Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economy
Economy
Uploaded by
Weiming LinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economy
Economy
Uploaded by
Weiming LinCopyright:
Available Formats
Economy - overview: Characterized by large and well-developed agricultural, mining,
manufacturing, and service sectors, Brazil's economy outweighs that of all other South
American countries, and Brazil is expanding its presence in world markets. Since 2003, Brazil
has steadily improved its macroeconomic stability, building up foreign reserves, and reducing its
debt profile by shifting its debt burden toward real denominated and domestically held
instruments. In 2008, Brazil became a net external creditor and two ratings agencies awarded
investment grade status to its debt. After record growth in 2007 and 2008, the onset of the
global financial crisis hit Brazil in September 2008. Brazil experienced two quarters of recession,
as global demand for Brazil's commodity-based exports dwindled and external credit dried up.
However, Brazil was one of the first emerging markets to begin a recovery. Consumer and
investor confidence revived and GDP growth returned to positive in 2010, boosted by an export
recovery. Brazil's strong growth and high interest rates make it an attractive destination for
foreign investors. Large capital inflows over the past year have contributed to the rapid
appreciation of its currency and led the government to raise taxes on some foreign investments.
President Dilma ROUSSEFF has pledged to retain the previous administration's commitment to
inflation targeting by the Central Bank, a floating exchange rate, and fiscal restraint.
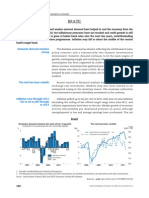
Brazil 2011 inflationBrazils GDP reversed the drop seen in 2009 and expanded 7.5%
in 2010. Investment was one of the main drivers of the robust GDP growth.
Brazilian GDP grew by 7.5% in 2010 to some BRL 3.6tn, in line with market expectations. This was the
strongest economic performance since the 1980s.
GDP Performance (YoY) & GDP Evolution
forecast at 6.52 percent
You might also like
- European Tour Operators AnalysisDocument8 pagesEuropean Tour Operators AnalysisrandoalboNo ratings yet
- Uem 3Document13 pagesUem 3Manan DesaiNo ratings yet
- Fdi and Economic Environment in Brazil: Ace Institute of ManagementDocument16 pagesFdi and Economic Environment in Brazil: Ace Institute of ManagementShristiNo ratings yet
- Brazil: Absolute Guide SeriesDocument24 pagesBrazil: Absolute Guide SeriesDave SmikkenNo ratings yet
- Fisher Capital Management South Korea, Brazil's Economy: 1st QuarterDocument2 pagesFisher Capital Management South Korea, Brazil's Economy: 1st QuarterfishercapitalNo ratings yet
- International Finance Assignment (Fin 411) Country: Brazil: Introduction: Brief Country ProfileDocument9 pagesInternational Finance Assignment (Fin 411) Country: Brazil: Introduction: Brief Country ProfileJenni TylerNo ratings yet
- Trade Policy ReviewDocument3 pagesTrade Policy ReviewOana MariaNo ratings yet
- Brazil: Brazil's Economy Is The Largest in South America and The Country Boasts Well DevelopedDocument16 pagesBrazil: Brazil's Economy Is The Largest in South America and The Country Boasts Well DevelopedMandar JehurkarNo ratings yet
- Economy Chosen: Brazil: Introduction BriefDocument10 pagesEconomy Chosen: Brazil: Introduction BriefckNo ratings yet
- BrazilDocument2 pagesBrazilhana_kimi_91No ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration: Assignment Mark SheetDocument22 pagesMaster of Business Administration: Assignment Mark SheetEvgenia LyapunovaNo ratings yet
- For Brazil and The Other BRIC Countries, Credit Quality Is About More Than Just SizeDocument18 pagesFor Brazil and The Other BRIC Countries, Credit Quality Is About More Than Just Sizemarcos_de_carvalhoNo ratings yet
- Como Exportar para o BrasilDocument113 pagesComo Exportar para o BrasilFabio Alexander de PauliNo ratings yet
- Services Sector: Largest EconomiesDocument6 pagesServices Sector: Largest EconomiesRupaam DebNo ratings yet
- BricDocument14 pagesBricAnanth RamanNo ratings yet
- Berita 9 November 2016 (Asli)Document2 pagesBerita 9 November 2016 (Asli)PuputNo ratings yet
- BR G20 PDFDocument10 pagesBR G20 PDFjjopaNo ratings yet
- Brazil BubbleDocument1 pageBrazil BubbleDanillo Gabriel NakanoNo ratings yet
- Brazil Fights A Real BattleDocument6 pagesBrazil Fights A Real Battlehongyen10% (1)
- What Are Emerging Markets?: Supply-DemandDocument3 pagesWhat Are Emerging Markets?: Supply-DemandMisbah UllahNo ratings yet
- Serrano e Summa, 2015Document31 pagesSerrano e Summa, 2015Fabiane PerondiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Outlook For BRICsDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Outlook For BRICstrolaiNo ratings yet
- Brazil OECD Econ OutlookDocument4 pagesBrazil OECD Econ OutlookScott FairbanksNo ratings yet
- Tough Encounter To BricsDocument5 pagesTough Encounter To BricsShiva Shankar PandianNo ratings yet
- Brazil Times WebDocument12 pagesBrazil Times Weblucianof1987No ratings yet
- Economic Analysis of Brazil's GDPDocument3 pagesEconomic Analysis of Brazil's GDPmarcello.didonatoNo ratings yet
- Press Release Fich BrasilDocument7 pagesPress Release Fich BrasilBruno Enrique Silva AndradeNo ratings yet
- ECW3301 Case Studies in International Trade: BrazilDocument30 pagesECW3301 Case Studies in International Trade: BrazilDenagamage de SilvaNo ratings yet
- Bolivia's Economic Transformation: Macroeconomic Policies, Institutional Changes and ResultsDocument23 pagesBolivia's Economic Transformation: Macroeconomic Policies, Institutional Changes and ResultsCenter for Economic and Policy Research100% (1)
- Case Study 2 HW 4 BRICS CountriesDocument6 pagesCase Study 2 HW 4 BRICS CountriesmilagrosNo ratings yet
- BrazilDocument4 pagesBrazilprashantNo ratings yet
- Brazil Currency Slide To New LowDocument2 pagesBrazil Currency Slide To New LowFunded FXNo ratings yet
- Brazil Overview 2010Document21 pagesBrazil Overview 2010anzetteNo ratings yet
- BricDocument3 pagesBricManhao TangNo ratings yet
- Impact of Credit Crisis in International BusinessDocument5 pagesImpact of Credit Crisis in International BusinessshebinaluvaNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy of Pakistan: Submitted To: Mirza Aqeel BaigDocument9 pagesMonetary Policy of Pakistan: Submitted To: Mirza Aqeel BaigAli AmjadNo ratings yet
- CFLCBrazil Impact of Western Public Finance in Least Developed CountriesDocument10 pagesCFLCBrazil Impact of Western Public Finance in Least Developed Countriescluadine dinerosNo ratings yet
- The Pharmaceutical Industry in BrazilDocument16 pagesThe Pharmaceutical Industry in BrazilAlexandreNo ratings yet
- Directors' Report: Bismillahir Rahmanir RahimDocument27 pagesDirectors' Report: Bismillahir Rahmanir RahimKhalid FirozNo ratings yet
- Impact of Global Financial Crisis On South AsiaDocument6 pagesImpact of Global Financial Crisis On South AsiaAli ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Juggling Technocrats and Party HatsDocument3 pagesJuggling Technocrats and Party HatsAndreea FloreaNo ratings yet
- History of Brazil GrowthDocument22 pagesHistory of Brazil GrowthArvind Mohit100% (1)
- Philippines Gross International Reserves Hit Record High in AugustDocument3 pagesPhilippines Gross International Reserves Hit Record High in AugustChristal Jam LaureNo ratings yet
- Group9 Brazil Macroecoomics PDFDocument12 pagesGroup9 Brazil Macroecoomics PDFANJULI AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Recent Global Financial CrisisDocument2 pagesRecent Global Financial Crisishasan.17854721No ratings yet
- Brazil Country OverviewDocument1 pageBrazil Country OverviewjearodriguesNo ratings yet
- India Economic Update: September, 2011Document17 pagesIndia Economic Update: September, 2011Rahul KaushikNo ratings yet
- India Amidst Global Crisis: by Mihir RakshitDocument4 pagesIndia Amidst Global Crisis: by Mihir RakshitSatavisha RayNo ratings yet
- Globalisation (Brazil) SpeechDocument2 pagesGlobalisation (Brazil) SpeechCarlin SloanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BordarioDocument16 pagesChapter 5 BordarioMichael Jay LingerasNo ratings yet
- Economic Situation in BrazilDocument3 pagesEconomic Situation in BrazilAnıl AlbayrakNo ratings yet
- Country Strategy 2011-2014 BulgariaDocument20 pagesCountry Strategy 2011-2014 BulgariaBeeHoofNo ratings yet
- Americas: Economic Review January 2011: at A GlanceDocument9 pagesAmericas: Economic Review January 2011: at A Glancemathew_rexNo ratings yet
- 5 World Economy Reading BrazilDocument4 pages5 World Economy Reading BrazilNeyl Joud BoujemaouiNo ratings yet
- October 2012 Volume XII Number 2Document116 pagesOctober 2012 Volume XII Number 2Kyren GreiggNo ratings yet
- January-June: Bangladesh BankDocument14 pagesJanuary-June: Bangladesh BankzsadiqueNo ratings yet
- The World Economy... - 14/7/2010Document3 pagesThe World Economy... - 14/7/2010Rhb InvestNo ratings yet
- Latin America: Regional OutlookDocument16 pagesLatin America: Regional OutlookrevathykrNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument4 pagesTutorialDibya sahaNo ratings yet
- Brazil PESTLEDocument6 pagesBrazil PESTLEyash sharmaNo ratings yet
- Made By:Freshers Vii: Project Outline: Management of An Organization Organization: The Ramada Plaza, KarachiDocument18 pagesMade By:Freshers Vii: Project Outline: Management of An Organization Organization: The Ramada Plaza, Karachinadapervez100% (1)
- 8 Talk A Lot Elementary Book 3Document419 pages8 Talk A Lot Elementary Book 3MariaPerezNo ratings yet
- Nestle PPT ReportDocument8 pagesNestle PPT ReportHamza AzharNo ratings yet
- World Cup 2014 Brazil Wall Chart PDF Fixture Schedule Brasil Eastern Time Timezone V.2 Smartcoder 247Document1 pageWorld Cup 2014 Brazil Wall Chart PDF Fixture Schedule Brasil Eastern Time Timezone V.2 Smartcoder 247Francesco BeniniNo ratings yet
- Psychological ManipulationDocument2 pagesPsychological ManipulationAndrea ZanattaNo ratings yet
- Types of ESPDocument17 pagesTypes of ESPWinter Bacalso100% (2)
- SoR - 2019-20 Roads and Bridges Andhrapradesh PDFDocument123 pagesSoR - 2019-20 Roads and Bridges Andhrapradesh PDFSIBMOST-TATA PROJECTS JV LMNo ratings yet
- IrRADIARE BrochureDocument6 pagesIrRADIARE BrochureIrRADIARE, Science for EvolutionNo ratings yet
- LCPC QueriesDocument11 pagesLCPC QueriesjomarNo ratings yet
- 13 RCBC Bankard Services Corp. v. Oracion JRDocument2 pages13 RCBC Bankard Services Corp. v. Oracion JRRonnie Garcia Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Advance Expert Test 1Document2 pagesAdvance Expert Test 1Несс ШварцNo ratings yet
- 2015 Rondy GuideDocument60 pages2015 Rondy GuideJeffrey RivetNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Penalty Fare Leaflet May 2021Document8 pagesPenalty Fare Leaflet May 2021emmanuelakinrinade64No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Alternate Marketing StrategiesDocument45 pagesChapter 10 Alternate Marketing StrategiessharosdNo ratings yet
- RPSL Data - UpdatedDocument74 pagesRPSL Data - Updatedvoo7o7No ratings yet
- Rules 113 114 126Document202 pagesRules 113 114 126Anthony RoblesNo ratings yet
- Biography of Kate ChopinDocument12 pagesBiography of Kate Chopinskhanmerali7No ratings yet
- Ra List ReportDocument188 pagesRa List Reportmohdahmed12345No ratings yet
- Running A Lottery Quick Guide PDFDocument2 pagesRunning A Lottery Quick Guide PDFsyeddilNo ratings yet
- SNTCSSC 2024 Admission Web Ad PDFDocument3 pagesSNTCSSC 2024 Admission Web Ad PDFSweeti SoultalkNo ratings yet
- Mid Session Exam SolutionsDocument20 pagesMid Session Exam SolutionssaravanansatkumaranNo ratings yet
- El Imaginario Colonial. FilipinasDocument45 pagesEl Imaginario Colonial. FilipinasvalidezNo ratings yet
- Celtic MonasticismDocument17 pagesCeltic MonasticismStrand Philips100% (1)
- Analysis of The Role of Cooperatives in Agricultural InputDocument147 pagesAnalysis of The Role of Cooperatives in Agricultural InputmogesgirmayNo ratings yet
- The Analytical Potential of Philosophical Anthropology Towards Technological Innovations inDocument54 pagesThe Analytical Potential of Philosophical Anthropology Towards Technological Innovations inAntonie de ManNo ratings yet
- A Home in Fiction - Gerlaldine BrooksDocument5 pagesA Home in Fiction - Gerlaldine BrooksZhou.Zhang2No ratings yet
- ACCN08B. Module 3 - Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument6 pagesACCN08B. Module 3 - Statement of Comprehensive IncomeYolly DiazNo ratings yet
- Study NoteDocument3 pagesStudy NoteBezalel OwusuNo ratings yet