Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Savannahpbmodel
Savannahpbmodel
Uploaded by
api-284281704Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Classroom-Based Teacher-Led Action Research As A Process For EnhDocument16 pagesClassroom-Based Teacher-Led Action Research As A Process For Enhsell hassNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Curriculum DevelopmentDocument15 pagesModule 4 Curriculum Developmentreyma panerNo ratings yet
- Models of Curriculum Development PPT 25 NOVDocument44 pagesModels of Curriculum Development PPT 25 NOVPriyanka SheoranNo ratings yet
- Cleary Validacion SRsI SRDocument16 pagesCleary Validacion SRsI SRLou GabyNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking in The Business Curriculum: Nora M. BraunDocument6 pagesCritical Thinking in The Business Curriculum: Nora M. BraunSteven ChoNo ratings yet
- Book - (J - Scheerens - Cees - A - W - Glas - Sally - Thomas) - Education Evaluation, Assessment and Monitoring PDFDocument425 pagesBook - (J - Scheerens - Cees - A - W - Glas - Sally - Thomas) - Education Evaluation, Assessment and Monitoring PDFSyamsul Anwar100% (3)
- Chapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of EvaluationDocument11 pagesChapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of Evaluationvea verzonNo ratings yet
- SavannahinquirymodelDocument1 pageSavannahinquirymodelapi-284281704No ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University Semester Terminal Exam Autumn 2020 Program /level: B. ED Title /course Code: Curriculum Development (8603)Document8 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University Semester Terminal Exam Autumn 2020 Program /level: B. ED Title /course Code: Curriculum Development (8603)Osama Yaqoob0% (1)
- Action - Research - Final Paper (REVISED) - 100Document29 pagesAction - Research - Final Paper (REVISED) - 100Jacquin MokayaNo ratings yet
- DWYER Assessment and Classroom Learning Theory and PracticeDocument8 pagesDWYER Assessment and Classroom Learning Theory and PracticeSAMIR ARTURO IBARRA BOLAÑOSNo ratings yet
- How Far Have We Moved Toward The Integration of THDocument14 pagesHow Far Have We Moved Toward The Integration of THpthanhthuy459No ratings yet
- 1299760628curriculum Development ModelsDocument13 pages1299760628curriculum Development Modelshoangsang79No ratings yet
- Theoretical Conceptual Methodological and InstructDocument10 pagesTheoretical Conceptual Methodological and InstructJaenelyn AlquizarNo ratings yet
- 6462 Assignment No 1Document16 pages6462 Assignment No 1Muhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- What We Learn in Action ResearchDocument3 pagesWhat We Learn in Action ResearchAnonymous pHooz5aH6VNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data-Driven Educational Decision MakingDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Data-Driven Educational Decision MakingThe Holy KashmirNo ratings yet
- Interventional Research CRMEF CASADocument6 pagesInterventional Research CRMEF CASAIbtissam LaNo ratings yet
- 61dc2ca57649a4 83414233Document6 pages61dc2ca57649a4 83414233mandyndawana71No ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument61 pagesAction ResearchLance Aldrin Adion67% (3)
- ARTIKEL Sigit SusetiadiDocument4 pagesARTIKEL Sigit Susetiadimiftahul rahmat9No ratings yet
- Loyen Set AlDocument20 pagesLoyen Set AlRiana RurmanNo ratings yet
- Self-Directed Learning in Problem-Based Learning and Its Relationships With Self-Regulated LearningDocument19 pagesSelf-Directed Learning in Problem-Based Learning and Its Relationships With Self-Regulated LearningRiana RurmanNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 11Document9 pagesSummary Chapter 11IO OutletsNo ratings yet
- 4 HolisticAssessmentDocument10 pages4 HolisticAssessmentSmriti BalyanNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Attitudes Towards Values Across The Curriculum-A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesTeachers' Attitudes Towards Values Across The Curriculum-A Systematic Literature Reviewliza83tintabahasaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Classroom AssessmentDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Classroom Assessmentapi-405351173No ratings yet
- DiominoDocument4 pagesDiominoMicah Joy DiominoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in Writing The ResearchDocument62 pagesGuidelines in Writing The ResearchKaren GayNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter 2Document55 pages09 Chapter 2krishanNo ratings yet
- Are You Assessment Literate?Document23 pagesAre You Assessment Literate?Eddy White, PhD100% (2)
- Traditional and Alternative Issues in Students' Evaluation: Simona EftimieDocument6 pagesTraditional and Alternative Issues in Students' Evaluation: Simona Eftimievinoelnino10No ratings yet
- Edu 602 Action Research WritingDocument40 pagesEdu 602 Action Research WritingJohn Lopez CruzNo ratings yet
- How Formative Assessments Drive Instructional Decision Making in The ClassroomDocument7 pagesHow Formative Assessments Drive Instructional Decision Making in The ClassroomCharles Anthony RamosNo ratings yet
- Understand Theories Principles and MoDocument9 pagesUnderstand Theories Principles and MoWahyu Adi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Inquiry ModelDocument1 pageInquiry Modelapi-284127506No ratings yet
- Education Policy Analysis ArchivesDocument18 pagesEducation Policy Analysis ArchivesNoldy PelenkahuNo ratings yet
- Final Reflection and ConclusionDocument6 pagesFinal Reflection and Conclusionapi-245618331No ratings yet
- Learning Theories: Theories and Models of Learning For Educational Research and Practice. This KnowledgeDocument14 pagesLearning Theories: Theories and Models of Learning For Educational Research and Practice. This KnowledgeDiane ChuNo ratings yet
- 1st READING Learning StrategiesDocument3 pages1st READING Learning Strategiesnirak875No ratings yet
- Loyens, 2008Document18 pagesLoyens, 2008CatharinaWidiartiniNo ratings yet
- OERDoc 575 35579 11 08 2021Document28 pagesOERDoc 575 35579 11 08 2021Hanifa NorodinNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesPresident Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityElvin Francis LabandeloNo ratings yet
- Labao Curriculum Instruction Paper 2Document8 pagesLabao Curriculum Instruction Paper 2Arnelyn LabaoNo ratings yet
- Formative and Summative Assessment 2Document8 pagesFormative and Summative Assessment 2Ryan Neil CajucomNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Kaedah PenyelidikanDocument8 pagesPengenalan Kaedah Penyelidikanrapunzel777No ratings yet
- Fass 352 Literature Review Ranim AnnousDocument16 pagesFass 352 Literature Review Ranim Annousapi-610160797No ratings yet
- Comparative Study Assessment For of and As LearningDocument15 pagesComparative Study Assessment For of and As LearningCristina SalenNo ratings yet
- NITTTR Module 6Document169 pagesNITTTR Module 6Indrajeet MoreNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Metacognition and SelfDocument4 pagesThe Difference Between Metacognition and Selfarhodes777No ratings yet
- Statistics Test Questions: Content and TrendsDocument16 pagesStatistics Test Questions: Content and TrendsAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Strategi Pembelajaran Dalam Penelitian Tindakan KelasDocument10 pagesStrategi Pembelajaran Dalam Penelitian Tindakan KelasCitraNo ratings yet
- Action Research Paper Classroom ManagementDocument4 pagesAction Research Paper Classroom Managementgzzjhsv9100% (1)
- Student Self Assessment Processes and ConsequencesDocument12 pagesStudent Self Assessment Processes and ConsequencesPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Document (12) (10) .EditedDocument22 pagesDocument (12) (10) .EditedSumaya Binte KashemNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument12 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentDa dang100% (6)
- Investigating Self-Regulation and Motivation: Historical Background, Methodological Developments, and Future ProspectsDocument18 pagesInvestigating Self-Regulation and Motivation: Historical Background, Methodological Developments, and Future ProspectskidNo ratings yet
- Beyond Behavioral ObjectivesREPORTDocument24 pagesBeyond Behavioral ObjectivesREPORTeugene louie ibarraNo ratings yet
- PSSST : Silence Please!Document48 pagesPSSST : Silence Please!dharwin geronimoNo ratings yet
- Bell-Shape Testing System: Testing the Students Based on Simple and Complex Teachings Related to Bloom’S Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesFrom EverandBell-Shape Testing System: Testing the Students Based on Simple and Complex Teachings Related to Bloom’S Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesNo ratings yet
- SavannahresumeDocument2 pagesSavannahresumeapi-284281704No ratings yet
- SavannahinquirymodelDocument1 pageSavannahinquirymodelapi-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahgdmodel 3Document1 pageSavannahgdmodel 3api-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahcamodel 2Document1 pageSavannahcamodel 2api-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahldmodel 2Document1 pageSavannahldmodel 2api-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahdimodel 2Document1 pageSavannahdimodel 2api-284281704No ratings yet
- SavannahdiscussionmodelDocument1 pageSavannahdiscussionmodelapi-284281704No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument57 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementSudarshan MankadNo ratings yet
- Hataraku Maou-Sama! - 17 (Yen Press)Document223 pagesHataraku Maou-Sama! - 17 (Yen Press)Mike Chui100% (1)
- A Study On Consumer Behaviour in Real Estate SectorDocument94 pagesA Study On Consumer Behaviour in Real Estate SectorNadeem khan100% (2)
- Booking Report 11-18-2020Document2 pagesBooking Report 11-18-2020WCTV Digital Team0% (2)
- Anls Pressure DiagDocument15 pagesAnls Pressure DiagazareiforoushNo ratings yet
- De Thi Thu THPT Tieng Anh 2016 MR BaoDocument14 pagesDe Thi Thu THPT Tieng Anh 2016 MR BaoMai Long TânNo ratings yet
- Diagn Org EffDocument33 pagesDiagn Org Effmargonomitro1No ratings yet
- Chikungunya Virus DiseaseDocument25 pagesChikungunya Virus DiseasemamaluNo ratings yet
- Praise of White Tara by Gedun DrukpaDocument2 pagesPraise of White Tara by Gedun DrukpaŚīla ViśodhanaNo ratings yet
- Foucault, Michel - What Is EnlightenmentDocument15 pagesFoucault, Michel - What Is EnlightenmentDhiraj Menon100% (1)
- Written Statement SwapnilDocument5 pagesWritten Statement SwapnilMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- FN-LM07 Filipinos Conquering The WorldDocument3 pagesFN-LM07 Filipinos Conquering The WorldMichelle Em GerabanNo ratings yet
- Thesis Guidelines UitmDocument6 pagesThesis Guidelines UitmBuyAPhilosophyPaperSingapore100% (2)
- Rabagia - MatenTertiary Tectonic and Sedimentological Evolution of The South Carpathians Foredeep: Tectonic Versus Eustatic Controlco (1999)Document22 pagesRabagia - MatenTertiary Tectonic and Sedimentological Evolution of The South Carpathians Foredeep: Tectonic Versus Eustatic Controlco (1999)Lex AlexaNo ratings yet
- Essay On How To Conduct Oneself Inside The CompanyDocument4 pagesEssay On How To Conduct Oneself Inside The CompanyMadielyn Santarin MirandaNo ratings yet
- EDU Development of Malaysian EducationDocument47 pagesEDU Development of Malaysian EducationNabilFikriChumiNo ratings yet
- Imrad FormatDocument34 pagesImrad FormatKc MostachoNo ratings yet
- A Dios Le Pido - by Juanes, English Translation of Lyrics - SonglationsDocument4 pagesA Dios Le Pido - by Juanes, English Translation of Lyrics - SonglationsaguasamargasNo ratings yet
- Job Designing Analysis BSNLDocument75 pagesJob Designing Analysis BSNLpavanNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect TenseDocument17 pagesThe Present Perfect TenseHugo AldereteNo ratings yet
- S3 Proofreading Answer 1-10Document10 pagesS3 Proofreading Answer 1-10Edwin FongNo ratings yet
- Learner Analysis QuestionsDocument1 pageLearner Analysis Questionsapi-323641842No ratings yet
- Violated and Transcended BodiesDocument80 pagesViolated and Transcended BodiesFideblaymid CruzNo ratings yet
- PerDev Learning ActivityDocument4 pagesPerDev Learning ActivitydwacindyfjNo ratings yet
- An Appraisal of The Impact of Holy Spirit in The Life of BelieversDocument8 pagesAn Appraisal of The Impact of Holy Spirit in The Life of BelieversAnonymous ftifJFgbNo ratings yet
- Haddad v. Indiana Pacers Et Al - Document No. 82Document17 pagesHaddad v. Indiana Pacers Et Al - Document No. 82Justia.com100% (1)
- Criminal Law 2Document79 pagesCriminal Law 2aris apridNo ratings yet
- Financing Foreign Trade PDFDocument16 pagesFinancing Foreign Trade PDFHemanth Kumar89% (9)
- List of Secretary Union Councils District Sialkot No. & Name of Union Council Name of Secretary UC Cell NumbersDocument8 pagesList of Secretary Union Councils District Sialkot No. & Name of Union Council Name of Secretary UC Cell NumbersAhmed MaherNo ratings yet
- 17th International Conference On Multiphase Technology 2015: Cannes, France 10 - 12 June 2015Document6 pages17th International Conference On Multiphase Technology 2015: Cannes, France 10 - 12 June 2015kglorstadNo ratings yet
Savannahpbmodel
Savannahpbmodel
Uploaded by
api-284281704Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Savannahpbmodel
Savannahpbmodel
Uploaded by
api-284281704Copyright:
Available Formats
Reading: Phonemics
Box frame
TM
Makes Sense
Sense Strategies
Strategies
Makes
Name: Savannah Smith
2008 Edwin Ellis, All Rights Reserved Published by Makes Sense Strategies, LLC, Northport, AL www.MakesSenseStrategies.com
Date: March
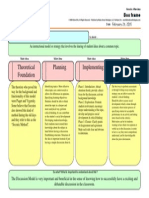
ProblemSolvingModel
19, 2015
Is about
Asetofteachingmodelsthatusesproblemsasthefocusfordevelopingproblemsolvingskills,content,andselfregulation.
TheoreticalFoundation
Problem-Based Learning can be thought of as a
combination of cognitive and social constructivist theories
that were developed by Piaget and Vygotsky.
Problem-Based Learning and the Models that go along with
it (PBL) were introduced not only by those two theorists
but was also improved by Howard Burrows, an American
physician and medical educator, in the late 60s within the
framework of the medical program at McMaster University
in Canada.
Assessment
Alternatetestingisimportantandcrucialwiththemodel
becauseitallowstheteachertogradeprocessoutcomes.
Performanceassessments,systematicobservations,
checklists,andratingsarealsoadditionalwaysassessment
canbedonetogradetheprocesses.
Casesstudiesareanadditionalwaytoassesslearning
duringthismodelaswellbecauseitallowsteachersto
assessthedifferentcomponentprocessesinInquiry.
Planning
IdentifyTopicMustbecomplexandabstractcomparedtoother
models,theywonthavespecificcharacteristics.
SpecifyLearningObjectivesTherearetwotypesoflearning
objectives,onecanbemetduringonelessonandtheothertakes
time(developingproblemsolvingabilitiesandbecomingself
learners.
IdentifyProblemMosteffectiveifclear,concrete,and
personalized,studentsmusthaveenoughpriorknowledgetosolve
theproblem.
AccessMaterialsStudentsmusthaveaccesstomaterialstosolve
theproblem.
Implementing
Phase1:ReviewandPresentProblemTeacherwillreviewknowledge
neededtosolvetheproblem,thenwillgiveaspecific,concreteproblem
forthestudentstosolve.
Phase2:DeviseaStrategyStudentswilldeviseastrategytosolvethe
concreteanddetailedproblemandthentheteacherwilloffereffective
feedback.
Phase3:ImplementingtheStrategyStudentsimplementtheirstrategies
whiletheteachercontinuouslymonitorsandmaygivesomefeedback.
Phase4:DiscussandEvaluateResultsTheteacherguidesadiscussion
ofthestudentsstrategiesandtheresultsortheireffortsthattheyhave
found.
Motivation
AuthenticTaskRequireunderstandingthatcanbeused
outsideoftheclassroom,whichmotivatesstudents
becausetheywilluseitsomewhereelse.
InvolvementandAutonomyMotivationincreases
whenstudentshaveachoice,whentheyareabletohave
thechoiceofchoosingtheirownroutessuchas
problemstoparticipateon,hypothesestogenerateand
ininvestigatingandreportingonthem.
So what? What is important to understand about this?
Thismodelisimportantandcrucialtoteachingbecauseitallowsstudentstoworkindependentlyintheirlearning,shapesthefoundationfor
problemsolvingandtheskillsthatgoalongwithit.
You might also like
- Classroom-Based Teacher-Led Action Research As A Process For EnhDocument16 pagesClassroom-Based Teacher-Led Action Research As A Process For Enhsell hassNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Curriculum DevelopmentDocument15 pagesModule 4 Curriculum Developmentreyma panerNo ratings yet
- Models of Curriculum Development PPT 25 NOVDocument44 pagesModels of Curriculum Development PPT 25 NOVPriyanka SheoranNo ratings yet
- Cleary Validacion SRsI SRDocument16 pagesCleary Validacion SRsI SRLou GabyNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking in The Business Curriculum: Nora M. BraunDocument6 pagesCritical Thinking in The Business Curriculum: Nora M. BraunSteven ChoNo ratings yet
- Book - (J - Scheerens - Cees - A - W - Glas - Sally - Thomas) - Education Evaluation, Assessment and Monitoring PDFDocument425 pagesBook - (J - Scheerens - Cees - A - W - Glas - Sally - Thomas) - Education Evaluation, Assessment and Monitoring PDFSyamsul Anwar100% (3)
- Chapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of EvaluationDocument11 pagesChapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of Evaluationvea verzonNo ratings yet
- SavannahinquirymodelDocument1 pageSavannahinquirymodelapi-284281704No ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University Semester Terminal Exam Autumn 2020 Program /level: B. ED Title /course Code: Curriculum Development (8603)Document8 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University Semester Terminal Exam Autumn 2020 Program /level: B. ED Title /course Code: Curriculum Development (8603)Osama Yaqoob0% (1)
- Action - Research - Final Paper (REVISED) - 100Document29 pagesAction - Research - Final Paper (REVISED) - 100Jacquin MokayaNo ratings yet
- DWYER Assessment and Classroom Learning Theory and PracticeDocument8 pagesDWYER Assessment and Classroom Learning Theory and PracticeSAMIR ARTURO IBARRA BOLAÑOSNo ratings yet
- How Far Have We Moved Toward The Integration of THDocument14 pagesHow Far Have We Moved Toward The Integration of THpthanhthuy459No ratings yet
- 1299760628curriculum Development ModelsDocument13 pages1299760628curriculum Development Modelshoangsang79No ratings yet
- Theoretical Conceptual Methodological and InstructDocument10 pagesTheoretical Conceptual Methodological and InstructJaenelyn AlquizarNo ratings yet
- 6462 Assignment No 1Document16 pages6462 Assignment No 1Muhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- What We Learn in Action ResearchDocument3 pagesWhat We Learn in Action ResearchAnonymous pHooz5aH6VNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data-Driven Educational Decision MakingDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Data-Driven Educational Decision MakingThe Holy KashmirNo ratings yet
- Interventional Research CRMEF CASADocument6 pagesInterventional Research CRMEF CASAIbtissam LaNo ratings yet
- 61dc2ca57649a4 83414233Document6 pages61dc2ca57649a4 83414233mandyndawana71No ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument61 pagesAction ResearchLance Aldrin Adion67% (3)
- ARTIKEL Sigit SusetiadiDocument4 pagesARTIKEL Sigit Susetiadimiftahul rahmat9No ratings yet
- Loyen Set AlDocument20 pagesLoyen Set AlRiana RurmanNo ratings yet
- Self-Directed Learning in Problem-Based Learning and Its Relationships With Self-Regulated LearningDocument19 pagesSelf-Directed Learning in Problem-Based Learning and Its Relationships With Self-Regulated LearningRiana RurmanNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 11Document9 pagesSummary Chapter 11IO OutletsNo ratings yet
- 4 HolisticAssessmentDocument10 pages4 HolisticAssessmentSmriti BalyanNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Attitudes Towards Values Across The Curriculum-A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesTeachers' Attitudes Towards Values Across The Curriculum-A Systematic Literature Reviewliza83tintabahasaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Classroom AssessmentDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Classroom Assessmentapi-405351173No ratings yet
- DiominoDocument4 pagesDiominoMicah Joy DiominoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in Writing The ResearchDocument62 pagesGuidelines in Writing The ResearchKaren GayNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter 2Document55 pages09 Chapter 2krishanNo ratings yet
- Are You Assessment Literate?Document23 pagesAre You Assessment Literate?Eddy White, PhD100% (2)
- Traditional and Alternative Issues in Students' Evaluation: Simona EftimieDocument6 pagesTraditional and Alternative Issues in Students' Evaluation: Simona Eftimievinoelnino10No ratings yet
- Edu 602 Action Research WritingDocument40 pagesEdu 602 Action Research WritingJohn Lopez CruzNo ratings yet
- How Formative Assessments Drive Instructional Decision Making in The ClassroomDocument7 pagesHow Formative Assessments Drive Instructional Decision Making in The ClassroomCharles Anthony RamosNo ratings yet
- Understand Theories Principles and MoDocument9 pagesUnderstand Theories Principles and MoWahyu Adi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Inquiry ModelDocument1 pageInquiry Modelapi-284127506No ratings yet
- Education Policy Analysis ArchivesDocument18 pagesEducation Policy Analysis ArchivesNoldy PelenkahuNo ratings yet
- Final Reflection and ConclusionDocument6 pagesFinal Reflection and Conclusionapi-245618331No ratings yet
- Learning Theories: Theories and Models of Learning For Educational Research and Practice. This KnowledgeDocument14 pagesLearning Theories: Theories and Models of Learning For Educational Research and Practice. This KnowledgeDiane ChuNo ratings yet
- 1st READING Learning StrategiesDocument3 pages1st READING Learning Strategiesnirak875No ratings yet
- Loyens, 2008Document18 pagesLoyens, 2008CatharinaWidiartiniNo ratings yet
- OERDoc 575 35579 11 08 2021Document28 pagesOERDoc 575 35579 11 08 2021Hanifa NorodinNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesPresident Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityElvin Francis LabandeloNo ratings yet
- Labao Curriculum Instruction Paper 2Document8 pagesLabao Curriculum Instruction Paper 2Arnelyn LabaoNo ratings yet
- Formative and Summative Assessment 2Document8 pagesFormative and Summative Assessment 2Ryan Neil CajucomNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Kaedah PenyelidikanDocument8 pagesPengenalan Kaedah Penyelidikanrapunzel777No ratings yet
- Fass 352 Literature Review Ranim AnnousDocument16 pagesFass 352 Literature Review Ranim Annousapi-610160797No ratings yet
- Comparative Study Assessment For of and As LearningDocument15 pagesComparative Study Assessment For of and As LearningCristina SalenNo ratings yet
- NITTTR Module 6Document169 pagesNITTTR Module 6Indrajeet MoreNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Metacognition and SelfDocument4 pagesThe Difference Between Metacognition and Selfarhodes777No ratings yet
- Statistics Test Questions: Content and TrendsDocument16 pagesStatistics Test Questions: Content and TrendsAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Strategi Pembelajaran Dalam Penelitian Tindakan KelasDocument10 pagesStrategi Pembelajaran Dalam Penelitian Tindakan KelasCitraNo ratings yet
- Action Research Paper Classroom ManagementDocument4 pagesAction Research Paper Classroom Managementgzzjhsv9100% (1)
- Student Self Assessment Processes and ConsequencesDocument12 pagesStudent Self Assessment Processes and ConsequencesPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Document (12) (10) .EditedDocument22 pagesDocument (12) (10) .EditedSumaya Binte KashemNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument12 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentDa dang100% (6)
- Investigating Self-Regulation and Motivation: Historical Background, Methodological Developments, and Future ProspectsDocument18 pagesInvestigating Self-Regulation and Motivation: Historical Background, Methodological Developments, and Future ProspectskidNo ratings yet
- Beyond Behavioral ObjectivesREPORTDocument24 pagesBeyond Behavioral ObjectivesREPORTeugene louie ibarraNo ratings yet
- PSSST : Silence Please!Document48 pagesPSSST : Silence Please!dharwin geronimoNo ratings yet
- Bell-Shape Testing System: Testing the Students Based on Simple and Complex Teachings Related to Bloom’S Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesFrom EverandBell-Shape Testing System: Testing the Students Based on Simple and Complex Teachings Related to Bloom’S Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesNo ratings yet
- SavannahresumeDocument2 pagesSavannahresumeapi-284281704No ratings yet
- SavannahinquirymodelDocument1 pageSavannahinquirymodelapi-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahgdmodel 3Document1 pageSavannahgdmodel 3api-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahcamodel 2Document1 pageSavannahcamodel 2api-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahldmodel 2Document1 pageSavannahldmodel 2api-284281704No ratings yet
- Savannahdimodel 2Document1 pageSavannahdimodel 2api-284281704No ratings yet
- SavannahdiscussionmodelDocument1 pageSavannahdiscussionmodelapi-284281704No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument57 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementSudarshan MankadNo ratings yet
- Hataraku Maou-Sama! - 17 (Yen Press)Document223 pagesHataraku Maou-Sama! - 17 (Yen Press)Mike Chui100% (1)
- A Study On Consumer Behaviour in Real Estate SectorDocument94 pagesA Study On Consumer Behaviour in Real Estate SectorNadeem khan100% (2)
- Booking Report 11-18-2020Document2 pagesBooking Report 11-18-2020WCTV Digital Team0% (2)
- Anls Pressure DiagDocument15 pagesAnls Pressure DiagazareiforoushNo ratings yet
- De Thi Thu THPT Tieng Anh 2016 MR BaoDocument14 pagesDe Thi Thu THPT Tieng Anh 2016 MR BaoMai Long TânNo ratings yet
- Diagn Org EffDocument33 pagesDiagn Org Effmargonomitro1No ratings yet
- Chikungunya Virus DiseaseDocument25 pagesChikungunya Virus DiseasemamaluNo ratings yet
- Praise of White Tara by Gedun DrukpaDocument2 pagesPraise of White Tara by Gedun DrukpaŚīla ViśodhanaNo ratings yet
- Foucault, Michel - What Is EnlightenmentDocument15 pagesFoucault, Michel - What Is EnlightenmentDhiraj Menon100% (1)
- Written Statement SwapnilDocument5 pagesWritten Statement SwapnilMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- FN-LM07 Filipinos Conquering The WorldDocument3 pagesFN-LM07 Filipinos Conquering The WorldMichelle Em GerabanNo ratings yet
- Thesis Guidelines UitmDocument6 pagesThesis Guidelines UitmBuyAPhilosophyPaperSingapore100% (2)
- Rabagia - MatenTertiary Tectonic and Sedimentological Evolution of The South Carpathians Foredeep: Tectonic Versus Eustatic Controlco (1999)Document22 pagesRabagia - MatenTertiary Tectonic and Sedimentological Evolution of The South Carpathians Foredeep: Tectonic Versus Eustatic Controlco (1999)Lex AlexaNo ratings yet
- Essay On How To Conduct Oneself Inside The CompanyDocument4 pagesEssay On How To Conduct Oneself Inside The CompanyMadielyn Santarin MirandaNo ratings yet
- EDU Development of Malaysian EducationDocument47 pagesEDU Development of Malaysian EducationNabilFikriChumiNo ratings yet
- Imrad FormatDocument34 pagesImrad FormatKc MostachoNo ratings yet
- A Dios Le Pido - by Juanes, English Translation of Lyrics - SonglationsDocument4 pagesA Dios Le Pido - by Juanes, English Translation of Lyrics - SonglationsaguasamargasNo ratings yet
- Job Designing Analysis BSNLDocument75 pagesJob Designing Analysis BSNLpavanNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect TenseDocument17 pagesThe Present Perfect TenseHugo AldereteNo ratings yet
- S3 Proofreading Answer 1-10Document10 pagesS3 Proofreading Answer 1-10Edwin FongNo ratings yet
- Learner Analysis QuestionsDocument1 pageLearner Analysis Questionsapi-323641842No ratings yet
- Violated and Transcended BodiesDocument80 pagesViolated and Transcended BodiesFideblaymid CruzNo ratings yet
- PerDev Learning ActivityDocument4 pagesPerDev Learning ActivitydwacindyfjNo ratings yet
- An Appraisal of The Impact of Holy Spirit in The Life of BelieversDocument8 pagesAn Appraisal of The Impact of Holy Spirit in The Life of BelieversAnonymous ftifJFgbNo ratings yet
- Haddad v. Indiana Pacers Et Al - Document No. 82Document17 pagesHaddad v. Indiana Pacers Et Al - Document No. 82Justia.com100% (1)
- Criminal Law 2Document79 pagesCriminal Law 2aris apridNo ratings yet
- Financing Foreign Trade PDFDocument16 pagesFinancing Foreign Trade PDFHemanth Kumar89% (9)
- List of Secretary Union Councils District Sialkot No. & Name of Union Council Name of Secretary UC Cell NumbersDocument8 pagesList of Secretary Union Councils District Sialkot No. & Name of Union Council Name of Secretary UC Cell NumbersAhmed MaherNo ratings yet
- 17th International Conference On Multiphase Technology 2015: Cannes, France 10 - 12 June 2015Document6 pages17th International Conference On Multiphase Technology 2015: Cannes, France 10 - 12 June 2015kglorstadNo ratings yet