Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsSuch As Aluminum or Zinc, Is Melted in The Furnace and Then Injected Into The Dies in The Die
Such As Aluminum or Zinc, Is Melted in The Furnace and Then Injected Into The Dies in The Die
Uploaded by
KumarChirraDie casting is a manufacturing process that uses reusable molds called dies to produce complex metal parts. Molten metal is injected into dies in a die casting machine, where it rapidly cools and solidifies. There are two main types of die casting machines - hot chamber machines for low melting point metals like zinc, and cold chamber machines for higher melting metals like aluminum. Die cast parts can vary greatly in size from ounces to 100 pounds, and are commonly used for appliance and automobile housings, pistons, and other mechanical components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pressure Die CastingDocument62 pagesPressure Die CastingChetan Nehete100% (2)
- Die Casting With TypesDocument4 pagesDie Casting With TypesAdarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Report On Material Used For Making Dies For Pressure Die Casting of Alluminium Alloys.2Document21 pagesReport On Material Used For Making Dies For Pressure Die Casting of Alluminium Alloys.2Maroof Alam100% (2)
- Interview QuestionDocument22 pagesInterview QuestionsugeshNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die CastingDocument62 pagesPressure Die CastingARUNSFRH83% (6)
- Q2. What Is Rolling and Recrystallization Temperature. Explain The Methods of Rolling Steel and Highlight The Major DifferencesDocument6 pagesQ2. What Is Rolling and Recrystallization Temperature. Explain The Methods of Rolling Steel and Highlight The Major DifferencesArslan RaoNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Industrial Processes of Steel Metal Cement PresentationDocument57 pagesManufacturing and Industrial Processes of Steel Metal Cement PresentationFrancis John Fuentes BorjaNo ratings yet
- Sess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Document7 pagesSess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Prakash RagupathyNo ratings yet
- Cold and Hot ForgingDocument6 pagesCold and Hot ForgingAnonymous vvO0nZWflrNo ratings yet
- ME - 32021 Chapter (3) Hard Mold Casting ProcessesDocument26 pagesME - 32021 Chapter (3) Hard Mold Casting ProcessesWILYNo ratings yet
- Processes, Uses, Properties, MethodsDocument93 pagesProcesses, Uses, Properties, MethodsMicho CalimaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Part C RevisedDocument72 pagesUnit3 Part C Revisedraymon sharmaNo ratings yet
- Metal Mould-Casting Processes: Unit Iv Moulding ProcessesDocument26 pagesMetal Mould-Casting Processes: Unit Iv Moulding ProcessesMr. T. Anjaneyulu Mr. T. AnjaneyuluNo ratings yet
- BME B Project Armaan SinghDocument16 pagesBME B Project Armaan Singharmaansingh 2K20B1220No ratings yet
- Zinc High Pressure Die CastingDocument1 pageZinc High Pressure Die CastingGutierrezOmar5No ratings yet
- Casting 1Document26 pagesCasting 1Lal KishanNo ratings yet
- 1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IDocument8 pages1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IChinmay Das100% (2)
- Aircraft Materials, Construction and RepairDocument41 pagesAircraft Materials, Construction and RepairMark Jovince CardenasNo ratings yet
- 2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting ProcessesDocument3 pages2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting Processesaman chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereDocument36 pagesDr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereNikhil PawarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 5Document10 pagesLaboratory 5Andy BirdieNo ratings yet
- Machining ProcessDocument16 pagesMachining ProcessPoonam MargajNo ratings yet
- Die CastingDocument29 pagesDie CastingUmair MirzaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die-CastingDocument12 pagesPressure Die-CastingAyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Casting Its Types 1 (29-40) - 2Document12 pagesCasting Its Types 1 (29-40) - 2VDNo ratings yet
- E Mat: Engineering MaterialsDocument135 pagesE Mat: Engineering MaterialsStevenson CacNo ratings yet
- FoundryDocument12 pagesFoundrykarkiak075No ratings yet
- Mechanical Working of MetalsDocument53 pagesMechanical Working of Metalsmurari100% (3)
- Hot Working: Forming Can Be Divided Into Two CategoriesDocument9 pagesHot Working: Forming Can Be Divided Into Two CategoriesNelson AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cold Hot Working AnnealingDocument40 pagesCold Hot Working AnnealingBaljeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Hot Working of MetalsDocument27 pagesHot Working of MetalsRommel Blanco100% (1)
- METALWORKINGDocument3 pagesMETALWORKINGIrene FranchinNo ratings yet
- Industrial Materials and ProcessesDocument14 pagesIndustrial Materials and ProcessesMNM100% (1)
- Pressure Die PPT InPDFDocument84 pagesPressure Die PPT InPDFSree RamichettyNo ratings yet
- Estelar: Asting Process Can Be Divided Into Two Basic CategoriesDocument15 pagesEstelar: Asting Process Can Be Divided Into Two Basic CategoriesVDNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument28 pagesMetal CastingAngel ChanteyNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in - Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryDocument5 pagesFdocuments - in - Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryPooja BanNo ratings yet
- Steel Terminologies: Alloy SteelsDocument9 pagesSteel Terminologies: Alloy SteelsMartine CastroNo ratings yet
- DV03PUB23 Study GuideDocument4 pagesDV03PUB23 Study GuidesobheysaidNo ratings yet
- University of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 2 Rolling MillDocument17 pagesUniversity of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 2 Rolling MillJOHNEDERSON PABLONo ratings yet
- Manuf ProcessDocument15 pagesManuf ProcessKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Die Casting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesDie Casting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediagodseNo ratings yet
- Discuss at Least Four Techniques in Forming MetalsDocument3 pagesDiscuss at Least Four Techniques in Forming MetalsJeffrey JimenezNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Is A Manufacturing Process That Can Produce Geometrically Complex Metal Parts Through The Use of Reusable MoldsDocument13 pagesDie Casting Is A Manufacturing Process That Can Produce Geometrically Complex Metal Parts Through The Use of Reusable MoldsSanjay MukalaNo ratings yet
- Die Casting - WikipediaDocument11 pagesDie Casting - WikipediaKyaw Bhone WinNo ratings yet
- Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryDocument5 pagesAutomatic Ingot Feeder For Boundaryieee4mybusinessonlyNo ratings yet
- Continuous Casting and Mould Level ControlDocument15 pagesContinuous Casting and Mould Level ControlmehdihaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Die CastingDocument12 pagesLab Report Die CastingaaqibaminNo ratings yet
- Hand Out CMTDocument6 pagesHand Out CMTAlden TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Steel Forging: What Is The Metal Forging Process?Document11 pagesSteel Forging: What Is The Metal Forging Process?Lobna CHEBBINo ratings yet
- Hot Chamber Die Casting MachineDocument3 pagesHot Chamber Die Casting MachineAnand BossNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Language of SteelDocument7 pagesA Guide To The Language of SteelIwona AnkaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Casting: Equipment and ProcessDocument8 pagesContinuous Casting: Equipment and ProcessErickman Simorangkir100% (1)
- Steel Manufacturing ProcessDocument1 pageSteel Manufacturing ProcessdalyemNo ratings yet
- Iron RecyclingDocument9 pagesIron RecyclingYousef SailiniNo ratings yet
- Steel Industry Fact SheetDocument4 pagesSteel Industry Fact SheetYbonnie Mae T. LAPINIGNo ratings yet
- Ecway Technologies: Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryDocument6 pagesEcway Technologies: Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryPooja BanNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941From EverandTechnical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941No ratings yet
- Forging - Manual of Practical Instruction in Hand Forging of Wrought Iron, Machine Steel and Tool Steel; Drop Forging; and Heat Treatment of Steel, Including Annealing, Hardening and TemperingFrom EverandForging - Manual of Practical Instruction in Hand Forging of Wrought Iron, Machine Steel and Tool Steel; Drop Forging; and Heat Treatment of Steel, Including Annealing, Hardening and TemperingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- INC SessionDocument2 pagesINC SessionKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- C16 DaeDocument319 pagesC16 DaeKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Enjoy LifeDocument2 pagesEnjoy LifeKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Al AlloysDocument17 pagesAl AlloysKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Telangana HistoryDocument6 pagesTelangana HistoryKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Super Finishing ProcessDocument14 pagesSuper Finishing ProcessKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Bottle NecksDocument1 pageBottle NecksKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity: Property Conduct Heat Fourier's Law Heat ConductionDocument3 pagesThermal Conductivity: Property Conduct Heat Fourier's Law Heat ConductionKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- FractionsDocument14 pagesFractionsKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument13 pagesHardness Testhaizum_adamNo ratings yet
- A Report: Manufacturing of Machine Tool BedsDocument11 pagesA Report: Manufacturing of Machine Tool BedsKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering National Institute of TechnologyDocument7 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering National Institute of TechnologyKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- 3 MaticDocument17 pages3 MaticKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Graphite MouldDocument2 pagesGraphite MouldKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComparatorsDocument20 pagesElectronic ComparatorsKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Limit, Fit &toleranceDocument11 pagesLimit, Fit &toleranceKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Inter Chang IbilityDocument20 pagesInter Chang IbilityKumarChirraNo ratings yet
Such As Aluminum or Zinc, Is Melted in The Furnace and Then Injected Into The Dies in The Die
Such As Aluminum or Zinc, Is Melted in The Furnace and Then Injected Into The Dies in The Die
Uploaded by
KumarChirra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageDie casting is a manufacturing process that uses reusable molds called dies to produce complex metal parts. Molten metal is injected into dies in a die casting machine, where it rapidly cools and solidifies. There are two main types of die casting machines - hot chamber machines for low melting point metals like zinc, and cold chamber machines for higher melting metals like aluminum. Die cast parts can vary greatly in size from ounces to 100 pounds, and are commonly used for appliance and automobile housings, pistons, and other mechanical components.
Original Description:
Introduction to Die casting
Original Title
1.Introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDie casting is a manufacturing process that uses reusable molds called dies to produce complex metal parts. Molten metal is injected into dies in a die casting machine, where it rapidly cools and solidifies. There are two main types of die casting machines - hot chamber machines for low melting point metals like zinc, and cold chamber machines for higher melting metals like aluminum. Die cast parts can vary greatly in size from ounces to 100 pounds, and are commonly used for appliance and automobile housings, pistons, and other mechanical components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageSuch As Aluminum or Zinc, Is Melted in The Furnace and Then Injected Into The Dies in The Die
Such As Aluminum or Zinc, Is Melted in The Furnace and Then Injected Into The Dies in The Die
Uploaded by
KumarChirraDie casting is a manufacturing process that uses reusable molds called dies to produce complex metal parts. Molten metal is injected into dies in a die casting machine, where it rapidly cools and solidifies. There are two main types of die casting machines - hot chamber machines for low melting point metals like zinc, and cold chamber machines for higher melting metals like aluminum. Die cast parts can vary greatly in size from ounces to 100 pounds, and are commonly used for appliance and automobile housings, pistons, and other mechanical components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
INTRODUCTION
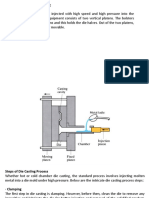
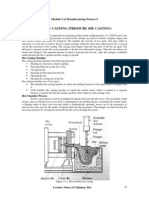
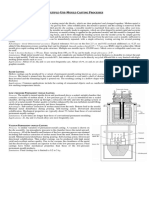
Die casting is a manufacturing process that can produce geometrically complex
metal parts through the use of reusable molds, called dies. The die casting process involves the
use of a furnace, metal, die casting machine, and die. The metal, typically a nonferrous alloy
such as aluminum or zinc, is melted in the furnace and then injected into the dies in the die
casting machine. There are two main types of die casting machines hot chamber machines
(used for alloys with low melting temperatures, such as zinc) and cold chamber machines (used
for alloys with high melting temperatures, such as aluminum). The differences between these
machines will be detailed in the sections on equipment and tooling. However, in both
machines ,after the molten metal is injected into the dies, it rapidly cools and solidifies into the
final part, called the casting. The steps in this process are described in greater detail in the next
section.
The castings that are created in this process can vary greatly in size and weight,
ranging from a couple ounces to 100 pounds. One common application of die cast parts are
housings thin walled enclosures, often requiring many ribs and bosses on the interior. Metal
housings for a variety of appliances and equipment are often die cast. Several automobile
components are also manufactured using die casting, including pistons, cylinder heads, and
engine blocks. Other common die cast parts include propellers, gears, bushings, pumps, and
valves.
You might also like
- Pressure Die CastingDocument62 pagesPressure Die CastingChetan Nehete100% (2)
- Die Casting With TypesDocument4 pagesDie Casting With TypesAdarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Report On Material Used For Making Dies For Pressure Die Casting of Alluminium Alloys.2Document21 pagesReport On Material Used For Making Dies For Pressure Die Casting of Alluminium Alloys.2Maroof Alam100% (2)
- Interview QuestionDocument22 pagesInterview QuestionsugeshNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die CastingDocument62 pagesPressure Die CastingARUNSFRH83% (6)
- Q2. What Is Rolling and Recrystallization Temperature. Explain The Methods of Rolling Steel and Highlight The Major DifferencesDocument6 pagesQ2. What Is Rolling and Recrystallization Temperature. Explain The Methods of Rolling Steel and Highlight The Major DifferencesArslan RaoNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Industrial Processes of Steel Metal Cement PresentationDocument57 pagesManufacturing and Industrial Processes of Steel Metal Cement PresentationFrancis John Fuentes BorjaNo ratings yet
- Sess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Document7 pagesSess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Prakash RagupathyNo ratings yet
- Cold and Hot ForgingDocument6 pagesCold and Hot ForgingAnonymous vvO0nZWflrNo ratings yet
- ME - 32021 Chapter (3) Hard Mold Casting ProcessesDocument26 pagesME - 32021 Chapter (3) Hard Mold Casting ProcessesWILYNo ratings yet
- Processes, Uses, Properties, MethodsDocument93 pagesProcesses, Uses, Properties, MethodsMicho CalimaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Part C RevisedDocument72 pagesUnit3 Part C Revisedraymon sharmaNo ratings yet
- Metal Mould-Casting Processes: Unit Iv Moulding ProcessesDocument26 pagesMetal Mould-Casting Processes: Unit Iv Moulding ProcessesMr. T. Anjaneyulu Mr. T. AnjaneyuluNo ratings yet
- BME B Project Armaan SinghDocument16 pagesBME B Project Armaan Singharmaansingh 2K20B1220No ratings yet
- Zinc High Pressure Die CastingDocument1 pageZinc High Pressure Die CastingGutierrezOmar5No ratings yet
- Casting 1Document26 pagesCasting 1Lal KishanNo ratings yet
- 1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IDocument8 pages1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IChinmay Das100% (2)
- Aircraft Materials, Construction and RepairDocument41 pagesAircraft Materials, Construction and RepairMark Jovince CardenasNo ratings yet
- 2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting ProcessesDocument3 pages2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting Processesaman chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereDocument36 pagesDr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereNikhil PawarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 5Document10 pagesLaboratory 5Andy BirdieNo ratings yet
- Machining ProcessDocument16 pagesMachining ProcessPoonam MargajNo ratings yet
- Die CastingDocument29 pagesDie CastingUmair MirzaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die-CastingDocument12 pagesPressure Die-CastingAyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Casting Its Types 1 (29-40) - 2Document12 pagesCasting Its Types 1 (29-40) - 2VDNo ratings yet
- E Mat: Engineering MaterialsDocument135 pagesE Mat: Engineering MaterialsStevenson CacNo ratings yet
- FoundryDocument12 pagesFoundrykarkiak075No ratings yet
- Mechanical Working of MetalsDocument53 pagesMechanical Working of Metalsmurari100% (3)
- Hot Working: Forming Can Be Divided Into Two CategoriesDocument9 pagesHot Working: Forming Can Be Divided Into Two CategoriesNelson AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cold Hot Working AnnealingDocument40 pagesCold Hot Working AnnealingBaljeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Hot Working of MetalsDocument27 pagesHot Working of MetalsRommel Blanco100% (1)
- METALWORKINGDocument3 pagesMETALWORKINGIrene FranchinNo ratings yet
- Industrial Materials and ProcessesDocument14 pagesIndustrial Materials and ProcessesMNM100% (1)
- Pressure Die PPT InPDFDocument84 pagesPressure Die PPT InPDFSree RamichettyNo ratings yet
- Estelar: Asting Process Can Be Divided Into Two Basic CategoriesDocument15 pagesEstelar: Asting Process Can Be Divided Into Two Basic CategoriesVDNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument28 pagesMetal CastingAngel ChanteyNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in - Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryDocument5 pagesFdocuments - in - Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryPooja BanNo ratings yet
- Steel Terminologies: Alloy SteelsDocument9 pagesSteel Terminologies: Alloy SteelsMartine CastroNo ratings yet
- DV03PUB23 Study GuideDocument4 pagesDV03PUB23 Study GuidesobheysaidNo ratings yet
- University of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 2 Rolling MillDocument17 pagesUniversity of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 2 Rolling MillJOHNEDERSON PABLONo ratings yet
- Manuf ProcessDocument15 pagesManuf ProcessKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Die Casting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesDie Casting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediagodseNo ratings yet
- Discuss at Least Four Techniques in Forming MetalsDocument3 pagesDiscuss at Least Four Techniques in Forming MetalsJeffrey JimenezNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Is A Manufacturing Process That Can Produce Geometrically Complex Metal Parts Through The Use of Reusable MoldsDocument13 pagesDie Casting Is A Manufacturing Process That Can Produce Geometrically Complex Metal Parts Through The Use of Reusable MoldsSanjay MukalaNo ratings yet
- Die Casting - WikipediaDocument11 pagesDie Casting - WikipediaKyaw Bhone WinNo ratings yet
- Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryDocument5 pagesAutomatic Ingot Feeder For Boundaryieee4mybusinessonlyNo ratings yet
- Continuous Casting and Mould Level ControlDocument15 pagesContinuous Casting and Mould Level ControlmehdihaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Die CastingDocument12 pagesLab Report Die CastingaaqibaminNo ratings yet
- Hand Out CMTDocument6 pagesHand Out CMTAlden TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Steel Forging: What Is The Metal Forging Process?Document11 pagesSteel Forging: What Is The Metal Forging Process?Lobna CHEBBINo ratings yet
- Hot Chamber Die Casting MachineDocument3 pagesHot Chamber Die Casting MachineAnand BossNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Language of SteelDocument7 pagesA Guide To The Language of SteelIwona AnkaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Casting: Equipment and ProcessDocument8 pagesContinuous Casting: Equipment and ProcessErickman Simorangkir100% (1)
- Steel Manufacturing ProcessDocument1 pageSteel Manufacturing ProcessdalyemNo ratings yet
- Iron RecyclingDocument9 pagesIron RecyclingYousef SailiniNo ratings yet
- Steel Industry Fact SheetDocument4 pagesSteel Industry Fact SheetYbonnie Mae T. LAPINIGNo ratings yet
- Ecway Technologies: Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryDocument6 pagesEcway Technologies: Automatic Ingot Feeder For BoundaryPooja BanNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941From EverandTechnical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941No ratings yet
- Forging - Manual of Practical Instruction in Hand Forging of Wrought Iron, Machine Steel and Tool Steel; Drop Forging; and Heat Treatment of Steel, Including Annealing, Hardening and TemperingFrom EverandForging - Manual of Practical Instruction in Hand Forging of Wrought Iron, Machine Steel and Tool Steel; Drop Forging; and Heat Treatment of Steel, Including Annealing, Hardening and TemperingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- INC SessionDocument2 pagesINC SessionKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- C16 DaeDocument319 pagesC16 DaeKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Enjoy LifeDocument2 pagesEnjoy LifeKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Al AlloysDocument17 pagesAl AlloysKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Telangana HistoryDocument6 pagesTelangana HistoryKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Super Finishing ProcessDocument14 pagesSuper Finishing ProcessKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Bottle NecksDocument1 pageBottle NecksKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity: Property Conduct Heat Fourier's Law Heat ConductionDocument3 pagesThermal Conductivity: Property Conduct Heat Fourier's Law Heat ConductionKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- FractionsDocument14 pagesFractionsKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument13 pagesHardness Testhaizum_adamNo ratings yet
- A Report: Manufacturing of Machine Tool BedsDocument11 pagesA Report: Manufacturing of Machine Tool BedsKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering National Institute of TechnologyDocument7 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering National Institute of TechnologyKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- 3 MaticDocument17 pages3 MaticKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Graphite MouldDocument2 pagesGraphite MouldKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComparatorsDocument20 pagesElectronic ComparatorsKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Limit, Fit &toleranceDocument11 pagesLimit, Fit &toleranceKumarChirraNo ratings yet
- Inter Chang IbilityDocument20 pagesInter Chang IbilityKumarChirraNo ratings yet