Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pyrosequencing For SNP Genotyping: Mostafa Ronaghi
Pyrosequencing For SNP Genotyping: Mostafa Ronaghi
Uploaded by
yylf2016Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pyrosequencing For SNP Genotyping: Mostafa Ronaghi
Pyrosequencing For SNP Genotyping: Mostafa Ronaghi
Uploaded by
yylf2016Copyright:
Available Formats
Pyrosequencing
189
13
Pyrosequencing for SNP Genotyping
Mostafa Ronaghi
1. Introduction
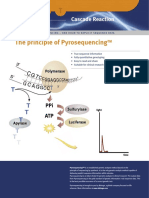
Pyrosequencing is a new DNA sequencing technique based on
sequencing-by-synthesis (1). This technique enables real-time
detection using an enzyme-cascade system, consisting of four
enzymes and specific substrates, to produce light whenever a nucleotide forms a base pair with the complementary nucleotide in a DNA
template strand. As a result of nucleotide incorporation inorganic
pyrophosphate (PPi) is released and is subsequently converted to
ATP by ATP sulfurylase which is used by luciferase to generate
proportional amount of light. Unreacted nucleotides are degraded
by the enzyme apyrase, allowing iterative addition of nucleotides
(see Fig. 1). DNA template generated by PCR is hybridized with a
sequencing primer prior to Pyrosequencing. Using one pmol of
DNA, 6 1011 ATP molecules can be obtained per nucleotide incorporation which, in turn, generate more than 6 109 photons at a
wavelength of 560 nanometers. This amount of light is easily
detected by a photodiode, photomultiplier tube, or a CCD-camera.
Pyrosequencing has the potential advantages of accuracy, flexibility, parallel processing, and simple automation. Furthermore, the
technique avoids the use of labeled primers, labeled nucleotides,
From: Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 212:
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms: Methods and Protocols
Edited by: P-Y. Kwok Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ
189
You might also like
- Abcam Fluorochrome ChartDocument1 pageAbcam Fluorochrome Chartyylf2016No ratings yet
- What Is PyrosequencingDocument6 pagesWhat Is PyrosequencingAshish SachanNo ratings yet
- 454 Pyrosequencing (Bastareche Et Al.)Document17 pages454 Pyrosequencing (Bastareche Et Al.)Adrian BornillaNo ratings yet
- PyrosequencingDocument4 pagesPyrosequencingFarzini100% (3)
- Nuclic Acid Squencing Sanjeev MainDocument16 pagesNuclic Acid Squencing Sanjeev MainSonu Rampal SainiNo ratings yet
- Next Gen SequencingDocument19 pagesNext Gen SequencingthesiscraftsmanNo ratings yet
- The Principle of PyrosequencingDocument2 pagesThe Principle of PyrosequencingClau¿ R.No ratings yet
- Bleidorn 2017Document18 pagesBleidorn 2017Felipe CardosoNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument8 pagesDNA SequencingAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- DNA Bases Genome Human Genome ProjectDocument5 pagesDNA Bases Genome Human Genome ProjectSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Synthesis NMNDocument12 pagesEnzymatic Synthesis NMNTron TronNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing & ApplicationDocument15 pagesDNA Sequencing & Applicationshamidr99No ratings yet
- 5.2.15-Abt 605 Molecular Diagnostics-Term Paper-PyrosequencingDocument30 pages5.2.15-Abt 605 Molecular Diagnostics-Term Paper-PyrosequencingVinod SivadasanNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument60 pagesDNA Sequencingabimbolagrace356No ratings yet
- Long, Processive Enzymatic Dna Synthesis Using 100% Dye-Labeled Terminal Phosphate-Linked NucleotidesDocument12 pagesLong, Processive Enzymatic Dna Synthesis Using 100% Dye-Labeled Terminal Phosphate-Linked NucleotidesAlessandroNo ratings yet
- Product Distribution and Pre-Steady-State Kinetic Analysis of Escherichia Coli Undecaprenyl Pyrophosphate Synthase ReactionDocument7 pagesProduct Distribution and Pre-Steady-State Kinetic Analysis of Escherichia Coli Undecaprenyl Pyrophosphate Synthase Reactionkittipot_rs68No ratings yet
- Pyrosequencing 180209114248Document17 pagesPyrosequencing 180209114248JohnNo ratings yet
- Lec-7 Methods of DNA SequencingDocument51 pagesLec-7 Methods of DNA Sequencingmark phinhasNo ratings yet
- Sequence by Synthesis.Document6 pagesSequence by Synthesis.bladeralienNo ratings yet
- CSIR-NET Life Science - Short Notes On Nucleotide Biosynthesis (Purine & Pyrimidine Synthesis)Document10 pagesCSIR-NET Life Science - Short Notes On Nucleotide Biosynthesis (Purine & Pyrimidine Synthesis)Arun DubeyNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-1957-Preiss-759-70Document13 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-1957-Preiss-759-70Nace AtanasovNo ratings yet
- Ingabire Munyentwali Angelique BSN 1-8 2018Document5 pagesIngabire Munyentwali Angelique BSN 1-8 2018Aime MvuyekureNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression in Eukaryotes 3Document3 pagesGene Expression in Eukaryotes 3Tadhg Ó MaoldhomhnaighNo ratings yet
- Techniques of DNA Sequencing (ASSIGNMENT)Document6 pagesTechniques of DNA Sequencing (ASSIGNMENT)Speech's ClubNo ratings yet
- 1516260242FSC P13 M13 E-Text PDFDocument10 pages1516260242FSC P13 M13 E-Text PDFKanchanNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide Biosynthesis: DR/ Gamal AlhazmiDocument16 pagesNucleotide Biosynthesis: DR/ Gamal Alhazmihamada999No ratings yet
- DNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins: BiologyDocument7 pagesDNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins: BiologyclchioNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument21 pagesDNA SequencingShiv KumarNo ratings yet
- NUS 123 NotesDocument14 pagesNUS 123 NotesBrevine Oduor OsoroNo ratings yet
- Early History of Microbiological TechniqueDocument5 pagesEarly History of Microbiological TechniqueFadare Shadrach ONo ratings yet
- New Sequencing TechnologyDocument21 pagesNew Sequencing Technologyforgetme_not059753100% (4)
- Science 1987 Prober 336 41Document6 pagesScience 1987 Prober 336 41biomathNo ratings yet
- PCR Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument30 pagesPCR Polymerase Chain ReactionWuLan TetapphMeynandtieNo ratings yet
- Sequencing ReviewDocument5 pagesSequencing ReviewjamimmsNo ratings yet
- Sequencing of ProteinsDocument5 pagesSequencing of ProteinsAime MvuyekureNo ratings yet
- BCH 313 2nd Part Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesBCH 313 2nd Part Lecture NotesaualbidawyNo ratings yet
- Dna Sequencing MethodsDocument29 pagesDna Sequencing MethodsWilson Anandaraj92% (13)
- 759 FullDocument13 pages759 FullNace AtanasovNo ratings yet
- DNA Polymerase Primer: The PCR Reaction Requires The Following ComponentsDocument2 pagesDNA Polymerase Primer: The PCR Reaction Requires The Following ComponentsChristopher BeckerNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument34 pagesDNA Sequencingmnouma1612No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument23 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismMSc Biotech/MicroNo ratings yet
- Design of A Coupled Bioluminescent Assay For A Recombinant Pyruvate Kinase From A Thermophilic GeobacillusDocument8 pagesDesign of A Coupled Bioluminescent Assay For A Recombinant Pyruvate Kinase From A Thermophilic Geobacillusd2champNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (Notes) : Group (-OH Group Attached To 3'-End of DNA), It Needs A Primer, To Which It CanDocument9 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (Notes) : Group (-OH Group Attached To 3'-End of DNA), It Needs A Primer, To Which It CanRakesh GedalaNo ratings yet
- Sintesis Dan Karakterisasi Nukleotida Bertanda (Α-P) AtpDocument6 pagesSintesis Dan Karakterisasi Nukleotida Bertanda (Α-P) AtpVivi yenni aryantiNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing SlidesDocument64 pagesDNA Sequencing SlideskittyngameNo ratings yet
- DNA Binding Properties of The Adenovirus DNA Replication Priming Protein PTPDocument13 pagesDNA Binding Properties of The Adenovirus DNA Replication Priming Protein PTPThanga Rajan PannerselvamNo ratings yet
- A Novel DNA Joining Activity Catalyzed by T4 DNA LigaseDocument5 pagesA Novel DNA Joining Activity Catalyzed by T4 DNA LigaseMelanie DiBiasioNo ratings yet
- Translated Version of Real Time PCRDocument8 pagesTranslated Version of Real Time PCRSonu SomanathNo ratings yet
- Pyrimidine BiosynthesisDocument45 pagesPyrimidine BiosynthesisJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : Principle of The PCRDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : Principle of The PCRSalvador MartinezNo ratings yet
- Presentacion EntenderDocument37 pagesPresentacion EntenderJuan David Marin ChiguachiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9-DNA SequencingDocument22 pagesLecture 9-DNA SequencingTehreem JahangiriNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsDocument38 pagesHydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsSHIFA ALTAFNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction: BackgroundDocument11 pagesReal-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction: BackgroundCareless WhisperrNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Purification of Putative Pentr4:Campari ClonesDocument10 pagesIsolation and Purification of Putative Pentr4:Campari ClonesBrittani HyltonNo ratings yet
- Azotobacter Vinela NdiiDocument17 pagesAzotobacter Vinela NdiiSantiago RjverosNo ratings yet
- Breaking The Code Required Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesBreaking The Code Required Organic ChemistrySAMUELNo ratings yet
- Safari - Jan 12, 2024 at 3:30 AMDocument1 pageSafari - Jan 12, 2024 at 3:30 AMjegiwod963No ratings yet
- Credit Seminar II (PHD)Document61 pagesCredit Seminar II (PHD)bhakthaNo ratings yet
- Natural Products Analysis: Instrumentation, Methods, and ApplicationsFrom EverandNatural Products Analysis: Instrumentation, Methods, and ApplicationsVladimir HavlicekNo ratings yet
- Cancer Metabolism in Space and Time - Beyond The Warburg EffectDocument17 pagesCancer Metabolism in Space and Time - Beyond The Warburg Effectyylf2016No ratings yet
- An Essential Role of The Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in Cell Proliferation Is To Enable Aspartate SynthesisDocument13 pagesAn Essential Role of The Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in Cell Proliferation Is To Enable Aspartate Synthesisyylf2016No ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Apolipoprotein A-I MimeticsDocument10 pagesNIH Public Access: Apolipoprotein A-I Mimeticsyylf2016No ratings yet
- Circulation-2002-Cardiovascular Influences of A1b-Adrenergic Receptor Defect in MiceDocument9 pagesCirculation-2002-Cardiovascular Influences of A1b-Adrenergic Receptor Defect in Miceyylf2016No ratings yet
- Circ Res-2014-High-Density LipoproteinDocument13 pagesCirc Res-2014-High-Density Lipoproteinyylf2016No ratings yet
- EnPosdeloSupremo PDFDocument1 pageEnPosdeloSupremo PDFyylf2016No ratings yet
- Fidel Castro by Nick CaistorDocument159 pagesFidel Castro by Nick Caistoryylf2016100% (2)
- Cuba in A Global ContextDocument350 pagesCuba in A Global Contextyylf2016100% (1)
- Photographic Atlas of PediatricDocument371 pagesPhotographic Atlas of Pediatricyylf2016100% (2)
- Mathematics The Music of ReasonDocument292 pagesMathematics The Music of Reasonyylf2016100% (3)
- Walking in Humility-SeminarDocument4 pagesWalking in Humility-Seminaryylf2016No ratings yet