Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Three Types of Static Stresses
Three Types of Static Stresses
Uploaded by
Naganathan SivabalanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Three Types of Static Stresses
Three Types of Static Stresses
Uploaded by
Naganathan SivabalanCopyright:
Available Formats
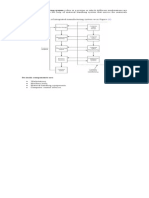
Three types of static stresses:
Tensile stress
While pulling (tensile) force acts on a material, and it tends to increase the length in the
tensile force direction. The material elongates, hence the cross-section area decreases.
Compressive stress
While pushing (compressive) force acts on a material, and it tends to decrease the length
in the compressive direction. The material shortens, hence the cross-section area
increases.
Shear stress
When forces equal in magnitude and in opposite direction are applied on a thin element,
the element deflects causing the material to shear. In other words, the shear force will
cause the internal structures of the material to slide against each other.
You might also like
- Types of Loadings: Strength of Materials Is A Subject Which Deals With Loads, Deformations and The ForcesDocument2 pagesTypes of Loadings: Strength of Materials Is A Subject Which Deals With Loads, Deformations and The ForcesErick John Perez SinforosoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechaics: Fluid Mechanics Is The Branch of Physics Concerned With The Mechanics of FluidsDocument6 pagesFluid Mechaics: Fluid Mechanics Is The Branch of Physics Concerned With The Mechanics of FluidsTofik MohammedNo ratings yet
- Stress:: Single Shear: Double ShearDocument2 pagesStress:: Single Shear: Double ShearSAFINA KAMAL SHOILYNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Yield Strength and Tensile StrengthDocument3 pagesDifference Between Yield Strength and Tensile StrengthFarobi Tetuko PujikuncoroNo ratings yet
- 7K. ForcesDocument4 pages7K. ForcesKeril MasonNo ratings yet
- Som Stress and StrainDocument11 pagesSom Stress and StrainYogendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Stress Is Measured by Pascal (P) - Stress Pressure: The Amount of Strain Is Measured in Percentage (%)Document4 pagesStress Is Measured by Pascal (P) - Stress Pressure: The Amount of Strain Is Measured in Percentage (%)Kadir GNo ratings yet
- Ariola Stress and StrainDocument2 pagesAriola Stress and StrainRose Andreih AriolaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesKyaw Htoo MyatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Sajad AliNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain Definitions and ChartDocument3 pagesStress Strain Definitions and ChartreeNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS NOTES Forces and ShapeDocument3 pagesPHYSICS NOTES Forces and ShapeMinal Shahbaz saeedNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument20 pagesElasticityindianindia0001No ratings yet
- Mosf Unit - 1Document94 pagesMosf Unit - 1Sayan MajumderNo ratings yet
- 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument4 pages9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsMokshNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledCABALIDA, FELICITY H.No ratings yet
- Physics 11th Investigatory ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics 11th Investigatory Projectaryantiwariabc724No ratings yet
- BAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - QUIZ 1 PRELIM TERM - Part 1Document1 pageBAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - QUIZ 1 PRELIM TERM - Part 1DARLENE JOY C. BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mechanics Part 1Document4 pagesFundamentals of Mechanics Part 1vinscarfNo ratings yet
- Science-Class 8 - Part 1Document27 pagesScience-Class 8 - Part 1Arnav MalasiNo ratings yet
- Lec. 2 D.MDocument3 pagesLec. 2 D.MYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNo ratings yet
- My CEG Lab Report (1) (AutoRecovered)Document63 pagesMy CEG Lab Report (1) (AutoRecovered)akinyemi.favour.isaacNo ratings yet
- In Materials EngineeringDocument2 pagesIn Materials EngineeringGreatestEver EvergreatestNo ratings yet
- BAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - QUIZ 1 PRELIM TERM - Part 1Document1 pageBAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - QUIZ 1 PRELIM TERM - Part 1DARLENE JOY C. BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Review of Concepts in StructuresDocument14 pagesReview of Concepts in StructuresSulthan sNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Elastic Properties of MaterialsDocument13 pagesUnit - 1 Elastic Properties of MaterialssullaNo ratings yet
- Physics VivaDocument19 pagesPhysics VivaAkhila ANo ratings yet
- Phy VivaqaDocument19 pagesPhy VivaqaAkhila ANo ratings yet
- Chapter force and pressure notes class 8th PDFDocument5 pagesChapter force and pressure notes class 8th PDFojasvmiglaniNo ratings yet
- Dental Materials: Lec. 2 Dr. Hayder SabeehDocument3 pagesDental Materials: Lec. 2 Dr. Hayder SabeehYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNo ratings yet
- ST00602 Lec2 Forces and MotionDocument115 pagesST00602 Lec2 Forces and MotionImran AminNo ratings yet
- 1 - ForceDocument42 pages1 - ForceJessa YaunNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: Unit 1Document20 pagesStrength of Materials: Unit 1Pranjyoti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Chennai Public School: Friction FrictionDocument2 pagesChennai Public School: Friction FrictionAbishek ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Solids FnotesDocument12 pagesMechanical Properties of Solids Fnotespiyushdua01No ratings yet
- Difference Between Space Frame and TrussDocument6 pagesDifference Between Space Frame and TrussKhalida ParveenNo ratings yet
- Forces and Changing ShapeDocument2 pagesForces and Changing ShapeShirley DeniceNo ratings yet
- Phy CH 3Document3 pagesPhy CH 3rishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- STATICS NotesDocument7 pagesSTATICS Noteschaengchong95No ratings yet
- Summary 7KDocument2 pagesSummary 7KTHJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Section 1 Newton's Second LawDocument16 pagesChapter 3 Section 1 Newton's Second LawMelissa MilfordNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument4 pagesFORCESNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- MECS Unit1 Notes1Document14 pagesMECS Unit1 Notes1michaelrithishNo ratings yet
- Elasticity, Sterss and StrainDocument19 pagesElasticity, Sterss and StrainKhairunnisa PutryNo ratings yet
- Force EditedDocument20 pagesForce EditedCirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Notes Fore Fiction and Pressure For VIII PhysicsDocument3 pagesNotes Fore Fiction and Pressure For VIII PhysicsBhavesh Desai100% (1)
- Properties of Materials and TestingDocument8 pagesProperties of Materials and Testingsatyendra singhNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure Handout Std8 PDFDocument8 pagesForce and Pressure Handout Std8 PDFSaghana SaravanakarthikNo ratings yet
- UNIT-8 Power PointDocument28 pagesUNIT-8 Power PointDesta LelagoNo ratings yet
- ch11 Sec3 Motion and ForceDocument15 pagesch11 Sec3 Motion and Forceapi-266280305No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Chapter 5 FrictionDocument5 pagesLecture Notes Chapter 5 FrictionNguyễn Sơn LâmNo ratings yet
- As Level Physics Key WordsDocument6 pagesAs Level Physics Key Words林仁超No ratings yet
- Basics of DesignDocument22 pagesBasics of Designgajendra yadavNo ratings yet
- 1st Puc Physics Chapter9-Mechanical Properties of Solids Notes by U N SwamyDocument7 pages1st Puc Physics Chapter9-Mechanical Properties of Solids Notes by U N Swamyashwinikumari bNo ratings yet
- Mechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsDocument7 pagesMechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsJenniferNo ratings yet
- R2 JMNZS1 Tid Evhu ALo 1 ZDocument12 pagesR2 JMNZS1 Tid Evhu ALo 1 ZAradhana GuptaNo ratings yet
- CE-213 Lecture 1 Fundamental of Stress & StrainDocument17 pagesCE-213 Lecture 1 Fundamental of Stress & StrainNazia ZamanNo ratings yet
- Greek Tau Stress Force Vector Parallel Normal Stress Perpendicular AntiparallelDocument4 pagesGreek Tau Stress Force Vector Parallel Normal Stress Perpendicular AntiparallelInah FrondaNo ratings yet
- Re Write Chapter 1Document25 pagesRe Write Chapter 1biruk geseseNo ratings yet
- What Is Stress and StainDocument1 pageWhat Is Stress and Stainzhungjian586No ratings yet
- Normal Statistical Table Standard Normal TableDocument1 pageNormal Statistical Table Standard Normal TableNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Growth: Vascular Plant Zygote Fertilisation EmbryoDocument9 pagesGrowth: Vascular Plant Zygote Fertilisation EmbryoNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Refers To A Tool That Removes The Material From The Work Part by ShearDocument1 pageCutting Tool Refers To A Tool That Removes The Material From The Work Part by ShearNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument1 pageStoichiometryNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Family, and Specific Code Is Given To Each Family. in This System, Machine Tools Are Arranged in A Cell and Used For Each Part FamilyDocument1 pageFamily, and Specific Code Is Given To Each Family. in This System, Machine Tools Are Arranged in A Cell and Used For Each Part FamilyNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- TRS BT: Point Bending or Four Point Bending Test Is UsedDocument1 pageTRS BT: Point Bending or Four Point Bending Test Is UsedNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocument1 pageFlexible Manufacturing SystemNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Integrated Manufacturing SystemDocument1 pageIntegrated Manufacturing SystemNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Punch Is Used in Blanking Operation To Apply Pressure, Which Makes The Sheet Metal To GoDocument1 pagePunch Is Used in Blanking Operation To Apply Pressure, Which Makes The Sheet Metal To GoNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- A Tolerance Is Defined As Physical Dimensions, Physical Property and Other Measured Values That May Vary in The Size and Geometry of The PartDocument1 pageA Tolerance Is Defined As Physical Dimensions, Physical Property and Other Measured Values That May Vary in The Size and Geometry of The PartNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- The Precision of A Measurement System Is Defined As Degree of Exactness of A Measurement or How Measured Values Are Close To Each OtherDocument1 pageThe Precision of A Measurement System Is Defined As Degree of Exactness of A Measurement or How Measured Values Are Close To Each OtherNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Some of The Additives Combined With Rubber During Compounding Are As FollowsDocument1 pageSome of The Additives Combined With Rubber During Compounding Are As FollowsNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Materials With Crystalline StructureDocument1 pageMaterials With Crystalline StructureNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- in This Defect, ThereDocument1 pagein This Defect, ThereNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- P P P P: M H H M H H H H M M H HDocument2 pagesP P P P: M H H M H H H H M M H HNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Fusion Weld Is A Type of Weld in Which Melting of The Two Surfaces Takes Place To ObtainDocument1 pageFusion Weld Is A Type of Weld in Which Melting of The Two Surfaces Takes Place To ObtainNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Specific HeatDocument1 pageSpecific HeatNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Value of Time Period of The Oscillation For The Given System. 2 100 KG 2 2 KN M 1.4 SDocument1 pageCalculate The Value of Time Period of The Oscillation For The Given System. 2 100 KG 2 2 KN M 1.4 SNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- P KHH K Is Active Earth Pressure, P KHH HHDocument3 pagesP KHH K Is Active Earth Pressure, P KHH HHNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet