Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simple Spreadsheet Exercise of Water Balance Simulation: G G S S
Simple Spreadsheet Exercise of Water Balance Simulation: G G S S
Uploaded by
EdieAbiAzzamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Spreadsheet Exercise of Water Balance Simulation: G G S S
Simple Spreadsheet Exercise of Water Balance Simulation: G G S S
Uploaded by
EdieAbiAzzamCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Simple Spreadsheet Exercise of Water Balance Simulation
In this computer lab we will estimate net groundwater input to an alpine lake using the water balance
equation. The lab is based on Hood et al. (2006, Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L13405).
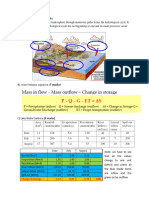
The water balance equation of a lake is;
IG OG = V/t Pcp + ET IS + OS
(1)
Lake area (A) is a function of water level (h) in general, but in this simple example we assume
that A is constant at 0.26 km2.
Your data set contains lake water level h (m) with respect to a local bench mark, daily
precipitation P (mm), estimated daily evaporation E (mm), and daily average stream inflow IS (m3
s-1) and outflow OS (m3 s-1). Note that there are four inflow streams, and IS is the total of all four
streams.
(a) For 03/06/2005 (Row 3), calculate the volumetric rate of precipitation Pcp (m3 s-1) falling on
the lake by multiplying P by the lake area:
Pcp = P mm 0.001 m mm-1 (0.26 106 m2) / 86400 s
(2)
In terms of cell formula, Eq. (2) can be written as:
H3 = D3*0.001*C3*1e6/86400
(b) Similarly, calculate the volumetric rate of evaporation ET (m3 s-1) leaving the lake surface by
multiplying E by the lake area:
(3)
ET = E mm 0.001 m mm-1 (0.26 106 m2) / 86400 s
In terms of cell formula, Eq. (3) can be written as:
I3 = E3*0.001*C3*1e6/86400
(c) Calculate the rate of storage change:
V/t = (Change in water level between June 3 and June 4) (0.26 106 m2) / 86400 s
Or in terms of cell formula,
J3 = (B4 B3)*C3*1e6/86400
(d) Calculate the net groundwater flow rate IG OG from Eq. (1) using the cell formula:
K3 = J3 H3 + I3 F3 + G3
(e) Repeat the same calculation up to October 17 (Row 139) by copying the cell formula.
(f) Plot the time series of h on a chart.
(g) Plot the time series of IS and IG OG on a single chart, compare it with the water level chart
f
from
(f).
(f) Discuss
i
the
h seasonall trends
d off these
h
variables.
i bl
You might also like
- Homework 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesHomework 1 SolutionNaveen100% (1)
- Hydo RepoDocument7 pagesHydo RepoGrs205100% (1)
- Water Resources Final Equation SheetDocument6 pagesWater Resources Final Equation SheetIBNo ratings yet
- Pe Civil Hydrology Fall 2011Document109 pagesPe Civil Hydrology Fall 2011SamsonOgungbile75% (4)
- Hydrology Project 5Document11 pagesHydrology Project 5Jizelle JumaquioNo ratings yet
- IESO 2011 Hydrosphere Written Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesIESO 2011 Hydrosphere Written Test Questionslelo2k3No ratings yet
- We1 07 10 2021Document4 pagesWe1 07 10 2021Elif yıldırımNo ratings yet
- Article Cos Par 2004Document11 pagesArticle Cos Par 2004avirgiliisNo ratings yet
- CE 334 - Module 1.0Document42 pagesCE 334 - Module 1.0Samson EbengaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HydrologyDocument26 pagesChapter 1 HydrologyAsyraf Malik80% (5)
- LovepreetSandhawalia Assignment5Document2 pagesLovepreetSandhawalia Assignment5MellaniNo ratings yet
- Hydro HomeworkDocument5 pagesHydro HomeworkChristian Cannon0% (1)
- Hydrology-Lecture Notes PDFDocument83 pagesHydrology-Lecture Notes PDFalialjazaeryNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Distributed Hydrological Model Response by Using Spatial Input Data With Variable ResolutionDocument9 pagesAnalysis of A Distributed Hydrological Model Response by Using Spatial Input Data With Variable Resolutionfre123456789No ratings yet
- Balanço de Água em Eucaliptos Com A Caracterização Do Dossel Por Técnicas de Sensoriamento RemotoDocument9 pagesBalanço de Água em Eucaliptos Com A Caracterização Do Dossel Por Técnicas de Sensoriamento RemotoIuri AmazonasNo ratings yet
- LectureWeek2Chapter 1 Introduction PDFDocument17 pagesLectureWeek2Chapter 1 Introduction PDFAmira SyazanaNo ratings yet
- Automated System of Runoff Forecasting For The Amudarya River BasinDocument9 pagesAutomated System of Runoff Forecasting For The Amudarya River Basinsameer lalNo ratings yet
- Canopy Transpiration Response To Environmental Variations inDocument5 pagesCanopy Transpiration Response To Environmental Variations inayesha ilyaskhanNo ratings yet
- Hypsographic Curve of Earth's Surface From ETOPO1Document3 pagesHypsographic Curve of Earth's Surface From ETOPO1yadduaditya01No ratings yet
- HW11 - Fluids PDFDocument5 pagesHW11 - Fluids PDFBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- IESO 2012 WR Atmosphere and HydrosphereDocument11 pagesIESO 2012 WR Atmosphere and Hydrospherelelo2k3No ratings yet
- Answer For Mid ExamDocument7 pagesAnswer For Mid Examtedy yidegNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 LectureDocument78 pagesChapter 4 LectureAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- 05 Hydrologic LossesDocument39 pages05 Hydrologic LossesMaan HinolanNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional FlowDocument75 pagesOne Dimensional FlowJashia IslamNo ratings yet
- K. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 80Document1 pageK. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 80ramsinghmahatNo ratings yet
- Energy 1998Document8 pagesEnergy 1998أمير معروفNo ratings yet
- Analytical Exercise Solutions PDFDocument7 pagesAnalytical Exercise Solutions PDFct constructionNo ratings yet
- River Water Circulation Model On The Natural EnvironmentDocument6 pagesRiver Water Circulation Model On The Natural EnvironmentBruno VernochiNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Groundwater Balance and Safe Yield of Porous Aquifer in The Anthemountas Basin and Peraia'S Coastal AreaDocument10 pagesEstimation of Groundwater Balance and Safe Yield of Porous Aquifer in The Anthemountas Basin and Peraia'S Coastal AreaFisseha TekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter ADocument2 pagesChapter Ahashil1No ratings yet
- Groundwater Analysis Using FunctionDocument59 pagesGroundwater Analysis Using Functionrotciv132709No ratings yet
- Lecture - 8-Water Surface Profile ComputationDocument7 pagesLecture - 8-Water Surface Profile ComputationDanny ChengNo ratings yet
- Lakes and ReservoirsDocument10 pagesLakes and ReservoirsIsaac KandaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2017Document2 pagesAssignment 1 2017Nitin KumarNo ratings yet
- IrrigationDocument7 pagesIrrigationSaad ShauketNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument20 pagesFluid DynamicsIndah DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three EvaporationDocument41 pagesChapter Three EvaporationAbdizalaam ElmiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Model of Solar Swimming PoolsDocument5 pagesThermal Model of Solar Swimming PoolsUmer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Hydrological CycleDocument7 pagesHydrological CycleMiguel MarshallNo ratings yet
- Tut2 HydrologyDocument2 pagesTut2 HydrologyKomal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Simple Albedo Feedback Models of The IcecapsDocument17 pagesSimple Albedo Feedback Models of The IcecapsenidblytonNo ratings yet
- Low Rank Modeling of Primary AtomizationDocument6 pagesLow Rank Modeling of Primary AtomizationКирилл ВеселовNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Irrigation 2017 2018Document28 pagesCH 1 Irrigation 2017 2018Ahmed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Geo 513Document3 pagesAssignment 2 Geo 513Fredrick Oduor OmondiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Main Hydrological ConceptsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - Main Hydrological ConceptsWhy Merah0% (1)
- Immbbhl: Grand Hotel, Taipei, TaiwanDocument17 pagesImmbbhl: Grand Hotel, Taipei, TaiwanMed Ali MaatougNo ratings yet
- 3-Evaporation - READY - FINAL - 2019-20 - ModifiedDocument28 pages3-Evaporation - READY - FINAL - 2019-20 - ModifiedDanNo ratings yet
- Linear Wave TheoryDocument3 pagesLinear Wave TheoryOdofin GbengaNo ratings yet
- 057 Efita 2011 CDDocument12 pages057 Efita 2011 CDBill JonesNo ratings yet
- Formula de WeissDocument17 pagesFormula de WeissJorgeIndNo ratings yet
- Problems Hydrology Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesProblems Hydrology Lecture NotesAnonymous hE0IDl7No ratings yet
- Evaporacion y EvapotranspiracionDocument50 pagesEvaporacion y EvapotranspiracionRaul Cordova Alvarado100% (1)
- PrecipitationDocument9 pagesPrecipitationSaad ShauketNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Estimation of Evaporation From Surfaces.Document4 pagesMeasurement and Estimation of Evaporation From Surfaces.Mukudzei Gumbo-MberiNo ratings yet
- Hydrogeochemistry Fundamentals and Advances, Environmental Analysis of GroundwaterFrom EverandHydrogeochemistry Fundamentals and Advances, Environmental Analysis of GroundwaterNo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationGuilhem BourriéNo ratings yet
- Marine Ecological Field Methods: A Guide for Marine Biologists and Fisheries ScientistsFrom EverandMarine Ecological Field Methods: A Guide for Marine Biologists and Fisheries ScientistsAnne Gro Vea SalvanesNo ratings yet