Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrostatics
Electrostatics
Uploaded by
Crystal WellsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrostatics
Electrostatics
Uploaded by
Crystal WellsCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrostatics
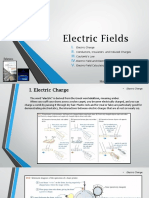
Electric Charge.
(1) Definition : Charge is the property associated with matter due to which it produces and experiences
electrical and magnetic effects.
(2) Origin of electric charge : It is known that every atom is electrically neutral, containing as many electrons as
the number of protons in the nucleus.
Charged particles can be created by disturbing neutrality of an atom. Loss of electrons gives positive charge
(as then np > ne) and gain of electrons gives negative charge (as then ne > np) to a particle. When an object is
negatively charged it gains electrons and therefore its mass increases negligibly. Similarly, on charging a body with
positive electricity its mass decreases. Change in mass of object is equal to n me. Where, n is the number of
Electron < Proton
Mass M
Electron = Proton
Mass M
electrons transferred and me is the mass of electron = 9.1 10 31 Kg .
Neutral
Electron > Proton
Negatively charged
Positively charged
M > M
M < M
(3) Type : There exists two types of charges in nature (i) Positive charge
(ii) Negative charge
Charges with the same electrical sign repel each other, and charges with opposite electrical sign attract each other.
dQ
dt
dQ = idt , hence S.I. unit of charge is Ampere sec = coulomb (C), smaller S.I. units are mC, C, nC
(1mC = 10 3 C, 1 C = 10 6 C, 1nC = 10 9 C) . C.G.S. unit of charge is Stat coulomb or e.s.u. Electromagnetic unit
(4) Unit and dimensional formula : Rate of flow of electric charge is called electric current i.e., i =
of charge is ab coulomb 1C = 3 109 stat coulomb =
Note :
1
ab coulomb . Dimensional formula [Q] = [AT ]
10
Benjamin Franklin was the first to assign positive and negative sign of charge.
The existence of two type of charges was discovered by Dufog.
Franklin ( i.e. , e.s.u . of charge) is the smallest unit of charge while faraday is largest
(1 Faraday = 96500 C ).
You might also like
- 12Chapter1ELECTRICCHARGESDocument23 pages12Chapter1ELECTRICCHARGESBitan DasNo ratings yet
- 10.3.1 Electric ForceDocument17 pages10.3.1 Electric Forcegjrf2qzk25No ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument38 pagesElectric Charge and Electric FieldRannah ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-1Document15 pagesChapter 1-1eyobNo ratings yet
- Genphy-Pt Alaga0 Lailo SoDocument32 pagesGenphy-Pt Alaga0 Lailo SoLex AlagaoNo ratings yet
- Physics Test - Chapter 1Document4 pagesPhysics Test - Chapter 1ameena-11173No ratings yet
- Electric Charge: Topic 1Document36 pagesElectric Charge: Topic 1Muhammad Shaqeem RosdiNo ratings yet
- Book content Physics CL12 CH1Document50 pagesBook content Physics CL12 CH1Prachi SinghNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument22 pagesElectrostaticsMohammed Aftab Ahmed78% (9)
- Electric ChargeDocument34 pagesElectric Chargeglaizamaeodinario5No ratings yet
- Applied PhysicsDocument35 pagesApplied PhysicswertyNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and FieldsDocument42 pagesElectric Forces and FieldsRado JaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsnuhaminteferi940No ratings yet
- V 4 Chap 1Document16 pagesV 4 Chap 1gurveer sainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Basic Concepts and UnitsDocument93 pagesChapter One: Basic Concepts and UnitsAmir ShakirNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Reporting Physics 1Document39 pagesGroup 5 Reporting Physics 1chloekritzkasilag100% (1)
- Chapter7 Notes1Document26 pagesChapter7 Notes1WesrineNo ratings yet
- Jit ElectrostaticsDocument11 pagesJit Electrostaticssthembisomabena942No ratings yet
- Properties of Electric Charges, Electric ForceDocument44 pagesProperties of Electric Charges, Electric ForceDyan NavarroNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1-1Document18 pagesChapter - 1-1Layike AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument46 pagesElectrostaticsAmaan RizviNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture (Electromagnetism)Document71 pages02 Lecture (Electromagnetism)reduanulalamhridoyNo ratings yet
- Unit ADocument16 pagesUnit AvondutchlgNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic 1Document23 pagesElectrostatic 1rizal123No ratings yet
- Lectures Physics 2Document354 pagesLectures Physics 2Uranium PlatinumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Electric FieldDocument33 pagesChapter 1-Electric FieldThông LêNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Selected Topics of Physics-Stage 3Document25 pagesPresentation-Selected Topics of Physics-Stage 3diego reyesNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostaticsLast UnknownNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostaticsLast UnknownNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1234123Document3 pagesElectrostatics 1234123Last UnknownNo ratings yet
- 01 Electric ChargeDocument26 pages01 Electric ChargeJohaina NorNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics OneDocument59 pagesElectrostatics OneAkNo ratings yet
- Keystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsDocument60 pagesKeystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsAakash RathiNo ratings yet
- Keystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsDocument60 pagesKeystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsAakash RathiNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - Splash +2 Physics 2022 FinalDocument52 pagesHSSRPTR - Splash +2 Physics 2022 Finalbijijiju8129No ratings yet
- Electricity I 1Document9 pagesElectricity I 1Charles Daniel Torre MalolesNo ratings yet
- Electric ForceDocument15 pagesElectric ForceJasmin grace BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Electricity BDocument36 pagesElectricity BSean Patrick AlteaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document17 pagesChapter 21Pelin SoyluNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument12 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsAdrjydumpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts: ECEG-1351 - Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Introductory Concepts: ECEG-1351 - Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsSolomon AsefaNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Ayesha Anwer Ul Haq Qureshi MCS Karachi University (UBIT) E-Mail: Ayesha - Anwer@indus - Edu.pkDocument37 pagesApplied Physics: Ayesha Anwer Ul Haq Qureshi MCS Karachi University (UBIT) E-Mail: Ayesha - Anwer@indus - Edu.pkEhsan JavedNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge Cluster Demostration by Michael R. MaglaqueDocument22 pagesElectric Charge Cluster Demostration by Michael R. MaglaqueMichael Conan MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument21 pagesElectric Charges and Fieldsadvaith0% (1)
- Lecture 3.5 Electricity 1Document25 pagesLecture 3.5 Electricity 1SYACHBANI AMIN HIDAYATNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge: Chapter V: The Unification of Electricity, Magnetism and LightDocument5 pagesElectric Charge: Chapter V: The Unification of Electricity, Magnetism and LightRuby GoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 ElectrostaticsDocument8 pagesClass 12 ElectrostaticsMathew AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Ec1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfDocument61 pagesEc1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfYathavan A/l KalaichlvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document164 pagesChapter 16Phillip Bishop67% (3)
- Electrostatics TheoryDocument75 pagesElectrostatics TheoryAim Iit100% (1)
- Junior PhysicsDocument9 pagesJunior PhysicsVishesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICSDocument10 pagesELECTROSTATICSmabhelethabiso763No ratings yet
- General Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Document53 pagesGeneral Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Ronnel MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Electric Charges and ForcesDocument56 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Electric Charges and ForcesPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldsDocument21 pagesElectric FieldsMark Lorenz BertulfoNo ratings yet
- Electrcity Magnetism and Optics: Samra SyedDocument11 pagesElectrcity Magnetism and Optics: Samra SyedFA20-BCS-063 (SUBHAN SHAHZAD) UnknownNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument200 pagesElectricityNurul FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument76 pagesElectric Charge and Electric FieldGladys Lambayong100% (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Word ProblemsDocument1 pageTrigonometry Word ProblemsCrystal WellsNo ratings yet
- Table For T-Ratios of Some Standard Angles:: Tan Not Defined NotDocument1 pageTable For T-Ratios of Some Standard Angles:: Tan Not Defined NotCrystal WellsNo ratings yet
- Unit Tri60Nometry: Trigonometrical RatiosDocument1 pageUnit Tri60Nometry: Trigonometrical RatiosCrystal WellsNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors - Reference ContentDocument1 pageSpherical Mirrors - Reference ContentCrystal WellsNo ratings yet