Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diseases of The Skin: Physiology & Function
Diseases of The Skin: Physiology & Function
Uploaded by
Manjunath SripathyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diseases of The Skin: Physiology & Function
Diseases of The Skin: Physiology & Function
Uploaded by
Manjunath SripathyCopyright:
Available Formats
10/16/2012
Diseases of the Skin
Physiology & Function
Epidermis/Dermis Communication
Protection
Holds us together
Water regulation
Vitamin D
Immune
processing
Basic Patterns
Interplay between epidermis and dermis.
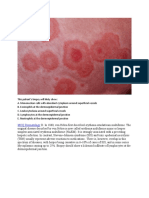
Rash, reddened
Changes in pigmentation
Shape of isolated lesions
Macule: flat, close your eyes
Papule: raised
Vesicle: fluid filled
10/16/2012
Inflammatory Dermatosis
Hives
Urticaria (wheal)
Generalized
Allergic reaction
Urticaria
Bee sting
Medications
IgE mediated
Histamine release
Vascular dilation
Fluid in tissues
Eczema, Boiling Over
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Local reaction to toxic agent.
Epidermal spongiosis
Vesicles
Poison ivy
Erythema Multiforme
Error in notes: Red macule with darker center.
Immunologic in most cases
Degeneration of basal layer of epithelium with
Lymphocytic infiltrate of dermis
Rather nonspecific reaction
10/16/2012
Psoriasis
Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses
Persistent
Epithelial reaction characterized by
increased turnover rate
Thickening
Scaling
Roughening
Variable inflammation of dermis
Ag/Ab reaction?
Knees, elbows,
scalp, glans
Whole body is
pretty bad
At areas of
trauma
Salmon skin
Lichen Planus
Psoriasis
Acanthosis
Thickening of the epi
Purple plaques
Saw-tooth epidermis
Band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in dermis.
Self limiting but may last years.
Hypopigmentation when resolves
Long rete pegs
Thinned granulosa
Ag/Ab and C
Microscopic
abscesses in epi.
Lupus Eyrthematosis
Autoimmune
Two forms
Kidney failure
Vasculitis and
DVT with emboli
Chronic inflammation
Systemic problems
Systemic ->
Discoid (skin only)
Lupus Eyrthematosis
Derm/epi junction
Adenexal structures
Antibodies at
derm/epi junction
Antibodies in serum
Anti-DNA
Other nuclear
10/16/2012
Acne
Lupus Erythematosis
Antihuman IgG
Concentration at
basal layer.
Acne vulgaris
Males mostly
Testosterone
Observations
Keratin plugging of
hair shafts
Proprionum
bacteria grows
Other Direct Infections of Skin
Bacterial
Fungal
Breaks down
sebaceous oils
Very reactive
Gram+ Bugs
Abscesses
Ringworm
Worms
Viruses
Smallpox
Viruses
10/16/2012
Blistering Conditions
Pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus
Ab against skin and basement membrane.
Acantholysis
Suprabasalar cleft
Blisters with sloughing of skin
Pressure points
Bullous Pemphigoid
Cleft Position is Important
Subcorneal: Impetigo
Suprabasalar: Pemphigus vulgaris
Subepidermal or basilar:
Bullous pemphigoid
Dermatitis herpatiformis
Bullous Pemphigoid
Note antibody staining along BM
Antibodies against hemidesmosomes
Epidermis lifts off the basement membrane
Antibodies against hemidesmosomes.
Hemidesomsomes anchor epidermis to
basement membrane
Dermatitis Herpatiformis
Not actually the virus herpes
Herpes describes radial spread of a lesion.
In some the symptoms are associated with wheat
products (gluten)
IgA deposits in the tips of the dermal papillae
Microabscesses in the dermal papillae
10/16/2012
A Brief Commercial Message
John West Red Salmon Company
Vitiligo
Changes in Pigmentation
Nevus
Proliferative Melanocytic Lesions
Nevi
Dysplastic nevus
Benign growths of young melanocytes.
Born with them. We all have about 20
Not a freckle
Abnormal maturation.
May become malignant
Malignant melanoma
Mole, benign proliferation of young
melanocytes.
Where are the nevus cells
Spitz nevus
Epidermal
Dermal
Compound
Young people.
Looks aggressive, but not.
Halo nevus (one undergoing regression)
10/16/2012
Dermal Nevus
Nevi
Clusters of young melanocytes.
Confined to dermis.
Maturation from surface to base.
Large Nevi
Make Lemonade
Dysplastic Nevus
Malignant Melanoma
Abnormal maturation of nevus cells
May proceed to malignant melanoma
Sometimes part of a familial syndrome.
Malignant melanocytic tumor
Very unpredictable tumor
Genetics
Solar and UV exposure
Ethnic
Radial growth followed by
Penetrating phase
Metastasis
Persistent
Transplant 15 years later died with it
10/16/2012
Melanoma History
Melanoma
Malignant Melanoma
Malignant Melanoma
Flag sign
Nodular or vertical
growth very
important
Depth >2 mm
Sites
Bad development
Skin
Conjunctiva
Retina
Iris
Meninges
Clusters
Nucleoli
Nuclear
margins
Lack of
cohesion
Depth
Ocular Melanomas
Conjunctival
Iris
Retinal ->
Histology
Spindle
Epitheloid ->
Bad
Liver mets
10/16/2012
Actinic Keratosis
Epithelial Tumors
Seborrheic keratosis
Older people
Pucker up big boy
Stuck on appearance
Greasy looking
Keratin rich
Benign
Epithelial proliferation
Solar exposed
skin
Epithelial
proliferation
Dysplasia
+/- malignant
potential
Keratoacanthoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Now considered a low
grade squamous cell
malignancy
Often will regress
Solar exposed skin
Rapidly growing
Cup or crater shaped
Epithelial proliferation
Marked atypia
The most common
malignancy we suffer from.
Solar exposed skin.
Pearly
Raised edges
Maybe central ulceration
Stays at home, but
Can locally invade and
cause havoc.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Arises from basal
layer of epithelium.
Invades locally
Grows in clusters
Peripheral palisade
Sometimes
adenexal skin
structure
differentiation
Arises from
differentiated
squamous epithelium
Sun exposed
UV
Age of incidence is
dropping.
Metastasizes
10/16/2012
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Keratin Pearls
Cells produce keratin
Pearls
Invade and spread
High mitotic count
Dermal Tumors
Xanthomas
Kaposis Sarcoma
Fibroma
HIV & Herpes 8
Vascular malignancy
Histiocytes
containing lipid
Around eyes
Extensor surfaces
of extremities
Diabetes
Liver disease
Hyperlipidemia
10
10/16/2012
Kaposis Sarcoma
Kaposis Sarcoma
11
You might also like
- Skin PathologyDocument42 pagesSkin PathologykateNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Skin DiseasesDocument43 pagesHandbook of Skin DiseasesTrixDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Interface Dermatitis: Rajendra Singh, MDDocument97 pagesInterface Dermatitis: Rajendra Singh, MDsatkriti100% (3)
- (Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) National Guidelines For The Treatment of Atopic DermatitisDocument25 pages(Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) National Guidelines For The Treatment of Atopic DermatitisFebtri IRnawitaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Abnormal KeratinizationDocument36 pagesDisorders of Abnormal KeratinizationdayangNo ratings yet
- Skin in Clinical DiagnosisDocument64 pagesSkin in Clinical Diagnosisadamu mohammad0% (1)
- Kuliah SMTR VDocument117 pagesKuliah SMTR VHorakhty PrideNo ratings yet
- DermatitisDocument5 pagesDermatitisAzriatul Farahain Ahmad ZamiliNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument93 pagesDermatologyneha100% (5)
- Dermatology NotesDocument6 pagesDermatology NotesAhmed TeebiNo ratings yet
- DR Pallavi - Dermatology FMGEDocument74 pagesDR Pallavi - Dermatology FMGEVickyNo ratings yet
- Rosacea 2022Document10 pagesRosacea 2022ucarecufinochiettoNo ratings yet
- Pics MCQSDocument22 pagesPics MCQStania100% (1)
- Dermatology Short NotesDocument3 pagesDermatology Short NotesOA POOJITHANo ratings yet
- Majocchi GranulomaDocument8 pagesMajocchi GranulomaEmily EresumaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DermatosesDocument58 pagesPediatric DermatosesSajin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Skin and MSK EverythingDocument31 pagesSkin and MSK EverythingBernard HernandezNo ratings yet
- Patho-Physiology Pharm Lecture 11Document15 pagesPatho-Physiology Pharm Lecture 11Manar AlzobiNo ratings yet
- Rashid 2015Document6 pagesRashid 2015Francesca BizzocoNo ratings yet
- Dermatita SeboreicaDocument4 pagesDermatita SeboreicaFlorian MaghearNo ratings yet
- Erythema MultiformeDocument29 pagesErythema MultiformeSurabhi Sharma100% (1)
- 9-Patologi Skin PDFDocument34 pages9-Patologi Skin PDFririnNo ratings yet
- Skin Diseases Affecting The VulvaDocument7 pagesSkin Diseases Affecting The VulvaNoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document28 pagesChapter 6cabdinuux32No ratings yet
- Robinson HC CT105003132Document5 pagesRobinson HC CT105003132Francesca BizzocoNo ratings yet
- Amyloidosis SkinDocument6 pagesAmyloidosis SkinGoran MaliNo ratings yet
- Combined ChartDocument32 pagesCombined Chartapi-26938624100% (1)
- Medicine Notes Dr. Fatima and Dr. Rowida2Document38 pagesMedicine Notes Dr. Fatima and Dr. Rowida2qbnc8727s5No ratings yet
- PemphigusDocument8 pagesPemphiguszuqiri ChanelNo ratings yet
- DBST Dlja INO Studentov (PDF - Io)Document6 pagesDBST Dlja INO Studentov (PDF - Io)eidNo ratings yet
- 961 Atharav CandidiasisDocument25 pages961 Atharav CandidiasisDevender MittalNo ratings yet
- Leg, Arm, and Chest Papules: ERM ASEDocument9 pagesLeg, Arm, and Chest Papules: ERM ASEdeenutz93No ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi KuliitDocument40 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi KuliitZulfani AdhiyatmiNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis DR Citra 260907Document56 pagesDermatitis DR Citra 260907Adam AriwibawaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Skin TumorsDocument56 pages7 - Skin TumorsRazane AbouzaidNo ratings yet
- M13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO6Document8 pagesM13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO6medipro clinicNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumDocument6 pagesBy Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Genodermatosis: The IchthyosisDocument4 pagesGenodermatosis: The IchthyosisOman ArifNo ratings yet
- 7-Skin Path.Document89 pages7-Skin Path.Lea MonzerNo ratings yet
- Kegawat Daruratan KulitDocument175 pagesKegawat Daruratan KulitDzulkifli SukriNo ratings yet
- SBRC DermatologyDocument83 pagesSBRC DermatologyErin HillNo ratings yet
- Diseases Study Guide 2007Document6 pagesDiseases Study Guide 2007Bahaa Ibrahim HelmiNo ratings yet
- 08-Skin TumoursDocument8 pages08-Skin TumoursChris Tan100% (1)
- Skin Disorders Affecting Oral Cavity: DR. Parul Khare Iii Mds Sarsawati Dental CollegeDocument204 pagesSkin Disorders Affecting Oral Cavity: DR. Parul Khare Iii Mds Sarsawati Dental CollegeAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis:: Dr. Francisco Eizayaga, MD PHDDocument18 pagesAtopic Dermatitis:: Dr. Francisco Eizayaga, MD PHDAngelaNo ratings yet
- Derma-LmrDocument7 pagesDerma-LmrKannan KannanNo ratings yet
- Oral Ulceration AND Vesiculobullous LesionsDocument54 pagesOral Ulceration AND Vesiculobullous LesionsAbbas Qahtan JameelNo ratings yet
- DermaDocument30 pagesDermalydia_chandraNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Components of Skin: The Skin: Basic Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesQ.1 Components of Skin: The Skin: Basic Structure and Functionnani100No ratings yet
- Spongiotic ReactionDocument21 pagesSpongiotic Reactionahmad syarifNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis 1. Atopic Dermatitis History TakingDocument13 pagesDifferential Diagnosis 1. Atopic Dermatitis History TakingCocoi MellaNo ratings yet
- Derm StuffDocument7 pagesDerm StuffSudesna Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Lection 3 EczemaDocument37 pagesLection 3 EczemaAtawna AtefNo ratings yet
- 2 EczemaDocument5 pages2 Eczemaحسين طاهر حاتم طاهرNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis & Urticaria: Department of Dermato Venereology Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityDocument34 pagesDermatitis & Urticaria: Department of Dermato Venereology Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityadystiNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Atlas for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Atlas for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Complete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisFrom EverandComplete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisNo ratings yet
- Impetigo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandImpetigo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- JEE (Main) AcknowledgementPageDocument1 pageJEE (Main) AcknowledgementPageManjunath SripathyNo ratings yet
- Physics Wave Optics MCQDocument3 pagesPhysics Wave Optics MCQManjunath Sripathy100% (4)
- Parishilana Pramana PatraDocument1 pageParishilana Pramana PatraManjunath SripathyNo ratings yet
- Government PU College Musuvinakoppalu, T.Narasipura Taluk Mysore Dist College Code: NN 260Document2 pagesGovernment PU College Musuvinakoppalu, T.Narasipura Taluk Mysore Dist College Code: NN 260Manjunath SripathyNo ratings yet