Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetism: (South-Seeking Pole)
Magnetism: (South-Seeking Pole)
Uploaded by
Chathunika0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesMagnetism is a force that causes magnetic materials like iron to be attracted or repelled. It is strongest at the magnetic poles of a magnet, with the north pole seeking the north and the south pole seeking the south. Iron can be magnetized by exposing it to a magnetic field, which causes the internal magnetic domains within the iron to align, creating an overall magnetic field. Steel is a harder magnetic material than iron, making it better for creating permanent magnets.
Original Description:
Notes
Original Title
Magnetism
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMagnetism is a force that causes magnetic materials like iron to be attracted or repelled. It is strongest at the magnetic poles of a magnet, with the north pole seeking the north and the south pole seeking the south. Iron can be magnetized by exposing it to a magnetic field, which causes the internal magnetic domains within the iron to align, creating an overall magnetic field. Steel is a harder magnetic material than iron, making it better for creating permanent magnets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesMagnetism: (South-Seeking Pole)
Magnetism: (South-Seeking Pole)
Uploaded by
ChathunikaMagnetism is a force that causes magnetic materials like iron to be attracted or repelled. It is strongest at the magnetic poles of a magnet, with the north pole seeking the north and the south pole seeking the south. Iron can be magnetized by exposing it to a magnetic field, which causes the internal magnetic domains within the iron to align, creating an overall magnetic field. Steel is a harder magnetic material than iron, making it better for creating permanent magnets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Magnetism
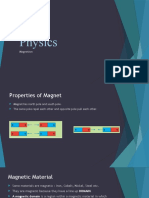
Magnetism is a non-contact force that pushes or pulls magnetic material.
These are called ferromagnetic materials. Steel is also magnetic as it
contains some iron.
Magnetic pole is region at each end of a magnet where the external magnetic
force is strongest.
The poles are called North pole (north-seeking pole) and South pole
(south-seeking pole).
Like poles repel and opposite poles attract
Is a piece of iron a magnet?
It will be attracted to a magnet. But will they repel each other? No!
If two metals repel they must have magnetic poles and so they must both be
magnets.
How to magnetise iron?
Inside a piece of iron each atom acts as a small magnet called a dipole.
They are grouped together in domains and each domain acts as a tiny magnet.
Domains
Domains in an unmagnetised piece of iron are arranged in random directions and
their effects cancel each other out.
When the iron is exposed to a magnetic
field, the domains line up in the direction
of the magnetic field. All the north poles
point in the same direction.
If you cut a magnet in half you will have
two magnets. Each magnet will have its
own north and south pole.
Iron is a soft magnetic material. It is easy to
magnetise but it loses its magnetism very easily.
Steel is a hard magnetic material. It is harder to magnetise but keeps its
magnetism (it is used to make magnets!)
Destroying magnetism Give energy to domains to move and revert back to a
random arrangement. The magnet becomes weaker if dropped or heated.
The magnetic field The space around a magnet where it can affect magnetic
materials is called the magnetic field.
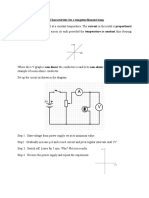
The Earths Magnetic Field
The Earths inner core is molten and always spinning acting like a giant magnet
as shown in the left hand diagram above.
The magnetic north pole is 15
off the geographic north.
The north pole of a magnet will point to magnetic north.
You might also like
- Chap10no1 PDFDocument2 pagesChap10no1 PDFTajiriMollel23% (13)
- MAGNETISM Notes PDFDocument10 pagesMAGNETISM Notes PDFChisha Mwewa100% (3)
- Report # 4 MagnetismDocument3 pagesReport # 4 Magnetismbnolasco0% (1)
- Magnetism Part 1Document8 pagesMagnetism Part 1AnonymousNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument20 pagesMagnetismmadhumitharajNo ratings yet
- Science PPT MagnetsDocument8 pagesScience PPT Magnetsapi-313062442No ratings yet
- Form5 Unit1 Magnetism NotesDocument10 pagesForm5 Unit1 Magnetism NotesJus BetikNo ratings yet
- The MagnetsDocument6 pagesThe Magnetsromethsunsuka678No ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument12 pagesMagnetismtshiamo.dintweNo ratings yet
- What Is A MagnetDocument2 pagesWhat Is A MagnetMariam BurhanNo ratings yet
- Simple Phenomena of Magnetism - Free Exam AcademyDocument1 pageSimple Phenomena of Magnetism - Free Exam AcademyMisheel BatzorigNo ratings yet
- Science MagnetsDocument2 pagesScience MagnetsAlvinNo ratings yet
- Magnetism QRDocument36 pagesMagnetism QRJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument20 pagesMagnetismaleenawaltersNo ratings yet
- Science Magnets WorksheetsDocument2 pagesScience Magnets WorksheetselmalynNo ratings yet
- Other. For Example, Pair of North Poles Repel Each Other and A Pair of South Poles Repel EachDocument1 pageOther. For Example, Pair of North Poles Repel Each Other and A Pair of South Poles Repel EachatkindsonNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Notes FinalDocument29 pagesMagnetism Notes FinalMuryum SalmanNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument17 pagesMagnetismKarina Charmaine LimNo ratings yet
- Science Magnets WorksheetsDocument2 pagesScience Magnets WorksheetselmalynNo ratings yet
- Form 2 11 MagnetismDocument15 pagesForm 2 11 MagnetismFELIX KIPRONONo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 MagnetsDocument8 pagesChapter 16 Magnetsyunekhinkhin0No ratings yet
- 4.1 Simple Phenomena of MagnetismDocument6 pages4.1 Simple Phenomena of MagnetismAbdul Hadi Tahir100% (1)
- 16 MagnetismDocument34 pages16 MagnetismKato Bruno DominicNo ratings yet
- What Is MagnetDocument9 pagesWhat Is Magnetarsc123No ratings yet
- ElectromagneticDocument2 pagesElectromagneticAiman Zylle MosotNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Guided Notes Brainpop AnswersDocument3 pagesMagnetism Guided Notes Brainpop Answersapi-457194169No ratings yet
- Topic - MagnetismDocument12 pagesTopic - Magnetismsom277342No ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument73 pagesMagnetismjohnNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument78 pagesMagnetismDennis CheruiyotNo ratings yet
- 12.0 MAGNETISM My NC Note PDFDocument14 pages12.0 MAGNETISM My NC Note PDFgentifredoNo ratings yet
- Uses of MagnetsDocument10 pagesUses of Magnetsapi-238979374No ratings yet
- Compass For OOW Class IIIDocument260 pagesCompass For OOW Class IIIKyaw Mya OoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MagnetismDocument17 pagesUnit 5 MagnetismTofe YusufNo ratings yet
- Physics Study GuideDocument5 pagesPhysics Study Guidesolomon celestineNo ratings yet
- 14 MagnetismDocument17 pages14 Magnetismapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Written Report Physics 4 Characterize Magnetic ForceDocument3 pagesWritten Report Physics 4 Characterize Magnetic Forceellamaecariaga2021No ratings yet
- Magnets PPT To WriteDocument3 pagesMagnets PPT To Writezarapark95No ratings yet
- Physics MagnetismDocument10 pagesPhysics MagnetismMaulana Digisel DesainNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument7 pagesMagnetismNaeem MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Latch Magnet-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesLatch Magnet-WPS OfficeMa Eloisa E BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Magnetism DefinitionsDocument2 pagesMagnetism DefinitionsJonathanNo ratings yet
- Magnetism For o LevelDocument54 pagesMagnetism For o LevelKYALISIIMA ODRAENo ratings yet
- Local Media2477199841487123126Document3 pagesLocal Media2477199841487123126Haimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- Earth MagnetismDocument7 pagesEarth Magnetismisa_diogo8170No ratings yet
- KD 3.4 MagnetismDocument8 pagesKD 3.4 MagnetismPlaystation SitumorangNo ratings yet
- S.4 Magnetism Notes EDITED PDFDocument17 pagesS.4 Magnetism Notes EDITED PDFPrince O Noah100% (1)
- Null 5Document8 pagesNull 5victormwamwaziNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument9 pagesMagnetismthabang mabitleNo ratings yet
- More Free Powerpoints at HTTPDocument56 pagesMore Free Powerpoints at HTTPhamang khullafah100% (1)
- CSEC Physics - MagnetismDocument5 pagesCSEC Physics - MagnetismCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Magnetic PropertiesDocument1 pageMagnetic PropertiesnauvalluthfiaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics ProjectMandeep TanwarNo ratings yet
- Magnetism - Summary - 084650Document50 pagesMagnetism - Summary - 084650Maricar Faraon100% (1)
- Domain Theory and ReviewDocument2 pagesDomain Theory and ReviewJohnson RubasinghNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Document21 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Ahmed tarek gaballahNo ratings yet
- Ch.13 Fun With Magnets Class 6Document4 pagesCh.13 Fun With Magnets Class 6Verma Sheela100% (1)
- The Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Los imanes atraen, los imanes repelen/Magnets Push, Magnets PullFrom EverandLos imanes atraen, los imanes repelen/Magnets Push, Magnets PullNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Astronomy Questions For Term 1 ExaminationDocument1 pageYear 10 Astronomy Questions For Term 1 ExaminationChathunikaNo ratings yet
- A Language For MeasurementsDocument3 pagesA Language For MeasurementsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- I-V For Tungstan FilamentDocument2 pagesI-V For Tungstan FilamentChathunikaNo ratings yet
- SPA5000 Student Essays: Notes For Students BackgroundDocument2 pagesSPA5000 Student Essays: Notes For Students BackgroundChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Electromotive Force E.m.f, Internal Resistance and Terminal P.DDocument1 pageElectromotive Force E.m.f, Internal Resistance and Terminal P.DChathunikaNo ratings yet
- S2!3!01 - Distance Time Graphs - SimulationDocument8 pagesS2!3!01 - Distance Time Graphs - SimulationChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Python Lesson 3Document3 pagesPython Lesson 3ChathunikaNo ratings yet
- C4 Parallel Circuits - CurrentDocument2 pagesC4 Parallel Circuits - CurrentChathunika100% (1)
- Lesson 5: Practical InvestigationDocument4 pagesLesson 5: Practical InvestigationChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Practical Activity 1) Series Circuit. A) One BulbDocument2 pagesPractical Activity 1) Series Circuit. A) One BulbChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Essential Skills For Croom Management Micro - SkillsDocument30 pagesEssential Skills For Croom Management Micro - SkillsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument3 pagesLesson 3: Introduction To Information TechnologyChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 - Formatting Page ContentDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 3 - Formatting Page ContentChathunikaNo ratings yet
- What Are SI Units?: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolDocument1 pageWhat Are SI Units?: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Tobeabletodrawa Circuit Diagram For A Parallel Circuit To Describe How Parallel Circuits Differ To Series CircuitsDocument10 pagesTobeabletodrawa Circuit Diagram For A Parallel Circuit To Describe How Parallel Circuits Differ To Series CircuitsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- C3 Series CircuitsDocument2 pagesC3 Series CircuitsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Particle Physics SummaryDocument2 pagesParticle Physics SummaryChathunikaNo ratings yet
- A Language For MeasurementsDocument3 pagesA Language For MeasurementsChathunikaNo ratings yet