Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 1 Table 1 - 2
Lecture 1 Table 1 - 2
Uploaded by
ZUL KAMARUDDIN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views4 pagesThe document summarizes the effects of heat on different solid materials. It describes how organic and polymer materials will char or burn with little residues, metals will blacken and form oxides, and some materials like salts will melt at low or high temperatures. Certain materials like ammonium chloride or iodine will sublime as the solid transitions directly to a gas. Heating materials like hydrates or nitrates can release vapors like water, oxygen, or nitrogen oxide. Physical changes from heating include materials becoming maleable, expanding, swelling, shrinking or showing no effect.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lecture 1 Table 1_2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the effects of heat on different solid materials. It describes how organic and polymer materials will char or burn with little residues, metals will blacken and form oxides, and some materials like salts will melt at low or high temperatures. Certain materials like ammonium chloride or iodine will sublime as the solid transitions directly to a gas. Heating materials like hydrates or nitrates can release vapors like water, oxygen, or nitrogen oxide. Physical changes from heating include materials becoming maleable, expanding, swelling, shrinking or showing no effect.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views4 pagesLecture 1 Table 1 - 2
Lecture 1 Table 1 - 2
Uploaded by
ZUL KAMARUDDINThe document summarizes the effects of heat on different solid materials. It describes how organic and polymer materials will char or burn with little residues, metals will blacken and form oxides, and some materials like salts will melt at low or high temperatures. Certain materials like ammonium chloride or iodine will sublime as the solid transitions directly to a gas. Heating materials like hydrates or nitrates can release vapors like water, oxygen, or nitrogen oxide. Physical changes from heating include materials becoming maleable, expanding, swelling, shrinking or showing no effect.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
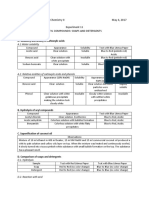
Table 1.
2 The effect of heat on solid materials (Haines, 1995)
Effect Conclusion Example
Colour effect
Charred, burned with Organic, polymer Combustion of
little residues papers
Blackened with plenty Metal oxide is formed CuCO3
residues CuO + CO2
Metal changed into Oxidation 2 Mg + O2
powder 2 MgO
Next
Lecture 1 Table 1.2 1
Table 1.2 The effect of heat on solid materials (Haines, 1995) Cont’d.
Effect Conclusion Example
Melting Materials
Melt at low Covalent ? Organic
temperature
Melt at high Ionic salts NaCl
temperature
Sublime Materials
White sublimation The solid is easily NH4Cl
evaporated
Ammonium salts
Violet sublimation Iodine I2 Next
Lecture 1 Table 1.2 2
Table 1.2 The effect of heat on solid materials (Haines, 1995) Cont’d.
Effect Conclusion Example
Released Vapours
(characterised by other
tests)
Water droplets Hidrate CuSO4.5H2O
Oksigen Nitrate, chlorate 2KNO3
2KNO2 + O2
Nitrogen oxide (brown Nitrate 2AgNO3
fume) 2Ag + 2NO2 +
O2
Carbon dioxide Carbonate ZnCO3 ZnO
+ CO2
Next
Lecture 1 Table 1.2 3
Table 1.2 The effect of heat on solid materials (Haines, 1995) Cont’d.
Effect Conclusion Example
Physical change
Maleable Plastic at greater than Tg
Expansion Normal expansion
(a) gradual Phase change
(b) abrupt
Swelling Some swelling materials Polyphosphate
Shrinkage Some strained polymers Fibres
No effect Oxide that is stable towards MgO, Al2O3
heat or very low temperature
Return
Lecture 1 Table 1.2 4
You might also like
- 1028 AnswersDocument1 page1028 AnswersAJ Millard0% (3)
- Bahtera MerdekaDocument1 pageBahtera MerdekaZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1backupDocument16 pagesLecture 1backupZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report Gas Law JonathanDocument3 pagesChemistry Lab Report Gas Law JonathanJonathan BryanNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument37 pagesChemical ReactionsGlydel GealonNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesDocument9 pagesReactions of Aldehydes and Ketonesmoon star angelNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Chem - Reactions &equationsDocument43 pagesCh-1 Chem - Reactions &equationsakhil.jNo ratings yet
- CBSE G+10 Chemical+Reactions+and+Equations NotesDocument9 pagesCBSE G+10 Chemical+Reactions+and+Equations Notesrd199159No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemical Reactions and Equations: Co + 2H CH OhDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Chemical Reactions and Equations: Co + 2H CH Oh22550No ratings yet
- Corrosion - Chapter 1Document2 pagesCorrosion - Chapter 1roasterji190No ratings yet
- Upload PDFDocument5 pagesUpload PDFPatrick James OngNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Notes With Imp MCQs of Science Term 1Document59 pagesFinal Revision Notes With Imp MCQs of Science Term 1Amarjeet kaurNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Gas Law: Gsci1103L-General Chemistry 1 LabDocument4 pagesLaboratory Gas Law: Gsci1103L-General Chemistry 1 LabAndrea AurielleNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Note On Nitrogen and Its CompoundsDocument4 pagesWeek 8 Note On Nitrogen and Its CompoundsDenzel MusaNo ratings yet
- 2 Effect of Heat On SaltDocument3 pages2 Effect of Heat On SaltJacelynNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - Short NotesDocument4 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - Short NotesuszgsticdxnkkrbxwyNo ratings yet
- Experiment Ii Oxidation Number of Nitrogen 1.1 ObjectivesDocument9 pagesExperiment Ii Oxidation Number of Nitrogen 1.1 ObjectivesAhlish Rahma AlfianaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Lab Report 4 Gas Law Hans Sebastian, Fadhly, Ignatius, Wahid, BayuDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry Lab Report 4 Gas Law Hans Sebastian, Fadhly, Ignatius, Wahid, BayuAbabab AbabNo ratings yet
- 02.laws of Chemical Combination (22-36)Document15 pages02.laws of Chemical Combination (22-36)Vaibhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10 CHEMISTRY PART 1 of 2Document73 pagesCLASS 10 CHEMISTRY PART 1 of 2Akash SadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument31 pagesChemical ReactionGail DomingoNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Typs of Chemical ReactionsDocument5 pagesChap 4 Typs of Chemical ReactionsnongyaikeisamcodesNo ratings yet
- Njesc 101Document7 pagesNjesc 101deeppratap67890No ratings yet
- Results and Observations: Title: Table Showing The Observations When Heating Ammonium Dichromate, Copper (I) Carbonate, Lead (I Nitrate and IodineDocument4 pagesResults and Observations: Title: Table Showing The Observations When Heating Ammonium Dichromate, Copper (I) Carbonate, Lead (I Nitrate and IodineHailey RagbirNo ratings yet
- How Do Bases React With Metals?: Activity 2.3Document1 pageHow Do Bases React With Metals?: Activity 2.3sciencee2009No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Ch-1 NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry - Ch-1 NoteskomalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry C2 (GDW52) PDFDocument43 pagesChemistry C2 (GDW52) PDFBrain MasterNo ratings yet
- Sree?Document44 pagesSree?Mohammed RamzanNo ratings yet
- MYBM Classes Prabhdeep: Chapter 1-Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument12 pagesMYBM Classes Prabhdeep: Chapter 1-Chemical Reactions and EquationsaaronNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsDocument18 pagesChemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsproodootNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry AnalysisDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry AnalysisfathiyaNo ratings yet
- CHAP 1.pmd3Document3 pagesCHAP 1.pmd3Ezhil CNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 1 of 2Document73 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 1 of 2Killer boy SidNo ratings yet
- Practical SCDocument2 pagesPractical SCnsamy2213No ratings yet
- 3 Dec - Science - Imp Concept - 1511844465Document20 pages3 Dec - Science - Imp Concept - 1511844465Syed nameerNo ratings yet
- P BLOCK Class 12Document26 pagesP BLOCK Class 12Parth BajajNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document10 pagesLab 4kms jodie lazuardi haickalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationsDocument10 pagesChemical Reaction and EquationsRobin SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesChemical ReactionsSharlene RobertsNo ratings yet
- Synopsis - Grade 10 Science Term I: Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument14 pagesSynopsis - Grade 10 Science Term I: Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and EquationsdheekshithNo ratings yet
- LAB ACT 5 Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument12 pagesLAB ACT 5 Types of Chemical ReactionsJerome MosadaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements: Muhammad Hassaan Arshad Shayan Haider Yaman TariqDocument13 pagesThe Periodic Table of Elements: Muhammad Hassaan Arshad Shayan Haider Yaman TariqPro IdiotNo ratings yet
- Group I & IIDocument3 pagesGroup I & IINoor Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDenzel MusaNo ratings yet
- LABREPDocument3 pagesLABREPJay SoonNo ratings yet
- 10th - CH 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations PDFDocument6 pages10th - CH 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations PDFMahesh KumawatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations 1 2 PDFDocument6 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations 1 2 PDFkrishna veniNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 PDFDocument4 pagesActivity 7 PDFpeter vanderNo ratings yet
- 11.4 SummaryDocument1 page11.4 Summaryfifth193No ratings yet
- Gas Test Observation Inference: Wooden Splinter RekindlesDocument3 pagesGas Test Observation Inference: Wooden Splinter RekindlesNur Siti FatimahNo ratings yet
- Gas Test Observation Inference: Wooden Splinter RekindlesDocument3 pagesGas Test Observation Inference: Wooden Splinter RekindlesNur Siti FatimahNo ratings yet
- Y4 ChemDocument7 pagesY4 Chembendadick cloneNo ratings yet
- 007 Activity ZoneDocument6 pages007 Activity ZoneTusharNo ratings yet
- S Block Lecture 1 PDFDocument29 pagesS Block Lecture 1 PDFRobiul AlomNo ratings yet
- X Chem Pract 5 Effect of Heat On Certain SubstancesDocument3 pagesX Chem Pract 5 Effect of Heat On Certain SubstancesAdi KripalNo ratings yet
- SSC GK Batch 2.0Document9 pagesSSC GK Batch 2.0deepeshNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Soalan Seni PPT 2018Document5 pagesSoalan Seni PPT 2018ZUL KAMARUDDIN100% (1)
- Lecture 6 Table 6.1Document1 pageLecture 6 Table 6.1ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Coiling TembikarDocument2 pagesCoiling TembikarZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Application DTA & DSC01Document34 pagesLecture 7 Application DTA & DSC01ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Dta & Dsc01Document22 pagesLecture 6 Dta & Dsc01ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Figure 6 - 2 Compare Thermal DTADocument1 pageLecture 6 Figure 6 - 2 Compare Thermal DTAZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Figure 6 - 8 ThermocoupleDocument1 pageLecture 6 Figure 6 - 8 ThermocoupleZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Figure 4 - 8 TGA PT OxidesDocument1 pageLecture 5 Figure 4 - 8 TGA PT OxidesZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Partial Pressure Figure 3 - 19Document1 pageLecture 4 Partial Pressure Figure 3 - 19ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Figure 4 - 5 Detn of CA MG Ba by TGADocument1 pageLecture 5 Figure 4 - 5 Detn of CA MG Ba by TGAZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Atmos Pressure Figure 3 - 22Document1 pageLecture 4 Atmos Pressure Figure 3 - 22ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Heating Rate Figure 3 - 17Document1 pageLecture 4 Heating Rate Figure 3 - 17ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Atmosphere Figure 3 - 18Document1 pageLecture 4 Atmosphere Figure 3 - 18ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Atmos Pressure Figure 3 - 21Document1 pageLecture 4 Atmos Pressure Figure 3 - 21ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
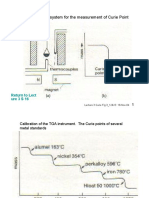
- Lecture 3 Curie Fig 3 - 12& 13Document2 pagesLecture 3 Curie Fig 3 - 12& 13ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis SSK 4242Document16 pagesThermal Analysis SSK 4242ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
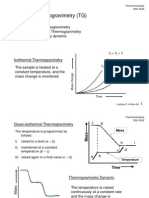
- Thermogravimetry (TG) : 1. Isothermal Thermogravimetry 2. Quasi-Isothermal Thermogravimetry 3. Thermogravimetry DynamicDocument19 pagesThermogravimetry (TG) : 1. Isothermal Thermogravimetry 2. Quasi-Isothermal Thermogravimetry 3. Thermogravimetry DynamicZUL KAMARUDDIN100% (1)
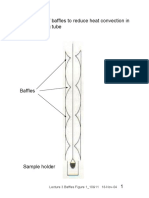
- Lecture 3 Baffles Fig 3 - 10& 11Document2 pagesLecture 3 Baffles Fig 3 - 10& 11ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Crucibles Sample HoldersDocument2 pagesCrucibles Sample HoldersZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1backupDocument16 pagesLecture 1backupZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Table 1 - 3Document1 pageLecture 1 Table 1 - 3ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Polymers QP1Document16 pagesSynthetic Polymers QP1Chandradeep 8200No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2-MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY - Part 4Document59 pagesCHAPTER 2-MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY - Part 4fatin harrisNo ratings yet
- ExamView - Sch4u Organic TestDocument6 pagesExamView - Sch4u Organic TestMahir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsDocument5 pagesKate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsKateNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes ch11 The P Block Element PDFDocument4 pages11 Chemistry Notes ch11 The P Block Element PDFRangbaaz DA FIRENZENo ratings yet
- Cement CompositionDocument4 pagesCement Compositionren salazarNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic Reactions and Their MechanismsDocument88 pagesAn Introduction To Organic Reactions and Their MechanismsBurcu Gözde BilolNo ratings yet
- Science9 - q2 - Mod4 - Carbon Compound - v3Document32 pagesScience9 - q2 - Mod4 - Carbon Compound - v3Kristine Ibarreta-Jazul100% (2)
- To Find Fatty Material of Different Soap SamplesDocument17 pagesTo Find Fatty Material of Different Soap SamplesRohan Singh0% (2)
- 13 Organics v1Document30 pages13 Organics v1api-209402888No ratings yet
- Synthesis and Application of Cationic Softeners PDFDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Application of Cationic Softeners PDFHuseini PatanwalaNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Aldehydes & KetonesDocument8 pagesNomenclature of Aldehydes & KetonesChristian Dave Abelardo BernaldezNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE D BlockDocument48 pagesIIT JEE D BlockARKO KASHYAP50% (2)
- 9701 w12 Ms 41Document11 pages9701 w12 Ms 41Matthew Vinodh RajNo ratings yet
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 455, September 20, 1884 by VariousDocument83 pagesScientific American Supplement, No. 455, September 20, 1884 by VariousGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Ash, Water, Extractive and Crude Fiber Content DeterminationDocument23 pagesModule 6 - Ash, Water, Extractive and Crude Fiber Content DeterminationPRINCESS NOELLEE TRAYVILLANo ratings yet
- Boiler System Chemical TreatmentDocument36 pagesBoiler System Chemical TreatmentNavaganesh Kannappen100% (1)
- Textile Wet Processing UNIT-3Document7 pagesTextile Wet Processing UNIT-3Chaarvi SaranyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Document16 pagesHydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Soham NagNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryCik ApaiNo ratings yet
- NHT Isom DraftDocument221 pagesNHT Isom DraftAnjani Ganti100% (1)
- Indium and ThalliumDocument15 pagesIndium and ThalliumAuliaRahmanNo ratings yet
- Csi 2020 9 4 58Document7 pagesCsi 2020 9 4 58JavadAminpourNo ratings yet
- Why Caustic Addition Is Bad For Amine SystemsDocument7 pagesWhy Caustic Addition Is Bad For Amine SystemsIng Antony MatosNo ratings yet
- Boric Acid - WikipediaDocument54 pagesBoric Acid - Wikipediarock2903No ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Jojoba OilDocument5 pagesPhytochemical Analysis and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Jojoba OilRahma SantosoNo ratings yet
- Analysis I Worksheet Ss Edited PDFDocument5 pagesAnalysis I Worksheet Ss Edited PDFBinyam Asfaw100% (1)
- Chemistry Project For Class 12 BoardsDocument27 pagesChemistry Project For Class 12 BoardsAkash Sharma Trend Setter0% (1)
- Norma Astm E407.1093127-1Document22 pagesNorma Astm E407.1093127-1Gabriela AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 4541/2 Chemistry Paper 2 Mei 2014 2 Hours: For ExaminerDocument19 pages4541/2 Chemistry Paper 2 Mei 2014 2 Hours: For ExaminerndianaoNo ratings yet