Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamics EM PED Lecture6 1
Dynamics EM PED Lecture6 1
Uploaded by
DarioSpCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SCS, Lascr, Diac and TriacDocument16 pagesSCS, Lascr, Diac and TriacRyan Paul RiwarinNo ratings yet
- General Tutorial PHY 122Document3 pagesGeneral Tutorial PHY 122Mirabel SikaNo ratings yet
- Induction Machine ModelDocument7 pagesInduction Machine Modelahmed s. NourNo ratings yet
- Machines EPM405A Presentation 06Document18 pagesMachines EPM405A Presentation 06Ibrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Model of Induction Machine: MEP 1522 Electric DrivesDocument46 pagesDynamic Model of Induction Machine: MEP 1522 Electric Drivessameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- DQ TransformationDocument51 pagesDQ TransformationWGSNo ratings yet
- 4 (A) - IM Drives BasicsDocument27 pages4 (A) - IM Drives BasicsimdadamuNo ratings yet
- D-Q Transformation: J. MccalleyDocument51 pagesD-Q Transformation: J. MccalleyRicardo TironeNo ratings yet
- ECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 5: Dynamic Simulation of Induction MotorDocument26 pagesECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 5: Dynamic Simulation of Induction MotorSentamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196890401000164 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0196890401000164 MainKaderNo ratings yet
- IJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchDocument5 pagesIJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Dynamic Model Identification of Induction Motors Using Intelligent Search Techniques With Taking Core Loss Into AccountDocument8 pagesDynamic Model Identification of Induction Motors Using Intelligent Search Techniques With Taking Core Loss Into AccountYasir AlameenNo ratings yet
- Sensorless Speed Detection of Squirrel-Cage Induction Machines Using Stator Neutral Point Voltage HarmonicsDocument9 pagesSensorless Speed Detection of Squirrel-Cage Induction Machines Using Stator Neutral Point Voltage HarmonicsJonas BorgesNo ratings yet
- Anitha PPTDocument17 pagesAnitha PPTDr. Sarath DuvvuriNo ratings yet
- (25434292 - Power Electronics and Drives) Stator Winding Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Modelling of A Squirrel-Cage Induction MotorDocument10 pages(25434292 - Power Electronics and Drives) Stator Winding Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Modelling of A Squirrel-Cage Induction Motorronaldo rmaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Single-Phase Capacitor Induction Motor Operating at Two Power Line FrequenciesDocument16 pagesAnalysis of A Single-Phase Capacitor Induction Motor Operating at Two Power Line FrequenciesshazzadNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcessesDocument4 pagesMathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcessesMadarwi SarwaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modelling and Simulation of Salient Pole Synchronous Motor Using Embedded MatlabDocument8 pagesDynamic Modelling and Simulation of Salient Pole Synchronous Motor Using Embedded MatlabmarcosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Synchronous Machine ModelingDocument57 pagesLecture 7 Synchronous Machine ModelingManuelNo ratings yet
- DQ TransformationDocument51 pagesDQ Transformationwan ismail ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Icate2016 Id23Document14 pagesIcate2016 Id23Marcel NicolaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument50 pagesInduction Motorsolo4000100% (1)
- Help - Asynchronous Machine - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™) PDFDocument23 pagesHelp - Asynchronous Machine - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™) PDFnmulyonoNo ratings yet
- Commutation Techniques of SCR PDFDocument2 pagesCommutation Techniques of SCR PDFLeasaNo ratings yet
- G Owacz - V13i2 - 6mathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcesseDocument4 pagesG Owacz - V13i2 - 6mathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcesseDante GuajardoNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motor Drive Control System With Prescribed Closed-Loop Speed DynamicsDocument20 pagesSynchronous Motor Drive Control System With Prescribed Closed-Loop Speed DynamicsVijay RajuNo ratings yet
- Acta 2013 1 07 PDFDocument6 pagesActa 2013 1 07 PDFAhmet Yasin BaltacıNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled Rectifiers: Chapter - 15Document3 pagesSilicon Controlled Rectifiers: Chapter - 15lvsaruNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of The Three-Phase Induction Motor Using SimulinkDocument10 pagesModelling and Simulation of The Three-Phase Induction Motor Using Simulinksajs201100% (1)
- Flow in One Direction and Opposes It in Another Direction. SCR Has Three TerminalsDocument6 pagesFlow in One Direction and Opposes It in Another Direction. SCR Has Three TerminalsEdelson Mark GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Induction Motor (Dynamic)Document29 pagesChapter 7-Induction Motor (Dynamic)arifulNo ratings yet
- Sensorless Speed Control of Induction MotorDocument5 pagesSensorless Speed Control of Induction MotorItipun SakunwanthanasakNo ratings yet
- A Generalized Two Axes Model of A Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor For A Rotor Fault DiagnosisDocument16 pagesA Generalized Two Axes Model of A Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor For A Rotor Fault DiagnosisJorge Luis SotoNo ratings yet
- DQ TransformationDocument51 pagesDQ Transformationafnan saadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Speed-Torque Characteristics of Electric MotorsDocument46 pagesChapter 5: Speed-Torque Characteristics of Electric MotorsFrozenTuxNo ratings yet
- Em-2 Lab ManualDocument9 pagesEm-2 Lab Manualsomnath banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis by Parameter Estimation of Stator and Rotor Faults Occuring in Induction MachinesDocument9 pagesDiagnosis by Parameter Estimation of Stator and Rotor Faults Occuring in Induction MachinesStephano Saucedo ReyesNo ratings yet
- L-35 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document15 pagesL-35 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Mahua ChandaNo ratings yet
- Syll AM (Elect) APGCL 11 2023 08062023Document3 pagesSyll AM (Elect) APGCL 11 2023 08062023BikashDeyNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives: Notes of Lesson PlanDocument24 pagesSolid State Drives: Notes of Lesson PlanetasureshNo ratings yet
- SCR DC Motor Forward/Reverse Control: Experiment #6Document6 pagesSCR DC Motor Forward/Reverse Control: Experiment #6Zeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Silicon Control SwitchDocument4 pagesSilicon Control SwitchKi RoyNo ratings yet
- 02-1 Synchronous MachinesDocument48 pages02-1 Synchronous MachinesvenikiranNo ratings yet
- InTech-Speed Sensorless Control of Motor For Railway VehiclesDocument25 pagesInTech-Speed Sensorless Control of Motor For Railway VehiclesdimitaringNo ratings yet
- Simulation of A Three-Phase Induction MachineDocument19 pagesSimulation of A Three-Phase Induction MachineOyekunle Emmanuel DareNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control System of Speed of Synchronous Motor: SciencedirectDocument6 pagesAutomatic Control System of Speed of Synchronous Motor: SciencedirectRedkit ofFootHillNo ratings yet
- Aee 2013 0046Document23 pagesAee 2013 0046Butch Apa GestaNo ratings yet
- Induction Machines: Principle of Operation and Equivalent Circuit ModelDocument15 pagesInduction Machines: Principle of Operation and Equivalent Circuit ModelRyan BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsFrom EverandFoundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Sheet2 PDFDocument2 pagesSheet2 PDFDarioSpNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Statistics: October 7, 2014 Robert Dahl JacobsenDocument32 pagesProbability Theory and Statistics: October 7, 2014 Robert Dahl JacobsenDarioSpNo ratings yet
- Preparation For LessonDocument6 pagesPreparation For LessonDarioSpNo ratings yet
- Maglev FileDocument25 pagesMaglev FileDarioSpNo ratings yet
- 0900-73 Manual (US)Document2 pages0900-73 Manual (US)Paramedico GuadalajaraNo ratings yet
- Cv2d Ej2 Starex04f ArdanDocument10 pagesCv2d Ej2 Starex04f ArdanIna Therese ArdanNo ratings yet
- Vector DPP-1 - 2022Document6 pagesVector DPP-1 - 2022ShashankNo ratings yet
- Generalphysics1 - q1 - Mod2 - Kinematics Motion in A Straight Line - v1Document32 pagesGeneralphysics1 - q1 - Mod2 - Kinematics Motion in A Straight Line - v1Park JiminshiiNo ratings yet
- Notes ESO205Document44 pagesNotes ESO205muditNo ratings yet
- Gas Molecules in MotionDocument59 pagesGas Molecules in MotionMathew Angelo Perez GamboaNo ratings yet
- Belt FrictionDocument5 pagesBelt FrictionShah NawazNo ratings yet
- PHY-502 (Mathematical Methods of Physics-II) Mid Term 2017-I (GC University)Document1 pagePHY-502 (Mathematical Methods of Physics-II) Mid Term 2017-I (GC University)Ghulam Farid0% (1)
- Polytropic Process PDFDocument1 pagePolytropic Process PDFClarence De LeonNo ratings yet
- Engineering PhysicsDocument13 pagesEngineering PhysicsLa Vien RoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Stage and Continuous Gas-Liquid Separation ProcessesDocument46 pagesChapter 3 - Stage and Continuous Gas-Liquid Separation Processesomarfhassan0% (1)
- Transformer Design NotesDocument15 pagesTransformer Design Notesrishabh100% (2)
- BS en ISO 9934-3-2007, NondestructiveDocument20 pagesBS en ISO 9934-3-2007, Nondestructivescofiel1No ratings yet
- Pre-Mock Practice 3Document2 pagesPre-Mock Practice 3Michelle ChungNo ratings yet
- Disc 15 SolutionDocument4 pagesDisc 15 Solutionmmounir79No ratings yet
- Foundation Analyzing of Centrifugal ID Fans in Cement PlantsDocument11 pagesFoundation Analyzing of Centrifugal ID Fans in Cement PlantsDhiviya KumarNo ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 6Document7 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 6Abdurrahman AdigunNo ratings yet
- The High Voltage Homopolar GeneratorDocument6 pagesThe High Voltage Homopolar Generatorapi-241035124No ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document29 pagesLecture 21rajamatheNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Nithisri BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Materials - J. B. GuptaDocument70 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering Materials - J. B. GuptakundanabcNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Half-Life NotesDocument1 pageChemistry - Half-Life NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics IDocument21 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics ImihretuNo ratings yet
- Braun and Mitchell 1983Document6 pagesBraun and Mitchell 1983Antony BanderasNo ratings yet
- This Kisssoft Demoversion May Not Be Used For Professional Application ! Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The CalculationDocument7 pagesThis Kisssoft Demoversion May Not Be Used For Professional Application ! Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The Calculationpablo_stzNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Quantum ChemistryDocument10 pagesMCQ On Quantum ChemistryRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaDocument10 pagesChemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaWaqas LuckyNo ratings yet
- Pankaj EMT AssignDocument6 pagesPankaj EMT AssignpankajmadhuNo ratings yet
- Waves: How Do Waves Travel Through Matter?Document4 pagesWaves: How Do Waves Travel Through Matter?ToyNerd Collectors100% (1)
Dynamics EM PED Lecture6 1
Dynamics EM PED Lecture6 1
Uploaded by
DarioSpOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamics EM PED Lecture6 1
Dynamics EM PED Lecture6 1
Uploaded by
DarioSpCopyright:
Available Formats
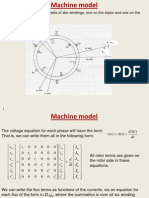
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Lecture 6 - contents
Modeling of IM in an arbitrary reference-frame
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Modeling of IM in an arbitrary reference-frame
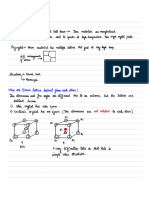
Reference frame definition - mapping the synchronous
machine to the induction machine
b
d
r
q
c
An arbitrary rotating reference frame (qd0):
ar
as
as-axis
ar
d
d
cr
bs
cs
br
as
r
q
bs
cr
cs
br
2
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Stator self-inductance matrix
ar
as
cr
bs
cs
Lms
Lms
L
L
ls ms
2
2 ias
ias
as
Lms
L i Lms L L
ibs
ls
ms
bs s bs
2
2
ics
ics L
cs
L
ms
ms Lls Lms
2
2
br
Learned from lecture 3 how the inductances are
determined
Observation of these two values
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Rotor self-inductance matrix
ar
as
cr
bs
cs
Lmr
Lmr
L
L
lr mr
2
2 iar
iar
ar
Lmr
L i Lmr L L
ibr
lr
mr
br r br
2
2
icr
icr L
cr
L
mr
mr Llr Lmr
2
2
br
Stator and rotor self-inductances are position independent
Stator and rotor self-inductance matrices have the similar form
2
It could be expected that
N
Lmr s Lms
Nr
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Rotor to stator mutual inductance matrix
ar
as
cr
bs
cs
br
2
2
cos
cos
cos
r
r
r
3
3
iar
asr
iar
2
L i M cos 2
cos
cos
ibr
bsr
sr
br
sr
r
r
r
3
3
csr
icr
icr
2
cos cos
cosr
r
r 3
Flux-axis, the phase with current for
producing that flux linkage
From stator to rotor:
j 2 j 2
e 3 e 3
2
M sr Re 2 Re 2 M sr cos r
3
jr j
e 3 e 3
j r 2 j r 2
e 3 e 3
2
M sr Re 2 Re 2 M sr cos r
3
j jr
e 3 e 3
Rotor phase b axis
Stator phase c axis
rs L rs i abcs L sr T i abcs
5
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Transform the stator flux linkage to an arbitrary qd0 system
ar
as
abcs L s i abcs L sr i abcr
cr
bs
qd 0 s K s L s K s 1 i qd 0 s K s L sr K r 1 i qd 0 r
cs
br
cos
2
K s sin
3
1
2
2
cos
cos
3
3
2
2
sin
sin
3
3
1
1
2
2
cos
2
K r sin
3
1
2
2
cos
cos
3
3
2
2
sin
sin
3
3
1
1
2
2
K 1s
cos
cos
3
cos
3
K 1r
cos
cos
3
cos
3
sin
2
sin
3
sin
3
sin
2
sin
3
sin
3
1
1
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Transform the stator flux linkage to an arbitrary qd0 system
3
2 Msr
1
Lsrqd0 K s Lsr K r 0
0
0
Lls 2 Lms
3
Lsqd0 K s Ls K s 1
0
Lls Lms 0
2
0
0
L
ls
Define
qd 0 s
Lls L m
0
i' j
3
Lms Lm
2
0
Lls L m
0
M sr
0
3
M sr
2
0
Ns
2
Lms Lm
Nr
3
0
Lm
0 i qd 0 s 0
0
Lls
0
Lm
0
Nr
i j , j qr , dr ,0r , ar , br , cr
Ns
Nr
i qr
0 N s
N
0 r i dr
N
0 N s
r
i0 r
N s
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Transform the rotor flux linkage to an arbitrary qd0 system
abcr L r i abcr L sr T i abcs
qd 0 r K r L r K r 1 i qd 0 r K r L sr T K s 1 i qd 0 s
qd 0 r
L
Lmr
lr
0
Llr
3
Lmr
2
0
'
s
Define j N j
r
3
0
2 M sr
0 i qd 0 r 0
Llr
0
u' j
N
2
Lmr s Lms Lm ,
3
Nr
' qd 0 r
L'lr Lm
0
0
M sr
Ns
uj
Nr
0
3
M sr
2
0
j qr , dr ,0r , ar , br , cr
Ns
2
Lms Lm
Nr
3
0
L'lr Lm
0
0 i qd 0 s
0
Lm
'
0 i qd 0 r 0
0
L'lr
N
i j r ij
Ns
'
0
Lm
0
N
L'lr Llr s
Nr
0
0 i qd 0 s
0
8
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Transform the voltage equations to an arbitrary qd0 system
According to the slide P11-12, lecture 4, the stator voltage equations
0 1 0qs
uqs Rs 0 0 iqs qs
u 0 R 0 i p 1 0 0
s
ds
ds ds
ds
0 0 00s
u0s 0 0 Rs i0s 0s
Similarly, the rotor voltage equations would be
ar
as
cr
bs
cs
br
'
u'qr R'r 0 0 i'qr 'qr
0 1 0qr
'
' '
1 0 0'
'
u
R
i
p
0
0
dr
r
dr
dr
r
dr
u'0r 0 0 R'r i'0r '0r
0 0 0'0r
Why?
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Advanced notes
Another method - Using the vectors instead of the matrices
Please refer to Vector control and dynamics of AC machines
By D.W. Novotny, and T.A. Lipo, pp43~61
ar
u abcs
uas
2
d
1 2 ubs Rs i abcs Lls Lm i abcs Lm i abcr e j r
3
dt
ucs
abcs Lls Lm i abcs Lm i abcr e
j r
i abcs i qds e j ,
abcs qds e j ,
i abcr i qdr e j
qds Lls Lm i qds Lm i abcr e j Lls Lm i qds Lm i qdr
cr
cs
br
f qd f q jf d
No zero component involved
in the qd vectors!
d
Lls Lm i abcs Lm i abcr e jr
dt
d
d
Rs i qds Lls Lm i qds Lm i qdr e j Lls Lm i abcs Lm i abcr e j r
dt
dt
d
Rs i qds qds j qds
dt
bs
u abcs u qds e j ,
u qds Rs i qds e j
as
10
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Advanced notes
Another method - Using the vectors instead of the matrices
For the rotor side equations
'
u abcr
u ' ar
ar
'
'
2
d
1 2 u 'br R ' r i abcr L'ls Lm i abcr Lm i abcs e j r
3
dt
u 'cr
q
abcr L'lr Lm i abcr Lm i abcs e j
'
'
'
cr
bs
'
qdr L lr Lm i qdr Lm i qds
'
as
cs
br
'
'
'
R ' r i qdr
'
'
d '
L ls Lm i abcr Lm i abcs e j r
dt
j
'
d
de
L'ls L i ' abcr L i abcs e j r
L'ls Lm i qdr Lm i qds
m
m
dt
dt
u qdr R ' r i qdr e j
R ' r i qdr
'
d '
qdr j r qdr
dt
It is not recommended to apply this method to the synchronous motor!
11
Dynamic modeling of electrical machines
Exercises
Use the obtained induction machine qd model, please give
the machine equations when the q-axis of the rotating qd reference frame
is aligned with the rotor flux vector.
What the machine equations will be when in afa-beta reference frame?
12
You might also like
- SCS, Lascr, Diac and TriacDocument16 pagesSCS, Lascr, Diac and TriacRyan Paul RiwarinNo ratings yet
- General Tutorial PHY 122Document3 pagesGeneral Tutorial PHY 122Mirabel SikaNo ratings yet
- Induction Machine ModelDocument7 pagesInduction Machine Modelahmed s. NourNo ratings yet
- Machines EPM405A Presentation 06Document18 pagesMachines EPM405A Presentation 06Ibrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Model of Induction Machine: MEP 1522 Electric DrivesDocument46 pagesDynamic Model of Induction Machine: MEP 1522 Electric Drivessameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- DQ TransformationDocument51 pagesDQ TransformationWGSNo ratings yet
- 4 (A) - IM Drives BasicsDocument27 pages4 (A) - IM Drives BasicsimdadamuNo ratings yet
- D-Q Transformation: J. MccalleyDocument51 pagesD-Q Transformation: J. MccalleyRicardo TironeNo ratings yet
- ECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 5: Dynamic Simulation of Induction MotorDocument26 pagesECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 5: Dynamic Simulation of Induction MotorSentamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196890401000164 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0196890401000164 MainKaderNo ratings yet
- IJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchDocument5 pagesIJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Dynamic Model Identification of Induction Motors Using Intelligent Search Techniques With Taking Core Loss Into AccountDocument8 pagesDynamic Model Identification of Induction Motors Using Intelligent Search Techniques With Taking Core Loss Into AccountYasir AlameenNo ratings yet
- Sensorless Speed Detection of Squirrel-Cage Induction Machines Using Stator Neutral Point Voltage HarmonicsDocument9 pagesSensorless Speed Detection of Squirrel-Cage Induction Machines Using Stator Neutral Point Voltage HarmonicsJonas BorgesNo ratings yet
- Anitha PPTDocument17 pagesAnitha PPTDr. Sarath DuvvuriNo ratings yet
- (25434292 - Power Electronics and Drives) Stator Winding Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Modelling of A Squirrel-Cage Induction MotorDocument10 pages(25434292 - Power Electronics and Drives) Stator Winding Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Modelling of A Squirrel-Cage Induction Motorronaldo rmaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Single-Phase Capacitor Induction Motor Operating at Two Power Line FrequenciesDocument16 pagesAnalysis of A Single-Phase Capacitor Induction Motor Operating at Two Power Line FrequenciesshazzadNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcessesDocument4 pagesMathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcessesMadarwi SarwaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modelling and Simulation of Salient Pole Synchronous Motor Using Embedded MatlabDocument8 pagesDynamic Modelling and Simulation of Salient Pole Synchronous Motor Using Embedded MatlabmarcosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Synchronous Machine ModelingDocument57 pagesLecture 7 Synchronous Machine ModelingManuelNo ratings yet
- DQ TransformationDocument51 pagesDQ Transformationwan ismail ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Icate2016 Id23Document14 pagesIcate2016 Id23Marcel NicolaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument50 pagesInduction Motorsolo4000100% (1)
- Help - Asynchronous Machine - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™) PDFDocument23 pagesHelp - Asynchronous Machine - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™) PDFnmulyonoNo ratings yet
- Commutation Techniques of SCR PDFDocument2 pagesCommutation Techniques of SCR PDFLeasaNo ratings yet
- G Owacz - V13i2 - 6mathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcesseDocument4 pagesG Owacz - V13i2 - 6mathematical Model of DC Motor For Analysis of Commutation ProcesseDante GuajardoNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motor Drive Control System With Prescribed Closed-Loop Speed DynamicsDocument20 pagesSynchronous Motor Drive Control System With Prescribed Closed-Loop Speed DynamicsVijay RajuNo ratings yet
- Acta 2013 1 07 PDFDocument6 pagesActa 2013 1 07 PDFAhmet Yasin BaltacıNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled Rectifiers: Chapter - 15Document3 pagesSilicon Controlled Rectifiers: Chapter - 15lvsaruNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of The Three-Phase Induction Motor Using SimulinkDocument10 pagesModelling and Simulation of The Three-Phase Induction Motor Using Simulinksajs201100% (1)
- Flow in One Direction and Opposes It in Another Direction. SCR Has Three TerminalsDocument6 pagesFlow in One Direction and Opposes It in Another Direction. SCR Has Three TerminalsEdelson Mark GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Induction Motor (Dynamic)Document29 pagesChapter 7-Induction Motor (Dynamic)arifulNo ratings yet
- Sensorless Speed Control of Induction MotorDocument5 pagesSensorless Speed Control of Induction MotorItipun SakunwanthanasakNo ratings yet
- A Generalized Two Axes Model of A Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor For A Rotor Fault DiagnosisDocument16 pagesA Generalized Two Axes Model of A Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor For A Rotor Fault DiagnosisJorge Luis SotoNo ratings yet
- DQ TransformationDocument51 pagesDQ Transformationafnan saadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Speed-Torque Characteristics of Electric MotorsDocument46 pagesChapter 5: Speed-Torque Characteristics of Electric MotorsFrozenTuxNo ratings yet
- Em-2 Lab ManualDocument9 pagesEm-2 Lab Manualsomnath banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis by Parameter Estimation of Stator and Rotor Faults Occuring in Induction MachinesDocument9 pagesDiagnosis by Parameter Estimation of Stator and Rotor Faults Occuring in Induction MachinesStephano Saucedo ReyesNo ratings yet
- L-35 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document15 pagesL-35 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Mahua ChandaNo ratings yet
- Syll AM (Elect) APGCL 11 2023 08062023Document3 pagesSyll AM (Elect) APGCL 11 2023 08062023BikashDeyNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives: Notes of Lesson PlanDocument24 pagesSolid State Drives: Notes of Lesson PlanetasureshNo ratings yet
- SCR DC Motor Forward/Reverse Control: Experiment #6Document6 pagesSCR DC Motor Forward/Reverse Control: Experiment #6Zeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Silicon Control SwitchDocument4 pagesSilicon Control SwitchKi RoyNo ratings yet
- 02-1 Synchronous MachinesDocument48 pages02-1 Synchronous MachinesvenikiranNo ratings yet
- InTech-Speed Sensorless Control of Motor For Railway VehiclesDocument25 pagesInTech-Speed Sensorless Control of Motor For Railway VehiclesdimitaringNo ratings yet
- Simulation of A Three-Phase Induction MachineDocument19 pagesSimulation of A Three-Phase Induction MachineOyekunle Emmanuel DareNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control System of Speed of Synchronous Motor: SciencedirectDocument6 pagesAutomatic Control System of Speed of Synchronous Motor: SciencedirectRedkit ofFootHillNo ratings yet
- Aee 2013 0046Document23 pagesAee 2013 0046Butch Apa GestaNo ratings yet
- Induction Machines: Principle of Operation and Equivalent Circuit ModelDocument15 pagesInduction Machines: Principle of Operation and Equivalent Circuit ModelRyan BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsFrom EverandFoundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Sheet2 PDFDocument2 pagesSheet2 PDFDarioSpNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Statistics: October 7, 2014 Robert Dahl JacobsenDocument32 pagesProbability Theory and Statistics: October 7, 2014 Robert Dahl JacobsenDarioSpNo ratings yet
- Preparation For LessonDocument6 pagesPreparation For LessonDarioSpNo ratings yet
- Maglev FileDocument25 pagesMaglev FileDarioSpNo ratings yet
- 0900-73 Manual (US)Document2 pages0900-73 Manual (US)Paramedico GuadalajaraNo ratings yet
- Cv2d Ej2 Starex04f ArdanDocument10 pagesCv2d Ej2 Starex04f ArdanIna Therese ArdanNo ratings yet
- Vector DPP-1 - 2022Document6 pagesVector DPP-1 - 2022ShashankNo ratings yet
- Generalphysics1 - q1 - Mod2 - Kinematics Motion in A Straight Line - v1Document32 pagesGeneralphysics1 - q1 - Mod2 - Kinematics Motion in A Straight Line - v1Park JiminshiiNo ratings yet
- Notes ESO205Document44 pagesNotes ESO205muditNo ratings yet
- Gas Molecules in MotionDocument59 pagesGas Molecules in MotionMathew Angelo Perez GamboaNo ratings yet
- Belt FrictionDocument5 pagesBelt FrictionShah NawazNo ratings yet
- PHY-502 (Mathematical Methods of Physics-II) Mid Term 2017-I (GC University)Document1 pagePHY-502 (Mathematical Methods of Physics-II) Mid Term 2017-I (GC University)Ghulam Farid0% (1)
- Polytropic Process PDFDocument1 pagePolytropic Process PDFClarence De LeonNo ratings yet
- Engineering PhysicsDocument13 pagesEngineering PhysicsLa Vien RoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Stage and Continuous Gas-Liquid Separation ProcessesDocument46 pagesChapter 3 - Stage and Continuous Gas-Liquid Separation Processesomarfhassan0% (1)
- Transformer Design NotesDocument15 pagesTransformer Design Notesrishabh100% (2)
- BS en ISO 9934-3-2007, NondestructiveDocument20 pagesBS en ISO 9934-3-2007, Nondestructivescofiel1No ratings yet
- Pre-Mock Practice 3Document2 pagesPre-Mock Practice 3Michelle ChungNo ratings yet
- Disc 15 SolutionDocument4 pagesDisc 15 Solutionmmounir79No ratings yet
- Foundation Analyzing of Centrifugal ID Fans in Cement PlantsDocument11 pagesFoundation Analyzing of Centrifugal ID Fans in Cement PlantsDhiviya KumarNo ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 6Document7 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 6Abdurrahman AdigunNo ratings yet
- The High Voltage Homopolar GeneratorDocument6 pagesThe High Voltage Homopolar Generatorapi-241035124No ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document29 pagesLecture 21rajamatheNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Nithisri BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Materials - J. B. GuptaDocument70 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering Materials - J. B. GuptakundanabcNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Half-Life NotesDocument1 pageChemistry - Half-Life NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics IDocument21 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics ImihretuNo ratings yet
- Braun and Mitchell 1983Document6 pagesBraun and Mitchell 1983Antony BanderasNo ratings yet
- This Kisssoft Demoversion May Not Be Used For Professional Application ! Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The CalculationDocument7 pagesThis Kisssoft Demoversion May Not Be Used For Professional Application ! Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The Calculationpablo_stzNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Quantum ChemistryDocument10 pagesMCQ On Quantum ChemistryRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaDocument10 pagesChemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaWaqas LuckyNo ratings yet
- Pankaj EMT AssignDocument6 pagesPankaj EMT AssignpankajmadhuNo ratings yet
- Waves: How Do Waves Travel Through Matter?Document4 pagesWaves: How Do Waves Travel Through Matter?ToyNerd Collectors100% (1)