Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsCpu Time Example: Computer A: 2Ghz Clock, 10S Cpu Time Designing Computer B
Cpu Time Example: Computer A: 2Ghz Clock, 10S Cpu Time Designing Computer B
Uploaded by
Hassaan SohailComputer A has a clock speed of 2GHz and takes 10 seconds of CPU time to complete a task. Computer B needs to complete the same task in 6 seconds. To do so, it must have a clock speed of 4GHz, as it takes 1.2 times as many clock cycles as Computer A but needs to finish in less time. CPU time depends on the instruction count, average cycles per instruction (CPI), and clock cycle time. Different computers or instruction types may have different CPI values, affecting their relative performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Computer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface, 2nd Edition Patterson & HennessyDocument118 pagesComputer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface, 2nd Edition Patterson & HennessyMr.Puppy80% (5)
- Computer Organization and Design 4th Edition Chapter 1 SlidesDocument9 pagesComputer Organization and Design 4th Edition Chapter 1 SlidesMark PerkinsNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1Document4 pagesAssignment - 1ZAEEM SULTAN KHAN0% (1)
- HW#2Document4 pagesHW#2Muhammad JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - CH 01Document18 pagesLecture 3 - CH 01aliNo ratings yet
- CS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3Document52 pagesCS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3ZunairaNazirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Lect2Document26 pagesChapter 01 Lect2Nhật Tân Võ VươngNo ratings yet
- Computer Abstractions and Technology Measuring PerformanceDocument21 pagesComputer Abstractions and Technology Measuring PerformanceS M Shamim শামীমNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyDocument46 pagesChapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyRony CudiJr PolisaintNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document12 pagesLecture 2Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2Document33 pagesLecture # 2Qamar SultanaNo ratings yet
- Ca Lecture 3Document23 pagesCa Lecture 3Nurislam ShouravNo ratings yet
- 02 PerformanceDocument13 pages02 PerformanceAliaa TarekNo ratings yet
- Topics in This Course ..: BITS Pilani, Pilani CampusDocument24 pagesTopics in This Course ..: BITS Pilani, Pilani Campusritik12041998No ratings yet
- Performance NumericalsDocument24 pagesPerformance Numericalsbbuli0510No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 2: Computer Abstractions and TechnologyDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Part 2: Computer Abstractions and TechnologyAfs AsgNo ratings yet
- 05 PerformanceDocument16 pages05 Performancesanjanamooli77No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Measuring PerformanceDocument30 pagesLecture 2 - Measuring PerformanceXrsamixNo ratings yet
- Chap1 PPADocument30 pagesChap1 PPAAmanda Judy AndradeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3Anam GhaffarNo ratings yet
- CS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3Document56 pagesCS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3Sohaib MehmoodNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 Edition Computer Evolution and PerformanceDocument28 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 Edition Computer Evolution and PerformanceHaider Ali ButtNo ratings yet
- Ca02 2014 PDFDocument79 pagesCa02 2014 PDFPance CvetkovskiNo ratings yet
- Cse - 321 - 2Document37 pagesCse - 321 - 2lizuNo ratings yet
- Advance Computer Architecture: Dr. Haroon Mahmood Assistant Professor NUCES LahoreDocument17 pagesAdvance Computer Architecture: Dr. Haroon Mahmood Assistant Professor NUCES Lahoreabbas zaidiNo ratings yet
- Sof108 Computer Architecture SESSION: September 2019 TUTORIAL 2 - Quantitative Principles of Computer DesignDocument3 pagesSof108 Computer Architecture SESSION: September 2019 TUTORIAL 2 - Quantitative Principles of Computer DesignMariamNo ratings yet
- The Role of Performance: Chapter - 2Document40 pagesThe Role of Performance: Chapter - 2Jafrin Iqbal ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture QuestionsDocument1 pageComputer Architecture QuestionsDEBJYOTI SARKARNo ratings yet
- Module 3.3 - Problems On PerformanceDocument54 pagesModule 3.3 - Problems On PerformanceKshitiz SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 2Document17 pagesComputer Architecture 2Hassan AsgharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyDocument46 pagesChapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyOmar Bin MohammedNo ratings yet
- CA184 - COA - AssignmentDocument5 pagesCA184 - COA - AssignmentTamaada JbNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document1 pageHW 1213k2j3hj2h3j2g1No ratings yet
- COA ASSIGNMENT 1 - AnswersDocument6 pagesCOA ASSIGNMENT 1 - AnswersPadmanaban MNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Lecture 2 - Performance MeasurementDocument25 pagesWeek 2 - Lecture 2 - Performance MeasurementViệt HưngNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Answers)Document35 pagesWeek 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Answers)dewierbarbell0nNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Q Only) - Tagged 2Document23 pagesWeek 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Q Only) - Tagged 2dewierbarbell0nNo ratings yet
- Wednesday 03 March, 2021: Computer Performance MeasurementDocument19 pagesWednesday 03 March, 2021: Computer Performance MeasurementTwinomugisha MorrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Computing For PerformanceDocument38 pagesLesson 3 - Computing For PerformanceROMMEL DORINNo ratings yet
- CA 02 PerformanceDocument21 pagesCA 02 Performancewlsh2001No ratings yet
- 08 PerformanceDocument25 pages08 PerformanceNguyễn Quốc TrungNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture Unit 1 - Phase 2 PDFDocument26 pagesComputer Architecture Unit 1 - Phase 2 PDFvithyaNo ratings yet
- 1 Computer - Component PerformanceDocument4 pages1 Computer - Component Performancekhoipn.23bi14228No ratings yet
- Inroduction and Performance AnalysisDocument29 pagesInroduction and Performance AnalysisUmang AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cpu PerformanceDocument13 pagesCpu PerformanceParth ChauhanNo ratings yet
- PerformanceDocument26 pagesPerformanceStarqueenNo ratings yet
- Performance MeasuresDocument25 pagesPerformance MeasuresMuckie MarfeNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 Performance Evaluation 2011Document34 pagesLecture4 Performance Evaluation 2011bakaasamaNo ratings yet
- COMP 303 Computer ArchitectureDocument34 pagesCOMP 303 Computer ArchitectureShivani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Muhammad SalahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Borotho Molemo100% (1)
- Chapter 01 ExercicesDocument5 pagesChapter 01 ExercicesYassine BlaliNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Architecture: Van-Khoa Pham (PHD.)Document25 pagesComputer Organization & Architecture: Van-Khoa Pham (PHD.)thuan phamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Performance/Power, MIPS InstructionsDocument18 pagesLecture 3: Performance/Power, MIPS Instructionskotewed571No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - 7 - On - PerformanceDocument31 pagesLecture 6 - 7 - On - PerformanceNagendraNo ratings yet
- 09 PerfDocument22 pages09 PerfPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Understanding PerformanceDocument31 pagesAssessing and Understanding PerformanceHoang Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 & 12Document17 pagesExercise 3 & 12perreiragabriel172No ratings yet
- PerformanceDocument42 pagesPerformanceapi-26072581No ratings yet
- Electronic Structure Calculations on Graphics Processing Units: From Quantum Chemistry to Condensed Matter PhysicsFrom EverandElectronic Structure Calculations on Graphics Processing Units: From Quantum Chemistry to Condensed Matter PhysicsRoss C. WalkerNo ratings yet
Cpu Time Example: Computer A: 2Ghz Clock, 10S Cpu Time Designing Computer B
Cpu Time Example: Computer A: 2Ghz Clock, 10S Cpu Time Designing Computer B
Uploaded by
Hassaan Sohail0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesComputer A has a clock speed of 2GHz and takes 10 seconds of CPU time to complete a task. Computer B needs to complete the same task in 6 seconds. To do so, it must have a clock speed of 4GHz, as it takes 1.2 times as many clock cycles as Computer A but needs to finish in less time. CPU time depends on the instruction count, average cycles per instruction (CPI), and clock cycle time. Different computers or instruction types may have different CPI values, affecting their relative performance.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chapter 1 Part 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentComputer A has a clock speed of 2GHz and takes 10 seconds of CPU time to complete a task. Computer B needs to complete the same task in 6 seconds. To do so, it must have a clock speed of 4GHz, as it takes 1.2 times as many clock cycles as Computer A but needs to finish in less time. CPU time depends on the instruction count, average cycles per instruction (CPI), and clock cycle time. Different computers or instruction types may have different CPI values, affecting their relative performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesCpu Time Example: Computer A: 2Ghz Clock, 10S Cpu Time Designing Computer B
Cpu Time Example: Computer A: 2Ghz Clock, 10S Cpu Time Designing Computer B
Uploaded by
Hassaan SohailComputer A has a clock speed of 2GHz and takes 10 seconds of CPU time to complete a task. Computer B needs to complete the same task in 6 seconds. To do so, it must have a clock speed of 4GHz, as it takes 1.2 times as many clock cycles as Computer A but needs to finish in less time. CPU time depends on the instruction count, average cycles per instruction (CPI), and clock cycle time. Different computers or instruction types may have different CPI values, affecting their relative performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
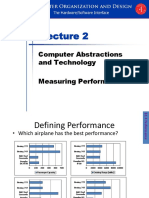
CPU Time Example
Computer A: 2GHz clock, 10s CPU time
Designing Computer B
Aim for 6s CPU time
Can do faster clock, but causes 1.2 clock cycles
How fast must Computer B clock be?
Clock CyclesB 1.2 Clock Cycles A
Clock RateB
CPU Time B
6s
Clock Cycles A CPU Time A Clock Rate A
10s 2GHz 20 10 9
1.2 20 10 9 24 10 9
Clock RateB
4GHz
6s
6s
Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and Technology 1
Instruction Count and CPI
Clock Cycles Instruction Count Cycles per Instruction
CPU Time Instruction Count CPI Clock Cycle Time
Instruction Count CPI
Clock Rate
Instruction Count for a program
Determined by program, ISA and compiler
Average cycles per instruction
Determined by CPU hardware
If different instructions have different CPI
Average CPI affected by instruction mix
Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and Technology 2
CPI Example
Computer A: Cycle Time = 250ps, CPI = 2.0
Computer B: Cycle Time = 500ps, CPI = 1.2
Same ISA
Which is faster, and by how much?
CPU Time
CPU Time
Instruction Count CPI Cycle Time
A
A
I 2.0 250ps I 500ps
A is faster
Instruction Count CPI Cycle Time
B
B
I 1.2 500ps I 600ps
CPU Time
B I 600ps 1.2
CPU Time
I 500ps
A
by this much
Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and Technology 3
CPI in More Detail
If different instruction classes take different
numbers of cycles
n
Clock Cycles (CPIi Instruction Count i )
i1
Weighted average CPI
n
Clock Cycles
Instruction Count i
CPI
CPIi
Instruction Count i1
Instruction Count
Relative frequency
Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and Technology 4
You might also like
- Computer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface, 2nd Edition Patterson & HennessyDocument118 pagesComputer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface, 2nd Edition Patterson & HennessyMr.Puppy80% (5)
- Computer Organization and Design 4th Edition Chapter 1 SlidesDocument9 pagesComputer Organization and Design 4th Edition Chapter 1 SlidesMark PerkinsNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1Document4 pagesAssignment - 1ZAEEM SULTAN KHAN0% (1)
- HW#2Document4 pagesHW#2Muhammad JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - CH 01Document18 pagesLecture 3 - CH 01aliNo ratings yet
- CS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3Document52 pagesCS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3ZunairaNazirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Lect2Document26 pagesChapter 01 Lect2Nhật Tân Võ VươngNo ratings yet
- Computer Abstractions and Technology Measuring PerformanceDocument21 pagesComputer Abstractions and Technology Measuring PerformanceS M Shamim শামীমNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyDocument46 pagesChapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyRony CudiJr PolisaintNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document12 pagesLecture 2Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2Document33 pagesLecture # 2Qamar SultanaNo ratings yet
- Ca Lecture 3Document23 pagesCa Lecture 3Nurislam ShouravNo ratings yet
- 02 PerformanceDocument13 pages02 PerformanceAliaa TarekNo ratings yet
- Topics in This Course ..: BITS Pilani, Pilani CampusDocument24 pagesTopics in This Course ..: BITS Pilani, Pilani Campusritik12041998No ratings yet
- Performance NumericalsDocument24 pagesPerformance Numericalsbbuli0510No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 2: Computer Abstractions and TechnologyDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Part 2: Computer Abstractions and TechnologyAfs AsgNo ratings yet
- 05 PerformanceDocument16 pages05 Performancesanjanamooli77No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Measuring PerformanceDocument30 pagesLecture 2 - Measuring PerformanceXrsamixNo ratings yet
- Chap1 PPADocument30 pagesChap1 PPAAmanda Judy AndradeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3Anam GhaffarNo ratings yet
- CS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3Document56 pagesCS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3Sohaib MehmoodNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 Edition Computer Evolution and PerformanceDocument28 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 Edition Computer Evolution and PerformanceHaider Ali ButtNo ratings yet
- Ca02 2014 PDFDocument79 pagesCa02 2014 PDFPance CvetkovskiNo ratings yet
- Cse - 321 - 2Document37 pagesCse - 321 - 2lizuNo ratings yet
- Advance Computer Architecture: Dr. Haroon Mahmood Assistant Professor NUCES LahoreDocument17 pagesAdvance Computer Architecture: Dr. Haroon Mahmood Assistant Professor NUCES Lahoreabbas zaidiNo ratings yet
- Sof108 Computer Architecture SESSION: September 2019 TUTORIAL 2 - Quantitative Principles of Computer DesignDocument3 pagesSof108 Computer Architecture SESSION: September 2019 TUTORIAL 2 - Quantitative Principles of Computer DesignMariamNo ratings yet
- The Role of Performance: Chapter - 2Document40 pagesThe Role of Performance: Chapter - 2Jafrin Iqbal ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture QuestionsDocument1 pageComputer Architecture QuestionsDEBJYOTI SARKARNo ratings yet
- Module 3.3 - Problems On PerformanceDocument54 pagesModule 3.3 - Problems On PerformanceKshitiz SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 2Document17 pagesComputer Architecture 2Hassan AsgharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyDocument46 pagesChapter 1 Computer Abstractions and TechnologyOmar Bin MohammedNo ratings yet
- CA184 - COA - AssignmentDocument5 pagesCA184 - COA - AssignmentTamaada JbNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document1 pageHW 1213k2j3hj2h3j2g1No ratings yet
- COA ASSIGNMENT 1 - AnswersDocument6 pagesCOA ASSIGNMENT 1 - AnswersPadmanaban MNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Lecture 2 - Performance MeasurementDocument25 pagesWeek 2 - Lecture 2 - Performance MeasurementViệt HưngNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Answers)Document35 pagesWeek 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Answers)dewierbarbell0nNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Q Only) - Tagged 2Document23 pagesWeek 10 Part 02 - Processor Performance (Q Only) - Tagged 2dewierbarbell0nNo ratings yet
- Wednesday 03 March, 2021: Computer Performance MeasurementDocument19 pagesWednesday 03 March, 2021: Computer Performance MeasurementTwinomugisha MorrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Computing For PerformanceDocument38 pagesLesson 3 - Computing For PerformanceROMMEL DORINNo ratings yet
- CA 02 PerformanceDocument21 pagesCA 02 Performancewlsh2001No ratings yet
- 08 PerformanceDocument25 pages08 PerformanceNguyễn Quốc TrungNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture Unit 1 - Phase 2 PDFDocument26 pagesComputer Architecture Unit 1 - Phase 2 PDFvithyaNo ratings yet
- 1 Computer - Component PerformanceDocument4 pages1 Computer - Component Performancekhoipn.23bi14228No ratings yet
- Inroduction and Performance AnalysisDocument29 pagesInroduction and Performance AnalysisUmang AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cpu PerformanceDocument13 pagesCpu PerformanceParth ChauhanNo ratings yet
- PerformanceDocument26 pagesPerformanceStarqueenNo ratings yet
- Performance MeasuresDocument25 pagesPerformance MeasuresMuckie MarfeNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 Performance Evaluation 2011Document34 pagesLecture4 Performance Evaluation 2011bakaasamaNo ratings yet
- COMP 303 Computer ArchitectureDocument34 pagesCOMP 303 Computer ArchitectureShivani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Muhammad SalahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Borotho Molemo100% (1)
- Chapter 01 ExercicesDocument5 pagesChapter 01 ExercicesYassine BlaliNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Architecture: Van-Khoa Pham (PHD.)Document25 pagesComputer Organization & Architecture: Van-Khoa Pham (PHD.)thuan phamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Performance/Power, MIPS InstructionsDocument18 pagesLecture 3: Performance/Power, MIPS Instructionskotewed571No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - 7 - On - PerformanceDocument31 pagesLecture 6 - 7 - On - PerformanceNagendraNo ratings yet
- 09 PerfDocument22 pages09 PerfPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Understanding PerformanceDocument31 pagesAssessing and Understanding PerformanceHoang Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 & 12Document17 pagesExercise 3 & 12perreiragabriel172No ratings yet
- PerformanceDocument42 pagesPerformanceapi-26072581No ratings yet
- Electronic Structure Calculations on Graphics Processing Units: From Quantum Chemistry to Condensed Matter PhysicsFrom EverandElectronic Structure Calculations on Graphics Processing Units: From Quantum Chemistry to Condensed Matter PhysicsRoss C. WalkerNo ratings yet