Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 viewsWolff Kishner Reduction - MECH
Wolff Kishner Reduction - MECH
Uploaded by
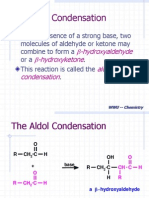
baskhemThe Wolff-Kishner Reduction uses hydrazine, a strong base like potassium hydroxide, and high heat to reduce an aldehyde or ketone to an alkane via a hydrazone intermediate. The mechanism involves the carbonyl group reacting with hydrazine to form a hydrazone, which then loses nitrogen gas to form the reduced alkane product and nitrogen gas. Diethylene glycol is used as the solvent due to its high boiling point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Singer 750 Series Service ManualDocument42 pagesSinger 750 Series Service ManualGinny Ross80% (5)
- Yamaha Owners Manual 40 50 HPDocument88 pagesYamaha Owners Manual 40 50 HPmnbvqwert100% (5)
- Modelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook InstructorDocument60 pagesModelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook Instructorsolid34100% (1)
- Crux and Reagents of Organic ChemDocument4 pagesCrux and Reagents of Organic ChemBILL RUSSO100% (5)
- Reagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-LDocument10 pagesReagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-Lbluebeary22No ratings yet
- 2 Ethyl 2520hexanol Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument10 pages2 Ethyl 2520hexanol Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - Useful ReagentsDocument3 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - Useful ReagentsTifoneitorNo ratings yet
- OCR F322 Organic Reactions and Conditions Flowchart + AnswersDocument2 pagesOCR F322 Organic Reactions and Conditions Flowchart + AnswersRozaiya RamliNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionsDocument36 pagesName Reactionsjonty7770% (1)
- Reagent TableDocument10 pagesReagent Tablebluebeary22No ratings yet
- 12 CARBOHYDRATES Reactions of MonosaccharidesDocument21 pages12 CARBOHYDRATES Reactions of MonosaccharidesRebecca CrossNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and PhenolDocument117 pagesAlcohol and Phenolsulihah12100% (2)
- Solomon Organic Chemistry Chapter 19 SlidesDocument35 pagesSolomon Organic Chemistry Chapter 19 Slidesdanrcg100% (1)
- MCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewDocument43 pagesMCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewVetina LirioNo ratings yet
- 19 Enolates Enamines-2Document59 pages19 Enolates Enamines-2ronNo ratings yet
- Carbanions IDocument38 pagesCarbanions ISagung DyahNo ratings yet
- Tautomeria y Oxido ReduccionDocument44 pagesTautomeria y Oxido ReduccionRoxana PerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPDocument18 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPKriti Tyagi100% (2)
- Lecture 3 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Document20 pagesLecture 3 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Koki KingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Changes in Acid TheoryDocument9 pagesChemistry Changes in Acid TheoryAlan SongNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument9 pagesAldehydes and KetonesCamille AdleNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetoneDocument39 pagesAldehyde and KetoneCitra Siti PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes ReportDocument48 pagesAlkenes Reportmychael14No ratings yet
- EP101 Sen LNT 008 Ketone&Aldehyde May11Document18 pagesEP101 Sen LNT 008 Ketone&Aldehyde May11Sàtz ÑÖÑïtNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Organic SynthesisDocument30 pagesAliphatic Organic SynthesisrationalwikiNo ratings yet
- Oxo SynthesisDocument1 pageOxo Synthesisdlr1233No ratings yet
- 2022 JC2 H2 Organic Concept MapsDocument13 pages2022 JC2 H2 Organic Concept MapsPriyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Document13 pagesLecture 5 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Koki KingNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument16 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- X UV Light or Heat: Reactions in Topic XIDocument3 pagesX UV Light or Heat: Reactions in Topic XImichelsonyip100% (1)
- Organic Notes Combined - RemovedDocument510 pagesOrganic Notes Combined - RemovedJanesh SumadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols 15.1: Sources of Alcohols (Please Read)Document9 pagesChapter 15: Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols 15.1: Sources of Alcohols (Please Read)Rammohan VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of AlcoholsDocument6 pagesDehydration of Alcoholsعبدالله هنيةNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document87 pagesChem 1Christopher Jordan EvoniukNo ratings yet
- 19 Enolates EnaminesDocument59 pages19 Enolates EnaminesTwas Anassin100% (2)
- Alcohol Ether EpoxideDocument31 pagesAlcohol Ether EpoxideANISTHESIAHYUNI BINTI DURMAN FKJNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones II. Oxidation and Reduction: SynthesisDocument34 pagesAldehydes and Ketones II. Oxidation and Reduction: SynthesisMatthew M. SeabaughNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Class 12 CbseDocument8 pagesAldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Class 12 CbseRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Document7 pagesAlcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Kaviraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds A-Level NotesDocument4 pagesCarbonyl Compounds A-Level Notesbumblebee9323No ratings yet
- Enol - Enolat - Pptenol - EnolatDocument19 pagesEnol - Enolat - Pptenol - Enolatalief ramdhanNo ratings yet
- Organic Flow Chart 16Document3 pagesOrganic Flow Chart 16Kshitiz JoshiNo ratings yet
- L1 Preparation of AlcoholsDocument12 pagesL1 Preparation of AlcoholsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document74 pagesChapter 17Vasudevan SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Conjugated DienesDocument80 pagesConjugated Dienestrie_79No ratings yet
- CHM 102 Lecture Note 3Document13 pagesCHM 102 Lecture Note 3alfreddanladi321No ratings yet
- Ald&Ketone IIDocument51 pagesAld&Ketone IIheraldas2421No ratings yet
- Alkyne Reactions: AdditionDocument9 pagesAlkyne Reactions: Additionbsesh1992No ratings yet
- 25.17 Carbohydrate Structure DeterminationDocument45 pages25.17 Carbohydrate Structure DeterminationnanbalaganNo ratings yet
- L.S.T. Leung Chik Wai Memorial School F.6 Chemistry Chapter 34: Hydroxy-Compounds 羥基化合物 chapt. 34: p.1Document21 pagesL.S.T. Leung Chik Wai Memorial School F.6 Chemistry Chapter 34: Hydroxy-Compounds 羥基化合物 chapt. 34: p.1IEyra ShaHeraNo ratings yet
- Wilkinson CatalystDocument19 pagesWilkinson Catalystjagabandhu_patraNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument30 pagesAlkenesapi-3734333No ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument5 pages4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsFin BrickmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21byDocument52 pagesChapter 21byRaja Abhilash100% (1)
- 10.4 Hydroxy Compounds Alcohols: Learning OutcomesDocument10 pages10.4 Hydroxy Compounds Alcohols: Learning OutcomesSaqib HussainNo ratings yet
- CH22Document23 pagesCH22David LiNo ratings yet
- ReductionDocument36 pagesReductionSayed Newaj ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- C21BDocument5 pagesC21BmohsensoadNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone ReactionsDocument21 pagesAldehyde and Ketone ReactionsChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- PM To Woo Foreign Investors: Us May Ban Tiktok, Other Chinese Social Media AppsDocument1 pagePM To Woo Foreign Investors: Us May Ban Tiktok, Other Chinese Social Media AppsbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Meghalaya Heads Towards Community Spread of COVID: Nazareth Launches Testing FacilityDocument1 pageMeghalaya Heads Towards Community Spread of COVID: Nazareth Launches Testing FacilitybaskhemNo ratings yet
- Session 7 Quiz PDFDocument2 pagesSession 7 Quiz PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum: Advertisement For The JRF Position in The CSIR Funded Project (Walk-In)Document1 pageCorrigendum: Advertisement For The JRF Position in The CSIR Funded Project (Walk-In)baskhemNo ratings yet
- Organometallic CompoundsDocument1 pageOrganometallic CompoundsbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Contain A Hydroxyl Group (OH Group) Bonded To An SPDocument2 pagesAlcohols Contain A Hydroxyl Group (OH Group) Bonded To An SPbaskhemNo ratings yet
- 11 Table of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature - Master Organic Chemistry PDFDocument8 pages11 Table of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature - Master Organic Chemistry PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Succinic Acid PDFDocument1 pageSuccinic Acid PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives PDFDocument6 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Priority Table of Functional Groups of Organic Chemistry: Formula Function Sufix (Main Function) Prefix ExampleDocument1 pagePriority Table of Functional Groups of Organic Chemistry: Formula Function Sufix (Main Function) Prefix ExamplebaskhemNo ratings yet
- Phenylhydrazone of Acetone Is Treated With Zinc Chloride?Document1 pagePhenylhydrazone of Acetone Is Treated With Zinc Chloride?baskhemNo ratings yet
- GlycolDocument10 pagesGlycolbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Reactions:: BSC 1 Semester - Chem Eh 101 - Organic Theory - Unit IvDocument1 pageAlkenes Reactions:: BSC 1 Semester - Chem Eh 101 - Organic Theory - Unit IvbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Woman Realizes She's Been Accidentally Abusing Her Husband - The Federalist PapersDocument10 pagesWoman Realizes She's Been Accidentally Abusing Her Husband - The Federalist PapersbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Heat of NeutralizationDocument5 pagesHeat of NeutralizationbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ICSE0002Document21 pagesChemistry ICSE0002baskhem100% (2)
- Chemistry ICSE0001Document12 pagesChemistry ICSE0001baskhem100% (2)
- Solvent Free Green Synthesis of 5-Arylidine Barbituric Acid Derivatives Catalyzed by Copper Oxide NanoparticlesDocument6 pagesSolvent Free Green Synthesis of 5-Arylidine Barbituric Acid Derivatives Catalyzed by Copper Oxide NanoparticlesbaskhemNo ratings yet
- North - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)Document10 pagesNorth - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)baskhemNo ratings yet
- North - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)Document5 pagesNorth - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)baskhemNo ratings yet
- Application For NETDocument2 pagesApplication For NETbaskhemNo ratings yet
- B.SC - Program ChemistryDocument66 pagesB.SC - Program ChemistrybaskhemNo ratings yet
- 5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesDocument96 pages5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesMauricio SantosNo ratings yet
- Klein GardDocument55 pagesKlein GardgpocobosNo ratings yet
- Water VariousDocument12 pagesWater VariousSugeili Valdez ValdezNo ratings yet
- CBIP RecommondationsDocument89 pagesCBIP Recommondationsgkpalepu100% (19)
- A Critical Review On Different Types of Wear of MaterialsDocument7 pagesA Critical Review On Different Types of Wear of MaterialsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- 1 Heat Exchanger VDFDocument26 pages1 Heat Exchanger VDFPablo TorresNo ratings yet
- My Love 2Document37 pagesMy Love 2WordjarNo ratings yet
- Optimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDocument9 pagesOptimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDanaNo ratings yet
- J28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengDocument17 pagesJ28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengLeeLowersNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument669 pagesUntitledKen Roden, L. PangantihonNo ratings yet
- Premio 20 DTDocument35 pagesPremio 20 DThyakueNo ratings yet
- Jcr-Vis Research: Pakistan Cement SectorDocument32 pagesJcr-Vis Research: Pakistan Cement SectorZohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- (Ijcst-V9i2p6) :p.deepa, V.subitha Varshini, D.vennila, V.harithaDocument4 pages(Ijcst-V9i2p6) :p.deepa, V.subitha Varshini, D.vennila, V.harithaEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- SERVICIO Ir2530 - 2525Document370 pagesSERVICIO Ir2530 - 2525solser digitalNo ratings yet
- 2100P Portable Turbidimeter Instrument & Procedure ManualDocument78 pages2100P Portable Turbidimeter Instrument & Procedure Manualkeiji01No ratings yet
- Soda Ash PDFDocument14 pagesSoda Ash PDFArunkumar ChandaranNo ratings yet
- American MFG Axg FG Axg Parts BookDocument19 pagesAmerican MFG Axg FG Axg Parts BookmarkNo ratings yet
- Fractional Calculus Author(s) : Bertram Ross Source: Mathematics Magazine, Vol. 50, No. 3 (May, 1977), Pp. 115-122 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/12/2010 23:54Document9 pagesFractional Calculus Author(s) : Bertram Ross Source: Mathematics Magazine, Vol. 50, No. 3 (May, 1977), Pp. 115-122 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/12/2010 23:54sathish256No ratings yet
- Pigmented Skin LesionsDocument51 pagesPigmented Skin LesionsclikgoNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report AnjaliDocument162 pagesSummer Internship Report AnjaliKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- 01 Taking A Pilot AboardDocument7 pages01 Taking A Pilot AboardEnder SemsedinNo ratings yet
- Aggregation Level and PDCCHDocument2 pagesAggregation Level and PDCCHMuhammad RizkiNo ratings yet
- Working Load To Break Load: Safety Factors in Composite Yacht StructuresDocument8 pagesWorking Load To Break Load: Safety Factors in Composite Yacht Structurescarlos ivan carvajal ortizNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Performance in Pulsed Disc and Doughnut Extraction ColumnsDocument10 pagesMass Transfer Performance in Pulsed Disc and Doughnut Extraction ColumnsSatria PNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0272884211004202 Main PDFDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0272884211004202 Main PDFMario Misael Machado LòpezNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument3 pagesMCQEkta ChawlaNo ratings yet
- 01 Technical Report Adama WWTPDocument97 pages01 Technical Report Adama WWTPaberraNo ratings yet
Wolff Kishner Reduction - MECH
Wolff Kishner Reduction - MECH
Uploaded by
baskhem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views2 pagesThe Wolff-Kishner Reduction uses hydrazine, a strong base like potassium hydroxide, and high heat to reduce an aldehyde or ketone to an alkane via a hydrazone intermediate. The mechanism involves the carbonyl group reacting with hydrazine to form a hydrazone, which then loses nitrogen gas to form the reduced alkane product and nitrogen gas. Diethylene glycol is used as the solvent due to its high boiling point.
Original Description:
Wolf
Original Title
Wolff Kishner Reduction_MECH
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Wolff-Kishner Reduction uses hydrazine, a strong base like potassium hydroxide, and high heat to reduce an aldehyde or ketone to an alkane via a hydrazone intermediate. The mechanism involves the carbonyl group reacting with hydrazine to form a hydrazone, which then loses nitrogen gas to form the reduced alkane product and nitrogen gas. Diethylene glycol is used as the solvent due to its high boiling point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views2 pagesWolff Kishner Reduction - MECH
Wolff Kishner Reduction - MECH
Uploaded by
baskhemThe Wolff-Kishner Reduction uses hydrazine, a strong base like potassium hydroxide, and high heat to reduce an aldehyde or ketone to an alkane via a hydrazone intermediate. The mechanism involves the carbonyl group reacting with hydrazine to form a hydrazone, which then loses nitrogen gas to form the reduced alkane product and nitrogen gas. Diethylene glycol is used as the solvent due to its high boiling point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
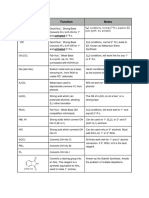
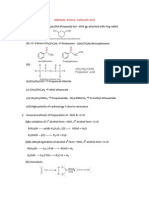
Wolff-Kishner Reduction Mechanisms
Wolff-Kishner Reduction of an aldehyde or ketone results in an alkane (and nitrogen gas) via a
hydrazone intermediate.
Requires hydrazine (NH2NH2), strong base (KOH or NaOH), diethylene glycol (BP 245 oC)
solvent and high temperature (180oC).
O
The mechanism *EtOH can be replaced with HO
O
OH
NH 2NH2
H
H 2O
NaOH, EtOH, ht
H
H
H
N
ketone
or aldehyde
-O
N+
H
H
hydrazine
O
Et
or H 2O
H
O
O
N
Et
or HO
H
H
O-
N
N
O
H
N+
-O
H
hydrazone
-O
H
H
N
-
NN
O
H
or EtOH
Page 1 of 2
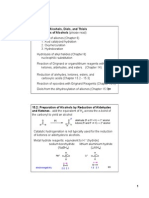
Wolff-Kishner Reduction Mechanisms
H
N
-O
H
N
N-
"C-" leaving
group
(uphill reaction but can
happen b/c hi T and form
stable N2)
O
H
H
-O
H
C-
alkane
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Singer 750 Series Service ManualDocument42 pagesSinger 750 Series Service ManualGinny Ross80% (5)
- Yamaha Owners Manual 40 50 HPDocument88 pagesYamaha Owners Manual 40 50 HPmnbvqwert100% (5)
- Modelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook InstructorDocument60 pagesModelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook Instructorsolid34100% (1)
- Crux and Reagents of Organic ChemDocument4 pagesCrux and Reagents of Organic ChemBILL RUSSO100% (5)
- Reagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-LDocument10 pagesReagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-Lbluebeary22No ratings yet
- 2 Ethyl 2520hexanol Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument10 pages2 Ethyl 2520hexanol Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - Useful ReagentsDocument3 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - Useful ReagentsTifoneitorNo ratings yet
- OCR F322 Organic Reactions and Conditions Flowchart + AnswersDocument2 pagesOCR F322 Organic Reactions and Conditions Flowchart + AnswersRozaiya RamliNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionsDocument36 pagesName Reactionsjonty7770% (1)
- Reagent TableDocument10 pagesReagent Tablebluebeary22No ratings yet
- 12 CARBOHYDRATES Reactions of MonosaccharidesDocument21 pages12 CARBOHYDRATES Reactions of MonosaccharidesRebecca CrossNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and PhenolDocument117 pagesAlcohol and Phenolsulihah12100% (2)
- Solomon Organic Chemistry Chapter 19 SlidesDocument35 pagesSolomon Organic Chemistry Chapter 19 Slidesdanrcg100% (1)
- MCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewDocument43 pagesMCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewVetina LirioNo ratings yet
- 19 Enolates Enamines-2Document59 pages19 Enolates Enamines-2ronNo ratings yet
- Carbanions IDocument38 pagesCarbanions ISagung DyahNo ratings yet
- Tautomeria y Oxido ReduccionDocument44 pagesTautomeria y Oxido ReduccionRoxana PerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPDocument18 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPKriti Tyagi100% (2)
- Lecture 3 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Document20 pagesLecture 3 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Koki KingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Changes in Acid TheoryDocument9 pagesChemistry Changes in Acid TheoryAlan SongNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument9 pagesAldehydes and KetonesCamille AdleNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetoneDocument39 pagesAldehyde and KetoneCitra Siti PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes ReportDocument48 pagesAlkenes Reportmychael14No ratings yet
- EP101 Sen LNT 008 Ketone&Aldehyde May11Document18 pagesEP101 Sen LNT 008 Ketone&Aldehyde May11Sàtz ÑÖÑïtNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Organic SynthesisDocument30 pagesAliphatic Organic SynthesisrationalwikiNo ratings yet
- Oxo SynthesisDocument1 pageOxo Synthesisdlr1233No ratings yet
- 2022 JC2 H2 Organic Concept MapsDocument13 pages2022 JC2 H2 Organic Concept MapsPriyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Document13 pagesLecture 5 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.Koki KingNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument16 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- X UV Light or Heat: Reactions in Topic XIDocument3 pagesX UV Light or Heat: Reactions in Topic XImichelsonyip100% (1)
- Organic Notes Combined - RemovedDocument510 pagesOrganic Notes Combined - RemovedJanesh SumadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols 15.1: Sources of Alcohols (Please Read)Document9 pagesChapter 15: Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols 15.1: Sources of Alcohols (Please Read)Rammohan VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of AlcoholsDocument6 pagesDehydration of Alcoholsعبدالله هنيةNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document87 pagesChem 1Christopher Jordan EvoniukNo ratings yet
- 19 Enolates EnaminesDocument59 pages19 Enolates EnaminesTwas Anassin100% (2)
- Alcohol Ether EpoxideDocument31 pagesAlcohol Ether EpoxideANISTHESIAHYUNI BINTI DURMAN FKJNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones II. Oxidation and Reduction: SynthesisDocument34 pagesAldehydes and Ketones II. Oxidation and Reduction: SynthesisMatthew M. SeabaughNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Class 12 CbseDocument8 pagesAldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Class 12 CbseRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Document7 pagesAlcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Kaviraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds A-Level NotesDocument4 pagesCarbonyl Compounds A-Level Notesbumblebee9323No ratings yet
- Enol - Enolat - Pptenol - EnolatDocument19 pagesEnol - Enolat - Pptenol - Enolatalief ramdhanNo ratings yet
- Organic Flow Chart 16Document3 pagesOrganic Flow Chart 16Kshitiz JoshiNo ratings yet
- L1 Preparation of AlcoholsDocument12 pagesL1 Preparation of AlcoholsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document74 pagesChapter 17Vasudevan SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Conjugated DienesDocument80 pagesConjugated Dienestrie_79No ratings yet
- CHM 102 Lecture Note 3Document13 pagesCHM 102 Lecture Note 3alfreddanladi321No ratings yet
- Ald&Ketone IIDocument51 pagesAld&Ketone IIheraldas2421No ratings yet
- Alkyne Reactions: AdditionDocument9 pagesAlkyne Reactions: Additionbsesh1992No ratings yet
- 25.17 Carbohydrate Structure DeterminationDocument45 pages25.17 Carbohydrate Structure DeterminationnanbalaganNo ratings yet
- L.S.T. Leung Chik Wai Memorial School F.6 Chemistry Chapter 34: Hydroxy-Compounds 羥基化合物 chapt. 34: p.1Document21 pagesL.S.T. Leung Chik Wai Memorial School F.6 Chemistry Chapter 34: Hydroxy-Compounds 羥基化合物 chapt. 34: p.1IEyra ShaHeraNo ratings yet
- Wilkinson CatalystDocument19 pagesWilkinson Catalystjagabandhu_patraNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument30 pagesAlkenesapi-3734333No ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument5 pages4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsFin BrickmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21byDocument52 pagesChapter 21byRaja Abhilash100% (1)
- 10.4 Hydroxy Compounds Alcohols: Learning OutcomesDocument10 pages10.4 Hydroxy Compounds Alcohols: Learning OutcomesSaqib HussainNo ratings yet
- CH22Document23 pagesCH22David LiNo ratings yet
- ReductionDocument36 pagesReductionSayed Newaj ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- C21BDocument5 pagesC21BmohsensoadNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone ReactionsDocument21 pagesAldehyde and Ketone ReactionsChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- PM To Woo Foreign Investors: Us May Ban Tiktok, Other Chinese Social Media AppsDocument1 pagePM To Woo Foreign Investors: Us May Ban Tiktok, Other Chinese Social Media AppsbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Meghalaya Heads Towards Community Spread of COVID: Nazareth Launches Testing FacilityDocument1 pageMeghalaya Heads Towards Community Spread of COVID: Nazareth Launches Testing FacilitybaskhemNo ratings yet
- Session 7 Quiz PDFDocument2 pagesSession 7 Quiz PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum: Advertisement For The JRF Position in The CSIR Funded Project (Walk-In)Document1 pageCorrigendum: Advertisement For The JRF Position in The CSIR Funded Project (Walk-In)baskhemNo ratings yet
- Organometallic CompoundsDocument1 pageOrganometallic CompoundsbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Contain A Hydroxyl Group (OH Group) Bonded To An SPDocument2 pagesAlcohols Contain A Hydroxyl Group (OH Group) Bonded To An SPbaskhemNo ratings yet
- 11 Table of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature - Master Organic Chemistry PDFDocument8 pages11 Table of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature - Master Organic Chemistry PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Succinic Acid PDFDocument1 pageSuccinic Acid PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives PDFDocument6 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives PDFbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Priority Table of Functional Groups of Organic Chemistry: Formula Function Sufix (Main Function) Prefix ExampleDocument1 pagePriority Table of Functional Groups of Organic Chemistry: Formula Function Sufix (Main Function) Prefix ExamplebaskhemNo ratings yet
- Phenylhydrazone of Acetone Is Treated With Zinc Chloride?Document1 pagePhenylhydrazone of Acetone Is Treated With Zinc Chloride?baskhemNo ratings yet
- GlycolDocument10 pagesGlycolbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Reactions:: BSC 1 Semester - Chem Eh 101 - Organic Theory - Unit IvDocument1 pageAlkenes Reactions:: BSC 1 Semester - Chem Eh 101 - Organic Theory - Unit IvbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Woman Realizes She's Been Accidentally Abusing Her Husband - The Federalist PapersDocument10 pagesWoman Realizes She's Been Accidentally Abusing Her Husband - The Federalist PapersbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Heat of NeutralizationDocument5 pagesHeat of NeutralizationbaskhemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ICSE0002Document21 pagesChemistry ICSE0002baskhem100% (2)
- Chemistry ICSE0001Document12 pagesChemistry ICSE0001baskhem100% (2)
- Solvent Free Green Synthesis of 5-Arylidine Barbituric Acid Derivatives Catalyzed by Copper Oxide NanoparticlesDocument6 pagesSolvent Free Green Synthesis of 5-Arylidine Barbituric Acid Derivatives Catalyzed by Copper Oxide NanoparticlesbaskhemNo ratings yet
- North - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)Document10 pagesNorth - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)baskhemNo ratings yet
- North - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)Document5 pagesNorth - Eastern Hill University: Permanent Campus, Mawlai Mawkynroh, Shillong - 793022 (Meghalaya)baskhemNo ratings yet
- Application For NETDocument2 pagesApplication For NETbaskhemNo ratings yet
- B.SC - Program ChemistryDocument66 pagesB.SC - Program ChemistrybaskhemNo ratings yet
- 5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesDocument96 pages5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesMauricio SantosNo ratings yet
- Klein GardDocument55 pagesKlein GardgpocobosNo ratings yet
- Water VariousDocument12 pagesWater VariousSugeili Valdez ValdezNo ratings yet
- CBIP RecommondationsDocument89 pagesCBIP Recommondationsgkpalepu100% (19)
- A Critical Review On Different Types of Wear of MaterialsDocument7 pagesA Critical Review On Different Types of Wear of MaterialsIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- 1 Heat Exchanger VDFDocument26 pages1 Heat Exchanger VDFPablo TorresNo ratings yet
- My Love 2Document37 pagesMy Love 2WordjarNo ratings yet
- Optimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDocument9 pagesOptimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDanaNo ratings yet
- J28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengDocument17 pagesJ28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengLeeLowersNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument669 pagesUntitledKen Roden, L. PangantihonNo ratings yet
- Premio 20 DTDocument35 pagesPremio 20 DThyakueNo ratings yet
- Jcr-Vis Research: Pakistan Cement SectorDocument32 pagesJcr-Vis Research: Pakistan Cement SectorZohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- (Ijcst-V9i2p6) :p.deepa, V.subitha Varshini, D.vennila, V.harithaDocument4 pages(Ijcst-V9i2p6) :p.deepa, V.subitha Varshini, D.vennila, V.harithaEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- SERVICIO Ir2530 - 2525Document370 pagesSERVICIO Ir2530 - 2525solser digitalNo ratings yet
- 2100P Portable Turbidimeter Instrument & Procedure ManualDocument78 pages2100P Portable Turbidimeter Instrument & Procedure Manualkeiji01No ratings yet
- Soda Ash PDFDocument14 pagesSoda Ash PDFArunkumar ChandaranNo ratings yet
- American MFG Axg FG Axg Parts BookDocument19 pagesAmerican MFG Axg FG Axg Parts BookmarkNo ratings yet
- Fractional Calculus Author(s) : Bertram Ross Source: Mathematics Magazine, Vol. 50, No. 3 (May, 1977), Pp. 115-122 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/12/2010 23:54Document9 pagesFractional Calculus Author(s) : Bertram Ross Source: Mathematics Magazine, Vol. 50, No. 3 (May, 1977), Pp. 115-122 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/12/2010 23:54sathish256No ratings yet
- Pigmented Skin LesionsDocument51 pagesPigmented Skin LesionsclikgoNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report AnjaliDocument162 pagesSummer Internship Report AnjaliKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- 01 Taking A Pilot AboardDocument7 pages01 Taking A Pilot AboardEnder SemsedinNo ratings yet
- Aggregation Level and PDCCHDocument2 pagesAggregation Level and PDCCHMuhammad RizkiNo ratings yet
- Working Load To Break Load: Safety Factors in Composite Yacht StructuresDocument8 pagesWorking Load To Break Load: Safety Factors in Composite Yacht Structurescarlos ivan carvajal ortizNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Performance in Pulsed Disc and Doughnut Extraction ColumnsDocument10 pagesMass Transfer Performance in Pulsed Disc and Doughnut Extraction ColumnsSatria PNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0272884211004202 Main PDFDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0272884211004202 Main PDFMario Misael Machado LòpezNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument3 pagesMCQEkta ChawlaNo ratings yet
- 01 Technical Report Adama WWTPDocument97 pages01 Technical Report Adama WWTPaberraNo ratings yet