Professional Documents
Culture Documents
17.1 Section Summary
17.1 Section Summary
Uploaded by
francis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThe document summarizes key concepts about the flow of energy as heat and work. It states that heat is the transfer of energy between objects due to a temperature difference, with heat flowing from warmer to cooler objects. Chemical potential energy is the energy stored in chemical bonds. Thermochemistry studies energy changes during chemical reactions and changes in state. The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 degree Celsius, with substances of higher specific heat capacities taking longer to heat up.
Original Description:
summary
Original Title
17.1 Section Summary (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key concepts about the flow of energy as heat and work. It states that heat is the transfer of energy between objects due to a temperature difference, with heat flowing from warmer to cooler objects. Chemical potential energy is the energy stored in chemical bonds. Thermochemistry studies energy changes during chemical reactions and changes in state. The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 degree Celsius, with substances of higher specific heat capacities taking longer to heat up.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 page17.1 Section Summary
17.1 Section Summary
Uploaded by
francisThe document summarizes key concepts about the flow of energy as heat and work. It states that heat is the transfer of energy between objects due to a temperature difference, with heat flowing from warmer to cooler objects. Chemical potential energy is the energy stored in chemical bonds. Thermochemistry studies energy changes during chemical reactions and changes in state. The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 degree Celsius, with substances of higher specific heat capacities taking longer to heat up.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
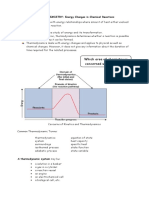
SECTION SUMMARY
17.1 The Flow of Energy-Heat and Work Summary:
The energy that flows from a warm object to a cool object is called heat. The
energy stored within the structural units of chemical substances is called chemical
potential energy. The study of heat transfer during chemical reactions and changes of
state is called thermochemistry. One of the units used to measure heat flow is the
calories defined as the amount of heat needed to raise 1 g of water 1oC. The SI unit
of heat and energy is joule, which is equal to 0.2390 cal. The specific heat capacity
of a substance is the amount of heat it takes to change the temperature of 1 g of the
substance 1oC.
Substances like water, which low heat capacities, take a shorter time to heat up
than substances with high heat capacities, such as metals.
17.1 The Flow of Energy-Heat and Work Vocabulary Terms:
thermochemistry:
the study of energy changes that occur during
chemical reactions and changes in state
chemical potential energy:
energy stored in chemical bonds
heat (q):
energy that transfers from one object to another
because of a temperature difference between the
objects - Heat always flows from a warmer object
to a cooler object.
system:
a part of the universe on which you focus your
attention
surroundings:
everything in the universe outside of the system
law of conservation of energy: in any chemical or physical process, energy is
neither created nor destroyed
endothermic process:
a process that absorbs heat from the surroundings
exothermic process:
a process that releases heat to its surroundings
heat capacity:
a amount of heat needed to increase the temperature
of an object exactly 1oC
specific heat:
the amount of heat needed to increase the
temperature of 1 g of substance 1oC; also called
specific heat capacity
1 Calorie = 1 kilocalorie = 1000 calories
4.184 J = 1 cal 1 J = 0.2390 cal
The End of the Summary
You might also like
- Heat and TemperatureDocument52 pagesHeat and TemperatureEazel SolanaNo ratings yet
- 17.1: The Flow of Energy-Heat and Work: Ch. 17: Thermochemistry Study GuideDocument1 page17.1: The Flow of Energy-Heat and Work: Ch. 17: Thermochemistry Study GuideMonica AbreuNo ratings yet
- "Thermochemistry": Chemistry Charles Page High School Stephen L. CottonDocument25 pages"Thermochemistry": Chemistry Charles Page High School Stephen L. CottonAminNo ratings yet
- Module - 1: ThermodynamicsDocument15 pagesModule - 1: ThermodynamicsApple VidalNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument36 pagesThermochemistryJayadevi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry PowerPointDocument33 pagesThermochemistry PowerPointissa sherryNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Ad Heat Thermal EquilibriumDocument6 pagesThermal Energy Ad Heat Thermal EquilibriumAmrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Thermo Notes No.1Document3 pagesThermo Notes No.1Makilan CharleneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Thermal Energy: What's Hot and What's NotDocument27 pagesChapter 12: Thermal Energy: What's Hot and What's Notkarina2227No ratings yet
- Mod 5Document17 pagesMod 5S M AkashNo ratings yet
- 8caie Physics Chapter 18: Heat Energy Transfer NotesDocument7 pages8caie Physics Chapter 18: Heat Energy Transfer NotesPrema KulkarniNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument38 pagesThermochemistryAji PangestuNo ratings yet
- Chap 8 ThermochemistryDocument58 pagesChap 8 ThermochemistryNur Shahirah Nasir Faculty of Social Science and FoundationNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument38 pagesThermochemistryAris GProNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument6 pagesHeat and TemperatureJavontay StewartNo ratings yet
- Cdi8reporting Sabbang&saldaDocument7 pagesCdi8reporting Sabbang&saldacelino.euniceeNo ratings yet
- ApoyDocument23 pagesApoyKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument38 pagesTemperature and Heatmistymint.crewneticNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. EnergyDocument26 pagesLesson 1. EnergyCelape CabanesNo ratings yet
- First LawDocument23 pagesFirst Lawnoah.sibulo2014No ratings yet
- PHYSICS21 Heat and TemperatureDocument15 pagesPHYSICS21 Heat and Temperatureapi-3805293100% (1)
- ThermochemistryDocument52 pagesThermochemistryBiddut DasNo ratings yet
- Pearson Ps CH 16 EdlineDocument20 pagesPearson Ps CH 16 EdlineRajendra PilludaNo ratings yet
- 4 PhyDocument64 pages4 PhymesfinNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument78 pagesThermodynamicsHarold Jan R. TeranoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemistry II Chapter 10 - THERMOCHEMISTRYDocument53 pagesFundamentals of Chemistry II Chapter 10 - THERMOCHEMISTRYBadr BouhsinaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Equilibrium: TemperatureDocument21 pagesThermal Equilibrium: TemperatureFadlan RoslanNo ratings yet
- LO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesLO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsAbo Alphotoh GamingNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 ThermodynamicsDocument31 pagesGrade 9 ThermodynamicsKaycee FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Phy TempDocument46 pagesPhy TempPavi MuruganathanNo ratings yet
- BME Unit V ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesBME Unit V ThermodynamicsArvind Bhosale100% (3)
- notes_thermochemistry and nuclear chemistryDocument10 pagesnotes_thermochemistry and nuclear chemistry예지No ratings yet
- Thermal Energy TransferDocument2 pagesThermal Energy Transferfatimahehe31323No ratings yet
- PHY210 CHAPTER 5 - THERMAL PHYSICS Students PDFDocument34 pagesPHY210 CHAPTER 5 - THERMAL PHYSICS Students PDFNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 VocabularyDocument2 pagesChapter 9 Vocabularydill1233No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Thermal EnergyDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Thermal EnergyAnnerlynn SolanoNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy w12 NotesDocument9 pages11 Phy w12 NotesPhilip FanaiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - Thermo NotesDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 5 - Thermo NotesIsha Nathalie GalimbaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics 12 Hour Crash Course Sections B and C Student Version-2Document107 pagesCSEC Physics 12 Hour Crash Course Sections B and C Student Version-2Mrs MendezNo ratings yet
- Which Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pagesWhich Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsSahada KanapiyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 2 Chem131Document13 pagesLesson 1 2 Chem131Yessenia MontillaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Power Point HS PhysicsDocument36 pagesThermal Energy Power Point HS PhysicsDan2929No ratings yet
- PHYSICS NotesDocument6 pagesPHYSICS NotesHAZEAL MENDOZANo ratings yet
- AP Physics Heat and Thermodynamics Chapter 11 and 12Document172 pagesAP Physics Heat and Thermodynamics Chapter 11 and 12Muhammad Sulthon SNo ratings yet
- 3D. Thermochemistry & ThermodynamicsDocument65 pages3D. Thermochemistry & ThermodynamicsMARAH ANTONETTE M. SUNNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2015Document27 pagesThermo 2015misganamarcos10No ratings yet
- HEATDocument3 pagesHEATCrystal Blue Sapphire Silver Ace FleminixNo ratings yet
- IB Measuring Energy ChangesDocument22 pagesIB Measuring Energy ChangesVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Notes - Temperature Class NotesDocument6 pagesNotes - Temperature Class NotesMohmmad AffanNo ratings yet
- Summary Group 2 Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesSummary Group 2 Laws of ThermodynamicsNorhida PantaranNo ratings yet
- Lighting Dan HeatDocument118 pagesLighting Dan HeatAndri Fayrina RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Heat and TempDocument28 pagesCH 16 Heat and TempSaif SbaihaNo ratings yet
- Create By: Basic Physics IIDocument7 pagesCreate By: Basic Physics IIM Umar Said TyhnNo ratings yet
- Duhok Polytechnic University Petrochemical Department Second Stage Physical ChemistryDocument6 pagesDuhok Polytechnic University Petrochemical Department Second Stage Physical Chemistrylya AhmedNo ratings yet
- 5.1 VocabularyDocument1 page5.1 VocabularyChandler BessNo ratings yet
- 2017-Dm No. 1227 - Senior High School Program Updated Class Scheduling Based On The Latest Released Curriculum GuidesDocument98 pages2017-Dm No. 1227 - Senior High School Program Updated Class Scheduling Based On The Latest Released Curriculum GuidesCJ DaodaoenNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TransferDocument17 pagesHeat and Mass TransferAbdullah RiazNo ratings yet
- Heat FOUNDATIONDocument9 pagesHeat FOUNDATIONHarilal K GNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)