Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES) : Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES) : Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Uploaded by
gthulasi7871260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage (FES) systems store energy by accelerating a rotor to high speeds using electricity on the grid, and generate electricity by decelerating the rotor. They have magnetic bearings and operate in a vacuum, allowing efficiencies over 80%. Flywheels can charge and discharge rapidly, require little maintenance, and have a long lifespan tolerant of deep discharges unlike batteries. The stored energy is directly proportional to the square of the angular momentum of the rotating flywheel.
Original Description:
EnergyStorage
Original Title
EnergyStorage_4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFlywheel Energy Storage (FES) systems store energy by accelerating a rotor to high speeds using electricity on the grid, and generate electricity by decelerating the rotor. They have magnetic bearings and operate in a vacuum, allowing efficiencies over 80%. Flywheels can charge and discharge rapidly, require little maintenance, and have a long lifespan tolerant of deep discharges unlike batteries. The stored energy is directly proportional to the square of the angular momentum of the rotating flywheel.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage (FES) : Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES) : Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Uploaded by
gthulasi787126Flywheel Energy Storage (FES) systems store energy by accelerating a rotor to high speeds using electricity on the grid, and generate electricity by decelerating the rotor. They have magnetic bearings and operate in a vacuum, allowing efficiencies over 80%. Flywheels can charge and discharge rapidly, require little maintenance, and have a long lifespan tolerant of deep discharges unlike batteries. The stored energy is directly proportional to the square of the angular momentum of the rotating flywheel.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)
The charging/discharging of the device is carried out through
an integrated electrical machine operating
- either as a motor to accelerate the rotor up to the
required high speeds by absorbing power from the
electric grid (charge mode)
- or as a generator to produce electrical power on
demand using the energy stored in the flywheel mass
by decelerating the rotor (discharge mode).
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)
The system has very low rotational losses due to the use
of magnetic bearings which prevent the contact between
the stationary and rotating parts, thus decreasing the
friction.
In addition, because the system operates in vacuum, the
aerodynamic resistance of the rotor is outstandingly
reduced.
These features permit the system to reach efficiencies
higher than 80%.
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)
Flywheels have the ability to charge and discharge rapidly,
and are almost immune to temperature fluctuations.
They take up relatively little space, have lower maintenance
requirements than batteries, and have a long life span.
Flywheel devices are relatively tolerant of abuse, i.e. the
lifetime of a flywheel system will not be shortened by a deep
discharge unlike a battery.
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)
The stored energy is directly proportional to the flywheel
rotor momentum and the square of the angular momentum,
a reason why increments in the rotation speed yield large
benefits on the storage energy density.
1
2
E I
2
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
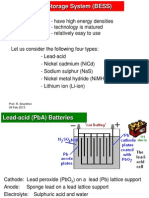
Battery Electric Storage System (BESS)
- have high energy densities
- technology is matured
- relatively easy to use
Let us consider the following four types:
- Lead-acid
- Nickel cadmium (NiCd)
- Sodium sulphur (NaS)
- Nickel metal hydride (NiMH)
- Lithium ion (Li-ion)
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)Document6 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage (FES)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage SystemDocument18 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage SystemImtiaz FiazNo ratings yet
- Research On Structure For Flywheel Energy Storage System in Long Lifetime UPSDocument7 pagesResearch On Structure For Flywheel Energy Storage System in Long Lifetime UPSchristineedealvaNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage SystemDocument4 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage SystemgnjuezNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy StorageDocument2 pagesFlywheel Energy StorageprasadsollapurNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy StorageDocument2 pagesFlywheel Energy Storagehayat umar bhatNo ratings yet
- 769 775 Vahidi - Tavakoli - SI - PaperDocument7 pages769 775 Vahidi - Tavakoli - SI - PaperMohamed AlNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy StorageDocument13 pagesFlywheel Energy StorageSARATH KRISHNAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Wind/Photovoltaic Hybrid Power System: Shenzhen Lemon Digitals LimitedDocument7 pagesWind/Photovoltaic Hybrid Power System: Shenzhen Lemon Digitals Limitedutpal1959No ratings yet
- Power Generation From Regenerative BrakingDocument9 pagesPower Generation From Regenerative BrakingTata OdoyNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Based Mechanical BatteryDocument2 pagesFlywheel Based Mechanical BatterySaksham TanejaNo ratings yet
- Flywheel As A Energy Storage Device: By:-Avinash Sengar Enroll. No. - 383/10Document15 pagesFlywheel As A Energy Storage Device: By:-Avinash Sengar Enroll. No. - 383/10jeganNo ratings yet
- Wind Power PlantDocument64 pagesWind Power PlantKenneth GabrielNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy StorageDocument4 pagesFlywheel Energy Storagetzw101No ratings yet
- Unit II - WInd EnergyDocument9 pagesUnit II - WInd EnergyM.ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage: Principles and Possibilities: 1 HistoryDocument4 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage: Principles and Possibilities: 1 HistorySarfarazHasanNo ratings yet
- Free Energy Generation by Using FlywheelDocument8 pagesFree Energy Generation by Using FlywheelWael Abdelgadir AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Hev M3Document17 pagesHev M3Anandhu ANo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage by Bhupendra Kumar, SRMGPCDocument19 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage by Bhupendra Kumar, SRMGPCDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Master Final Paper UpdatedDocument11 pagesMaster Final Paper Updatedadham samanoudyNo ratings yet
- Master Final DissertationDocument8 pagesMaster Final Dissertationadham samanoudyNo ratings yet
- Wind LabDocument10 pagesWind Labभूपेन्द्र कुमार साहूNo ratings yet
- 08042020093108introduction To Wind Energy and Their ApplicationDocument6 pages08042020093108introduction To Wind Energy and Their Applicationankitpatel122425990No ratings yet
- Flwheel Energy StorageDocument3 pagesFlwheel Energy StorageRoanak KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Dvanced Ngineering: Abstract: This Paper Deals With The Design of Kinetic Energy Recovery Systems (KERS) byDocument12 pagesDvanced Ngineering: Abstract: This Paper Deals With The Design of Kinetic Energy Recovery Systems (KERS) bypaulsonp_2No ratings yet
- Master Final Dissertation UpdatedDocument12 pagesMaster Final Dissertation Updatedadham samanoudyNo ratings yet
- InTech-Power Electronics in Small Scale Wind Turbine SystemsDocument32 pagesInTech-Power Electronics in Small Scale Wind Turbine Systemsshakil ahammedNo ratings yet
- Battery-Based Wind Turbine ReenDocument11 pagesBattery-Based Wind Turbine ReenJohn Reen MereteNo ratings yet
- Lorenzana Wind EnergyDocument7 pagesLorenzana Wind EnergyLister NambatacNo ratings yet
- MAster FInal DIssertation Updated 2Document11 pagesMAster FInal DIssertation Updated 2adham samanoudyNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Brake: The Motor As A GeneratorDocument14 pagesRegenerative Brake: The Motor As A GeneratorBhavin MehtaNo ratings yet
- Wind SystemDocument2 pagesWind SystemRushin MehtaNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Brake: The Motor As A GeneratorDocument4 pagesRegenerative Brake: The Motor As A GeneratorWhy VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Selecting and Maintaining Electric Motors and ControlsDocument109 pagesSelecting and Maintaining Electric Motors and ControlsppNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of Chapter 3Document8 pagesExercise Solution of Chapter 3Engr ShabirNo ratings yet
- Green PreviousDocument23 pagesGreen PreviousChinu PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking PPT FinalDocument18 pagesRegenerative Braking PPT FinalKrishna Prasad100% (2)
- Kinetic Energy Recovery SystemDocument13 pagesKinetic Energy Recovery SystemJainul PatelNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Wind Turbine Magnetic Levitation Rotor Dynamic Vertical TypeDocument4 pagesKeywords: Wind Turbine Magnetic Levitation Rotor Dynamic Vertical TypeHarshal KolheNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy: Department of Electrical Engineering Laxmi Devi Institute of Engineering & Technology, AlwarDocument29 pagesWind Energy: Department of Electrical Engineering Laxmi Devi Institute of Engineering & Technology, AlwarDileep SinghNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking SystemDocument6 pagesRegenerative Braking SystemA. A. SherpedoNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Energy Recovery SystemDocument33 pagesKinetic Energy Recovery SystemNaveenNo ratings yet
- SOLAR POWER SYSTEM RoanDocument34 pagesSOLAR POWER SYSTEM RoanroanNo ratings yet
- Flying Electric GeneratorDocument21 pagesFlying Electric GeneratorAbhishek100% (2)
- Amta4 8 Selecting and Maintaining Electric Motors and ControlsDocument102 pagesAmta4 8 Selecting and Maintaining Electric Motors and ControlsRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Regenerative BrakingDocument2 pages5.3 Regenerative Brakingneo viktorNo ratings yet
- Vikram Singh Dhabas Report FESS111Document20 pagesVikram Singh Dhabas Report FESS111Dipesh MogaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Brake ProjectDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Brake ProjectSwapnil GhoshNo ratings yet
- 25IJAERS 06202026 Designand PDFDocument8 pages25IJAERS 06202026 Designand PDFIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- W R B S: HapterDocument52 pagesW R B S: HapterAditya MishraNo ratings yet
- Wind A Motor Kit2Document14 pagesWind A Motor Kit2Gabriel SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage SystemDocument6 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage SystemImtiaz FiazNo ratings yet
- Fluid 1Document8 pagesFluid 1Kaneki SSSNo ratings yet
- Eeguc Unit IDocument28 pagesEeguc Unit IParventhan KannanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Generating Shock Absorber - Seminar Report, PPT, PDF For MechanicalDocument4 pagesElectricity Generating Shock Absorber - Seminar Report, PPT, PDF For MechanicalmobileNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument27 pagesWind EnergySeid EndrisNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Flywheel Based Battery Charging SystemDocument20 pagesAnalysis of Flywheel Based Battery Charging SystemBaljeetSinghKhoslaNo ratings yet
- Solar Electricity Generation System with a DIY Sun-Tracking PropositionFrom EverandSolar Electricity Generation System with a DIY Sun-Tracking PropositionNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρDocument5 pages2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 2Document6 pagesMaxwell - Equations 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electromagnetics 1 PDFDocument4 pagesElectromagnetics 1 PDFgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields and UnitsDocument3 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields and Unitsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument7 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Engine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument5 pagesEngine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learninggthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument3 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- 01maxwells Equations5Document5 pages01maxwells Equations5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
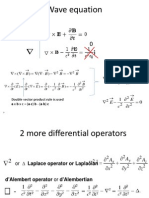
- Differential Operators: A A A A X y ZDocument3 pagesDifferential Operators: A A A A X y Zgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Choose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector FieldDocument4 pagesChoose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector Fieldgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Displacement Current & Maxwell's EquationsDocument4 pagesDisplacement Current & Maxwell's Equationsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- The Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are ConservativeDocument4 pagesThe Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are Conservativegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 1Document5 pagesMaxwell - Equations 1gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- We Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in DDocument4 pagesWe Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in Dgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- As Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)Document5 pagesAs Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Notice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)Document5 pagesNotice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- With This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of PathDocument6 pagesWith This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of Pathgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- F I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X yDocument6 pagesF I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X ygthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument6 pagesVector Calculusgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Most Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector FieldsDocument5 pagesMost Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector Fieldsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Lithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesLithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O HDocument3 pagesNickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O Hgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 2Document4 pagesEnergy Storage 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesNickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 5Document5 pagesEnergy Storage 5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Sodium Sulphur (Nas) BatteriesDocument4 pagesSodium Sulphur (Nas) Batteriesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Battery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To UseDocument6 pagesBattery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To Usegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Lead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: DrawbacksDocument5 pagesLead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: Drawbacksgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)Document6 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage (FES)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Mechanical Energy Storage-1Document4 pagesMechanical Energy Storage-1gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- BateriasDocument1 pageBateriasAlexanderNaranjoOsorioNo ratings yet
- Soler EnergyDocument8 pagesSoler EnergyKing NijashNo ratings yet
- gb6245g gf06180vDocument2 pagesgb6245g gf06180vkekarocNo ratings yet
- Industry Research Report On Renewable Energy, Green Technologies and Power-Focused NbfcsDocument181 pagesIndustry Research Report On Renewable Energy, Green Technologies and Power-Focused NbfcsAditya BhandakkarNo ratings yet
- A Review of Hybrid Renewable AlternativeDocument12 pagesA Review of Hybrid Renewable Alternativeeng_sham2No ratings yet
- Certification Process For Commercial Batteries For PayloadsDocument31 pagesCertification Process For Commercial Batteries For Payloadsgustavojorge12No ratings yet
- Illuminating The FutureDocument1 pageIlluminating The FutureDominique DemesaNo ratings yet
- .Tech Seminar 1ga15ee018Document22 pages.Tech Seminar 1ga15ee018Himalaya SinghNo ratings yet
- s65 Instruction Manual v2.0Document29 pagess65 Instruction Manual v2.0Julian COULETNo ratings yet
- Part Number System: Voltage Capacitance Size Material RemarkDocument1 pagePart Number System: Voltage Capacitance Size Material RemarksanazmeloNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Challenges and Opportunities in Battery TechnologiesDocument3 pagesA Review Paper On Challenges and Opportunities in Battery TechnologiesVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- s4134 Parker A279 Carroll Joint Oppose MemoDocument3 pagess4134 Parker A279 Carroll Joint Oppose MemoLuke ParsnowNo ratings yet
- Sailor Charger ManualDocument1 pageSailor Charger ManualJohn PerdyNo ratings yet
- GP Recyko Aa 2050mah PDFDocument2 pagesGP Recyko Aa 2050mah PDFDanielleNo ratings yet
- White Paper - Pumped Energy Storage v.9Document40 pagesWhite Paper - Pumped Energy Storage v.9Rob NikolewskiNo ratings yet
- Grid Power VM Brochure enDocument6 pagesGrid Power VM Brochure enlong bạchNo ratings yet
- Capacitor ManufacturerDocument14 pagesCapacitor ManufacturerSpandan ThakkarNo ratings yet
- General Catalogue 2010 2011 en 08Document43 pagesGeneral Catalogue 2010 2011 en 08Carlos PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Electric-Thermal Energy Storage For Large-Scale Renewables and A Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power CycleDocument10 pagesElectric-Thermal Energy Storage For Large-Scale Renewables and A Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power CycledavidNo ratings yet
- Crystal Caves Adventure SetDocument6 pagesCrystal Caves Adventure SetBoyd CNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Analysis of Hydrogen Compression and Pipeline Transportation From Thermodynamics and Safety AsepectsDocument11 pagesComprehensive Analysis of Hydrogen Compression and Pipeline Transportation From Thermodynamics and Safety Asepects기계공학과/김수빈No ratings yet
- Keltron CapacitorDocument2 pagesKeltron CapacitorDEBASHISHCHATTERJE78No ratings yet
- Electric WorldDocument12 pagesElectric WorldIshita ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Awaiting Image: 12V 100AH 12V 100AHDocument2 pagesAwaiting Image: 12V 100AH 12V 100AHMarcelo MoralesNo ratings yet
- 6 FMX 150BDocument2 pages6 FMX 150BsamersarasNo ratings yet
- Old Exam. Questions Chapter 25-082 (Dr. Naqvi, Phys.102.04-06)Document4 pagesOld Exam. Questions Chapter 25-082 (Dr. Naqvi, Phys.102.04-06)Mohamed SanadNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 (Rizwan Ali)Document4 pagesAssignment # 1 (Rizwan Ali)Rizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Growatt Ark BatteryDocument2 pagesGrowatt Ark Batterymaxx18fulNo ratings yet
- SPH NicdDocument7 pagesSPH NicdzakalyNo ratings yet
- ThesisL HosseiniDocument90 pagesThesisL Hosseiniannisa nur wahyuniNo ratings yet