Professional Documents
Culture Documents
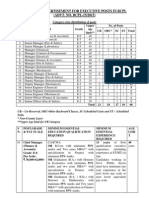
JTOC SRD PWD 2015 Syllabus
JTOC SRD PWD 2015 Syllabus
Uploaded by
Priyanka Chauhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesjto
Original Title
JTOC-SRD-PWD-2015-Syllabus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentjto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesJTOC SRD PWD 2015 Syllabus
JTOC SRD PWD 2015 Syllabus
Uploaded by
Priyanka Chauhanjto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 5
www.gatezor6.info
for Direct Recruitment of Junior Telecom Officer(Chil), an objective type Examination of
5 hours duration consisting of following sectional papers will be conducted
‘SCHEME
|. Civil Engineering Stream Section - 1 50 questions
8. Gwil Engineering Stream Section - 11: 50 questions
C._ General Ability Test Section ~ IIt + 20 questions
1. The standard of paper in Engineering subjects will be that of Engineering Degres
Examination of Indian University
2, Inthe general abilty test, special attention willbe paid to assess the cancldate's capacity
for general avareness. The standard of paper in general ability test will be such as may
be expected of 2°: Engineering Graduate.
3, The syllabus for Civil Engineering stream paper will be as alven below.
SYLLABUS:
SECTION-I- CIVIL ENGINEERING STREAM
4, BUILDING MATERIAL:
“Tmber: Different types and species of structural timber, density-moisture relationship,
strength in different directions, defects, influence of defects on permissible stress,
preservation, dry and wet rots, plywood, codal provision for design.
arieks: Types, Indian standard classification, absorption, saturation factor, strength ¥
‘masonry, influence of mortar strength and masonary strength.
‘Cement: Compounds, different types, setting times, strength
Cement Mortar: Ingredients, proportions, water demands, mortar for plastering and
masonry. 7
Concrete: Importance of WIC ratio, strength, Ingredients including admixtures,
workabity, testing, elasticity, non-destructive testing mix design method
Re
Page 20 of 28
~
NS
www.gatezo16.info
22 -
2. SOLID MECHANICS
Elastic constants, stress, plane stress, Mohrs circle of stress, strains, plain strain,
Mohr’s circle of strain, combined stress. Elastic theories of Failure, simple and shear
bending, Torsion of circular and rectangular section and simple members.
3. STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
Analysis of determinate structures- different methods including graphical methods.
Analysts of indeterminate skeletal frames- moment distribution, slope deflection,
stiffness and force methods, energy methods. Muller-Breslau principal and
application. Plastic analysis of indeterminate beams and simple frames-shape factors,
4. DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES
Principle of working stress method. Design of connections of simple members. Built
Up sections and frames. Design of Industral roofs. Principles of utimate load design
Design of memibe:s and frames.
DESIGN OF CONCRETE AND MASONRY STRUCTURES,
Limit state design for bending, shear, axial compression and combined forces, Codal
Provisions for slabs, beams, walls and footings. Working stress method of design of
A.C. members
Principles of prestressed concrete design, material, method of prestressing losses
Design of simple members and determinates structures. Introductions to prestressing
of indeterminate structures.
Design of brick masonary as per I.S. codes.
6. CONSTRUCTION PRACTICE, PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT.
Concreting Equipment:
Weight batcher, Mixer, vibrator, batching plant, concrete pump.
Cranes, nog eg equipment.
Ca
Page 21 of 28 CARS
& a
i-
wisw.gatezor
ot oe’
earthwork Equiprvent
power shovel, hoe, dozer, dumper, wales and Wactery rollers, sheep foot rollers,
ames:
onstruction, planning and Management:
ar char, inked bar chart, work reak down Suchet Activity-on-arrow diagrams.
rtical path, probabiistic activity durations: event-based networks.
SeRT network: Time-cost study, crashing; Resource allocation.
SECTION: II - CIVIL ENGINEERING STREAM
(a) FLUID: MECHANICS, OPEN CHANNEL, PIPE FLOW:
re properties, pressure, thas, Buoyanc, Fw Kine asy integration, of flow
equation, Flow measurement, Relative motion, Moment ‘of momentum, Viscosity,
‘Boundary layer and control, Drag, Lift, Dimensional analysis, Modeling, Cavitations,
roe ositations, Momentum and Eneray pines PSD cannel flow, Flow contol,
Hydraulic jump, Flow section and properties, Normal flow, Gradually varied flow, Flow
voerrpment and osses in pipe Hows, Measurements, PRON Surges and Water
hammer, Delvery =f Power Pipe networks.
(b) HYDRAULIC (MACHINES AND HYDROPOWER
er vefugat pumps, pertrmance parameter; seallng, PANES parallel, Reciprocating
pumps, ai vessels performance parametes
(a) HYDROLOGY:
Hydrological cycle, precipitation and related data analysis, PMP, unit and synthetic
ryeregraphs, Evaporation and venspraton Tents ‘and their management, PMG,
Streams and their gauging, -River morphology. Rooting ‘of floods, Capacity of
reservoirs.
{(b) WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING:
Water resources of the globe: Muttipurpose uses of Water, Soll Plant water
reiationships, irrigation systems, water demand assessment, ‘storage and their yields,
ground water yield and well Hydraulics, Water Jogging, drainage design, Irrigation
army, Design of id boundary canals, Lacey’ and TRAN force concepts in cena
vet, tring of canals, Sedent wansport i cana Non-Overfiow and overflow
sections of gravity dams and ther aesiany EreraY Gjgsipaters and tail water r@tNd,
On
Page 22 of 28
(Byes
W
www.gatez016.info
Mo oy
oe
x
Design of head works, distribution work, falls, cross-drainage work, outlets, River
training,
ENVIRONMENT ENGINEERING
(a)WATER SUPPLY ENGINEERING.
Sources of supply, yield, design of intakes and conductors, Estimation of demand,
Water quality standards, Control of water born diseases. Primary and secondary
treatment, detailing and maintenance of treatment units. Conveyance and distribution
systems of treated water, leakage and control, Rural water supply, Institutional and
Industrial water Supply.
(b) WASTE WATER ENGINEERING
Urban rain water disposal, system of sewage collection and disposal, Design of sewers
and sewerages systems, pumping, Characteristic of sewage and its treatment
pisposal of products of sewage treatment, stream flow rejuvenation, Insbtutionsl and
industrial sewage management, plumbing system, Rural and semi-urban sanitation
(c) SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT
Sources, classification, collection and disposal, Design and Management of land
(a) ATR AND NOISE POLLUTION AND ECOLOGY.
sources and effects of alr palltion, monitoring of Air pollution, Noise-poliution and
standards; Ecological Chain and balance, Environmental assessment.
(a)SOTL MECHANICS:
properties of soils, dassfication and interelationship, Compaction behavior, methoe
cof compaction and their choice, Permeability and seepage, flow nets, Inverter fers,
Compressiblity and consolidation ,shearing resistance, stresses and fallure, SO testing
in laboratory and rsity, Stress path and applications, Earth pressure theories
stress distribution in sol, soil exploration, samplers, load tests ,penetration test.
Be
Page 23 of 28
wwww.gatezo16.info
@ (>) FOUNDATION ENGINEERING
‘Type of foundations, Selection criteria, bearing capacity, settlement, laboratory and
field test, Types of piles and their design and layout, Foundations on expansive soils,
‘swelling and it prevention , foundation on swelling soils.
5. (a) SURVEYING
Classification of surveys, scales, accuracy, Measurement of distances-direct and
indirect methods, optical and electronic devices, Measurement of directions, prismatic
compass, local attraction, Theodolites-types Measurment of elevations, Spirit and
trigonometric leveling, Relief representation Contours,Digital elevation modeling
concept, Establishment of control by triangulations and traversing measurements and
adjustment of observations, computation of coordinates, Field astronomy, concept of
global positioning system, Map preparation by plane tabling and by photogrammetry,
Remote sensing concepts, map substitutes,
(b) TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING
Planning of highway systems, alignment and geometric design, horizontal and vertical
curves, grade separation, Materials and construction methods for different surfaces
and maintenance, Principles of pavement design, Drainage.
Traffic surveys, intersections, signaling, Mass transit systems, accessibility,
networking.
Planning of allway systems, terminology and designs, relating to gauge, track
controls, transits, rolling stock, tractive power and track modernization, Maintenance
‘Appurtenant works, Containerisation.
‘SECTION-I1I - GENERAL ABILITY TEST
‘The candidate's comprehension and understanding of general English shall be tested
through simple exercises. Questions on knowledge of current events and of such
matter of everyday observation and experience in their scientific aspects as may be
expected of an educated person, Questions will also be Included on events and
evelopments in Tele Communications, History of India and Geography. These will be
‘of a nature, which can be answered without special study by an educated person.
ye
Page 24 of 28 ©
” COQYAS
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Application Form - Recruitment New 2015Document4 pagesApplication Form - Recruitment New 2015Priyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Add Technical Post 2015Document1 pageAdd Technical Post 2015Priyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 108 - 44 1423218450 Detailed - Advt 15 2015 PDFDocument11 pages108 - 44 1423218450 Detailed - Advt 15 2015 PDFPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Greta Garbo Is Associated With: A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in ForumDocument2 pagesGreta Garbo Is Associated With: A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in ForumPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- AAI JE 2012 AnalysisDocument4 pagesAAI JE 2012 AnalysisPriyanka Chauhan100% (1)
- Bank Note Paper Mill India Private Limited: Employment Notification NoDocument13 pagesBank Note Paper Mill India Private Limited: Employment Notification NoPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 31. Valentina Tereshkova Sally Ride Naidia Comenci Tamara PressDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 31. Valentina Tereshkova Sally Ride Naidia Comenci Tamara PressPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in ForumDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in ForumPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 26. M. R. Jayakar V. S. Sastri G. D. Birla Jamanlal BajajDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 26. M. R. Jayakar V. S. Sastri G. D. Birla Jamanlal BajajPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Who Among The Following Is Not A Dramatist?: A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in ForumDocument2 pagesWho Among The Following Is Not A Dramatist?: A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in ForumPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 16. Painting Films Pop Music Fashion DesigningDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 16. Painting Films Pop Music Fashion DesigningPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 21. Painting Ballet Architecture Western MusicDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 21. Painting Ballet Architecture Western MusicPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 11. Kuchipudi Kathak Manipuri BahratanatyamDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D. View Answer Workspace Discuss in Forum: 11. Kuchipudi Kathak Manipuri BahratanatyamPriyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- FP 1Document1 pageFP 1Priyanka ChauhanNo ratings yet