Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition of Co-Operative Bank Devine Defines A Co-Operative Bank As, "A Mutual Society Formed Composed and
Definition of Co-Operative Bank Devine Defines A Co-Operative Bank As, "A Mutual Society Formed Composed and
Uploaded by
akhikonikkaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Co-Operative Bank Devine Defines A Co-Operative Bank As, "A Mutual Society Formed Composed and
Definition of Co-Operative Bank Devine Defines A Co-Operative Bank As, "A Mutual Society Formed Composed and
Uploaded by
akhikonikkaCopyright:
Available Formats
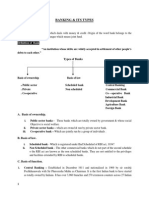
Definition of Co-operative bank
Devine defines a Co-operative Bank as, a mutual society formed composed and
governed by the working people themselves for encouraging regular savings and grinding
small loans on easy terms of interest and repayment
FEATURES OF CO-OPERATIVE BANK
They are organized and managed on the principles of Co-operation-self-help
and mutual help.
They function on no profit no loss basis.
Co-operative Bank performs all main banking functions of deposit mobilization,
supply of credit and provisions of remittance facilities.
Co-operative Bank does banking business mainly in the agricultural and rural
sector.
Co-operative Banks belongs to money market as well as capital market.
The sources of their funds are:
o Central and State Government.
o The RBI and NABARD.
o Other Co-operative Institution.
o Ownership funds.
o Deposits and debenture issues.
Co-operative Banks have federal structure of three tier linkage.
Some Co-operative Banks are Scheduled Banks and while other non-Scheduled
Banks.
Co-operative Banks accept current saving and fixed or time deposits from
individuals and institution.
You might also like
- Understand Banks & Financial Markets: An Introduction to the International World of Money & FinanceFrom EverandUnderstand Banks & Financial Markets: An Introduction to the International World of Money & FinanceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Cooperative BankDocument14 pagesCooperative Bank679shrishti Singh0% (1)
- Cooperative Banking ProjectDocument53 pagesCooperative Banking ProjectselvamNo ratings yet
- Co Operative Banking ProjectDocument55 pagesCo Operative Banking ProjectlizamandevNo ratings yet
- Co-Operative Bank: Sr. No. Topic NameDocument66 pagesCo-Operative Bank: Sr. No. Topic NameAmey DalviNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Between Two Co-Opertive BankDocument47 pagesComparative Study Between Two Co-Opertive BankParag More71% (7)
- Introduction To Co OpsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Co Opssapanamadas4540No ratings yet
- Banking InnovationDocument85 pagesBanking InnovationJaya DasNo ratings yet
- Commercial BanksDocument9 pagesCommercial BanksPrathyusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Akshit and AkshayDocument9 pagesAkshit and Akshaychaitali lakhaniNo ratings yet
- Co Operative Banking ProjectDocument55 pagesCo Operative Banking Projectamit9_prince91% (11)
- Introduction To Co-Operative Banking: DefinationDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Co-Operative Banking: DefinationHelloprojectNo ratings yet
- Banking TheoryDocument299 pagesBanking TheoryMohammedNo ratings yet
- NSDC - Banking Correspondent Power PointDocument114 pagesNSDC - Banking Correspondent Power PointsubiNo ratings yet
- All About Cooperative Banks in India GK Notes For SSC Banking Exams in PDFDocument8 pagesAll About Cooperative Banks in India GK Notes For SSC Banking Exams in PDFramuvindiaNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument38 pagesBankingسلطان علی طارقNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Banks: School of Law, Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, BangaloreDocument13 pagesCooperative Banks: School of Law, Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, BangaloreHIMANSHU GOYALNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Sarswat Co POOJADocument9 pagesComparative Study of Sarswat Co POOJARavi harhareNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument8 pagesBankingkarthiNo ratings yet
- Nature of Banking in IndiaDocument11 pagesNature of Banking in Indiasushma_namepalliNo ratings yet
- Co Operative Bank 48Document35 pagesCo Operative Bank 48Akanksha SawantNo ratings yet
- Co-Operative Bank 1Document14 pagesCo-Operative Bank 1aishu borseNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Deposits and Loans 7 (AutoRecovered)Document18 pagesAnalyzing Deposits and Loans 7 (AutoRecovered)samritisaini1No ratings yet
- Cooperative BankingDocument8 pagesCooperative BankingvmktptNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of BankingDocument63 pagesPrinciples and Practices of BankingbasuNo ratings yet
- Projct 2Document46 pagesProjct 2Varinder BhukalNo ratings yet
- Pooja Project BB (AutoRecovered)Document51 pagesPooja Project BB (AutoRecovered)Ravi harhareNo ratings yet
- Non Banking InstitutionsDocument42 pagesNon Banking Institutionsramesh.kNo ratings yet
- Pooja Project BBDocument22 pagesPooja Project BBRavi harhareNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1. Introduction To Co-Operative Banking: DefinationDocument54 pagesCh. 1. Introduction To Co-Operative Banking: DefinationBinoy MehtaNo ratings yet
- 1.industry Overview of Co-Operative Bank: 1.1 Defination: Co-Opertive BankingDocument6 pages1.industry Overview of Co-Operative Bank: 1.1 Defination: Co-Opertive BankingGokul KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Banking StructureDocument16 pagesBanking StructuresikandarNo ratings yet
- Commercial and Cooperative BanksDocument18 pagesCommercial and Cooperative BanksDODONo ratings yet
- Co-Operative Banks in IndiaDocument9 pagesCo-Operative Banks in Indiachaitali jadhavNo ratings yet
- Introduction PDCBDocument8 pagesIntroduction PDCBletter2lalNo ratings yet
- Co-Operative Banks: by Kaushal GaudDocument10 pagesCo-Operative Banks: by Kaushal GaudKunal GaudNo ratings yet
- Banking Law Draft 2022Document11 pagesBanking Law Draft 2022sehnaz NaazNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document4 pagesAssignment - 2VNo ratings yet
- Ssee Unit 05Document42 pagesSsee Unit 05NayanNo ratings yet
- Banking Unit 2Document61 pagesBanking Unit 2Nidharshanaa V RNo ratings yet
- Navyashree, B. M. PAMB 0118Document30 pagesNavyashree, B. M. PAMB 0118Navyashree B MNo ratings yet
- Pallavi Co-Operative Bank FinalDocument70 pagesPallavi Co-Operative Bank FinalS101117400076No ratings yet
- Notes UNIT 1Document9 pagesNotes UNIT 1Shashank SonkarNo ratings yet
- Regulation Financial Institutions GovernmentDocument4 pagesRegulation Financial Institutions GovernmentLeah DavalosNo ratings yet
- Full Info of Coperative BanksDocument15 pagesFull Info of Coperative BanksAkash ShirsatNo ratings yet
- Rajatha Acharya - 1ay21ba093 - Main ThesisDocument55 pagesRajatha Acharya - 1ay21ba093 - Main Thesisdeekshushetty18No ratings yet
- Co Operative BanksDocument13 pagesCo Operative Banksamyncharaniya100% (4)
- BII Final NOTES UNIT1Document26 pagesBII Final NOTES UNIT1SOHAIL makandarNo ratings yet
- What Is A BankDocument14 pagesWhat Is A BankNandini JaganNo ratings yet
- Bank ManagementDocument29 pagesBank Managementshivam kumarNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument13 pagesBanking in IndiaMurahari NANo ratings yet
- 9155IBT Excellent Book On Banking AwarenessDocument0 pages9155IBT Excellent Book On Banking Awarenesssundeep_100No ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- History of Co-Operative Banks in IndiaDocument2 pagesHistory of Co-Operative Banks in IndiaakhikonikkaNo ratings yet
- In The Words of Alina Mihaela Dima "Credit Analysis Is The Method by Which OneDocument1 pageIn The Words of Alina Mihaela Dima "Credit Analysis Is The Method by Which OneakhikonikkaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Level of Customers RMDocument3 pagesAcceptance Level of Customers RMakhikonikkaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Level of CustomersDocument6 pagesAcceptance Level of CustomersakhikonikkaNo ratings yet