Kaltim Siaga RamaniaDocument3 pagesEr Hospital Pupuk Kaltim Siaga RamaniaRoby4No ratings yet
- Nama: Renaldy Hermawan Kelas: X Akuntansi 1 Sekolah: SMK Negeri 15 SMD Describing PeopleDocument3 pagesNama: Renaldy Hermawan Kelas: X Akuntansi 1 Sekolah: SMK Negeri 15 SMD Describing PeopleRoby4No ratings yet
- Perspektif Keperawatan Pediatrik: Oleh: Rita Puspa Sari, A.Md - Kep, S.PD, MPH Akper Pemprov. KaltimDocument28 pagesPerspektif Keperawatan Pediatrik: Oleh: Rita Puspa Sari, A.Md - Kep, S.PD, MPH Akper Pemprov. KaltimRoby4No ratings yet
- MEILLER REVISI Jadwal Promosi Kas July 2013Document7 pagesMEILLER REVISI Jadwal Promosi Kas July 2013Roby4No ratings yet
- U-Kiss Neverland LyricsDocument1 pageU-Kiss Neverland LyricsRoby4No ratings yet
- Guyton Physiology 11th EditionDocument8 pagesGuyton Physiology 11th EditionRoby4No ratings yet