Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 TI MountingTech DS
5 TI MountingTech DS
Uploaded by
rodruren0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageThe mounting technique used to attach a vibration sensor to a machine affects the sensor's ability to accurately measure high frequency vibrations. Mounting methods that maximize surface area contact, like stud mounting, allow sensors to utilize their full high frequency measurement capability above 500 Hz. Conversely, probe tip mounting provides very little surface contact and limits accurate high frequency response to below 500 Hz. The mounting technique chosen impacts the sensor-machine system's overall high frequency response capabilities.
Original Description:
5 TI MountingTech DS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe mounting technique used to attach a vibration sensor to a machine affects the sensor's ability to accurately measure high frequency vibrations. Mounting methods that maximize surface area contact, like stud mounting, allow sensors to utilize their full high frequency measurement capability above 500 Hz. Conversely, probe tip mounting provides very little surface contact and limits accurate high frequency response to below 500 Hz. The mounting technique chosen impacts the sensor-machine system's overall high frequency response capabilities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 page5 TI MountingTech DS
5 TI MountingTech DS
Uploaded by
rodrurenThe mounting technique used to attach a vibration sensor to a machine affects the sensor's ability to accurately measure high frequency vibrations. Mounting methods that maximize surface area contact, like stud mounting, allow sensors to utilize their full high frequency measurement capability above 500 Hz. Conversely, probe tip mounting provides very little surface contact and limits accurate high frequency response to below 500 Hz. The mounting technique chosen impacts the sensor-machine system's overall high frequency response capabilities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
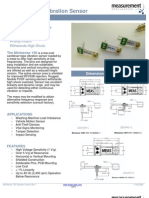
Sensor Mounting Techniques
Frequency Response / Mounting Techniques
The accuracy of your high frequency response is directly affected by the mounting technique that you
select for the sensor. In general, the greater the mounted surface area contact between the sensor
and the machine surface, the more accurate your high frequency response will be. High frequency
response is based on the sensor specified as well as the method of attachment (together as a
system). Stud mounted (or epoxy mounted) sensors are often able to utilize the entire high frequency
measurement capability of a sensor, because this technique will maximize the surface contact of the
sensor on the machine. Conversely, a probe tip mounted sensor has very little surface area contact
with the machine surface, and offers very little high frequency accuracy above 500 Hz (30,000 CPM).
SENSOR
SENSOR
SENSOR
SENSOR
SENSOR
MOUNTING
STUD
MOUNTING
PAD
MAGNET
TARGET
MOUNTING
PAD
RECEPTACLE
MAGNET
SENSOR
PROBE TIP
Vibration Analysis Hardware
Backed by our Unconditional Lifetime Warranty
Page 195
800-999-5290
Sensor Mounting Techniques
The following chart offers a general guideline for the range of mounting techniques available, and the
corresponding high frequency response expectations.*
Section 5 - Technical Info
Low frequency response may be accurately obtained by all of the below illustrated techniques,
because low frequency is not based on the mounting system resonance of the sensor and attachment
method. The ability to measure low frequency vibrations will be a function of the sensors specified
capability to measure a given low frequency, and not dependent on the mounting technique chosen.
You might also like
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Vibration Specifications Standards Gearboxes With Alarm LimitsDocument40 pagesVibration Specifications Standards Gearboxes With Alarm LimitsHemanth Kumar83% (6)
- Ultrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentFrom EverandUltrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Physics and Technology of Diagnostic Ultrasound: Study Guide (Second Edition)From EverandThe Physics and Technology of Diagnostic Ultrasound: Study Guide (Second Edition)No ratings yet
- Vibration Transducer Mounting SKF PDFDocument3 pagesVibration Transducer Mounting SKF PDFTheerayootNo ratings yet
- Vib - AccelerometerDocument16 pagesVib - AccelerometerMahmoud SobhyNo ratings yet
- A 6096 ManDocument9 pagesA 6096 ManLuis MaureraNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer Selection and InstallationDocument16 pagesAccelerometer Selection and InstallationLake HouseNo ratings yet
- TN16 - Sensor Selection GuideDocument13 pagesTN16 - Sensor Selection GuideAsitha KulasekeraNo ratings yet
- Mounting of AccelerometersDocument22 pagesMounting of AccelerometersLake HouseNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT2 Mech Vibration F2019Document27 pagesASSIGNMENT2 Mech Vibration F2019AbdulrehmanNo ratings yet
- Vibration Transducer MountingDocument4 pagesVibration Transducer MountingUmair NaseemNo ratings yet
- AN447Document20 pagesAN447Maxim FrewdellNo ratings yet
- 33-Accelerometer Mounting Basics 12-1-08Document2 pages33-Accelerometer Mounting Basics 12-1-08rodrurenNo ratings yet
- Envelope Acceleration LDocument10 pagesEnvelope Acceleration Lsumeet_soporiNo ratings yet
- Inspection of Composite Rocket Nozzle PDFDocument10 pagesInspection of Composite Rocket Nozzle PDFHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Measurement Optimization: Mounting Considerations and Sensor Mass EffectDocument10 pagesAcceleration Measurement Optimization: Mounting Considerations and Sensor Mass EffectNg Wei LihNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual of UD2301Document38 pagesOperating Manual of UD2301mreyes-aldamaNo ratings yet
- Project Review On Ultrasonic Distance Measurement: Prakhar Shrivastava, Praveen Kumar, Ankit TiwariDocument3 pagesProject Review On Ultrasonic Distance Measurement: Prakhar Shrivastava, Praveen Kumar, Ankit TiwarirajatpreetNo ratings yet
- Media Web ServerDocument4 pagesMedia Web Serverpantera00No ratings yet
- Improving Low Frequency Vibration AnalysisDocument21 pagesImproving Low Frequency Vibration AnalysisMohd Asiren Mohd SharifNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Control ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesSensors and Control ConsiderationsPrashanth BnNo ratings yet
- Leak Survey HandbookDocument11 pagesLeak Survey HandbookebbasinghNo ratings yet
- How Sensor Mounting Affects Measurments: Written by David A. CorelliDocument11 pagesHow Sensor Mounting Affects Measurments: Written by David A. CorelliGilbertoAndresDuarteNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Ultrasonic Sensor - Mohamad Aminnudin Mutalib - Mohamad Hafiszuddin AbdullahDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 - Ultrasonic Sensor - Mohamad Aminnudin Mutalib - Mohamad Hafiszuddin AbdullahamintfypNo ratings yet
- Phase-Shift Fizeau Interferometer in Presence of VibrationDocument12 pagesPhase-Shift Fizeau Interferometer in Presence of VibrationMircea BujorNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer Selection Based On ApplicationsDocument8 pagesAccelerometer Selection Based On Applicationspatilrushal824No ratings yet
- Festo SensorDocument22 pagesFesto SensorBRYSHARDS100% (1)
- Microchip Capacitive Proximity Design Guide: Author: Xiang Gao Microchip Technology IncDocument8 pagesMicrochip Capacitive Proximity Design Guide: Author: Xiang Gao Microchip Technology IncmhemaraNo ratings yet
- WPL 68 HowSensorMountingAffectsMeasurementsDocument11 pagesWPL 68 HowSensorMountingAffectsMeasurementsRoberto Eduardo Quintal PalomoNo ratings yet
- Diss Schneider PDFDocument166 pagesDiss Schneider PDF尤仁宏No ratings yet
- Vibration Sensors - SKFDocument44 pagesVibration Sensors - SKFnekoNcen100% (1)
- Ultrasonicproveup PDFDocument6 pagesUltrasonicproveup PDFleonciomavarezNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Nondestructive Testing - Advanced Concepts and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesUltrasonic Nondestructive Testing - Advanced Concepts and ApplicationsDhanasekaran RNo ratings yet
- Sound Intensity MeasuDocument9 pagesSound Intensity MeasuJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- 2 Q 01 HanifanDocument2 pages2 Q 01 HanifanHatem AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Radar Research PaperDocument6 pagesUltrasonic Radar Research PaperAbhishek KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: 2270 Ultrasonic Level SensorDocument36 pagesInstruction Manual: 2270 Ultrasonic Level Sensorabbas dehghanNo ratings yet
- REDUCTION of The SKI SLOPE EFFECTDocument8 pagesREDUCTION of The SKI SLOPE EFFECTEnzo MarquesNo ratings yet
- MiniSense 100Document4 pagesMiniSense 100Ing FermínNo ratings yet
- ADIS16223 Analog DevicesDocument3 pagesADIS16223 Analog DevicesvijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Vibration Specifications Standards Setup CriteriaDocument43 pagesVibration Specifications Standards Setup CriteriamaspanuciNo ratings yet
- An Application of Ultrasound Technology in Condition Monitoring-Rev.1-WebDocument16 pagesAn Application of Ultrasound Technology in Condition Monitoring-Rev.1-WebChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- Sensor Mounting Techniques - Power-MI: Aug 21, 2023 2:20 PMDocument5 pagesSensor Mounting Techniques - Power-MI: Aug 21, 2023 2:20 PMabdalla AljzNo ratings yet
- Vibrationsensor 171204042110Document18 pagesVibrationsensor 171204042110DRathikaNo ratings yet
- Proximity SensorsDocument4 pagesProximity SensorsRohit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Manual Weld Inspection With Ultrasound - Conventionally or With Phased Arrays?Document10 pagesManual Weld Inspection With Ultrasound - Conventionally or With Phased Arrays?Raul2307No ratings yet
- HC SR04 HandsOnDocument9 pagesHC SR04 HandsOnLygia freitasNo ratings yet
- Vibration AnalysisDocument4 pagesVibration Analysisrishan33100% (1)
- Jumping Into Industry 4.0 With Predictive Maintenance SolutionsDocument26 pagesJumping Into Industry 4.0 With Predictive Maintenance SolutionsNantha Kumara PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- 04main Measure Insp SensorsDocument66 pages04main Measure Insp SensorsJoao RobertoNo ratings yet
- Vibration SensorsDocument44 pagesVibration SensorsLarry Vilca DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Vibration Monitoring of Paper Mill MachineryDocument17 pagesVibration Monitoring of Paper Mill Machineryerick giovanniNo ratings yet
- Capsense Design Guide Line LearningsDocument51 pagesCapsense Design Guide Line Learningschintan.gopaniNo ratings yet
- Compact Product DataDocument16 pagesCompact Product DataMohammad MehdikhaniNo ratings yet
- Chime and Multiskip InspectionDocument10 pagesChime and Multiskip InspectionVignesh VelNo ratings yet
- En - MEMS Condition MonitoringDocument17 pagesEn - MEMS Condition MonitoringbogodavidNo ratings yet
- ENGG5024-1985 Electronic Systems Mini ProjectDocument8 pagesENGG5024-1985 Electronic Systems Mini ProjectAlfred LiNo ratings yet
- Video Data Analytics for Smart City Applications: Methods and TrendsFrom EverandVideo Data Analytics for Smart City Applications: Methods and TrendsNo ratings yet
- 1 Vs Csa Atex Overview DsDocument1 page1 Vs Csa Atex Overview DsrodrurenNo ratings yet
- 1 Vs Sensor HazArea IntroDocument1 page1 Vs Sensor HazArea IntrorodrurenNo ratings yet
- Test Equipment: The Pro LineDocument1 pageTest Equipment: The Pro LinerodrurenNo ratings yet
- Permanently Installed SensorsDocument2 pagesPermanently Installed SensorsrodrurenNo ratings yet
- Las Tres Virgenes Mexico Geothermal PlantDocument2 pagesLas Tres Virgenes Mexico Geothermal PlantrodrurenNo ratings yet
- BDocument3 pagesBrodrurenNo ratings yet
- About The DT901-08-S1 Linear Field Calibration UnitDocument1 pageAbout The DT901-08-S1 Linear Field Calibration UnitrodrurenNo ratings yet
- Wiring Triaxial Sensors in A Standard Junction BoxDocument1 pageWiring Triaxial Sensors in A Standard Junction BoxrodrurenNo ratings yet
- 33-Accelerometer Mounting Basics 12-1-08Document2 pages33-Accelerometer Mounting Basics 12-1-08rodrurenNo ratings yet
- Pro Apnote Prox Probe MountsFINALDocument1 pagePro Apnote Prox Probe MountsFINALrodrurenNo ratings yet
- CTC Bias Voltage Apps Note 3-14-10Document1 pageCTC Bias Voltage Apps Note 3-14-10rodrurenNo ratings yet
- Highest Quality Lowest Cost!: Mounting HardwareDocument1 pageHighest Quality Lowest Cost!: Mounting HardwarerodrurenNo ratings yet
- MODEL DX3301/ PRO DP/DD/DC 1001 Series: Product ManualDocument11 pagesMODEL DX3301/ PRO DP/DD/DC 1001 Series: Product ManualrodrurenNo ratings yet
- Bulletin 1492 DIN Rail Receptacle: AdvantagesDocument1 pageBulletin 1492 DIN Rail Receptacle: AdvantagesrodrurenNo ratings yet
- 6 PRO ProxProbe Blocks English DSDocument1 page6 PRO ProxProbe Blocks English DSrodrurenNo ratings yet
- Valence Training BrochureDocument12 pagesValence Training Brochurerodruren100% (1)