Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phase Modulation Frequency Shift Key Modulation
Phase Modulation Frequency Shift Key Modulation
Uploaded by
kishan300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesPhase modulation varies the phase angle of the carrier wave according to the modulating wave, keeping amplitude and frequency constant. Frequency shift keying changes the carrier frequency between two values depending on the input bit, while amplitude shift keying varies the carrier amplitude between two levels. Digital modulation techniques include amplitude shift keying, frequency shift keying, and phase shift keying which varies the phase of the carrier.
Original Description:
Original Title
Page 3
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhase modulation varies the phase angle of the carrier wave according to the modulating wave, keeping amplitude and frequency constant. Frequency shift keying changes the carrier frequency between two values depending on the input bit, while amplitude shift keying varies the carrier amplitude between two levels. Digital modulation techniques include amplitude shift keying, frequency shift keying, and phase shift keying which varies the phase of the carrier.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesPhase Modulation Frequency Shift Key Modulation
Phase Modulation Frequency Shift Key Modulation
Uploaded by
kishan30Phase modulation varies the phase angle of the carrier wave according to the modulating wave, keeping amplitude and frequency constant. Frequency shift keying changes the carrier frequency between two values depending on the input bit, while amplitude shift keying varies the carrier amplitude between two levels. Digital modulation techniques include amplitude shift keying, frequency shift keying, and phase shift keying which varies the phase of the carrier.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Phase Modulation
Frequency Shift Key Modulation
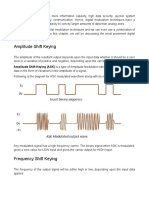
In this type of modulation, Amplitude and In this method, the frequency of the carrier is
changed to two different frequencies depending on
Frequency are kept constant. The phase angle of
the logic state of the input bit stream. The typical
the carrier wave is varied according to the output waveform of an FSK is shown below. Notice
modulating wave. The common name for "Phase that logic high causes the centre frequency to
modulation" and "Frequency modulation" is "Angle increase to a maximum and a logic low causes the
modulation". centre frequency to decrease to a minimum.
The digital transmission of analog signals involves
pulse modulation. In analog pulse modulation, time
is represented in discrete form. In digital pulse
modulation, both time and signal amplitude are
represented in discrete form.
DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES
Amplitude Shift Key Modulation
In this method the amplitude of the carrier assumes
one of the two amplitudes dependent on the logic
states of the input bit stream. A typical output
waveform of an ASK modulator is shown in the
figure below. The frequency components are the
USB and LSB with a residual carrier frequency. The
low amplitude carrier is allowed to be transmitted to
ensure that at the receiver the logic 1 and logic 0
conditions can be recognized uniquely.
Fig: Frequency Shift Key Modulation
Phase Shift Key Modulation
With this method, the phase of the carrier changes
between different phases determined by the logic
states of the input bit stream. Phase shift keying
(PSK) is a method of transmitting and receiving
digital signals in which the phase of a transmitted
signal is varied to convey information.
There are several different types of phase shift key
(PSK) modulators.
• Two-phase (2 PSK)
• Four-phase (4 PSK)
• Eight-phase (8 PSK)
• Sixteen-phase (16 PSK)
• Sixteen-Quadrature amplitude (16 QAM)
The 16 QAM is a composite modulator consisting of
amplitude modulation and phase modulation. The
Fig: Amplitude Shift Key Modulation 2 PSK, 4 PSK, 8 PSK and 16 PSK modulators are
generally referred to as binary phase shift key
(BPSK) modulators and the QAM modulators are can be regarded (using complex number
referred to as Quadrature phase shift key (QPSK) notation) as simple amplitude modulation
modulators. of a complex-valued carrier wave by a
Two-Phase Shift Key Modulation (BPSK) single complex-valued signal.
In this modulator the carrier assumes one of two
phases. Logic 1 produces no phase change and What this actually means is that the
logic 0 produces a 180° phase change. The output amplitude and the phase of the carrier
waveform for this modulator is shown below. The wave are simultaneously changed
simplest form of PSK has only two phases, 0 and 1. according to the information you want to
It is therefore a type of ASK taking the values -1 or transmit.
1, and its bandwidth is the same as that of ASK. The
digital signal is broken up time wise into individual
bits (binary digits).The state of each bit is
ANALOG VS DIGITAL MODULATION
determined according to the state of the preceding
bit. If the phase of the wave does not change, then
the signal state stays the same (low or high). If the
phase of the wave changes by 180 degrees, that is, Digital Modulation
if the phase reverses, then the signal state changes
(from low to high or from high to low). The modulation method is simple i.e. switch the
carrier on and off.
The receiver must have some form of
synchronization with the transmitter to decode the
digital information.
Synchronization wastes bandwidth because it is not
information.
Analog Modulation
Very simple demodulation techniques for AM and
FM (1 or 2 diodes, capacitors, and a transformer)
Linear amplifiers and modulators are used. No
digital circuit needed.
Modulation methods require lots of power
comparable with the carrier power.
Fig: Phase Shift Key Modulation
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM)
QAM is the encoding of information into a
carrier wave by variation of the amplitude
of both the carrier wave and a
'Quadrature' carrier that is 90° out of
phase with the main carrier in accordance
with two input signals. Alternately, this
You might also like
- Project PDF FinalDocument21 pagesProject PDF Finalramratanec100% (1)
- Phase Modulation Frequency Shift Key ModulationDocument2 pagesPhase Modulation Frequency Shift Key Modulationkishan30No ratings yet
- Icn Lab ManualDocument62 pagesIcn Lab ManualMohit JeshdiyaNo ratings yet
- Ex - No: 2 Digital Modulation: DateDocument6 pagesEx - No: 2 Digital Modulation: DatebbmathiNo ratings yet
- MSK and GMSKDocument72 pagesMSK and GMSKjameelahmadNo ratings yet
- Phase Shift Keying: The BPSK ModulatorDocument3 pagesPhase Shift Keying: The BPSK ModulatorHafid AlifiantoNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument34 pagesDigital Modulation TechniquesSerial SpyNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument17 pagesDigital Modulation TechniquesSharath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation For Wireless CommunicationsDocument72 pagesDigital Modulation For Wireless CommunicationslhslhinNo ratings yet
- ريهام خالد جوحي PskDocument9 pagesريهام خالد جوحي Pskريهام خالد جوحيNo ratings yet
- 3 ModulationDocument16 pages3 Modulation49 SRI RAM KARTHI PNo ratings yet
- ASK - Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument15 pagesASK - Amplitude Shift KeyingAbhijith C SNo ratings yet
- Modulation and What Is Amplitude Key ShiftDocument2 pagesModulation and What Is Amplitude Key ShiftFaiqNo ratings yet
- DC Unit - 2Document4 pagesDC Unit - 2Hari krishna PinakanaNo ratings yet
- Artikel QPSK Sistem ModulasiDocument3 pagesArtikel QPSK Sistem Modulasitholib candraNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii - Digital Modulation: Digital Information Analogue TransmissionDocument9 pagesUnit Ii - Digital Modulation: Digital Information Analogue TransmissionnimmycharanNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document23 pagesLec 6holyprogramingNo ratings yet
- DC-Lec-16 &17 (Digital To Analog Encoding)Document49 pagesDC-Lec-16 &17 (Digital To Analog Encoding)Farman AfridiNo ratings yet
- Idresss sir#4OKDocument12 pagesIdresss sir#4OKDil NawazNo ratings yet
- Digital Bandpass Modulation Techniques 2018Document11 pagesDigital Bandpass Modulation Techniques 2018harold cooperNo ratings yet
- Data Communications Lab One by Joseph NjoguDocument14 pagesData Communications Lab One by Joseph NjoguJoseph MagonduNo ratings yet
- DC 2Document6 pagesDC 2VijayNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation: - by Amitava Nath, FIEDocument10 pagesDigital Modulation: - by Amitava Nath, FIEUpakul007No ratings yet
- Elec 2 Modulation & DemodulationDocument17 pagesElec 2 Modulation & DemodulationChannveer MulgeNo ratings yet
- ASK or Amplitude Shift KeyDocument5 pagesASK or Amplitude Shift KeyDivyamani M PNo ratings yet
- Adc Unit 5 MaterialDocument60 pagesAdc Unit 5 MaterialsrinithaNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument15 pagesDigital Modulation TechniquesAvinaba BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Phase Shift Keying (PSK)Document2 pagesPhase Shift Keying (PSK)suniljitmNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems - II Spring 2017: Lecture - 06Document63 pagesCommunication Systems - II Spring 2017: Lecture - 06Muhaamad Haseeb KhokharNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument34 pagesUnit-Iii: Digital Modulation TechniquesKvnsumeshChandraNo ratings yet
- ASK or Amplitude Shift KeyDocument5 pagesASK or Amplitude Shift KeyDivyamani M PNo ratings yet
- What Is A Signal ?Document62 pagesWhat Is A Signal ?Paras MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Comm Sim Complete FileeeeeeeeDocument24 pagesComm Sim Complete Fileeeeeeeeanon_425875347No ratings yet
- Synopsis of ECE 304 Topic: Digital ModulationDocument3 pagesSynopsis of ECE 304 Topic: Digital ModulationrohitpowariNo ratings yet
- Modulation TechniquesDocument3 pagesModulation TechniquesNorliza Farhah Abdul RadzakNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Techniques.: Unit - 3 Presented by Mrs. M.P.SasirekhaDocument42 pagesDigital Modulation Techniques.: Unit - 3 Presented by Mrs. M.P.SasirekhasasirekhaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 - 4Document43 pagesLec 6 - 4Sajid MumtazNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 7. Phase Shift KeyingDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT 7. Phase Shift KeyingBenedict SungaNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation of PSK Project ReportDocument6 pagesAmplitude Modulation of PSK Project ReportEngr Muhammad Imran100% (2)
- Analog Transmission Modulastion - Gregorio Diovani W - c11180040Document7 pagesAnalog Transmission Modulastion - Gregorio Diovani W - c11180040ye KaaNo ratings yet
- PSK ModulationDocument12 pagesPSK ModulationHema Sundar100% (1)
- Amplitude Shift Keying: Sunny BabuDocument10 pagesAmplitude Shift Keying: Sunny BabuZahoor AbbasNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument4 pagesDigital Modulation TechniquestrusselNo ratings yet
- Rewa Engineering College: Department of Electronics and CommunicationDocument9 pagesRewa Engineering College: Department of Electronics and CommunicationAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication: Engr. Muhammad Farooq Ashfaq Hussain Hasib KhlaidDocument10 pagesDigital Communication: Engr. Muhammad Farooq Ashfaq Hussain Hasib KhlaidMuhammad Farooq AwanNo ratings yet
- CN 2nd MODULE Continue.Document31 pagesCN 2nd MODULE Continue.Mohith HNo ratings yet
- Communication Experiments: Bme LabDocument22 pagesCommunication Experiments: Bme LabshruitsmeNo ratings yet
- Digital ModulationDocument5 pagesDigital Modulationnaseem AhamdNo ratings yet
- Data and Digital Communication 1Document6 pagesData and Digital Communication 1Lou Andrei BahoyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Performance of Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument8 pagesProject Report On Performance of Digital Modulation Techniqueseshet chafNo ratings yet
- Automated Humidifier With Temperature LevelDocument14 pagesAutomated Humidifier With Temperature LevelEfren sibbaluca JrNo ratings yet
- DC File MergedDocument33 pagesDC File Mergedspareadd.23No ratings yet
- MTDCC103 ModelAnswerDocument8 pagesMTDCC103 ModelAnswerNoman Ali35No ratings yet
- Data Communications: Digital To Analog ConversionDocument16 pagesData Communications: Digital To Analog ConversionAmir fazilNo ratings yet
- ASK Mod & DemodDocument14 pagesASK Mod & Demodchairulsyah7874No ratings yet
- CommSim File YoyoDocument20 pagesCommSim File YoyoAnshul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Modulation (Class 12)Document14 pagesProject Report On Modulation (Class 12)Shivam Tripathi100% (9)
- Ask & PSK: Generation and Detection: Date Expt NoDocument6 pagesAsk & PSK: Generation and Detection: Date Expt NoRajesh EceNo ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Phase Modulation Frequency Shift Key ModulationDocument2 pagesPhase Modulation Frequency Shift Key Modulationkishan30No ratings yet
- Page 2Document2 pagesPage 2kishan30No ratings yet
- Page 2Document2 pagesPage 2kishan30No ratings yet
- Page 2Document1 pagePage 2kishan30No ratings yet
- Computer Networks Assignment 1Document5 pagesComputer Networks Assignment 1kishan30No ratings yet
- Computer Networks Assignment 1Document5 pagesComputer Networks Assignment 1kishan30No ratings yet