Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 2 Modified
Assignment 2 Modified
Uploaded by
zapzahtOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 2 Modified
Assignment 2 Modified
Uploaded by
zapzahtCopyright:
Available Formats
EE3006 POWER SYSTEMS II
Assignment No.2
Submission Date: 31/03/2015
2
1
3
1. For the single line diagram shown in figure 1, form Y Bus. The transmission line parameters are: line
lengths L1=120km; L2=90km; L3=195km. R=0.075/km/phase; L=0.511/km/phase;
1/C=0.311/km/phase. Nominal Equivalent circuit may be assumed for the lines. Express all
admittances in pu referred to the 3 phase base values: Sb=300 MVA, Vb=230kV.
L1
L2
L3
Figure 1
2. For the single line diagram shown in figure 2, use 2 iterations of Gauss-Seidel method with flat start
to hand-calculate the voltage phase angle 2 at bus 2. Choose the reference bus voltage as V 1 = 100
pu and specified bus voltage magnitude at bus 2 as 1pu. Line parameters are the same as in question
1 and the line length is 180km. Controllable reactive power source is available at bus 2 with the
constraint 0Qg20.5 pu. Compare the values with the values obtained after 2 iterations of NewtonRaphson method. Also determine the reactive power generation at bus 2, slack bus power, line power
flow and real power loss.
SG1
V1100 pu
SD1=1.1+j0.3 pu
|V2| = 1pu
SD2= 0.5+j0.15 pu
Figure 2
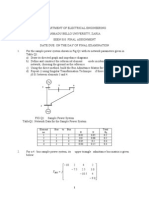
3. For the power system network shown in figure 3, write computer program to compute the bus
voltages using the Gauss-Seidel and Newton-Raphson iteration methods. Line reactance and loads
are shown in the figure. Bus 1 is the slack bus and buses 2 and 3 are the load and voltage-control
buses, respectively. Reactive power constraint at bus 3 is e -0.5puQg30.5 pu. Also determine line
currents, slack bus power and power losses in the line. Assume tolerance equal to 0.00001.
Figure 3
You might also like
- Pricing Games Sony Playstation and Microsoft XboxDocument8 pagesPricing Games Sony Playstation and Microsoft Xboxzapzaht33% (3)
- Module 3.2Document42 pagesModule 3.2JASPER PAYAPAYA100% (1)
- Power System AnalysisDocument23 pagesPower System AnalysisSaeed Al BlooshiNo ratings yet
- PS-III Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesPS-III Assignment QuestionsSanoxNo ratings yet
- ECE-522 CMOS Integrated Circuits-I Project Report:design of A Two Stage Miller Compensated Op-Amp Submitted By: Romesh Kumar NandwanaDocument9 pagesECE-522 CMOS Integrated Circuits-I Project Report:design of A Two Stage Miller Compensated Op-Amp Submitted By: Romesh Kumar NandwanaRiyaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document12 pagesWeek 2Ayyan MirNo ratings yet
- Cap 6Document67 pagesCap 6ccprado1100% (1)
- Trans TransmisiDocument31 pagesTrans TransmisimalikNo ratings yet
- Ferranti Effect PracticalDocument4 pagesFerranti Effect PracticalKishor Bhamare100% (2)
- Special Manpower Development Program in VLSI Design IEP: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit Design Shanthi@ee - Iitm.ac - inDocument2 pagesSpecial Manpower Development Program in VLSI Design IEP: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit Design Shanthi@ee - Iitm.ac - inalkjhlkjlkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 TL Modelling and PerformanceDocument9 pagesLecture 2 TL Modelling and PerformanceJustine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Document14 pagesUnit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Ragul RamNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument17 pagesQuestion BankNisarg PanchalNo ratings yet
- High Bandwidth Low Noise Amplifier With Improved Stability Over Radio Frequency RangeDocument11 pagesHigh Bandwidth Low Noise Amplifier With Improved Stability Over Radio Frequency Rangesushil4056No ratings yet
- Power System Analysis (Jan-2014)Document10 pagesPower System Analysis (Jan-2014)Likhitha YerraNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission and Distribution LabDocument7 pagesPower Transmission and Distribution Labasfand shaheryarNo ratings yet
- Analytic Calculation of The DC Link PDFDocument9 pagesAnalytic Calculation of The DC Link PDFjorrriqueNo ratings yet
- Chen 1995Document6 pagesChen 1995أمين توات الجزائريNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Modelling and PerformanceDocument8 pagesTransmission Line Modelling and PerformanceAlexis AguillonNo ratings yet
- PWM 2 Level and 3 LevelDocument7 pagesPWM 2 Level and 3 LevelnewrajasinghNo ratings yet
- User Guide: EVBD-ACPL-C87B/C87A/C870Document4 pagesUser Guide: EVBD-ACPL-C87B/C87A/C870Marcel BlinduNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument1 pageTransmission LinesPfunzo MammbaNo ratings yet
- GET-Electrical Test Paper PDFDocument10 pagesGET-Electrical Test Paper PDFatul sachanNo ratings yet
- Doc-A.9-Driver Card For Single Phase Inverter Using Skhi22br PDFDocument66 pagesDoc-A.9-Driver Card For Single Phase Inverter Using Skhi22br PDFsivananda11No ratings yet
- Chapter - I: Per Unit (PU) Representation of Power System Elements (Contd)Document9 pagesChapter - I: Per Unit (PU) Representation of Power System Elements (Contd)Asrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Behavior of BJT'S: University of Minnesota - EE 3101Document17 pagesHigh Frequency Behavior of BJT'S: University of Minnesota - EE 3101Gavin O'ConnellNo ratings yet
- Current and Voltage RelationshipDocument4 pagesCurrent and Voltage RelationshipMike AndayaNo ratings yet
- UEE602 Tut Sheets 1Document12 pagesUEE602 Tut Sheets 1Kulvinder Singh0% (1)
- PSRRDocument8 pagesPSRRAkhil MehtaNo ratings yet
- 87Document5 pages87vinay kumarNo ratings yet
- Code: R7310204 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R07) Supplementary Examinations, May 2013Document1 pageCode: R7310204 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R07) Supplementary Examinations, May 2013sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ps-Ii SubDocument10 pagesPs-Ii Subsusruthareddy01No ratings yet
- Assigment EPSD Lab PDFDocument5 pagesAssigment EPSD Lab PDFArjit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) - Electrical Power System-Transmission LineDocument2 pagesSheet (1) - Electrical Power System-Transmission LineMAHMOUD ELNUSSARYNo ratings yet
- 3-Lesson Notes Lec 30 Short Medium Line ModelDocument7 pages3-Lesson Notes Lec 30 Short Medium Line ModelAsadAliAwanNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Lab 1.revisedDocument38 pagesPower Systems Lab 1.revisedJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Cable Parameters For Different Cable ShapesDocument7 pagesCalculation of Cable Parameters For Different Cable ShapestechtricNo ratings yet
- PWMDocument7 pagesPWMsiddhartha_anirban100% (1)
- Eeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Document5 pagesEeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Kabir MohammedNo ratings yet
- PSS Lab (18EEL76) - Lab - Exam - QPDocument4 pagesPSS Lab (18EEL76) - Lab - Exam - QPkurdso kurizNo ratings yet
- 2.transmission Line TheoryDocument20 pages2.transmission Line Theoryhacker_05No ratings yet
- Ee 328 Lecture 11Document55 pagesEe 328 Lecture 11somethingfornowNo ratings yet
- Power System Steady State Analysis AssignmentDocument3 pagesPower System Steady State Analysis Assignmentosama munirNo ratings yet
- 04 ECE405Tut 2013 Solution PDFDocument8 pages04 ECE405Tut 2013 Solution PDFDavy MardamootooNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 PDFQaiSer Hayat BhabhaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Inductance and Capacitance in Power System Transmission Lines Using Finite Element Analysis MethodDocument6 pagesCalculation of Inductance and Capacitance in Power System Transmission Lines Using Finite Element Analysis Methodcommunist88No ratings yet
- Lecture PTD 9 and 10Document7 pagesLecture PTD 9 and 10Farhan MukhtiarNo ratings yet
- Compact Power Efficient Rail To Rail in Out Op Amp RonDocument9 pagesCompact Power Efficient Rail To Rail in Out Op Amp RonmartianiNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Cable Parameters For Different Cable Shapes: AbstractDocument7 pagesCalculation of Cable Parameters For Different Cable Shapes: AbstractSrëëdhär SriëëNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission Line Parameter EstimationDocument5 pagesPower Transmission Line Parameter EstimationBogdan VicolNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis ImportantDocument8 pagesPower System Analysis Importantsparkle courageNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Three Phase RectifiersDocument19 pagesUncontrolled Three Phase RectifiersTetsusaigaNo ratings yet
- Final Questions EPS-2 - 2019Document17 pagesFinal Questions EPS-2 - 2019punitsompuraNo ratings yet
- PowerSystem Set1Document9 pagesPowerSystem Set1shivansh gandhiNo ratings yet
- Operational Transconductance Amplifier For Highly Linear ApplicationDocument5 pagesOperational Transconductance Amplifier For Highly Linear ApplicationIJERDNo ratings yet
- Ee2404 Set1Document121 pagesEe2404 Set1Sachin Samy0% (1)
- Elimination of Dead-Time in PWM Controlled Inverters: Lihua Chen and Fang Z. PengDocument4 pagesElimination of Dead-Time in PWM Controlled Inverters: Lihua Chen and Fang Z. PengMarcel BlinduNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Session 14 and 15Document76 pagesSession 14 and 15zapzahtNo ratings yet
- Current Sources and Active LoadsDocument14 pagesCurrent Sources and Active LoadszapzahtNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Software CorpDocument2 pagesCambridge Software CorpzapzahtNo ratings yet
- Cc1 The Ice Breaker 2Document2 pagesCc1 The Ice Breaker 2zapzahtNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements and Measuring InstrumentsDocument317 pagesElectrical Measurements and Measuring InstrumentsbenwkgNo ratings yet
- Module I Part 3Document21 pagesModule I Part 3zapzahtNo ratings yet
- TempDocument14 pagesTempzapzahtNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Three Level Neutral Point Clamped Inverter Fed Induction Motor DriveDocument16 pagesThree Phase Three Level Neutral Point Clamped Inverter Fed Induction Motor DrivezapzahtNo ratings yet
- WEMPEC 30th BKLTDocument42 pagesWEMPEC 30th BKLTzapzahtNo ratings yet
- Updated Module 4Document117 pagesUpdated Module 4zapzahtNo ratings yet
- Delta Method: y y y yDocument32 pagesDelta Method: y y y yzapzahtNo ratings yet
- 10 InvertersDocument136 pages10 InverterszapzahtNo ratings yet
- duhhuv: 'R/Rxnqrzdq/Rqhdw7Hvod0Rwruv, QF" /lqnzloorshqlqqhzzlqgrzDocument4 pagesduhhuv: 'R/Rxnqrzdq/Rqhdw7Hvod0Rwruv, QF" /lqnzloorshqlqqhzzlqgrzzapzahtNo ratings yet
- Course Plan Ee3007 Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageCourse Plan Ee3007 Power ElectronicszapzahtNo ratings yet
- 13 AC RegulatorsDocument65 pages13 AC RegulatorszapzahtNo ratings yet
- 13 AC RegulatorsDocument65 pages13 AC RegulatorszapzahtNo ratings yet