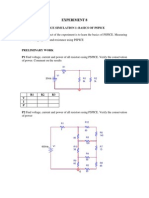
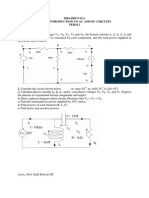
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
And Answers Since Even A Very Simple Mistake at The Beginning of Your Solution Will Lead To Erroneous Results
And Answers Since Even A Very Simple Mistake at The Beginning of Your Solution Will Lead To Erroneous Results
Uploaded by
Fatih TokgözOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
And Answers Since Even A Very Simple Mistake at The Beginning of Your Solution Will Lead To Erroneous Results
And Answers Since Even A Very Simple Mistake at The Beginning of Your Solution Will Lead To Erroneous Results
Uploaded by
Fatih TokgözCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF GAZIANTEP
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
EEE 285 Applied Differential Equations
Midterm Exam #1
Name:
Date: 6th April, 2005
Duration: 100 Minutes
1. Credit will only be given up to the point where your first mistake occurs. So be careful in your calculations
and answers since even a very simple mistake at the beginning of your solution will lead to erroneous results.
2. For each problem, you must show complete work and/or reasoning. No credit will be given if you do not show
the complete work, and you will get less credit if you dont give the reasoning, even if your answer is correct.
Q1) (15 pts) Consider the differential equation ty + y = 3t 2
a) Write down the method you use to find the solution.
b) Find the general solution.
c) Find the solution which satisfies y(1) = 3.
d) What is the interval of existence for the solution you found in part (c)?
Q2) (15pts) Consider the initial value problem
3x 2
, y (1) = 0
y = 2
3y 4
a) Write down the method you use to find the solution.
b) Find the solution implicitly.
c) Determine the interval in which the solution is valid. Hint: To find the interval of
definition look for the points where dy dx .
Q3) (15 pts) Consider the autonomous equation y ' = f ( y ) = y ( y + 2)( y 1) . (Do not forget to
give reasons at each step of the solution)
a) Find and classify the equilibrium points.
b) Draw the phase line.
c) Sketch the equilibrium solutions on ty-plane and the trajectories of the solutions in each
region divided by the equilibrium solutions.
Q4) (15pts) Find the general solution of the initial value problem 4 y + 4 y + y = xe x 2 ,
y (0) = 1, y (0) = 2 by using the method of undetermined coefficient method.
Q5) (20 pts) Find the general solution of the initial value problem y + 4 y + 4 y = xe 2 x + sin x ,
y (0) = 1, y (0) = 2 by using the inverse operator method. Hint: L1 (D ) e x = e x L1 ( ) , and
L1 (D ){e x f ( x)} = e x L1 (D + ){ f ( x)}.
{ }
Q6) (20pts) Find the general solution of the initial value problem
4( x 1) 2 y + 4( x 1) y + y = 0 , y (2) = 1, y (2) = 2 .
You might also like
- Midterm Question - Time Series Analysis - UpdatedDocument3 pagesMidterm Question - Time Series Analysis - UpdatedAakriti JainNo ratings yet
- HSC Trial 2021 Mathematics AdvancedDocument33 pagesHSC Trial 2021 Mathematics Advancedwill100% (1)
- Preparatory Mathematics - 2012 - Semester: 1 - Examination For MA1020 - CAIRNSDocument8 pagesPreparatory Mathematics - 2012 - Semester: 1 - Examination For MA1020 - CAIRNSThomasJohnnoStevensonNo ratings yet
- 16 130001 Mathematics 3Document2 pages16 130001 Mathematics 3Yash DesaiNo ratings yet
- Zeta Advanced Math Paper 2023Document26 pagesZeta Advanced Math Paper 2023Shadid AhadNo ratings yet
- Complement Chapter Test: CH 2 Rate of Change and Differentials Mathematics Course C Fall 2009: Macnvc08 Part I: G-LevelDocument3 pagesComplement Chapter Test: CH 2 Rate of Change and Differentials Mathematics Course C Fall 2009: Macnvc08 Part I: G-LevelEpic WinNo ratings yet
- CALN02E (Integral Calculus) Prelim - Quiz 1Document1 pageCALN02E (Integral Calculus) Prelim - Quiz 1Vin TVNo ratings yet
- Penrith 2022 Year 9 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument28 pagesPenrith 2022 Year 9 Maths Yearly & Solutionsrosiele7007No ratings yet
- Suggested Solutions Complement Chapter Test: CH 2 Rate of Change and Differentials Mathematics Course C Fall 2009: Macnvc08 Part I: G-LevelDocument3 pagesSuggested Solutions Complement Chapter Test: CH 2 Rate of Change and Differentials Mathematics Course C Fall 2009: Macnvc08 Part I: G-LevelEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Vize SorularıDocument4 pagesVize Sorularıyusufcgyln2001No ratings yet
- Final Term Assessment FALL 2020: Student's Name Noor Nabi Shaikh Registration Number 1711125Document8 pagesFinal Term Assessment FALL 2020: Student's Name Noor Nabi Shaikh Registration Number 1711125Noor Nabi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MAT2377F13 Midterm - SolDocument9 pagesMAT2377F13 Midterm - SolNizar MohammadNo ratings yet
- Math 2065 Review Exercises For Exam IIDocument11 pagesMath 2065 Review Exercises For Exam IITri Phương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- GATE 2013 Mathematics Previous Year Paper PDFDocument14 pagesGATE 2013 Mathematics Previous Year Paper PDFprsnthNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz 1Document16 pagesPractice Quiz 1bhumkaNo ratings yet
- National Test in Mathematics Course C SPRING 2002 (Syllabus 2000) DirectionsDocument4 pagesNational Test in Mathematics Course C SPRING 2002 (Syllabus 2000) DirectionsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Exam2 Final Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesExam2 Final Differential EquationshellooceanNo ratings yet
- ST107 2010 Commentary and SolutionsDocument13 pagesST107 2010 Commentary and SolutionsAlexis RheinNo ratings yet
- IIFT Entrance Test January 11, 2004: Total Number of Questions Total Time The Marking SchemeDocument0 pagesIIFT Entrance Test January 11, 2004: Total Number of Questions Total Time The Marking SchemeSundeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Quiz2 Spring2014Document1 pageQuiz2 Spring2014mhamwi93No ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument20 pagesLab ManualMuthukrishnan NNo ratings yet
- Maths c4 June 2012 Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesMaths c4 June 2012 Mark SchemeAditya NagrechàNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics MATHS 361 Partial Differential Equations Mid-Semester Test April 23, 2015Document10 pagesDepartment of Mathematics MATHS 361 Partial Differential Equations Mid-Semester Test April 23, 2015Harry LongNo ratings yet
- Engineering Math Level 6Document4 pagesEngineering Math Level 6Tutor OndwasiNo ratings yet
- .Archivetempsolved ECAT 2007 (Mathematics Portion) by MTMDocument9 pages.Archivetempsolved ECAT 2007 (Mathematics Portion) by MTMShahNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentmauryavks15No ratings yet
- 2021-22 Ordinaria ENUNCIADO - ENGLISH - SolutionsDocument6 pages2021-22 Ordinaria ENUNCIADO - ENGLISH - SolutionsIker PildainNo ratings yet
- 12 Gold 4 - C3 EdexcelDocument13 pages12 Gold 4 - C3 EdexcelmareiNo ratings yet
- TM2401Document4 pagesTM2401Wen ZhuNo ratings yet
- Calculus Exam+2 - Practice+testDocument2 pagesCalculus Exam+2 - Practice+testNaz SNo ratings yet
- S5 Mathematics First Term Examination 2010 Marking SchemeDocument5 pagesS5 Mathematics First Term Examination 2010 Marking Schemeandrewsource1No ratings yet
- Cce Final Exam Model 1 SolutionDocument4 pagesCce Final Exam Model 1 SolutionAbdelrhman GamalNo ratings yet
- 06 Silver 2 - C2 EdexcelDocument14 pages06 Silver 2 - C2 EdexcelKel1209No ratings yet
- Endsem ExamDocument3 pagesEndsem Exam1paper 1penNo ratings yet
- 2011 Ma 2011 MaDocument43 pages2011 Ma 2011 MaRajesh DesayNo ratings yet
- JUNE 2012: Dipiete - Et/Cs (New Scheme)Document3 pagesJUNE 2012: Dipiete - Et/Cs (New Scheme)tutulkarNo ratings yet
- SS20-BAET-Mathematical Basics-1-Inhalt - MLDocument3 pagesSS20-BAET-Mathematical Basics-1-Inhalt - MLBryan MaiaNo ratings yet
- ECON1203 HW Solution Week05Document6 pagesECON1203 HW Solution Week05Bad BoyNo ratings yet
- Test 2020Document2 pagesTest 2020semihkilic1997No ratings yet
- ECE 220, Sections 001, DE Test 1 16 February 2011: Name: SectionDocument8 pagesECE 220, Sections 001, DE Test 1 16 February 2011: Name: SectionScott RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 2022 Spring CS300 Midterm Solution Grading CriteriaDocument17 pages2022 Spring CS300 Midterm Solution Grading CriteriayunajessiNo ratings yet
- Math141 Final 2011wDocument15 pagesMath141 Final 2011wexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam.: Math 251H First Midterm ExamDocument8 pagesSample Exam.: Math 251H First Midterm ExamRAJESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Cse&Ece III Set 3 m3Document2 pagesCse&Ece III Set 3 m3Sanjay GomastaNo ratings yet
- Math156 - LQ2 Practice TestDocument1 pageMath156 - LQ2 Practice TestDean AcklesNo ratings yet
- Final EM2 2021 Perm 1 VNov22Document14 pagesFinal EM2 2021 Perm 1 VNov22Il MulinaioNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityPriteshShahNo ratings yet
- JUNE 2012: Dipiete - Et/Cs (New Scheme)Document3 pagesJUNE 2012: Dipiete - Et/Cs (New Scheme)tutulkarNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument6 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- THE SOS EXAM METH U1 2 CF CA Version 2Document32 pagesTHE SOS EXAM METH U1 2 CF CA Version 2sfp.genesis99No ratings yet
- Math 415 D3/D4 Exam # 1 - June 24, 2011 - R. MuncasterDocument8 pagesMath 415 D3/D4 Exam # 1 - June 24, 2011 - R. MuncasterSamuel Alfred ForemanNo ratings yet
- 102 2013 1 BDocument20 pages102 2013 1 BmatshonaNo ratings yet
- Specimen QP - FP1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSpecimen QP - FP1 EdexcelKenzy99No ratings yet
- BC Full 1Document29 pagesBC Full 1Its MENo ratings yet
- CS2705 Tut1 SolDocument4 pagesCS2705 Tut1 SolPuneet SangalNo ratings yet
- Solved ECAT 2006 (Mathematics Portion) by MTMDocument9 pagesSolved ECAT 2006 (Mathematics Portion) by MTMSaira Ali100% (2)
- 12 Gold 4 - C3 EdexcelDocument13 pages12 Gold 4 - C3 EdexcelYaseenTamerNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- University of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II First Midterm Exam Questions 14/04/2005 TIME 100 MinDocument1 pageUniversity of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II First Midterm Exam Questions 14/04/2005 TIME 100 MinFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- EEE 321 Electromechanical Energy Conversion 1 Experiment #3 The Magnetization Curve of Seperately and Self Excited D.C. GeneratorsDocument3 pagesEEE 321 Electromechanical Energy Conversion 1 Experiment #3 The Magnetization Curve of Seperately and Self Excited D.C. GeneratorsFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Ep106 2004 mt1Document1 pageEp106 2004 mt1Fatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- University of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II First Midterm Exam Questions ??/04/2003 TIME 100 MinDocument1 pageUniversity of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II First Midterm Exam Questions ??/04/2003 TIME 100 MinFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- 2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDocument6 pages2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- University of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II Second Midterm Exam Questions 15/05/2003 TIME 100 MinDocument1 pageUniversity of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II Second Midterm Exam Questions 15/05/2003 TIME 100 MinFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Ee361 HW6Document2 pagesEe361 HW6Fatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- University of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II Second Midterm Exam Questions 2002 TIME 100 MinDocument1 pageUniversity of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II Second Midterm Exam Questions 2002 TIME 100 MinFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- 2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDocument3 pages2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- 201 Lab Experiment7Document2 pages201 Lab Experiment7Fatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: and Maximum Power TheoremsDocument3 pagesExperiment 5: and Maximum Power TheoremsFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Current, Voltage, Power and Resistance Using PSPICEDocument2 pagesExperiment 8: Current, Voltage, Power and Resistance Using PSPICEFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- 201 Lab Experiment2Document5 pages201 Lab Experiment2Fatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- 2004-2005 Gantep 2Document5 pages2004-2005 Gantep 2Fatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- University of Gaziantep Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EEE 285 Applied Differential EquationsDocument1 pageUniversity of Gaziantep Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EEE 285 Applied Differential EquationsFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage (Soru Ve Çözümleri)Document23 pagesLow Voltage (Soru Ve Çözümleri)Fatih TokgözNo ratings yet