Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Exchanger Problem
Heat Exchanger Problem
Uploaded by
Luviano10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views1 pageA cross-flow heat exchanger cools blood from 37°C to 25°C during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure using ice water at 0°C. The ice water flow rate is adjusted to provide an outlet temperature of 15°C. Given the blood flow rate of 5 L/min, heat transfer coefficient of 750 W/m2K, and thermophysical properties of blood and ice water, the heat exchanger's surface area and ice water flow rate can be determined.
Original Description:
Heat exchanger problem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA cross-flow heat exchanger cools blood from 37°C to 25°C during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure using ice water at 0°C. The ice water flow rate is adjusted to provide an outlet temperature of 15°C. Given the blood flow rate of 5 L/min, heat transfer coefficient of 750 W/m2K, and thermophysical properties of blood and ice water, the heat exchanger's surface area and ice water flow rate can be determined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views1 pageHeat Exchanger Problem
Heat Exchanger Problem
Uploaded by
Luviano1A cross-flow heat exchanger cools blood from 37°C to 25°C during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure using ice water at 0°C. The ice water flow rate is adjusted to provide an outlet temperature of 15°C. Given the blood flow rate of 5 L/min, heat transfer coefficient of 750 W/m2K, and thermophysical properties of blood and ice water, the heat exchanger's surface area and ice water flow rate can be determined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
11.
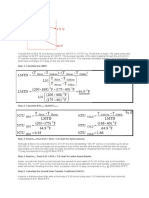
34 A cross-flow heat exchanger used in a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure cools
blood flowing at 5 liter/min from a body temperature of 37 C to 25 C in order to
induce body hypothermia, which reduces metabolic and oxygen requirements. The
coolant is ice water at 0 C, and its flow rate is adjusted to provide an outlet temperature
of 15 C. The heat exchanger operates with both fluids unmixed, and the overall heat
transfer coefficient is 750 W/m2 K. The density and specific heat of the blood are 1050
kg/m3 and 3740 J/kg K, respectively.
(a) Determine the heat transfer rate for the exchanger.
(b) Calculate the water flow rate.
(c) What is the surface area of the heat exchanger?
(d) (Optional) Calculate and plot the blood and water outlet temperatures as a function
of the water flow rate for the range 2 to 4 liter/min, assuming all other parameters
remain unchanged. Comment on how the changes in the outlet temperatures are affected
by changes in the water flow rate. Explain this behavior and why it is an advantage for
this application.
You might also like
- Mental Health and Healthy Lifestyle Workplace Policy and ProgramDocument7 pagesMental Health and Healthy Lifestyle Workplace Policy and ProgramDarryl Robles100% (5)
- 2018 End of Term 1 Test Computer Studies Grade 8Document6 pages2018 End of Term 1 Test Computer Studies Grade 8Tahpehs Phiri76% (17)
- H W5Document1 pageH W5Bahadır KayaNo ratings yet
- Is Is at At: P,/P P, P,/PDocument4 pagesIs Is at At: P,/P P, P,/PNaqqash SajidNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4 CalorDocument2 pagesTarea 4 CalorDenisse M. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Parallel Flow, A (m2) 2.624 Counter Flow, A (m2) 2.434 Shell and Tube HX, A (m2) 2.523Document4 pagesParallel Flow, A (m2) 2.624 Counter Flow, A (m2) 2.434 Shell and Tube HX, A (m2) 2.523Chinwuba Samuel EbukaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems - Heat Exchangers UNIT-4Document13 pagesSolved Problems - Heat Exchangers UNIT-4doddi.ajith2003No ratings yet
- F.L.lansing - Computer Modeling of LiBr - VAR SystemDocument11 pagesF.L.lansing - Computer Modeling of LiBr - VAR SystemRana Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Calculate The LMTD: HOT ColdDocument2 pagesStep 1: Calculate The LMTD: HOT ColdtobyNo ratings yet
- 03 ME 6022 Design of Heat Transfer EquipmentsDocument1 page03 ME 6022 Design of Heat Transfer EquipmentsVenkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Cycles of ConcentrationDocument2 pagesCycles of ConcentrationSagar PatilNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesPractice Problems For Heat ExchangerFour AyesNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument1 pageHeat ExchangerArpit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger NumericalsDocument1 pageHeat Exchanger NumericalskaushikNo ratings yet
- Ex. 11Document18 pagesEx. 11Zaher Zaher100% (1)
- Assignment - IVDocument4 pagesAssignment - IVdivyanshu.221ch018No ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger (Group 2) : Sl. No Questions CompetenceDocument1 pageHeat Exchanger (Group 2) : Sl. No Questions CompetencerajibaecNo ratings yet
- Examples MENG580 Chapter 11 PDFDocument14 pagesExamples MENG580 Chapter 11 PDFYasser TarhiniNo ratings yet
- Show A Simple Block Diagram of The Flash Tank Indicating The Different Streams 2. Calculate The Amount of Flash Steam Produced in The 3bar Flash TankDocument1 pageShow A Simple Block Diagram of The Flash Tank Indicating The Different Streams 2. Calculate The Amount of Flash Steam Produced in The 3bar Flash TankJamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit 6Document5 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit 6dongaNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIIDocument1 pageAssignment IIIBuckshu PhdNo ratings yet
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument7 pagesDouble Pipe Heat ExchangerPriyanshiVadaliaNo ratings yet
- Basic Design MethodologyDocument4 pagesBasic Design MethodologySatya SuryaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 6 Heat ExchangerDocument4 pagesTUTORIAL 6 Heat ExchangerFikri Rahim50% (2)
- Ejercicios PDFDocument4 pagesEjercicios PDFserepoesia10No ratings yet
- Group 3Document1 pageGroup 3rajibaecNo ratings yet
- 515MET02 HMT Unit 3 FinalDocument4 pages515MET02 HMT Unit 3 Finalntamilselvan.eecNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers LectureDocument37 pagesHeat Exchangers LectureTerna Orlanda100% (2)
- Heat ExchangersDocument33 pagesHeat Exchangersmohsin931No ratings yet
- Multipass Heat ExchangersDocument21 pagesMultipass Heat ExchangersBrando_BalagonNo ratings yet
- Con Cent Eric Tube Heat ExchangerDocument15 pagesCon Cent Eric Tube Heat ExchangerAmr BanawanNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - 2: Mechanical Engineering Department Asansol Engineering College, AsansolDocument1 pageHome Assignment - 2: Mechanical Engineering Department Asansol Engineering College, AsansolMd SohailNo ratings yet
- 04 Deaktivasi Katalisis HeterogenDocument44 pages04 Deaktivasi Katalisis HeterogenNajwaAinayaZawaidNo ratings yet
- HVAC Chilled Water Distribution SchemesDocument56 pagesHVAC Chilled Water Distribution SchemesJenson Joy100% (5)
- Taller 2 2023-1Document8 pagesTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizNo ratings yet
- Problems On VCRSDocument7 pagesProblems On VCRSFraol100% (1)
- Ma6651 Aerospace Lab: E3.5/E3.1A Heat ExchangerDocument8 pagesMa6651 Aerospace Lab: E3.5/E3.1A Heat ExchangerSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Document7 pagesJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2saiteja1234No ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger2Document33 pagesHeat Exchanger2Saloni.Dhawale Btech2018No ratings yet
- Cryogenic EquipmentDocument36 pagesCryogenic Equipmentkeshavnandi1969No ratings yet
- Tut 4 Heat ExchangersDocument2 pagesTut 4 Heat ExchangersGomolemo BaarxxNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Calculate The LMTD: HOT ColdDocument34 pagesStep 1: Calculate The LMTD: HOT ColdFrancisca Hanna0% (2)
- Heat ExchangerDocument29 pagesHeat Exchangerrodel rentaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger PDFDocument9 pagesHeat Exchanger PDFsunita45No ratings yet
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesDouble Pipe Heat Exchangerhhmanish100% (1)
- Energy Efficiency On Chilled Water SystemDocument56 pagesEnergy Efficiency On Chilled Water Systembalraj100% (1)
- RAC (ME 802) by Prof. Sangeev S. TomarDocument9 pagesRAC (ME 802) by Prof. Sangeev S. Tomarapi-19832143No ratings yet
- 05-1-Collection of Problems PDFDocument15 pages05-1-Collection of Problems PDFFistia MaulinaNo ratings yet
- C5 ExerciseDocument18 pagesC5 ExerciseHƯƠNG NGUYỄN LÊ NGỌCNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Assignment PDFDocument2 pagesCH 4 Assignment PDFAftab57.No ratings yet
- HMT Tutorial 2Document1 pageHMT Tutorial 2Prachi DasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document3 pagesTutorial 8CHANDAN RAJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Absorption Refrigeration ExercisesDocument2 pagesChapter 17 Absorption Refrigeration ExercisesAndrew PantaleonNo ratings yet
- The Theory Behind Heat TransferDocument7 pagesThe Theory Behind Heat TransferselisenNo ratings yet
- Sustainable and Green Electrochemical Science and TechnologyFrom EverandSustainable and Green Electrochemical Science and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Gas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingFrom EverandGas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingDaniel BrosetaNo ratings yet
- 05 - Intercambiador de Calor Shell and TubeDocument1 page05 - Intercambiador de Calor Shell and TubeLuviano1No ratings yet
- John Thompson's Easiest Piano Course Part OneDocument1 pageJohn Thompson's Easiest Piano Course Part OneLuviano1No ratings yet
- John Thompson's Modern Course Fot The PianoDocument1 pageJohn Thompson's Modern Course Fot The PianoLuviano10% (3)
- FlowDocument1 pageFlowLuviano1No ratings yet
- 1 - Young Paper On EXW HistoryDocument6 pages1 - Young Paper On EXW Historylastking_king17No ratings yet
- Tech Gr9 m3 Hydraulic Pneumatic SystemsDocument26 pagesTech Gr9 m3 Hydraulic Pneumatic SystemsEduBoard100% (1)
- Virginia SatirDocument12 pagesVirginia SatirGuadalupe PérezNo ratings yet
- Deleuze Guattariandthe Indian DiagramDocument19 pagesDeleuze Guattariandthe Indian DiagramManu KhannaNo ratings yet
- Wrench Time PaperDocument4 pagesWrench Time PaperJair TNo ratings yet
- CR, Cri, CRN, CRT ATEX-approved Pumps: Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument18 pagesCR, Cri, CRN, CRT ATEX-approved Pumps: Installation and Operating InstructionsXuan Man NguyenNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Induction Motor Drives: SyllabusDocument8 pagesModule 3: Induction Motor Drives: SyllabusManoj SkNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 NumericalsDocument29 pagesCh. 3 NumericalsMriduNo ratings yet
- KL202232 PSRPT 2022-05-18 18.01.51Document19 pagesKL202232 PSRPT 2022-05-18 18.01.51Thuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Advancement in Energy Storage DevicesDocument9 pagesAdvancement in Energy Storage Devicesash200459No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan DLP Format DATE LeaDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan DLP Format DATE LeaPablo JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Question Set 4 (20231107) AnswerkeyDocument9 pagesMicroeconomics Question Set 4 (20231107) AnswerkeyMegumi TsuchiyaNo ratings yet
- BBC Lottrey PROMOTION 1Document4 pagesBBC Lottrey PROMOTION 1Raj HarshNo ratings yet
- Report of The Task Force On DyslexiaDocument153 pagesReport of The Task Force On Dyslexiacumannstaire7586No ratings yet
- Collins - 2005 - The Concept of Stored Plastic Work or Frozen Elastic Energy in Soil MechanicsDocument10 pagesCollins - 2005 - The Concept of Stored Plastic Work or Frozen Elastic Energy in Soil MechanicsHUGINo ratings yet
- Design of PLC Using Arduino UNO: A Capstone Project ReportDocument57 pagesDesign of PLC Using Arduino UNO: A Capstone Project ReportSawan SoniNo ratings yet
- EBenefits Life Events White PaperDocument21 pagesEBenefits Life Events White PaperRahul VemuriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logic Design Experiments 1 Thru 10Document36 pagesIntroduction To Logic Design Experiments 1 Thru 10George Kokkinias100% (1)
- Astrolabe Free Chart From HTTP - AlabeDocument2 pagesAstrolabe Free Chart From HTTP - AlabeArijit AcharyaNo ratings yet
- B.Lib SyllabusDocument17 pagesB.Lib SyllabussantoshguptaaNo ratings yet
- Mothership-Unit Description - Game - StarCraft IIDocument8 pagesMothership-Unit Description - Game - StarCraft IIcalmansoorNo ratings yet
- Ats22 User Manual en Bbv51330 02Document85 pagesAts22 User Manual en Bbv51330 02Catalin PelinNo ratings yet
- Guide To Iso 9001 2015 PDFDocument15 pagesGuide To Iso 9001 2015 PDFahmed nawaz100% (2)
- Purlin DESIGN Car ParkDocument8 pagesPurlin DESIGN Car ParkNasrul Torres0% (1)
- Basic Hydrocyclone OperationDocument23 pagesBasic Hydrocyclone Operationgeo rayfandyNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Cost Civil Works SewaDocument3 pagesAbstract of Cost Civil Works SewaPrabhat MicNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Criminology and PsycholoDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Criminology and PsycholoSkier MishNo ratings yet
- Report Revenue ServicesDocument10 pagesReport Revenue ServicesaminakalifaNo ratings yet