Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gas Constant, 0.287 KJ KG K
Gas Constant, 0.287 KJ KG K
Uploaded by
gowthamAG07Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Homework 11Document8 pagesHomework 11Ha ViNo ratings yet
- FSFSDGDocument2 pagesFSFSDGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- T P H S I I I I: I I I I TH TH THDocument2 pagesT P H S I I I I: I I I I TH TH THSathyarazor21No ratings yet
- 300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KDocument2 pages300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Unit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SDocument5 pagesUnit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SAbubakar AdeniNo ratings yet
- T P V V U: I I I R IDocument3 pagesT P V V U: I I I R IgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument14 pagesGaseous StatemayankNo ratings yet
- Two-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KDocument3 pagesTwo-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 8-39E Oxygen Gas Is Compressed From A Specified Initial State To A Final Specified State. The Reversible WorkDocument8 pages8-39E Oxygen Gas Is Compressed From A Specified Initial State To A Final Specified State. The Reversible WorkAnonymous 5OI0ClBZNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- ChE234 F10 Exam2 Thermodynamics For Chemical EngineersDocument3 pagesChE234 F10 Exam2 Thermodynamics For Chemical EngineerskellykapperNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Ideal Gas Practice Problems SolutionsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics: Ideal Gas Practice Problems SolutionsMuqeem Uddin100% (1)
- Ideal Gas EntropyDocument6 pagesIdeal Gas EntropyAlan A. AlexanderNo ratings yet
- 11 74P - DoneDocument2 pages11 74P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Processes and Carnot CycleDocument4 pagesProcesses and Carnot CycleRagh AhmedNo ratings yet
- 11 77P - DoneDocument2 pages11 77P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- ENGG1500 Module 8 Tute SolutionsDocument15 pagesENGG1500 Module 8 Tute SolutionsKevin MalarkeyNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesDocument34 pagesIdeal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesJake SyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasDocument7 pagesEngineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasazzraNo ratings yet
- GweghewhDocument5 pagesGweghewhgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Solutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007Document7 pagesSolutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007clearcastingNo ratings yet
- Bölüm 12 Çalışma SorularıDocument16 pagesBölüm 12 Çalışma SorularıBuse Nur ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Thermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFDocument33 pagesThermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFFattihiEkhmalNo ratings yet
- K 1.4 (Table A-2)Document1 pageK 1.4 (Table A-2)Mohamad FaruqNo ratings yet
- T P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGDocument3 pagesT P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Question 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25Document11 pagesQuestion 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25fivos_rgNo ratings yet
- Exergy Analysis of A Low Temperature Heat Pump: H.A. Rangrej and K.G. NarayankhedkarDocument3 pagesExergy Analysis of A Low Temperature Heat Pump: H.A. Rangrej and K.G. NarayankhedkarPritish MohanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Questions On ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesThermal Physics Questions On ThermodynamicsIdania CazasNo ratings yet
- ES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument5 pagesES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat Transferyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Moving Boundary Work: 5 KG of Saturated Water Vapor in Cylinder Is Heated at Constant Pressure (300 Kpa)Document8 pagesMoving Boundary Work: 5 KG of Saturated Water Vapor in Cylinder Is Heated at Constant Pressure (300 Kpa)yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Tut-4Document15 pagesChapter 8 - Tut-4Raghav ChhaparwalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Thermal EngineeringDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank-Thermal EngineeringIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap17 P096Document19 pagesThermo 5th Chap17 P096UTA - Std - Elvin ChantreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (7th Edition)Document6 pagesChapter 3 (7th Edition)zaqbasalmau100% (1)
- Entropy Rate Balance For Closed Systems: ExampleDocument26 pagesEntropy Rate Balance For Closed Systems: ExampleDaniel García100% (1)
- EntropyDocument10 pagesEntropyShyam DevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document57 pagesChapter 17MS schNo ratings yet
- 2 - ProcessesDocument36 pages2 - ProcessesAljohn Mark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics NumericalsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Numericalspiyush mishraNo ratings yet
- ME3140Assignment 2Document2 pagesME3140Assignment 2me20btech11034No ratings yet
- 2300 HW 13 SolDocument4 pages2300 HW 13 SolFrederick DugayNo ratings yet
- E233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasDocument16 pagesE233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasYingyote LubphooNo ratings yet
- Example CH 4Document4 pagesExample CH 4Uday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7 - Entropy 2nd LawDocument3 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7 - Entropy 2nd Lawgrandw9524No ratings yet
- PR Kelas Termodinamika - Reza WDocument8 pagesPR Kelas Termodinamika - Reza WReza WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Jul-Nov 2015: ME-1101 Thermodynamics Tutorial - 4Document1 pageJul-Nov 2015: ME-1101 Thermodynamics Tutorial - 4mechmuthu1No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3kaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument41 pagesGas LawsGrey TapesNo ratings yet
- Thermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelDocument36 pagesThermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelFarhad MojaverNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesUnit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsRengganis Putri ParmudyaNo ratings yet
- Agus Haryanto Agreng Dept. 06 MARET 2008Document41 pagesAgus Haryanto Agreng Dept. 06 MARET 2008Cola JamNo ratings yet
- Reviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Document37 pagesReviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Austin BarrilleauxNo ratings yet
- ETD Question Bank 2021-22Document14 pagesETD Question Bank 2021-22Vinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Laws For Ideal & Real FLuidsDocument9 pagesSet 3 Laws For Ideal & Real FLuidsKhuram s6No ratings yet
- ME211 HW6 SolutionDocument7 pagesME211 HW6 Solutiontowerofgod77No ratings yet
- 6bab Iv (Cont'd)Document40 pages6bab Iv (Cont'd)Muhammad Randy AkbarNo ratings yet
- Assignment No: 2: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (110006) 28/10/2011Document3 pagesAssignment No: 2: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (110006) 28/10/2011SaumilNo ratings yet
- Problem Set#1Document2 pagesProblem Set#1ron ronnnNo ratings yet
- DfasfasdfDocument1 pageDfasfasdfgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Part A Rate at Which Entropy Leaves The TankDocument2 pagesPart A Rate at Which Entropy Leaves The TankgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- (A) Final Temperature Energy Balance 0 0: U U MCT T T T TDocument2 pages(A) Final Temperature Energy Balance 0 0: U U MCT T T T TgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- FSFSDGDocument2 pagesFSFSDGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- ZDXVDSGZSDHDocument2 pagesZDXVDSGZSDHgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- SDFSDF 11 SDFDocument2 pagesSDFSDF 11 SDFgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- SDGDG 07 CDocument10 pagesSDGDG 07 CgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V T M&: 251 KJ KGDocument3 pagesI P H S V T M&: 251 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Asdqw 6Document3 pagesAsdqw 6gowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 2 - Sheet Metal TrayDocument18 pages2 - Sheet Metal TraygowthamAG07No ratings yet
- GweghewhDocument5 pagesGweghewhgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- R K R I J: Position Vector of A and CDocument1 pageR K R I J: Position Vector of A and CgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 85P - DoneDocument1 page11 85P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 74P - DoneDocument2 pages11 74P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 69P - DoneDocument3 pages11 69P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 77P - DoneDocument2 pages11 77P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 46P - DoneDocument2 pages11 46P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Two-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KDocument3 pagesTwo-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V M& T: 191.81 KJ KGDocument4 pagesI P H S V M& T: 191.81 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- T P V V U: I I I R IDocument3 pagesT P V V U: I I I R IgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V T: 191.81 KJ KGDocument4 pagesI P H S V T: 191.81 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- T P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGDocument3 pagesT P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V M& T: I I I I I IDocument5 pagesI P H S V M& T: I I I I I IgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Kinetic Energy 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 Work 1 20 8 2: T T MV I V MV MR RDocument2 pagesKinetic Energy 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 Work 1 20 8 2: T T MV I V MV MR RgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KDocument2 pages300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KgowthamAG07No ratings yet
Gas Constant, 0.287 KJ KG K
Gas Constant, 0.287 KJ KG K
Uploaded by
gowthamAG07Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gas Constant, 0.287 KJ KG K
Gas Constant, 0.287 KJ KG K
Uploaded by
gowthamAG07Copyright:
Available Formats
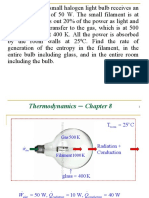
13468-9-150P
AID: 1825 | 28/11/2014
T s
Show the Carnot cycle, with air as the working fluid on
diagram as in Figure (1).
Use ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases table, to find the properties of
air.
Gas constant, R 0.287 kJ kg K
th
Express the thermal efficiency of the given Carnot cycle
T
th 1 L
TH
TH
Here, the temperature of the heat source is
(1)
TL
, and the temperature of the sink is .
th
TL
Rearrange Equation (1), and substitute 300 K for
T
TH L
1 th
, and 0.60 for
TH
to find
300K
1 0.6
750 K
s2 s1
Find the entropy change for the isothermal process 1-2
P
s2 s1 s2o s1o R ln 2
P1
s1
s2
Here, the specific entropy of air at state 1 is
,the specific entropy of air at state 2 is ,
s1o
specific entropy of air at state 1 as a function of temperature alone is , entropy of air at
P1
s2o
state 2 as a function of temperature alone is , pressure of air at state 1 is , pressure of
P2
R
air at state 2 is , and the gas constant of air is .
s1o
s2o
For isothermal process 1-2, temperature remains constant, hence
and
are equal, as
o
o
s2 s1 0.287 kJ kg K
they are functions of temperature only. Substitute 0 for
,
for R, 700
P2
P1
kPa for , and 1,000 kPa for .
700 kPa
s2 s1 0 0.287 kJ kg K ln
1, 000 kPa
0.1204 kJ kg K
Wnet
Find the net power developed in the Carnot cycle
Wnet m s2 s1 TH TL
Here, the mass of air is m.
0.1204 kJ kg K
s2 s1
TH
Substitute 0.0025 kg for m,
for
, 750K for
.
Wnet 0.0025 kg 0.1204 kJ kg K 750 300 K
=0.115 kJ
0.115 kJ
Hence, the net power developed in the Carnot cycle is
TL
, and 300 K for
You might also like
- Homework 11Document8 pagesHomework 11Ha ViNo ratings yet
- FSFSDGDocument2 pagesFSFSDGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- T P H S I I I I: I I I I TH TH THDocument2 pagesT P H S I I I I: I I I I TH TH THSathyarazor21No ratings yet
- 300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KDocument2 pages300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Unit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SDocument5 pagesUnit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SAbubakar AdeniNo ratings yet
- T P V V U: I I I R IDocument3 pagesT P V V U: I I I R IgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument14 pagesGaseous StatemayankNo ratings yet
- Two-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KDocument3 pagesTwo-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 8-39E Oxygen Gas Is Compressed From A Specified Initial State To A Final Specified State. The Reversible WorkDocument8 pages8-39E Oxygen Gas Is Compressed From A Specified Initial State To A Final Specified State. The Reversible WorkAnonymous 5OI0ClBZNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- ChE234 F10 Exam2 Thermodynamics For Chemical EngineersDocument3 pagesChE234 F10 Exam2 Thermodynamics For Chemical EngineerskellykapperNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Ideal Gas Practice Problems SolutionsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics: Ideal Gas Practice Problems SolutionsMuqeem Uddin100% (1)
- Ideal Gas EntropyDocument6 pagesIdeal Gas EntropyAlan A. AlexanderNo ratings yet
- 11 74P - DoneDocument2 pages11 74P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Processes and Carnot CycleDocument4 pagesProcesses and Carnot CycleRagh AhmedNo ratings yet
- 11 77P - DoneDocument2 pages11 77P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- ENGG1500 Module 8 Tute SolutionsDocument15 pagesENGG1500 Module 8 Tute SolutionsKevin MalarkeyNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesDocument34 pagesIdeal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesJake SyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasDocument7 pagesEngineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasazzraNo ratings yet
- GweghewhDocument5 pagesGweghewhgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Solutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007Document7 pagesSolutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007clearcastingNo ratings yet
- Bölüm 12 Çalışma SorularıDocument16 pagesBölüm 12 Çalışma SorularıBuse Nur ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Thermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFDocument33 pagesThermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFFattihiEkhmalNo ratings yet
- K 1.4 (Table A-2)Document1 pageK 1.4 (Table A-2)Mohamad FaruqNo ratings yet
- T P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGDocument3 pagesT P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Question 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25Document11 pagesQuestion 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25fivos_rgNo ratings yet
- Exergy Analysis of A Low Temperature Heat Pump: H.A. Rangrej and K.G. NarayankhedkarDocument3 pagesExergy Analysis of A Low Temperature Heat Pump: H.A. Rangrej and K.G. NarayankhedkarPritish MohanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Questions On ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesThermal Physics Questions On ThermodynamicsIdania CazasNo ratings yet
- ES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument5 pagesES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat Transferyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Moving Boundary Work: 5 KG of Saturated Water Vapor in Cylinder Is Heated at Constant Pressure (300 Kpa)Document8 pagesMoving Boundary Work: 5 KG of Saturated Water Vapor in Cylinder Is Heated at Constant Pressure (300 Kpa)yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Tut-4Document15 pagesChapter 8 - Tut-4Raghav ChhaparwalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Thermal EngineeringDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank-Thermal EngineeringIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap17 P096Document19 pagesThermo 5th Chap17 P096UTA - Std - Elvin ChantreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (7th Edition)Document6 pagesChapter 3 (7th Edition)zaqbasalmau100% (1)
- Entropy Rate Balance For Closed Systems: ExampleDocument26 pagesEntropy Rate Balance For Closed Systems: ExampleDaniel García100% (1)
- EntropyDocument10 pagesEntropyShyam DevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document57 pagesChapter 17MS schNo ratings yet
- 2 - ProcessesDocument36 pages2 - ProcessesAljohn Mark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics NumericalsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Numericalspiyush mishraNo ratings yet
- ME3140Assignment 2Document2 pagesME3140Assignment 2me20btech11034No ratings yet
- 2300 HW 13 SolDocument4 pages2300 HW 13 SolFrederick DugayNo ratings yet
- E233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasDocument16 pagesE233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasYingyote LubphooNo ratings yet
- Example CH 4Document4 pagesExample CH 4Uday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7 - Entropy 2nd LawDocument3 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7 - Entropy 2nd Lawgrandw9524No ratings yet
- PR Kelas Termodinamika - Reza WDocument8 pagesPR Kelas Termodinamika - Reza WReza WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Jul-Nov 2015: ME-1101 Thermodynamics Tutorial - 4Document1 pageJul-Nov 2015: ME-1101 Thermodynamics Tutorial - 4mechmuthu1No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3kaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument41 pagesGas LawsGrey TapesNo ratings yet
- Thermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelDocument36 pagesThermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelFarhad MojaverNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesUnit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsRengganis Putri ParmudyaNo ratings yet
- Agus Haryanto Agreng Dept. 06 MARET 2008Document41 pagesAgus Haryanto Agreng Dept. 06 MARET 2008Cola JamNo ratings yet
- Reviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Document37 pagesReviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Austin BarrilleauxNo ratings yet
- ETD Question Bank 2021-22Document14 pagesETD Question Bank 2021-22Vinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Laws For Ideal & Real FLuidsDocument9 pagesSet 3 Laws For Ideal & Real FLuidsKhuram s6No ratings yet
- ME211 HW6 SolutionDocument7 pagesME211 HW6 Solutiontowerofgod77No ratings yet
- 6bab Iv (Cont'd)Document40 pages6bab Iv (Cont'd)Muhammad Randy AkbarNo ratings yet
- Assignment No: 2: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (110006) 28/10/2011Document3 pagesAssignment No: 2: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (110006) 28/10/2011SaumilNo ratings yet
- Problem Set#1Document2 pagesProblem Set#1ron ronnnNo ratings yet
- DfasfasdfDocument1 pageDfasfasdfgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Part A Rate at Which Entropy Leaves The TankDocument2 pagesPart A Rate at Which Entropy Leaves The TankgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- (A) Final Temperature Energy Balance 0 0: U U MCT T T T TDocument2 pages(A) Final Temperature Energy Balance 0 0: U U MCT T T T TgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- FSFSDGDocument2 pagesFSFSDGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- ZDXVDSGZSDHDocument2 pagesZDXVDSGZSDHgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- SDFSDF 11 SDFDocument2 pagesSDFSDF 11 SDFgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- SDGDG 07 CDocument10 pagesSDGDG 07 CgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V T M&: 251 KJ KGDocument3 pagesI P H S V T M&: 251 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Asdqw 6Document3 pagesAsdqw 6gowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 2 - Sheet Metal TrayDocument18 pages2 - Sheet Metal TraygowthamAG07No ratings yet
- GweghewhDocument5 pagesGweghewhgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- R K R I J: Position Vector of A and CDocument1 pageR K R I J: Position Vector of A and CgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 85P - DoneDocument1 page11 85P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 74P - DoneDocument2 pages11 74P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 69P - DoneDocument3 pages11 69P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 77P - DoneDocument2 pages11 77P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 11 46P - DoneDocument2 pages11 46P - DonegowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Two-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KDocument3 pagesTwo-Stage Gas Turbine: C K C KgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V M& T: 191.81 KJ KGDocument4 pagesI P H S V M& T: 191.81 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- T P V V U: I I I R IDocument3 pagesT P V V U: I I I R IgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V T: 191.81 KJ KGDocument4 pagesI P H S V T: 191.81 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- T P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGDocument3 pagesT P U H V: 214.07 KJ KG 300.19 KJ KGgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- I P H S V M& T: I I I I I IDocument5 pagesI P H S V M& T: I I I I I IgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Kinetic Energy 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 Work 1 20 8 2: T T MV I V MV MR RDocument2 pagesKinetic Energy 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 Work 1 20 8 2: T T MV I V MV MR RgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- 300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KDocument2 pages300 Kpa 300 K 100 Kpa 900 KgowthamAG07No ratings yet