Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pitot Probes PDF
Pitot Probes PDF
Uploaded by
watson1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
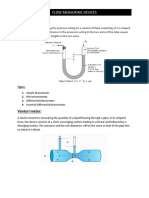
32 views1 pageA pitot-static probe is used to measure flow velocity at a point. It consists of a pitot tube to measure stagnation pressure and a static tube to measure static pressure. Stagnation pressure is measured by pointing the open end of the pitot tube into the oncoming flow, while static pressure is measured by a pressure tap parallel to the flow direction. By applying Bernoulli's equation using the measured stagnation and static pressures along with fluid density, the velocity of the airflow can be calculated.
Original Description:
Pitot
Original Title
Pitot Probes.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA pitot-static probe is used to measure flow velocity at a point. It consists of a pitot tube to measure stagnation pressure and a static tube to measure static pressure. Stagnation pressure is measured by pointing the open end of the pitot tube into the oncoming flow, while static pressure is measured by a pressure tap parallel to the flow direction. By applying Bernoulli's equation using the measured stagnation and static pressures along with fluid density, the velocity of the airflow can be calculated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 pagePitot Probes PDF
Pitot Probes PDF
Uploaded by
watson123A pitot-static probe is used to measure flow velocity at a point. It consists of a pitot tube to measure stagnation pressure and a static tube to measure static pressure. Stagnation pressure is measured by pointing the open end of the pitot tube into the oncoming flow, while static pressure is measured by a pressure tap parallel to the flow direction. By applying Bernoulli's equation using the measured stagnation and static pressures along with fluid density, the velocity of the airflow can be calculated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Union College
Mer331 Fluid Mechanics
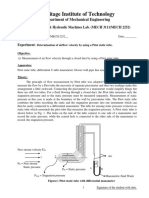
Using a Pitot-Static Probes to Measure Velocity
A pitot-static probe is a simple device used for measuring flow-velocity at a point.
A pitot probe measures stagnation pressure (the
pressure produced by bring the flow to a halt). It
consists of a tube connected at one end to a
pressure sensing device (such as a manometer or
pressure transducer) and open at the other.
Stagnation pressure is measured by pointing the
open end of the tube towards the oncoming flow.
Figure 1. Pitot Probe
A static probe measures static pressure (the actual
pressure in the flow). It consists of an opening (or
'pressure tap') parallel to the local flow direction.
The pressure tap may be located in a tube, or in the
surface of a model.
Figure 2. Static Pressure Probe
A pitot-static probe is a combination of a pitot tube
and static tube.
Figure 3. Pitot-Static Pressure Probe
The speed of the airflow can be found by applying Bernoullis equation along a streamline:
2 ( Po
P )
V is the velocity of the flow, Po is the stagnation pressure, P is the static pressure and is the
fluid density. Note: You will need the conversion 1H20 = 248.8 Pa.
Professor Anderson
You might also like
- Lab 1 Measurement of Airflow Lab Manual-1Document10 pagesLab 1 Measurement of Airflow Lab Manual-1Nadeem Rehman100% (1)
- Measurement of Fluid Velocity With A Pitot TubeDocument18 pagesMeasurement of Fluid Velocity With A Pitot TubeJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report On Pressure Mesurement DevicesDocument14 pagesLab Report On Pressure Mesurement DevicesRaisul Karim RiadNo ratings yet
- Pitot Tube Exper.Document4 pagesPitot Tube Exper.AbdulrazzaqAL-Maliky100% (1)
- Measurement of Air VelocityDocument3 pagesMeasurement of Air VelocityOsas OmoxxNo ratings yet
- Pitot Tube, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages: PrincipleDocument8 pagesPitot Tube, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages: PrincipleGeorge Anibor100% (1)
- Pitot Tubes: Prepared By: Ahmad Mohamed Ayman Abo Bakr ID:12p1125Document3 pagesPitot Tubes: Prepared By: Ahmad Mohamed Ayman Abo Bakr ID:12p1125Mohammed MohieNo ratings yet
- Determination of Static, Velocity and Total Pressure Using Manometer and Pitot Tube - OpaoDocument15 pagesDetermination of Static, Velocity and Total Pressure Using Manometer and Pitot Tube - OpaoIan Dave E. OPAONo ratings yet
- Prelab: Questions To Answer Before Doing The LabDocument4 pagesPrelab: Questions To Answer Before Doing The Labsuzette TabladaNo ratings yet
- Flow MeasurementDocument27 pagesFlow MeasurementRajdeep RoyNo ratings yet
- Power and Measurements of Pressure FlowsDocument7 pagesPower and Measurements of Pressure FlowsDanny ChengNo ratings yet
- SRLPN Power Plant Measurement and InstrumentationDocument77 pagesSRLPN Power Plant Measurement and InstrumentationRajneesh VachaspatiNo ratings yet
- Presentation Of: Fluid Flow LabDocument19 pagesPresentation Of: Fluid Flow LabRahulBhardwajNo ratings yet
- Fluid Velocity Measurement Using A Pitot TubeDocument6 pagesFluid Velocity Measurement Using A Pitot TubeSean GallegoNo ratings yet
- Pitot Static TubeDocument3 pagesPitot Static TubeArindam MandalNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration Lab ReportDocument24 pagesBernoulli's Theorem Demonstration Lab ReportCendolz IssZul50% (2)
- Explain in Details How Pitot Tube Device Can Be Used in Measurement of Flow VelocityDocument1 pageExplain in Details How Pitot Tube Device Can Be Used in Measurement of Flow VelocityImalah UgoachanumNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument10 pagesPressure MeasurementKefas SolomonNo ratings yet
- Based From The ExperimentDocument2 pagesBased From The ExperimentM Syafiq SamadNo ratings yet
- Aerody QuizDocument13 pagesAerody QuizCAJES, NICOLE RAYNE R.No ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Basic Mechanical Engineering (Bt-203) UNIT-2 Measurement of Pressure BY J.P.SinghDocument9 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Basic Mechanical Engineering (Bt-203) UNIT-2 Measurement of Pressure BY J.P.SinghDharmendra BelwanshiNo ratings yet
- FAQ: How Is Airspeed Really MeasuredDocument2 pagesFAQ: How Is Airspeed Really MeasuredMedaNo ratings yet
- Pitot TubeDocument11 pagesPitot TubeBabylyn AustriaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurement Using U-Tube Manometer: BITS PilaniDocument13 pagesPressure Measurement Using U-Tube Manometer: BITS PilaniTECH VAISHNAV ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Air Flow Velocity Measurement Using Point Static TubeDocument5 pagesAir Flow Velocity Measurement Using Point Static TubeIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project Report: "Overview and Role of C & I in Thermal Power Plant"Document109 pagesSummer Training Project Report: "Overview and Role of C & I in Thermal Power Plant"ysr3ee6926No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Me Lab FinalsDocument2 pagesUnit 8 Me Lab FinalsQUEENE FAYETH TAGANASNo ratings yet
- Volume Flow Rate GuideDocument8 pagesVolume Flow Rate Guidetfkthe46No ratings yet
- Automatic Control System CompressDocument116 pagesAutomatic Control System Compressswapnil28.08 k100% (1)
- Pitot Tube Investigation W18 December 11Document8 pagesPitot Tube Investigation W18 December 11ianNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument293 pagesPressure MeasurementGlen Lauren PerezNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementsDocument42 pagesPressure MeasurementsNicoleAmparoGarciaNo ratings yet
- Active Learning AssesmentFMDocument15 pagesActive Learning AssesmentFMNaisarg ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's EquationDocument4 pagesBernoulli's EquationTots HolaresNo ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment PDFsaikrishnaps31No ratings yet
- p19 PDFDocument1 pagep19 PDFSaradaPrasadChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Loss in Pipe and Fitting SystemDocument17 pagesLoss in Pipe and Fitting SystemGulshan Raza KhanNo ratings yet
- Muhammad LAbDocument17 pagesMuhammad LAbsikandar abbasNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote - 2103942165chapter 4 Flow MeasuremntDocument56 pagesLecturenote - 2103942165chapter 4 Flow MeasuremntPruthviraj KukadeNo ratings yet
- ECE Module 5 6Document35 pagesECE Module 5 6June Paulo TejereroNo ratings yet
- Problems With Pitots: Question-AIRDocument3 pagesProblems With Pitots: Question-AIRArnold StevenNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Pressure - Direct ReadingDocument12 pagesMeasurement of Pressure - Direct ReadingVedanta NairNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document9 pagesExperiment 2Ayan Ghosh0% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Lab MannualDocument14 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab MannualAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Pitot TubeDocument3 pagesPitot Tubeafif mustakimNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Pressure BasicsDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Pressure BasicsMoiz AamirNo ratings yet
- Manometer:: Flow Measuring DevicesDocument3 pagesManometer:: Flow Measuring DevicesMuhammad ZawarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MECHATRONICSDocument13 pagesUnit 5 MECHATRONICSpinku kumarNo ratings yet
- C&i SystemsDocument116 pagesC&i SystemsbamzNo ratings yet
- Pitot TubesDocument16 pagesPitot TubesKishan PatelNo ratings yet
- Module v. Calibration and Uses of Pressure & Temperature Measuring InstrumentsDocument25 pagesModule v. Calibration and Uses of Pressure & Temperature Measuring InstrumentsDomingo NoverasNo ratings yet
- Pi I Unit 2 Pressure MeasurementDocument41 pagesPi I Unit 2 Pressure MeasurementRahmat ElyasaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Theorem DemonstrationDocument27 pagesBernoulli Theorem DemonstrationmanzahuhuNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Lab ManualsDocument53 pagesGroup 5 Lab ManualsMUHAMMAD ALMASNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Josephine Bakewa A00224059Document9 pagesTutorial 3 Josephine Bakewa A00224059Josephine BakewaNo ratings yet
- Modern Sensors HandbookFrom EverandModern Sensors HandbookPavel RipkaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNo ratings yet
- Gridgen VersionDocument34 pagesGridgen Versionwatson123No ratings yet
- Homework 11Document2 pagesHomework 11watson123No ratings yet
- This Is The Title: Author One Author Two 29 February 2004Document1 pageThis Is The Title: Author One Author Two 29 February 2004watson123No ratings yet
- License AgreementDocument1 pageLicense Agreementwatson123No ratings yet
- TestoDocument5 pagesTestowatson123No ratings yet
- SolidmodelingDocument21 pagesSolidmodelingwatson123No ratings yet
- A Guide To The ANSI Z358.1-2009 StandardDocument3 pagesA Guide To The ANSI Z358.1-2009 Standardwatson123No ratings yet
- Time Integration: Splitting Methods: Marlis Hochbruck, D UsseldorfDocument16 pagesTime Integration: Splitting Methods: Marlis Hochbruck, D Usseldorfwatson123No ratings yet
- Low Temperature Technologies For SofcsDocument1 pageLow Temperature Technologies For Sofcswatson123No ratings yet
- Flue Gas 360 PDFDocument2 pagesFlue Gas 360 PDFwatson123No ratings yet
- Incubator Shaker: MODEL NO. - ACM-22063-IDocument8 pagesIncubator Shaker: MODEL NO. - ACM-22063-Iwatson123No ratings yet