Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11.mobile Station
11.mobile Station
Uploaded by
deepak19mOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11.mobile Station
11.mobile Station
Uploaded by
deepak19mCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
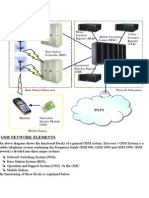
MOBILE STATION
A Mobile Station (MS) is used by a mobile subscriber to communicate with the cellular
system. Manufacturers of mobile stations offer a variety of designs and features to meet
the needs of different markets. Several types of mobile stations exist, each allowing the
subscriber to make and receive calls. The range or coverage area of a mobile station
depends on, the output power of the mobile station. Different types of mobile stations
have different output power capabilities and therefore, different ranges. For example,
hand-held telephones have a lower output power, (resulting in a shorter range), than a car
installed phone with roof mounted antenna.
A Mobile Station consists of two main elements:
The mobile equipment or terminal.
The Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
Unlike other standards, in GSM the subscriber is separated from the mobile terminal.
Each subscriber’s information is stored as a “smart card” SIM. The SIM can be plugged
into any GSM mobile terminal. This brings the advantages of security and portability for
subscribers.
The Terminal
Mobile units are classified according to the amount of power that they transmit. Three
classes of mobile units are available.
1. The Class I mobile unit can output up to 3 watts of power. This is the most
powerful mobile unit with the greatest range. The Class I mobile unit is called
a vehicle-mounted mobile unit. It is permanently mounted in a car and has an
antenna attached to the car roof.
2. The Class II mobile unit can output up to 1.2 watts of power. This is called a
transportable mobile unit because it is stored in a bag that can be carried from
place to place.
3. The Class III mobile unit can output up to 0.5 watts of power. This is called a
portable mobile unit because the equipment is contained in a unit small
enough to be held in one hand and easily carried from place to place.
You might also like
- Mobile JammerDocument27 pagesMobile Jammermaxrisk111100% (3)
- Proposal of Mobile JammerDocument16 pagesProposal of Mobile JammerMoata Haile50% (2)
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Advanced Mobile Phone Signal Jammer For GSM, CDMA and 3G Networks With Prescheduled Time Duration Using ARM 7Document4 pagesAdvanced Mobile Phone Signal Jammer For GSM, CDMA and 3G Networks With Prescheduled Time Duration Using ARM 7Kimberly McdanielNo ratings yet
- Mobile JammerDocument30 pagesMobile JammerFranklin-Noble Akwa-deltan UmohNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mobile Phone Signal Jammer For GSM, CDMA and 3G Networks With Prescheduled Time Duration Using ARM 7Document4 pagesAdvanced Mobile Phone Signal Jammer For GSM, CDMA and 3G Networks With Prescheduled Time Duration Using ARM 7Ahmet AltinNo ratings yet
- GSM 900 Mobile Jammer: Dept - of ECE TKM Institute of Technology 1Document38 pagesGSM 900 Mobile Jammer: Dept - of ECE TKM Institute of Technology 1Arun92% (37)
- Vtu Final Report Draft For Project On Smart Car Parking Security SystemDocument56 pagesVtu Final Report Draft For Project On Smart Car Parking Security SystemSkilladdi KingNo ratings yet
- How Mobile Phone WorksDocument7 pagesHow Mobile Phone WorksRoxzen Valera ColladoNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone How It WorksDocument8 pagesMobile Phone How It WorksVijay Chowdary DasariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To How Cell Phone JammersDocument6 pagesIntroduction To How Cell Phone Jammerssanjay95No ratings yet
- Mobile Phone TechnologiesDocument9 pagesMobile Phone TechnologiesMUKISA PHILICAYSNo ratings yet
- Mobilis Internship ReportDocument16 pagesMobilis Internship ReportAymEn SeKhri100% (1)
- FPGA Based Wireless Mobile JammerDocument6 pagesFPGA Based Wireless Mobile Jammeronkar.kapuskari221No ratings yet
- Tinaporwal,+01 IJETMR19 A12 1303Document5 pagesTinaporwal,+01 IJETMR19 A12 1303mrunofficial000No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document16 pagesChapter 2hajerpcNo ratings yet
- Cell Phone JammersDocument24 pagesCell Phone JammersRam VBITNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument49 pagesCommunicationSivakumar RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Cell Phone Technology-11-15Document5 pagesCell Phone Technology-11-15ArabeaNo ratings yet
- WCMC Chapter 5 - Cellular Networks ConDocument38 pagesWCMC Chapter 5 - Cellular Networks Conmelesew mossieNo ratings yet
- Name: Mandeep Chhabada Class: 5 Sem EC Roll No: 08BECR008Document6 pagesName: Mandeep Chhabada Class: 5 Sem EC Roll No: 08BECR008Sunil ShahuNo ratings yet
- TowersDocument30 pagesTowersadityasmartiNo ratings yet
- Cell Phone JammerDocument18 pagesCell Phone JammerPooja ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Technical Report On: GSM-900 Mobile JAMMERDocument24 pagesA Technical Report On: GSM-900 Mobile JAMMERvenukomnuNo ratings yet
- GggsssmmmrreeppoorrttDocument23 pagesGggsssmmmrreeppoorrttakshay099No ratings yet
- Mobile JammerDocument25 pagesMobile JammerRohit NarainNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Karan Kumar Goyal, 7080710244, Eee-Ii Guided By: - Vineet SharmaDocument25 pagesPresented By:-Karan Kumar Goyal, 7080710244, Eee-Ii Guided By: - Vineet SharmaAbhishiekh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Mobile JammerDocument24 pagesMobile Jammeryawar sajadkNo ratings yet
- Cellular Signals Jamming System in 2G and 3GDocument6 pagesCellular Signals Jamming System in 2G and 3GChansoriya ImNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone: Telephones or Cell PhonesDocument5 pagesMobile Phone: Telephones or Cell Phonesraunsekar100% (1)
- Mobile Computing Q&ADocument6 pagesMobile Computing Q&AAnonymous IJAAT2dqBNo ratings yet
- GSM RobotDocument18 pagesGSM Robotskarthikvasishta100% (3)
- Wireless Communication: An OverviewDocument10 pagesWireless Communication: An Overviewmihir_damNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Cellular CommunicationDocument53 pagesLecture 4 - Cellular CommunicationTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Blocking The Mobile Phones Signals With The Help of JammerDocument6 pagesBlocking The Mobile Phones Signals With The Help of JammerAhmet AltinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GSM: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Document12 pagesIntroduction To GSM: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Anuj KuradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Nandhini PNo ratings yet
- Development of Frequency GSM Signal Jammer: Oluwole Arowolo and Adefemi AdekunleDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Frequency GSM Signal Jammer: Oluwole Arowolo and Adefemi AdekunleTemesgen AtalayNo ratings yet
- Name: Sunil Shahu Class: 5 Sem EC Roll No: 08BECR049Document7 pagesName: Sunil Shahu Class: 5 Sem EC Roll No: 08BECR049sunil shahuNo ratings yet
- Cellular CommunicationDocument48 pagesCellular CommunicationLatika Parashar100% (1)
- GSM Based Moving Display For College For Notice BoardDocument42 pagesGSM Based Moving Display For College For Notice BoardSanjivee SachinNo ratings yet
- Cellular PhonesDocument14 pagesCellular PhonesCMYLNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone RMDocument15 pagesMobile Phone RMPOOJANo ratings yet
- Mobile Networks: Presented By: MR - Shubhad KumarDocument24 pagesMobile Networks: Presented By: MR - Shubhad KumarSneha WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Wireless Notice Board Full ReportDocument38 pagesWireless Notice Board Full Reportobula863100% (11)
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument5 pagesGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationssalmanpkplusNo ratings yet
- Paper of Mobile Phone Jammer-2Document6 pagesPaper of Mobile Phone Jammer-2SHUBHAM JAINNo ratings yet
- MIS-310 (GSM Notes)Document6 pagesMIS-310 (GSM Notes)adifa mahmudNo ratings yet
- Cell Phone Jammer: P.V.D.Satya Murthy (08MR1A0441)Document28 pagesCell Phone Jammer: P.V.D.Satya Murthy (08MR1A0441)Abraham BaduguNo ratings yet
- Title .. GSM (900 MHZ) Cell Phone Jammer: Submitted Date: 10/07/2010Document12 pagesTitle .. GSM (900 MHZ) Cell Phone Jammer: Submitted Date: 10/07/2010Samuel AdamuNo ratings yet
- GSM Brief History:: April 10, 2007 - 7:37 AmDocument14 pagesGSM Brief History:: April 10, 2007 - 7:37 Amnitin254No ratings yet
- How Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksFrom EverandHow Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksNo ratings yet
- Radio Resource Management in Multi-Tier Cellular Wireless NetworksFrom EverandRadio Resource Management in Multi-Tier Cellular Wireless NetworksNo ratings yet
- 33.benefits From TrainingDocument1 page33.benefits From Trainingdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- HandoffDocument1 pageHandoffdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 22.transmission Rate& Channel ConceptDocument1 page22.transmission Rate& Channel Conceptdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 24.air Interface ChannelsDocument2 pages24.air Interface Channelsdeepak19m100% (1)
- 30.trafic in Interfacing-MocDocument2 pages30.trafic in Interfacing-Mocdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 28.traffic ChannelsDocument1 page28.traffic Channelsdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 27.dedicated Control ChannelsDocument1 page27.dedicated Control Channelsdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- Oadcast ChannelsDocument2 pagesOadcast Channelsdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- Mon Control ChannelsDocument1 pageMon Control Channelsdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 23.bursts and FramesDocument1 page23.bursts and Framesdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 21.radio ChannelDocument2 pages21.radio Channeldeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 17.authentication CenterDocument2 pages17.authentication Centerdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 18.functions of EirDocument1 page18.functions of Eirdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 16.functioning of HLRDocument2 pages16.functioning of HLRdeepak19m100% (1)
- DatabaseDocument1 pageDatabasedeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 15.functioning of VLRDocument1 page15.functioning of VLRdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 13.the Base Station ControllerDocument1 page13.the Base Station Controllerdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 14.functioning of MSCDocument2 pages14.functioning of MSCdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 9.introduction To GSM TechnologyDocument2 pages9.introduction To GSM Technologydeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 12.the SIMDocument1 page12.the SIMdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- Work ElementsDocument1 pageWork Elementsdeepak19mNo ratings yet
- 8.tech. Dept.& Org - StructureDocument2 pages8.tech. Dept.& Org - Structuredeepak19mNo ratings yet
- Company ProfileDocument2 pagesCompany Profiledeepak19mNo ratings yet