Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HVAC Formulas
HVAC Formulas
Uploaded by
Talha MudassarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pagesBasic HVAC Formulas - Tech Tipgauravgujar24100% (1)
- IGCSE Mathematics A SoWDocument96 pagesIGCSE Mathematics A SoWMark McKinsnkeyNo ratings yet
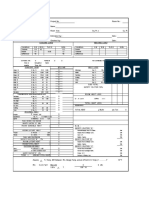
- HVAC Cooling Load Estimate SheetDocument1 pageHVAC Cooling Load Estimate Sheetjijk569% (13)
- Module 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFDocument3 pagesModule 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFNiwled UyNo ratings yet
- Hvac CalcsDocument1 pageHvac CalcsTim Lawrence100% (1)
- HVAC BasicsDocument18 pagesHVAC BasicsMohamad ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- AHU ManualDocument17 pagesAHU ManualwolfzemunNo ratings yet
- Esp CalCULATION DATA SHEET FinalDocument14 pagesEsp CalCULATION DATA SHEET Finalabdul70% (10)
- HVAC Design & Thumb RulesDocument61 pagesHVAC Design & Thumb RulesBommu RajNo ratings yet
- HVAC CalculationDocument2 pagesHVAC Calculationengrhabib07100% (1)
- HVAC Cooling Load Procedure Guideline Lo0Document62 pagesHVAC Cooling Load Procedure Guideline Lo0api-385802594% (36)
- Hvac Watt Per Square Meter CalculationsDocument2 pagesHvac Watt Per Square Meter Calculationsmohammed_hatem96% (24)
- HVAC CalculationDocument82 pagesHVAC Calculationfady100% (2)
- HVAC Supply Airflow Calculation SampleDocument7 pagesHVAC Supply Airflow Calculation Sampletankimsin100% (4)
- The Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationFrom EverandThe Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- A Guide in Practical Psychrometrics for Students and EngineersFrom EverandA Guide in Practical Psychrometrics for Students and EngineersNo ratings yet
- 07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pages07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipAslam100% (2)
- HVAC FormulasDocument7 pagesHVAC Formulasisaiaspaula80No ratings yet
- Mathematical Charts and FormulasDocument32 pagesMathematical Charts and FormulasCRISENTENANo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas PDFSaraswatapalit0% (1)
- Hd-54 Single Stage Air CompressorDocument8 pagesHd-54 Single Stage Air CompressorErGiteshAroraNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas and ValuesDocument13 pagesHvac Formulas and ValuesRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- Week 5 & 6Document10 pagesWeek 5 & 6Mariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- PSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipDocument4 pagesPSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipAfees OlajideNo ratings yet
- 03 FundamentalsDocument32 pages03 FundamentalsKavi BhandariNo ratings yet
- I. Calculation Procedure For Nozzle MethodDocument3 pagesI. Calculation Procedure For Nozzle Methodome solNo ratings yet
- 02-Gas Compression Fundamentals-1Document47 pages02-Gas Compression Fundamentals-1Muhammad Asad100% (3)
- 1a. Ganga EngineDocument10 pages1a. Ganga EngineShreyas JusticeNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion - II Lab ManualDocument33 pagesEnergy Conversion - II Lab ManualAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- 2016 NEBB Official Fundamental Formula Chart - V5 - 5.12.16Document8 pages2016 NEBB Official Fundamental Formula Chart - V5 - 5.12.16Vivek P P100% (1)
- Gpsa - M05Document21 pagesGpsa - M05mobywicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Midterm: T A U QDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet For Midterm: T A U QNguyễn Thành VũNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reversed Carnot CycleDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Reversed Carnot CyclejjNo ratings yet
- P C H C S C: RefrigerationDocument23 pagesP C H C S C: RefrigerationElisif DeFairNo ratings yet
- M13Document54 pagesM13Adrian GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorDocument5 pagesAir Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorTinku SharmaNo ratings yet
- ch04 PDFDocument19 pagesch04 PDFAkash Thummar100% (3)
- 8.assessment of CompresorsDocument14 pages8.assessment of CompresorsPrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- HVACR Formulas and SymbolsDocument46 pagesHVACR Formulas and SymbolsatiqNo ratings yet
- Section 5 - Relief SystemsDocument22 pagesSection 5 - Relief Systemslulis171No ratings yet
- BV Calculation Sheet - RADocument6 pagesBV Calculation Sheet - RAKrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- BGC QEP EPI Equation Sheets 1.docx 1Document3 pagesBGC QEP EPI Equation Sheets 1.docx 1Muzaffar AhmedNo ratings yet
- 02-Gas Compression FundamentalsDocument50 pages02-Gas Compression FundamentalsVikram JitNo ratings yet
- Rotary Screw Compressor Discussion and Calculations: NotesDocument9 pagesRotary Screw Compressor Discussion and Calculations: Notesfarshad100% (2)
- Section 5Document135 pagesSection 5tizeskiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesDocument6 pagesDetermination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesGustavo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perpindahan PanasDocument145 pagesTugas Perpindahan PanasHime_ChiakiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyDocument38 pagesThermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyAron H OcampoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7 Pin Fin ApparatusDocument5 pagesExperiment No 7 Pin Fin Apparatusgaur123450% (2)
- ManometersDocument20 pagesManometersAbed Alrahman QaddourNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Performance TestDocument7 pagesAir Compressor Performance TestRajneeshKrNo ratings yet
- Chap 8. CondenserDocument9 pagesChap 8. CondenserAli Ahsan100% (1)
- Calculations: 1.1 Hydrostatic PressureDocument10 pagesCalculations: 1.1 Hydrostatic PressureraoofNo ratings yet
- Boiler FormulasDocument5 pagesBoiler FormulasAnonymous 6Mb7PZjNo ratings yet
- 389H NO 5 PsychrometricsDocument31 pages389H NO 5 PsychrometricsAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- Sect 2 Eqns of StateDocument35 pagesSect 2 Eqns of State조기현/초빙교수/스마트소재부품공학No ratings yet
- Thermal Lab-2 Manual CompletedDocument69 pagesThermal Lab-2 Manual CompletedSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Correlaciones de GasDocument29 pagesCorrelaciones de GasKathlyn GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Flow Through The RegulatorDocument9 pagesFlow Through The Regulatorneel ranaNo ratings yet
- Complex Assignment-2 PDFDocument6 pagesComplex Assignment-2 PDFCelestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- Ptolemy: A Famous Mathematici AnDocument6 pagesPtolemy: A Famous Mathematici Anapi-316694669No ratings yet
- T4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstDocument3 pagesT4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstjuanesz98No ratings yet
- ChaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument20 pagesChaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbteenagerNo ratings yet
- Yusrina Nur Amalia - 15 U-068 - LP VHSDocument17 pagesYusrina Nur Amalia - 15 U-068 - LP VHSYusrina Nur AmaliaNo ratings yet
- CHAP TWO Worked Example Engineering Mecha-IDocument12 pagesCHAP TWO Worked Example Engineering Mecha-InvnrevNo ratings yet
- Vectors PDFDocument5 pagesVectors PDFBIKILA DESSUNo ratings yet
- Section 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: NameDocument2 pagesSection 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument57 pagesStatics of Rigid BodiesAnna Louise WyNo ratings yet
- Math-3 - Module-7 Calculus Integration by PartsDocument3 pagesMath-3 - Module-7 Calculus Integration by PartsAne CalimagNo ratings yet
- Shaft Footing ExampleDocument10 pagesShaft Footing Exampleอภิรักษ์ มานะกิจศิริสุทธิNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Specialist Math Ed1 Unit 1 & 2 VCEDocument856 pagesCambridge Specialist Math Ed1 Unit 1 & 2 VCEsongpengyuan123100% (1)
- C & DS NotesDocument83 pagesC & DS NotesAsif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Math Around UsDocument19 pagesMath Around UsashishranjanofflineNo ratings yet
- For Review Only: Trigonometry and The World Water CrisisDocument11 pagesFor Review Only: Trigonometry and The World Water CrisisROGEN DORONILANo ratings yet
- Mathematical Constant: Pi (Letter) Pi (Disambiguation)Document169 pagesMathematical Constant: Pi (Letter) Pi (Disambiguation)alinatrabNo ratings yet
- 10 TrigonometryDocument8 pages10 TrigonometryImran LupiyaNo ratings yet
- The Cosine Ratio Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDocument2 pagesThe Cosine Ratio Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorgcsemathstutorNo ratings yet
- Algebra in MATLABDocument8 pagesAlgebra in MATLABAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Math 2023 Practice QuestionsDocument30 pagesMath 2023 Practice QuestionsPixcasso 21No ratings yet
- MATH MELCs Grade 10Document3 pagesMATH MELCs Grade 10Jaylord Tayum100% (4)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/32Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/32Zaroon NasirNo ratings yet
- 2022 Specialist Mathematics: Year 12 Application TaskDocument12 pages2022 Specialist Mathematics: Year 12 Application TaskRobin MowlaNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument46 pagesCalculusDhruv KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Cylindrical Tanks PDFDocument3 pagesStresses in Cylindrical Tanks PDFMarlon TurnerNo ratings yet
- Even and Odd Signals PDFDocument2 pagesEven and Odd Signals PDFJonathanNo ratings yet
- 2021MATHADVHO2.6 - Selected Session 2 PPT SlidesDocument31 pages2021MATHADVHO2.6 - Selected Session 2 PPT SlidesChang CarelNo ratings yet
- Mathematical InductionDocument13 pagesMathematical InductionJyotsna SuraydevaraNo ratings yet
HVAC Formulas
HVAC Formulas
Uploaded by
Talha MudassarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HVAC Formulas
HVAC Formulas
Uploaded by
Talha MudassarCopyright:
Available Formats
HVAC FORMULAS
TON OF REFRIGERATION - The amount of heat required to melt
a ton (2000 lbs.) of ice at 32F
288,000 BTU/24 hr.
12,000 BTU/hr.
APPROXIMATELY 2 inches in Hg. (mercury) = 1 psi
WORK = Force (energy exerted) X Distance
Example: A 150 lb. man climbs a flight of stairs 100 ft.
high
Work = 150 lb. X 100 ft.
Work = 15,000 ft.-lb.
ONE HORSEPOWER = 33,000 ft.-lb. of work in 1 minute
ONE HORSEPOWER = 746 Watts
CONVERTING KW to BTU:
1 KW = 3413 BTUs
Example: A 20 KW heater (20 KW X 3413 BTU/KW = 68,260 BTUs
CONVERTING BTU to KW:
Example:
3413 BTUs = 1 KW
A 100,000 BTU/hr. oil or gas furnace
(100,000 3413 = 29.3 KW)
COULOMB = 6.24 X 1018
(1 Coulomb = 1 Amp)
E = voltage (emf)
I = Amperage (current)
R = Resistance (load)
WATTS (POWER) = volts x amps or P = E x I
P(in KW) = E x I
1,000
U FACTOR = reciprocal of R factor
Example:
1 R = .05U
19
= BTUs transferred / 1 Sq.Ft. / 1F / 1 Hour
VA (how the secondary of a transformer is rated) =
Example:
volts X amps
24V x .41A = 10 VA
ONE FARAD CAPACITY = 1 amp. stored under 1 volt of pressure
MFD (microfarad) =
1
Farad
1,000,000
LRA (Locked rotor amps) = FLA (Full Load Amps)
5
LRA = FLA x 5
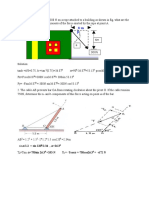
TXV (shown in equilibrium)
46.7
_______________
Spring
Pressure
9.7
37
Bulb Pressure
Evaporator Pressure
Bulb Pressure = opening force
Spring and Evaporator Pressures = closing forces
RPM of motor =
60Hz x 120_
No. of Poles
1800 RPM Motor slippage makes it about 1750
3600 RPM Motor slippage makes it about 3450
DRY AIR
78.0% Nitrogen
21.0% Oxygen
1.0% Other Gases
WET AIR
Same as dry air plus water vapor
SPECIFIC DENSITY =
1_______
Specific Volume
SPECIFIC DENSITY OF AIR = __1__ = .075 lbs./cu.ft.
13.33
STANDARD AIR = .24 Specific Heat (BTUs needed
to raise 1 lb. 1 degree)
SENSIBLE HEAT FORMULA (Furnaces):
BTU/hr. Specific Heat X Specific Density X 60 min./hr. =
X CFM X T
.24 X .075 X 60 X CFM X T = 1.08 X CFM X T
ENTHALPHY = Sensible heat and Latent heat
TOTAL HEAT FORMULA
(for cooling, humidifying or dehumidifying)
BTU/hr. = Specific Density X 60 min./hr. X CFM X H
= 0.75 x 60 x CFM x H
= 4.5 x CFM x H
RELATIVE HUMIDITY =
__Moisture present___
Moisture air can hold
SPECIFIC HUMIDITY = grains of moisture per dry air
7000 GRAINS in 1 lb. of water
DEW POINT = when wet bulb equals dry bulb
TOTAL PRESSURE (Ductwork) = Static Pressure plus
Velocity Pressure
CFM = Area (sq. ft.) X Velocity (ft. min.)
HOW TO CALCULATE AREA
Rectangular Duct
Round Duct
A = L x W
A =
D2__
4
OR
r2
RETURN AIR GRILLES Net free area = about 75%
3 PHASE VOLTAGE UNBALANCE =
100 x maximum deg. from average volts
Average Volts
NET OIL PRESSURE = Gross Oil Pressure Suction Pressure
COMPRESSION RATIO = Discharge Pressure Absolute
Suction Pressure Absolute
HEAT PUMP AUXILIARY HEAT sized at 100% of load
ARI HEAT PUMP RATING POINTS (SEER Ratings)
47
17
NON-BLEND REFRIGERANTS:
Constant Pressure = Constant Temperature during
Saturated Condition
BLENDS Rising Temperature during Saturated Condition
28 INCHES OF WC = 1 psi
NATURAL GAS COMBUSTION:
Excess Air = 50%
15 ft.3 of air to burn 1 ft.3 of methane produces:
16 ft.3 of flue gases:
1 ft.3 of oxygen
12 ft.3 of nitrogen
1 ft.3 of carbon dioxide
2 ft.3 of water vapor
Another 15 ft.3 of air is added at the draft hood
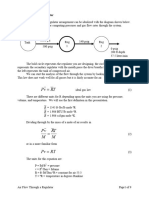
GAS PIPING (Sizing CF/hr.) =
Example:
Input BTUs
Heating Value
___
80,000 Input BTUs____________
1000 (Heating Value per CF of Natural Gas)
= 80 CF/hr.
Example:
_________ 80,000 Input BTUs_________
2550 (Heating Value per CF of Propane)
= 31 CF/hr.
FLAMMABILITY LIMITS
Propane
2.4-9.5
Butane_
1.9-8.5
Natural Gas
4-14
COMBUSTION AIR NEEDED
Propane
Natural Gas
(PC=Perfect Combustion)
23.5 ft.3 (PC)
10 ft.3 (PC)
(RC=Real Combustion)
36 ft.3
15 ft.3 (RC)
ULTIMATE CO2
13.7%
(RC)
11.8%
CALCULATING OIL NOZZLE SIZE (GPH):
_BTU Input___ = Nozzle Size (GPH)
140,000 BTUs
OR
_______
BTU Output___________
140,000 X Efficiency of Furnace
FURNACE EFFICIENCY:
% Efficiency = energy output
energy input
OIL BURNER STACK TEMPERATURE (Net) = Highest Stack
Temperature minus
Room Temperature
Example: 520 Stack Temp. 70 Room Temp. = Net Stack
Temperature of 450
KELVIN TO CELSIUS:
C = K 273
CELSIUS TO KELVIN:
K = C + 273
ABSOLUTE TEMPERATURE MEASURED IN KELVINS
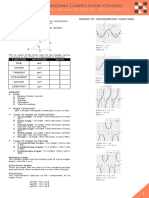
SINE = side opposite
COSINE
side adjacent
sin
hypotenuse
hypotenuse
cos
TANGENT
tan
side opposite
side adjacent
PERIMETER OF SQUARE:
P = 4s
PERIMETER OF RECTANGLE:
P = 2l + 2w
P = Perimeter
s = side
P Perimeter
l = length
w = width
PERIMETER OF TRIANGLE:
P = a + b + c
P
a
b
c
PERIMETER OF CIRCLE:
C = D
C = 2r
D
r
AREA OF SQUARE:
a = s2
A = Area
s = side
AREA OF RECTANGLE:
A = lw
A = Area
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
Perimeter
1st side
2nd side
3rd side
Circumference
3.1416
Diameter
radius
l = length
w = width
AREA OF TRIANGLE:
A = 1/2bh
A = Area
b = base
h = height
AREA OF CIRCLE:
A = r2
r
D
A = D2
4
VOLUME OF RECTANGULAR SOLID:
=
=
=
=
Area
3.1416
radius
Diameter
V = l wh
V = Volume
l = length
w = width
h = height
VOLUME OF CYLINDRICAL SOLID:
V = r2h
r
D
h
V = D2h
4
=
=
=
=
=
Volume
3.1416
radius
Diameter
height
CAPACITANCE IN SERIES:
C =
______1________________
1
+
1
+ . . . . .
C1
C2
C =
C1
CAPACITANCE IN PARALLEL:
+
C2
+ . . . . .
GAS LAWS:
Boyles Law:
P1 V 1
= P2 V 2
P = Pressure (absolute)
V = Volume
Charles Law:
P1
T1
P2
T2
P = Pressure (absolute)
T = Temperature (absolute)
P2 V 2
= _____
T2
P = Pressure (absolute)
V = Volume
T = Temperature (absolute)
General
Gas Law:
P1 V 1
_____
T1
PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM:
C2
= a2
b2
c = hypotenuse
a & b = sides
You might also like
- Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pagesBasic HVAC Formulas - Tech Tipgauravgujar24100% (1)
- IGCSE Mathematics A SoWDocument96 pagesIGCSE Mathematics A SoWMark McKinsnkeyNo ratings yet
- HVAC Cooling Load Estimate SheetDocument1 pageHVAC Cooling Load Estimate Sheetjijk569% (13)
- Module 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFDocument3 pagesModule 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFNiwled UyNo ratings yet
- Hvac CalcsDocument1 pageHvac CalcsTim Lawrence100% (1)
- HVAC BasicsDocument18 pagesHVAC BasicsMohamad ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- AHU ManualDocument17 pagesAHU ManualwolfzemunNo ratings yet
- Esp CalCULATION DATA SHEET FinalDocument14 pagesEsp CalCULATION DATA SHEET Finalabdul70% (10)
- HVAC Design & Thumb RulesDocument61 pagesHVAC Design & Thumb RulesBommu RajNo ratings yet
- HVAC CalculationDocument2 pagesHVAC Calculationengrhabib07100% (1)
- HVAC Cooling Load Procedure Guideline Lo0Document62 pagesHVAC Cooling Load Procedure Guideline Lo0api-385802594% (36)
- Hvac Watt Per Square Meter CalculationsDocument2 pagesHvac Watt Per Square Meter Calculationsmohammed_hatem96% (24)
- HVAC CalculationDocument82 pagesHVAC Calculationfady100% (2)
- HVAC Supply Airflow Calculation SampleDocument7 pagesHVAC Supply Airflow Calculation Sampletankimsin100% (4)
- The Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationFrom EverandThe Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- A Guide in Practical Psychrometrics for Students and EngineersFrom EverandA Guide in Practical Psychrometrics for Students and EngineersNo ratings yet
- 07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pages07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipAslam100% (2)
- HVAC FormulasDocument7 pagesHVAC Formulasisaiaspaula80No ratings yet
- Mathematical Charts and FormulasDocument32 pagesMathematical Charts and FormulasCRISENTENANo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas PDFSaraswatapalit0% (1)
- Hd-54 Single Stage Air CompressorDocument8 pagesHd-54 Single Stage Air CompressorErGiteshAroraNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas and ValuesDocument13 pagesHvac Formulas and ValuesRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- Week 5 & 6Document10 pagesWeek 5 & 6Mariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- PSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipDocument4 pagesPSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipAfees OlajideNo ratings yet
- 03 FundamentalsDocument32 pages03 FundamentalsKavi BhandariNo ratings yet
- I. Calculation Procedure For Nozzle MethodDocument3 pagesI. Calculation Procedure For Nozzle Methodome solNo ratings yet
- 02-Gas Compression Fundamentals-1Document47 pages02-Gas Compression Fundamentals-1Muhammad Asad100% (3)
- 1a. Ganga EngineDocument10 pages1a. Ganga EngineShreyas JusticeNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion - II Lab ManualDocument33 pagesEnergy Conversion - II Lab ManualAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- 2016 NEBB Official Fundamental Formula Chart - V5 - 5.12.16Document8 pages2016 NEBB Official Fundamental Formula Chart - V5 - 5.12.16Vivek P P100% (1)
- Gpsa - M05Document21 pagesGpsa - M05mobywicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Midterm: T A U QDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet For Midterm: T A U QNguyễn Thành VũNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reversed Carnot CycleDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Reversed Carnot CyclejjNo ratings yet
- P C H C S C: RefrigerationDocument23 pagesP C H C S C: RefrigerationElisif DeFairNo ratings yet
- M13Document54 pagesM13Adrian GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorDocument5 pagesAir Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorTinku SharmaNo ratings yet
- ch04 PDFDocument19 pagesch04 PDFAkash Thummar100% (3)
- 8.assessment of CompresorsDocument14 pages8.assessment of CompresorsPrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- HVACR Formulas and SymbolsDocument46 pagesHVACR Formulas and SymbolsatiqNo ratings yet
- Section 5 - Relief SystemsDocument22 pagesSection 5 - Relief Systemslulis171No ratings yet
- BV Calculation Sheet - RADocument6 pagesBV Calculation Sheet - RAKrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- BGC QEP EPI Equation Sheets 1.docx 1Document3 pagesBGC QEP EPI Equation Sheets 1.docx 1Muzaffar AhmedNo ratings yet
- 02-Gas Compression FundamentalsDocument50 pages02-Gas Compression FundamentalsVikram JitNo ratings yet
- Rotary Screw Compressor Discussion and Calculations: NotesDocument9 pagesRotary Screw Compressor Discussion and Calculations: Notesfarshad100% (2)
- Section 5Document135 pagesSection 5tizeskiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesDocument6 pagesDetermination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesGustavo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perpindahan PanasDocument145 pagesTugas Perpindahan PanasHime_ChiakiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyDocument38 pagesThermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyAron H OcampoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7 Pin Fin ApparatusDocument5 pagesExperiment No 7 Pin Fin Apparatusgaur123450% (2)
- ManometersDocument20 pagesManometersAbed Alrahman QaddourNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Performance TestDocument7 pagesAir Compressor Performance TestRajneeshKrNo ratings yet
- Chap 8. CondenserDocument9 pagesChap 8. CondenserAli Ahsan100% (1)
- Calculations: 1.1 Hydrostatic PressureDocument10 pagesCalculations: 1.1 Hydrostatic PressureraoofNo ratings yet
- Boiler FormulasDocument5 pagesBoiler FormulasAnonymous 6Mb7PZjNo ratings yet
- 389H NO 5 PsychrometricsDocument31 pages389H NO 5 PsychrometricsAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- Sect 2 Eqns of StateDocument35 pagesSect 2 Eqns of State조기현/초빙교수/스마트소재부품공학No ratings yet
- Thermal Lab-2 Manual CompletedDocument69 pagesThermal Lab-2 Manual CompletedSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Correlaciones de GasDocument29 pagesCorrelaciones de GasKathlyn GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Flow Through The RegulatorDocument9 pagesFlow Through The Regulatorneel ranaNo ratings yet
- Complex Assignment-2 PDFDocument6 pagesComplex Assignment-2 PDFCelestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- Ptolemy: A Famous Mathematici AnDocument6 pagesPtolemy: A Famous Mathematici Anapi-316694669No ratings yet
- T4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstDocument3 pagesT4 (8.3-10.5) sp17.tstjuanesz98No ratings yet
- ChaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument20 pagesChaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbteenagerNo ratings yet
- Yusrina Nur Amalia - 15 U-068 - LP VHSDocument17 pagesYusrina Nur Amalia - 15 U-068 - LP VHSYusrina Nur AmaliaNo ratings yet
- CHAP TWO Worked Example Engineering Mecha-IDocument12 pagesCHAP TWO Worked Example Engineering Mecha-InvnrevNo ratings yet
- Vectors PDFDocument5 pagesVectors PDFBIKILA DESSUNo ratings yet
- Section 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: NameDocument2 pagesSection 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument57 pagesStatics of Rigid BodiesAnna Louise WyNo ratings yet
- Math-3 - Module-7 Calculus Integration by PartsDocument3 pagesMath-3 - Module-7 Calculus Integration by PartsAne CalimagNo ratings yet
- Shaft Footing ExampleDocument10 pagesShaft Footing Exampleอภิรักษ์ มานะกิจศิริสุทธิNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Specialist Math Ed1 Unit 1 & 2 VCEDocument856 pagesCambridge Specialist Math Ed1 Unit 1 & 2 VCEsongpengyuan123100% (1)
- C & DS NotesDocument83 pagesC & DS NotesAsif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Math Around UsDocument19 pagesMath Around UsashishranjanofflineNo ratings yet
- For Review Only: Trigonometry and The World Water CrisisDocument11 pagesFor Review Only: Trigonometry and The World Water CrisisROGEN DORONILANo ratings yet
- Mathematical Constant: Pi (Letter) Pi (Disambiguation)Document169 pagesMathematical Constant: Pi (Letter) Pi (Disambiguation)alinatrabNo ratings yet
- 10 TrigonometryDocument8 pages10 TrigonometryImran LupiyaNo ratings yet
- The Cosine Ratio Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDocument2 pagesThe Cosine Ratio Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorgcsemathstutorNo ratings yet
- Algebra in MATLABDocument8 pagesAlgebra in MATLABAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Math 2023 Practice QuestionsDocument30 pagesMath 2023 Practice QuestionsPixcasso 21No ratings yet
- MATH MELCs Grade 10Document3 pagesMATH MELCs Grade 10Jaylord Tayum100% (4)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/32Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/32Zaroon NasirNo ratings yet
- 2022 Specialist Mathematics: Year 12 Application TaskDocument12 pages2022 Specialist Mathematics: Year 12 Application TaskRobin MowlaNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument46 pagesCalculusDhruv KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Cylindrical Tanks PDFDocument3 pagesStresses in Cylindrical Tanks PDFMarlon TurnerNo ratings yet
- Even and Odd Signals PDFDocument2 pagesEven and Odd Signals PDFJonathanNo ratings yet
- 2021MATHADVHO2.6 - Selected Session 2 PPT SlidesDocument31 pages2021MATHADVHO2.6 - Selected Session 2 PPT SlidesChang CarelNo ratings yet
- Mathematical InductionDocument13 pagesMathematical InductionJyotsna SuraydevaraNo ratings yet