Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Staining Techniques: Activity 2
Structural Staining Techniques: Activity 2
Uploaded by
Abi Diciembre Briones0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views11 pagesAfter treating samples with PAS reagent, parts of the cell with high carbohydrate content like mucins, glycogen, and the basement membrane can be observed. PAS staining highlights these molecules by using periodic acid to oxidize carbon bonds into aldehydes, which then react with Schiff's reagent to produce a magenta color. The key differences between Feulgen's reaction and PAS reaction are that Feulgen's specifically stains chromosomal material and DNA using fast green as a counterstain, whereas PAS stains a broader range of carbohydrates and uses Schiff's reagent with a blue counterstain.
Original Description:
Trial Upload
Staining Techniques
Original Title
Cell Bio
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAfter treating samples with PAS reagent, parts of the cell with high carbohydrate content like mucins, glycogen, and the basement membrane can be observed. PAS staining highlights these molecules by using periodic acid to oxidize carbon bonds into aldehydes, which then react with Schiff's reagent to produce a magenta color. The key differences between Feulgen's reaction and PAS reaction are that Feulgen's specifically stains chromosomal material and DNA using fast green as a counterstain, whereas PAS stains a broader range of carbohydrates and uses Schiff's reagent with a blue counterstain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views11 pagesStructural Staining Techniques: Activity 2
Structural Staining Techniques: Activity 2
Uploaded by
Abi Diciembre BrionesAfter treating samples with PAS reagent, parts of the cell with high carbohydrate content like mucins, glycogen, and the basement membrane can be observed. PAS staining highlights these molecules by using periodic acid to oxidize carbon bonds into aldehydes, which then react with Schiff's reagent to produce a magenta color. The key differences between Feulgen's reaction and PAS reaction are that Feulgen's specifically stains chromosomal material and DNA using fast green as a counterstain, whereas PAS stains a broader range of carbohydrates and uses Schiff's reagent with a blue counterstain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Activity 2
Structural Staining
Techniques
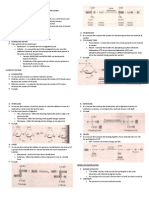
9.
After the samples were treated
with PAS reagent, what part of the
cell can be observed? Explain why.
PAS
reagent
Principle: The PAS stain is a
histochemical reaction in that the
periodic acid oxidizes the carbon to
carbon bond forming aldehydes which
react to the fuchsin-sulfurous acid which
form the magenta color.
PAS
staining is mainly used for staining
structures containing a high proportion
ofcarbohydratemacromolecules
(glycogen,glycoprotein,proteoglycans)
, typically found in e.g.connective
tissues,mucus, theglycocalyx,
andbasal laminae.
This
techniquehighlights molecules
in the cell with high carbohydrate
content such as mucins, glycogen,
and the basement membrane.
1.
Differentiate Feulgens reaction
from PAS reaction.
Technique
Feulgens Reaction
PAS Reaction
Stain
Fast Green
Periodic Acid (HCl)
Counterstain
Schiffs Reagent
Schiffs Reagent
Molecule
chromosomal
materialorDNA
Glycogen, neutral
mucosubstances,
basement membranes,
collagen fibers, glycolipids
and phospholipids
Carbon
Compound
dialdehydes
dialdehydes
Resulting Color
Magenta against
Green
Magenta against Blue
11.
Differentiation of blood cells and
neuron PAS method.
Neuron cells
Neuron cells
Blood cells
You might also like
- Unit V: Principles of Histology and HistochemistryDocument14 pagesUnit V: Principles of Histology and Histochemistryمروة صلاح50% (2)
- Thesis On Pre - Marital Sex.Document49 pagesThesis On Pre - Marital Sex.Charmaine Inah Abas Calumpang92% (145)
- Chapter 18-20Document50 pagesChapter 18-20Des MarquezNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Document30 pagesBiological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Mohammed shaffiqueNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ekta JajodiaDocument82 pagesDr. Ekta JajodiaRoshan SahuNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument14 pagesCARBOHYDRATESJey TeeNo ratings yet
- Histochemistry of GingivaDocument31 pagesHistochemistry of Gingivasandipladani100% (4)
- Histochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryDocument39 pagesHistochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryfomishisilasNo ratings yet
- Histochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryDocument39 pagesHistochemistry and Enzyme Histochemistrykay100% (2)
- Synthesis and Characterization of Lipid Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles With pH-Triggered Poly (Ethylene Glycol) SheddingDocument6 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Lipid Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles With pH-Triggered Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Shedding122866No ratings yet
- Activity 20 25Document8 pagesActivity 20 25wangshannahNo ratings yet
- Matecconf ICOMF14 02002Document4 pagesMatecconf ICOMF14 02002rifqiNo ratings yet
- Carbs StainingDocument32 pagesCarbs StainingIseth ISethNo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument30 pagesSpecial StainsNatalia HaikaliNo ratings yet
- Staining in Histopathologic TechniquesDocument3 pagesStaining in Histopathologic TechniquesJay Castillo50% (2)
- Qualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates ExperimentDocument12 pagesQualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates Experimentasdf6536525470% (1)
- Biochemistry of Hormones 1Document21 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones 1Hazel Grace BellenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohydrates - 1Document4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohydrates - 1Juliane JaynNo ratings yet
- Biochem Term 2Document28 pagesBiochem Term 2Michelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Special StainDocument45 pagesSpecial StainJerry TurtleNo ratings yet
- 1378968054.1856 - Histochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryDocument39 pages1378968054.1856 - Histochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryCarlos Ivan Cruz Cardenas100% (1)
- Chem 415 Experiment 1Document6 pagesChem 415 Experiment 1ttussenoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab DDocument45 pagesBiochem Lab DJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledIvy ManagNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Characterization of Novel Furan Based Polymeric Nanoparticles and Their Biological Activities"Document9 pagesSynthesis, Characterization of Novel Furan Based Polymeric Nanoparticles and Their Biological Activities"DakshayinihandrashekaracharNo ratings yet
- Treball Membranes BiomedDocument5 pagesTreball Membranes BiomedRamon Garcia CortadellaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal TEKPOLDocument10 pagesJurnal TEKPOLSinthiya Nur SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Biology Coursework Hydrogen PeroxideDocument6 pagesBiology Coursework Hydrogen Peroxidekezevifohoh3100% (1)
- BOTPG2201 - PG 2nd Sem - GlycolysisDocument16 pagesBOTPG2201 - PG 2nd Sem - GlycolysisAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- 08 Rivers JPRDocument7 pages08 Rivers JPRVenkata Suryanarayana GorleNo ratings yet
- Staining of Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesStaining of Proteins and Nucleic Acidsさあ ああさNo ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument79 pagesCellular MetabolismDr. Nachammai NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Transformation: Divakara R Asst. Professor Dept. of Biotechnology The Oxoford College of Engineering BengaluruDocument20 pagesEnzymatic Transformation: Divakara R Asst. Professor Dept. of Biotechnology The Oxoford College of Engineering BengaluruRamachandrappa DivakaraNo ratings yet
- CyclesDocument32 pagesCyclesSanjana VasistNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES Qualitative TestsDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATES Qualitative TestsEdith BelenNo ratings yet
- Effect of Organic Solvents Antigen Antibody InteractionsDocument7 pagesEffect of Organic Solvents Antigen Antibody InteractionsMohammad RehanNo ratings yet
- BIO 122 Recitation Week 1Document8 pagesBIO 122 Recitation Week 1Anonymous YXUt2RG1No ratings yet
- BCH421 2019-20 Harmattan 1Document7 pagesBCH421 2019-20 Harmattan 1idriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- Blazek 2012 (Glycosylation of Nucleoside Analogues Using B-Galactosidase From E.coli)Document8 pagesBlazek 2012 (Glycosylation of Nucleoside Analogues Using B-Galactosidase From E.coli)camilaNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of Super Paramagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Poly (D, L-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) MicroparticlesDocument6 pagesDispersion of Super Paramagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Poly (D, L-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) MicroparticlesPpa Gpat AmitNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4: Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 4: Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Bio CatalysisDocument6 pagesBio CatalysisNishi SainiNo ratings yet
- Asbmb Certification Exam Example QuestionsDocument14 pagesAsbmb Certification Exam Example QuestionsNishNo ratings yet
- Journal of Drug Delivery Science and TechnologyDocument5 pagesJournal of Drug Delivery Science and TechnologyFaizhal Dimas LeksonoNo ratings yet
- Life Processes SummaryDocument20 pagesLife Processes SummaryKlara EmperadoNo ratings yet
- Research Article A Molecular Recognition Hypothesis For Nonpeptides: Na K Atpase and Endogenous Digitalis-Like PeptidesDocument10 pagesResearch Article A Molecular Recognition Hypothesis For Nonpeptides: Na K Atpase and Endogenous Digitalis-Like Peptidesaanchal pathakNo ratings yet
- 05 EnzymesDocument35 pages05 EnzymesFrances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Midterm BiochemistryDocument12 pagesMidterm BiochemistryBiology BảoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LectureDocument115 pagesEnzymes LectureJane Tai100% (1)
- Lab 13 Enzymes Reading PDFDocument8 pagesLab 13 Enzymes Reading PDFLarryDengNo ratings yet
- Jamur Tiram 1Document6 pagesJamur Tiram 1Muhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsDocument43 pagesIsolation and Characterization of ProteinsMadeline SibuloNo ratings yet
- Enzyme HistochemistryDocument21 pagesEnzyme HistochemistryBoy blueNo ratings yet
- Chem 415 Experiment 1Document6 pagesChem 415 Experiment 1hanney zacNo ratings yet
- Role of Organelles in The Metabolism 141221Document44 pagesRole of Organelles in The Metabolism 141221Erdem Altun100% (1)
- Master 2 Project 1664062998Document1 pageMaster 2 Project 1664062998Ahmed ould aliyenneNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: A New Approach to the Molecular, Cellular, and Organismal LevelsFrom EverandPhotosynthesis: A New Approach to the Molecular, Cellular, and Organismal LevelsSuleyman I. AllakhverdievNo ratings yet
- Patch Testing and Prick Testing: A Practical Guide Official Publication of the ICDRGFrom EverandPatch Testing and Prick Testing: A Practical Guide Official Publication of the ICDRGNo ratings yet
- Auscultatory Method: Group 2: Briones, Botones, CabadingDocument15 pagesAuscultatory Method: Group 2: Briones, Botones, CabadingAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- Letter For Brgy 700 721Document22 pagesLetter For Brgy 700 721Abi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- Titration of Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument2 pagesTitration of Amino Acids and PeptidesAbi Diciembre Briones100% (1)
- Diagnostic Feature of EncystmentDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Feature of EncystmentAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- Test UploadDocument8 pagesTest UploadAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Elga Output in Med para Lab and LecDocument2 pagesGroup 5 Elga Output in Med para Lab and LecAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- SeretideDocument5 pagesSeretideAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissues: Abigail Loren D. Briones HUB34Document9 pagesNervous Tissues: Abigail Loren D. Briones HUB34Abi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- Classification of Hotels in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesClassification of Hotels in The PhilippinesAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument2 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet
- REED143 - Living Out Our Christian CommitmentDocument6 pagesREED143 - Living Out Our Christian CommitmentAbi Diciembre BrionesNo ratings yet