Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inercia Dpend Ratio2
Inercia Dpend Ratio2
Uploaded by
Alexander Diaz AlvarezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mece307 - Sertaç ŞimşekDocument18 pagesMece307 - Sertaç ŞimşekErtürk ErdiNo ratings yet
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Constant Volts/Hertz Operation For Variable Speed Control of Induction MotorsDocument24 pagesConstant Volts/Hertz Operation For Variable Speed Control of Induction MotorsSreerag Kunnathu SugathanNo ratings yet
- Dynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingFrom EverandDynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingNo ratings yet
- Bonfiglioli Reductoare C A F SDocument582 pagesBonfiglioli Reductoare C A F SAgache ValentinNo ratings yet
- Htass 3 Q 3Document4 pagesHtass 3 Q 3Dennis Wolfgang SpuddletonNo ratings yet
- TM DiagramsDocument7 pagesTM DiagramsblackmechanicalpantherNo ratings yet
- Rotordynamicsslides DR.K.SDocument29 pagesRotordynamicsslides DR.K.Spkpnitian_152297088No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of MotorDocument14 pagesBasic Principles of MotorAnkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ie8b05277 Si 001Document20 pagesIe8b05277 Si 001Nipun ChopraNo ratings yet
- T-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterDocument7 pagesT-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterHemant TradersNo ratings yet
- Experiments EMS IIDocument117 pagesExperiments EMS IIOsama Tahir100% (1)
- Outcome 1 T 3Document7 pagesOutcome 1 T 3Akib SheikhNo ratings yet
- Induction Motors: 8.1 What Does One Look Like?Document8 pagesInduction Motors: 8.1 What Does One Look Like?Gnua WazNo ratings yet
- Report 5Document28 pagesReport 5Chrome BrowserNo ratings yet
- EES612 Lab1Document25 pagesEES612 Lab1Levan LomidzeNo ratings yet
- Setting Out of CurveDocument19 pagesSetting Out of CurveshujaNo ratings yet
- HES3350 Machine Design Semester 1 2012 Assignment 1 Compound Reverted Gear Train Design PDFDocument18 pagesHES3350 Machine Design Semester 1 2012 Assignment 1 Compound Reverted Gear Train Design PDFrisirarocksNo ratings yet
- 10.6 - Serial Analog-Digital Converters: Serial Adcs Typically Require 2 Types: - Single-Slope - Dual-SlopeDocument4 pages10.6 - Serial Analog-Digital Converters: Serial Adcs Typically Require 2 Types: - Single-Slope - Dual-Slopejagriti kumariNo ratings yet
- Ijmet 07 06 050Document8 pagesIjmet 07 06 050dfdhNo ratings yet
- Table 2Document14 pagesTable 2dkp8098No ratings yet
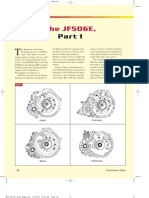
- JF506E Supplement Part 1Document6 pagesJF506E Supplement Part 1Eban FloresNo ratings yet
- 01m Adaptation Basic SettingDocument4 pages01m Adaptation Basic SettingEmma MummyNo ratings yet
- Transfer Functions For Systems With Gears: Group 6Document9 pagesTransfer Functions For Systems With Gears: Group 6Patty SeyoNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving On D C Machines PDFDocument16 pagesProblem Solving On D C Machines PDFSelvaraj ParamasivanNo ratings yet
- Gear TrainsDocument42 pagesGear Trainsmihai.banica100% (1)
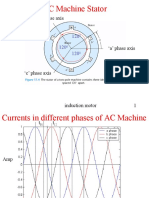
- Induction MotorDocument39 pagesInduction MotorSaneer M SaliNo ratings yet
- Ee 316 - Electrical Machines 1 Week 10: T Kϕ I T KciDocument8 pagesEe 316 - Electrical Machines 1 Week 10: T Kϕ I T KciLaurence Abrogena AlmazanNo ratings yet
- All ExpDocument37 pagesAll ExpMuhammad SameerNo ratings yet
- Air Compressed Vehicle: Shubhamsuryawanshi, Yashbharade, Pratik Shetkar, ChetanpakhaleDocument10 pagesAir Compressed Vehicle: Shubhamsuryawanshi, Yashbharade, Pratik Shetkar, ChetanpakhaleankNo ratings yet
- sm13 88Document2 pagessm13 88Carlos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Gear-Box Using Spur Gear and Eliminating The Differential UnitDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Gear-Box Using Spur Gear and Eliminating The Differential UnitmohanNo ratings yet
- Class 28 - Modeling of A Gear TrainDocument19 pagesClass 28 - Modeling of A Gear Trainapi-26676616100% (2)
- Parts 3121164 03-01-11 Global EnglishDocument64 pagesParts 3121164 03-01-11 Global EnglishСвятослав ВороновNo ratings yet
- Direct - Current Motor Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument58 pagesDirect - Current Motor Characteristics and ApplicationsMaman SomantriNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: D.C. Motor StudyDocument25 pagesUser's Manual: D.C. Motor Studymanoj_varma_1No ratings yet
- The Placidus House Division Formulas For AstrologyDocument1 pageThe Placidus House Division Formulas For AstrologyAnonymous WeDXoM1Q100% (3)
- Design Project 2 Auto TrannyDocument9 pagesDesign Project 2 Auto TrannyUnmil PatelNo ratings yet
- T-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterDocument7 pagesT-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterHemant TradersNo ratings yet
- Objectives: On Completion of This Period, You Would Be Able To Know AboutDocument14 pagesObjectives: On Completion of This Period, You Would Be Able To Know AboutMohanNo ratings yet
- EPE423a Exper9 231210 152105Document13 pagesEPE423a Exper9 231210 152105muhammed mouradNo ratings yet
- GX 3000 SFDocument28 pagesGX 3000 SFElif FotokopiNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Alignment PDFDocument15 pagesHorizontal Alignment PDFAnteneh Geremew100% (1)
- Epicyclic Gear Train Write UpDocument8 pagesEpicyclic Gear Train Write UpkulkajinkyaNo ratings yet
- Usa Tech Calculation PDFDocument35 pagesUsa Tech Calculation PDFRizwan HameedNo ratings yet
- Brakes Calculations Assumptions MadeDocument3 pagesBrakes Calculations Assumptions MadeMonojit KonarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Electronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Nissan-Infinity VehiclesFrom EverandElectronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Nissan-Infinity VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualFrom EverandThermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationFrom EverandShape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationNo ratings yet
- Refurbish Antique Telephones for Fun and Hobby: Step by Step Instructions to Take an Old Telephone and Return It to Its Original Working Order. No Electronics or Telephone Knowledge Needed.From EverandRefurbish Antique Telephones for Fun and Hobby: Step by Step Instructions to Take an Old Telephone and Return It to Its Original Working Order. No Electronics or Telephone Knowledge Needed.No ratings yet
- Worked Examples in Electrical Machines and Drives: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsFrom EverandWorked Examples in Electrical Machines and Drives: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- CMT-FHD Datasheet ENGDocument2 pagesCMT-FHD Datasheet ENGAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Motor 19: Motor: #2 Mixer (40 HP, 1800 RPM, TEFC)Document1 pageMotor 19: Motor: #2 Mixer (40 HP, 1800 RPM, TEFC)Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Haiwell Industry Application CaseDocument38 pagesHaiwell Industry Application CaseAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Motor 88: Motor: Ref Compressor #1 (60 HP, 1800 RPM, ODP)Document1 pageMotor 88: Motor: Ref Compressor #1 (60 HP, 1800 RPM, ODP)Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Directview: Manual Number D - 24view - MDocument188 pagesDirectview: Manual Number D - 24view - MAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Motor Savings Analysis - Replace ExistingDocument1 pageMotor Savings Analysis - Replace ExistingAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument193 pagesManualAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- MH500 Hydraulic Servo Project Case: SummaryDocument6 pagesMH500 Hydraulic Servo Project Case: SummaryAlexander Diaz Alvarez0% (1)
- Yea Sia c887 1.4b SFTWR ManDocument461 pagesYea Sia c887 1.4b SFTWR ManAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Sigma5Catalog PDFDocument392 pagesSigma5Catalog PDFAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- XGB Economic, Standard Catalogue (Eng) - 20100504Document2 pagesXGB Economic, Standard Catalogue (Eng) - 20100504Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Beta Vs Steinhart Hart EquationsDocument9 pagesBeta Vs Steinhart Hart EquationsAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Interpolation SICLABDocument16 pagesPolynomial Interpolation SICLABAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Delta Ia-Cnc NC300 Om en 20151202Document181 pagesDelta Ia-Cnc NC300 Om en 20151202Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Yea Kaeps800000042k SGMGVDocument24 pagesYea Kaeps800000042k SGMGVAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Calibrate Steinhart-Hart Coefficients For Thermistors: Stanford Research Systems (408) 744-9040Document3 pagesCalibrate Steinhart-Hart Coefficients For Thermistors: Stanford Research Systems (408) 744-9040Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
Inercia Dpend Ratio2
Inercia Dpend Ratio2
Uploaded by
Alexander Diaz AlvarezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inercia Dpend Ratio2
Inercia Dpend Ratio2
Uploaded by
Alexander Diaz AlvarezCopyright:
Available Formats
Zenith Division
Technical Bulletin
Date:
No:
To:
Cc:
Subject:
Effective:
January 9, 2001
ZTB-006
ATCs, ETMs, RM
AEs
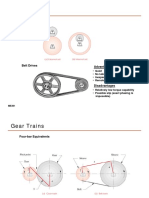
Squaring of Gear Ratio for inertia Matching
Long time ago
Gearhead Sizing
When sizing a gearhead for inertia matching the squaring of the ratio is often used without explanation.
Here are the simple equations and the algebra to explain why if anyone ever asks.
Variable definitions
T1 = motor torque
J1 = motor inertia
1 = motor angular acceleration
T2 = load torque
J2 = load inertia
2 = load angular acceleration
To determine why the gear ratio is squared we must first start with the following fundamental equations.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
T2= J2* 2
T1 / R1 = T2 / R2
T1 = J1 * 1
T2= J2* 2
T1 / R1 = T2 / R2
R1 * 1= R2 * 2
Gear ratio = R2 / R1
With simple algebra we manipulate equations 6 & 4 to get
8. 1 = (R2 / R1) * 2
9. 2 = T2 / J2
Then with substitution of equation 8 for 1 into 3,
10. T1 = J1 * (R2 / R1) * 2
Next we substitution of equation 9 for 2 into 10,
11. T1 = J1 * (R2 / R1) * (T2 / J2)
Page 1 of 2
Parker Hannifin Corp. Zenith Division Sanford, NC 27330 1-877-959-4327 Fax: 919-774-5952
Zenith Division
Technical Bulletin
Bring T2 to the left side of the equation
12. T1 / T2 = (R2 / R1) * (J1 / J2)
And cross-multiply on equation 5
13. T1 / T2 = R1 / R2
Equate equation 12 & 13
T1 / T2 = R1 / R2 = (R2 / R1) * (J1 / J2)
Finally bring the (R2 / R1) and J2 to the left.
J2 * 1 / (R2 / R1) = J1
J2 * 1 / (gear ratio) = J1
Page 2 of 2
Parker Hannifin Corp. Zenith Division Sanford, NC 27330 1-877-959-4327 Fax: 919-774-5952
You might also like
- Mece307 - Sertaç ŞimşekDocument18 pagesMece307 - Sertaç ŞimşekErtürk ErdiNo ratings yet
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Constant Volts/Hertz Operation For Variable Speed Control of Induction MotorsDocument24 pagesConstant Volts/Hertz Operation For Variable Speed Control of Induction MotorsSreerag Kunnathu SugathanNo ratings yet
- Dynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingFrom EverandDynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingNo ratings yet
- Bonfiglioli Reductoare C A F SDocument582 pagesBonfiglioli Reductoare C A F SAgache ValentinNo ratings yet
- Htass 3 Q 3Document4 pagesHtass 3 Q 3Dennis Wolfgang SpuddletonNo ratings yet
- TM DiagramsDocument7 pagesTM DiagramsblackmechanicalpantherNo ratings yet
- Rotordynamicsslides DR.K.SDocument29 pagesRotordynamicsslides DR.K.Spkpnitian_152297088No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of MotorDocument14 pagesBasic Principles of MotorAnkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ie8b05277 Si 001Document20 pagesIe8b05277 Si 001Nipun ChopraNo ratings yet
- T-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterDocument7 pagesT-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterHemant TradersNo ratings yet
- Experiments EMS IIDocument117 pagesExperiments EMS IIOsama Tahir100% (1)
- Outcome 1 T 3Document7 pagesOutcome 1 T 3Akib SheikhNo ratings yet
- Induction Motors: 8.1 What Does One Look Like?Document8 pagesInduction Motors: 8.1 What Does One Look Like?Gnua WazNo ratings yet
- Report 5Document28 pagesReport 5Chrome BrowserNo ratings yet
- EES612 Lab1Document25 pagesEES612 Lab1Levan LomidzeNo ratings yet
- Setting Out of CurveDocument19 pagesSetting Out of CurveshujaNo ratings yet
- HES3350 Machine Design Semester 1 2012 Assignment 1 Compound Reverted Gear Train Design PDFDocument18 pagesHES3350 Machine Design Semester 1 2012 Assignment 1 Compound Reverted Gear Train Design PDFrisirarocksNo ratings yet
- 10.6 - Serial Analog-Digital Converters: Serial Adcs Typically Require 2 Types: - Single-Slope - Dual-SlopeDocument4 pages10.6 - Serial Analog-Digital Converters: Serial Adcs Typically Require 2 Types: - Single-Slope - Dual-Slopejagriti kumariNo ratings yet
- Ijmet 07 06 050Document8 pagesIjmet 07 06 050dfdhNo ratings yet
- Table 2Document14 pagesTable 2dkp8098No ratings yet
- JF506E Supplement Part 1Document6 pagesJF506E Supplement Part 1Eban FloresNo ratings yet
- 01m Adaptation Basic SettingDocument4 pages01m Adaptation Basic SettingEmma MummyNo ratings yet
- Transfer Functions For Systems With Gears: Group 6Document9 pagesTransfer Functions For Systems With Gears: Group 6Patty SeyoNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving On D C Machines PDFDocument16 pagesProblem Solving On D C Machines PDFSelvaraj ParamasivanNo ratings yet
- Gear TrainsDocument42 pagesGear Trainsmihai.banica100% (1)
- Induction MotorDocument39 pagesInduction MotorSaneer M SaliNo ratings yet
- Ee 316 - Electrical Machines 1 Week 10: T Kϕ I T KciDocument8 pagesEe 316 - Electrical Machines 1 Week 10: T Kϕ I T KciLaurence Abrogena AlmazanNo ratings yet
- All ExpDocument37 pagesAll ExpMuhammad SameerNo ratings yet
- Air Compressed Vehicle: Shubhamsuryawanshi, Yashbharade, Pratik Shetkar, ChetanpakhaleDocument10 pagesAir Compressed Vehicle: Shubhamsuryawanshi, Yashbharade, Pratik Shetkar, ChetanpakhaleankNo ratings yet
- sm13 88Document2 pagessm13 88Carlos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Gear-Box Using Spur Gear and Eliminating The Differential UnitDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Gear-Box Using Spur Gear and Eliminating The Differential UnitmohanNo ratings yet
- Class 28 - Modeling of A Gear TrainDocument19 pagesClass 28 - Modeling of A Gear Trainapi-26676616100% (2)
- Parts 3121164 03-01-11 Global EnglishDocument64 pagesParts 3121164 03-01-11 Global EnglishСвятослав ВороновNo ratings yet
- Direct - Current Motor Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument58 pagesDirect - Current Motor Characteristics and ApplicationsMaman SomantriNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: D.C. Motor StudyDocument25 pagesUser's Manual: D.C. Motor Studymanoj_varma_1No ratings yet
- The Placidus House Division Formulas For AstrologyDocument1 pageThe Placidus House Division Formulas For AstrologyAnonymous WeDXoM1Q100% (3)
- Design Project 2 Auto TrannyDocument9 pagesDesign Project 2 Auto TrannyUnmil PatelNo ratings yet
- T-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterDocument7 pagesT-Rex Motorsports Department of Powertrain 1) Pitch Circle DiameterHemant TradersNo ratings yet
- Objectives: On Completion of This Period, You Would Be Able To Know AboutDocument14 pagesObjectives: On Completion of This Period, You Would Be Able To Know AboutMohanNo ratings yet
- EPE423a Exper9 231210 152105Document13 pagesEPE423a Exper9 231210 152105muhammed mouradNo ratings yet
- GX 3000 SFDocument28 pagesGX 3000 SFElif FotokopiNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Alignment PDFDocument15 pagesHorizontal Alignment PDFAnteneh Geremew100% (1)
- Epicyclic Gear Train Write UpDocument8 pagesEpicyclic Gear Train Write UpkulkajinkyaNo ratings yet
- Usa Tech Calculation PDFDocument35 pagesUsa Tech Calculation PDFRizwan HameedNo ratings yet
- Brakes Calculations Assumptions MadeDocument3 pagesBrakes Calculations Assumptions MadeMonojit KonarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Electronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Nissan-Infinity VehiclesFrom EverandElectronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Nissan-Infinity VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualFrom EverandThermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationFrom EverandShape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationNo ratings yet
- Refurbish Antique Telephones for Fun and Hobby: Step by Step Instructions to Take an Old Telephone and Return It to Its Original Working Order. No Electronics or Telephone Knowledge Needed.From EverandRefurbish Antique Telephones for Fun and Hobby: Step by Step Instructions to Take an Old Telephone and Return It to Its Original Working Order. No Electronics or Telephone Knowledge Needed.No ratings yet
- Worked Examples in Electrical Machines and Drives: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsFrom EverandWorked Examples in Electrical Machines and Drives: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- CMT-FHD Datasheet ENGDocument2 pagesCMT-FHD Datasheet ENGAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Motor 19: Motor: #2 Mixer (40 HP, 1800 RPM, TEFC)Document1 pageMotor 19: Motor: #2 Mixer (40 HP, 1800 RPM, TEFC)Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Haiwell Industry Application CaseDocument38 pagesHaiwell Industry Application CaseAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Motor 88: Motor: Ref Compressor #1 (60 HP, 1800 RPM, ODP)Document1 pageMotor 88: Motor: Ref Compressor #1 (60 HP, 1800 RPM, ODP)Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Directview: Manual Number D - 24view - MDocument188 pagesDirectview: Manual Number D - 24view - MAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Motor Savings Analysis - Replace ExistingDocument1 pageMotor Savings Analysis - Replace ExistingAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument193 pagesManualAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- MH500 Hydraulic Servo Project Case: SummaryDocument6 pagesMH500 Hydraulic Servo Project Case: SummaryAlexander Diaz Alvarez0% (1)
- Yea Sia c887 1.4b SFTWR ManDocument461 pagesYea Sia c887 1.4b SFTWR ManAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Sigma5Catalog PDFDocument392 pagesSigma5Catalog PDFAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- XGB Economic, Standard Catalogue (Eng) - 20100504Document2 pagesXGB Economic, Standard Catalogue (Eng) - 20100504Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Beta Vs Steinhart Hart EquationsDocument9 pagesBeta Vs Steinhart Hart EquationsAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Interpolation SICLABDocument16 pagesPolynomial Interpolation SICLABAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Delta Ia-Cnc NC300 Om en 20151202Document181 pagesDelta Ia-Cnc NC300 Om en 20151202Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Yea Kaeps800000042k SGMGVDocument24 pagesYea Kaeps800000042k SGMGVAlexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Calibrate Steinhart-Hart Coefficients For Thermistors: Stanford Research Systems (408) 744-9040Document3 pagesCalibrate Steinhart-Hart Coefficients For Thermistors: Stanford Research Systems (408) 744-9040Alexander Diaz AlvarezNo ratings yet